Optical fiber
A technology of optical fiber and fiber core, applied in cladding optical fiber, optics, light guide, etc., to achieve the effect of low loss characteristics, high-speed and high-quality optical data transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
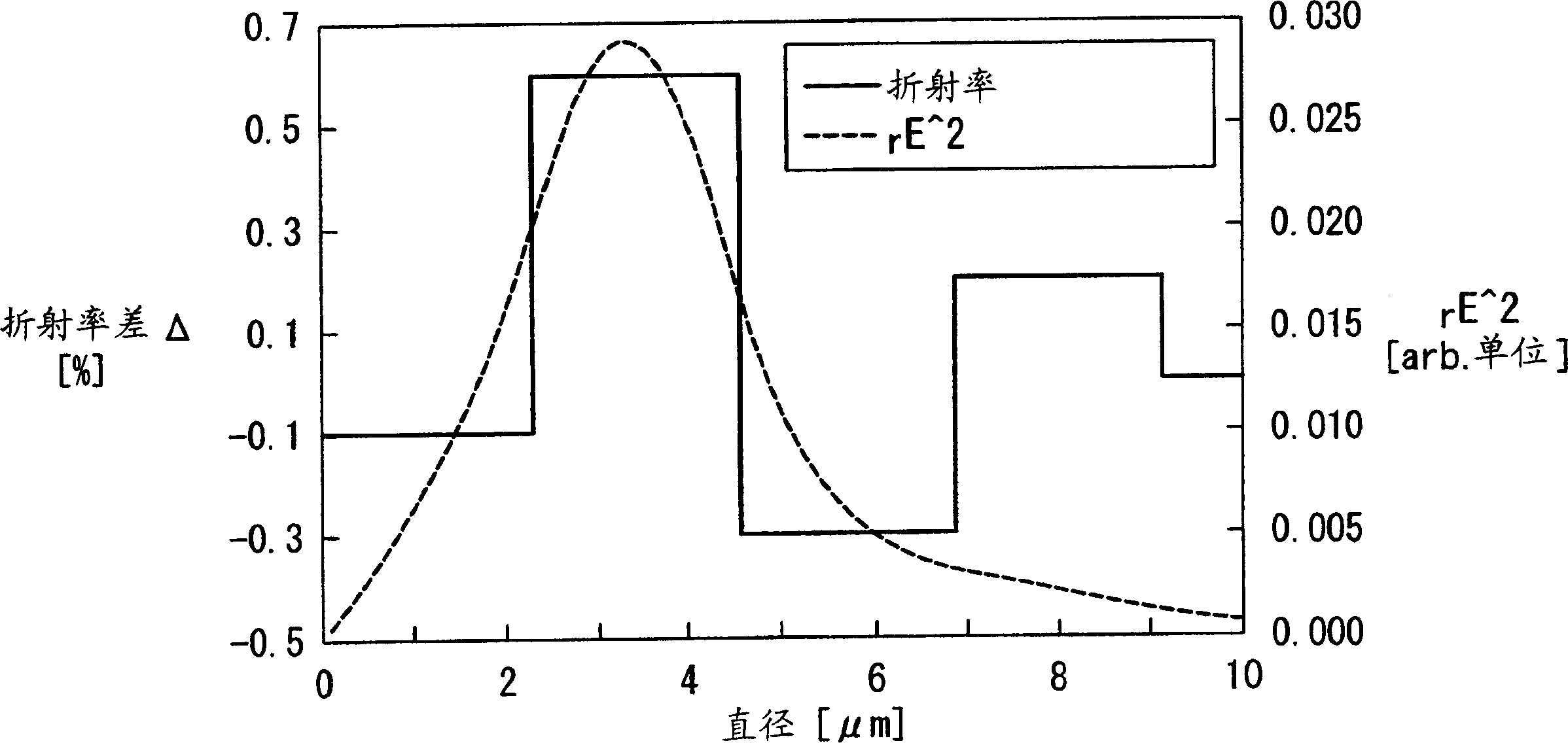
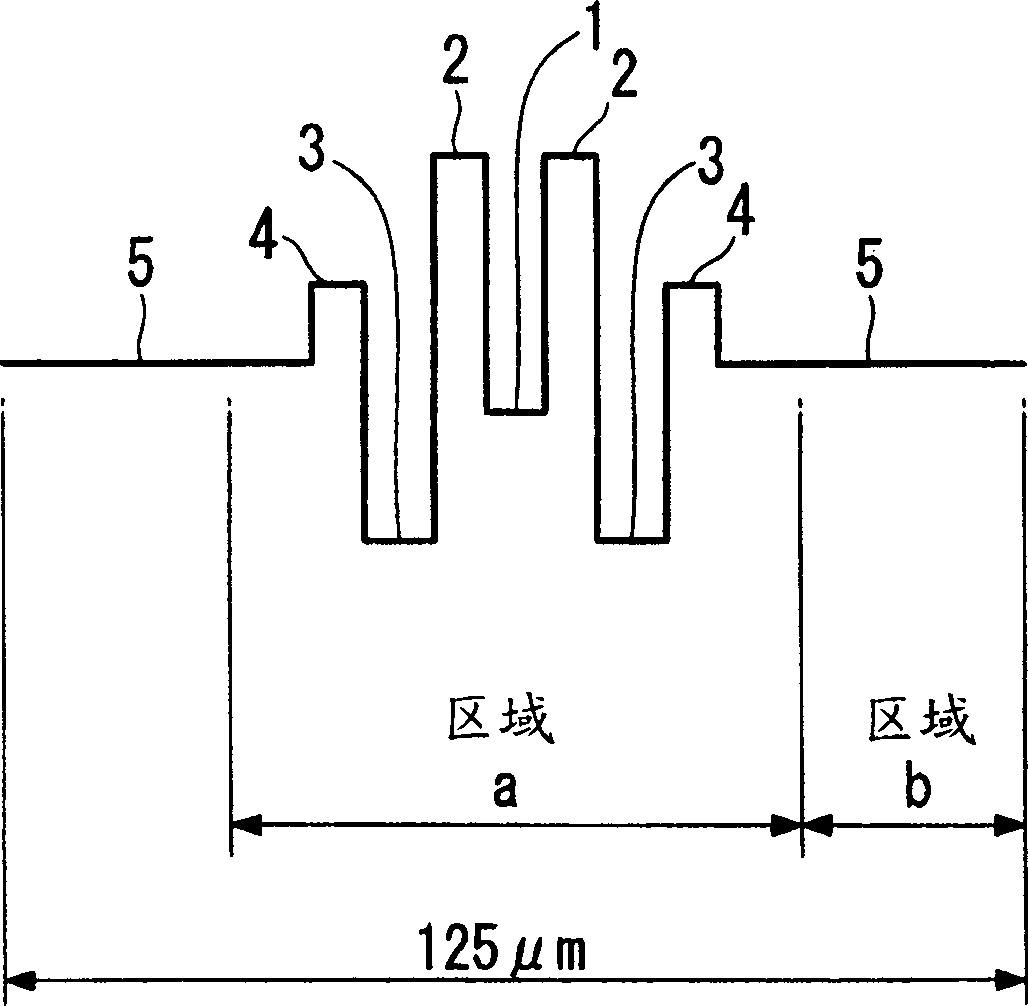
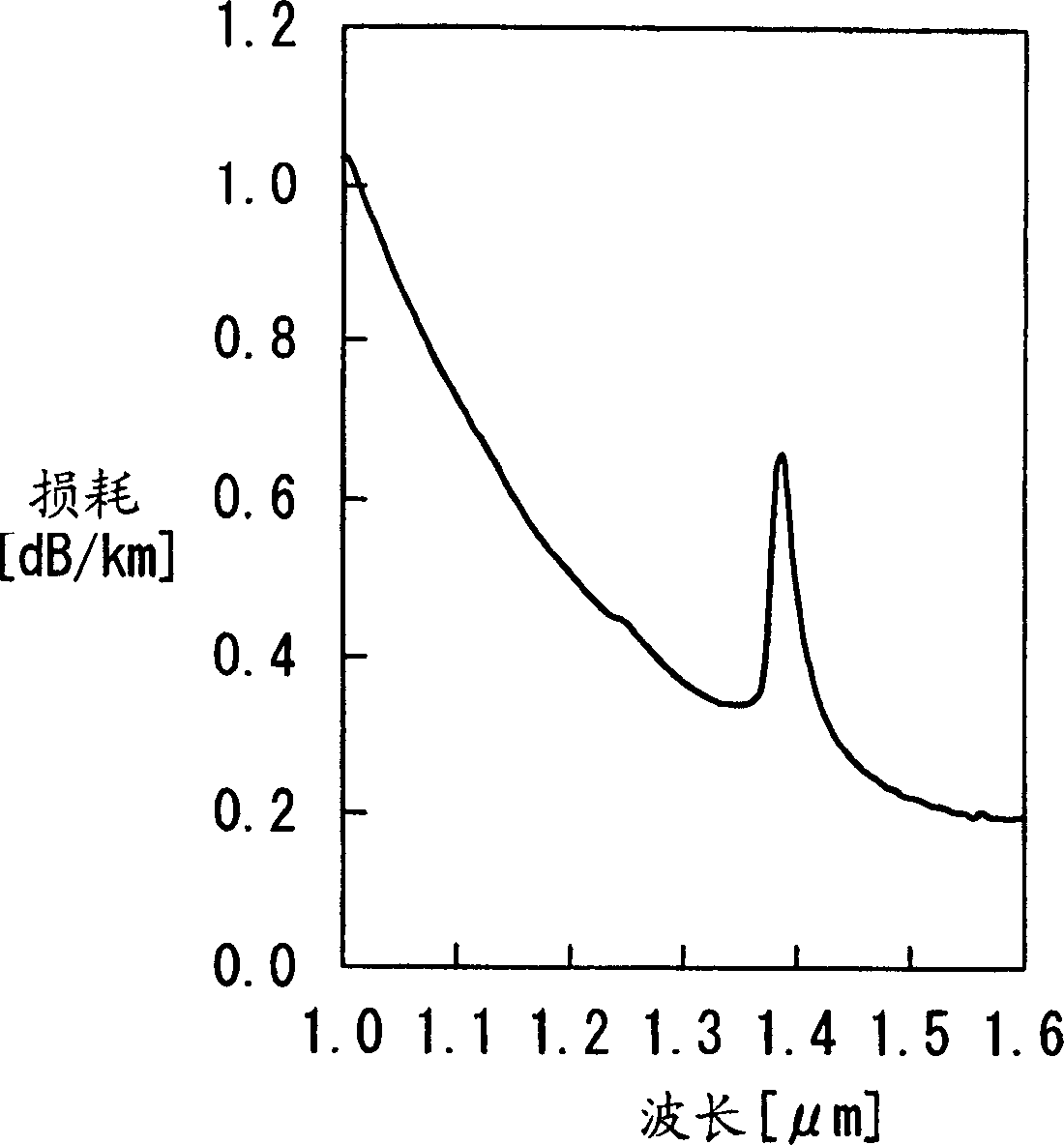
[0067] has produced a figure 1 Fiber with refractive index profile shown. This optical fiber is manufactured by using chemical vapor deposition (hereinafter referred to as CVD) method to produce figure 2 The region (a) in the optical fiber with the shown refractive index profile, this region (a) contains the core; figure 2 The region (b) in the fiber of the shown refractive index profile, this region (b) contains the cladding. attached here figure 2 As shown, the outer diameter of the fiber cladding is 125 μm. The chromatic dispersion at the wavelength of 1550nm in this fiber is +8ps / nm / km, which meets the requirements of product design. The properties of this fiber are shown in Table 2.
[0068] transmission loss
[dB / km]
0.206
Cable cut-off wavelength λcc
[nm]
1450
Effective core cross-sectional area A eff
[μm 2 ]
100.6
Mode Field Diameter MFD
[μm]
9.26
Dispersion
[ps / nm / km]
8.0
...
no. 2 approach
[0074] has produced a Figure 5 , 6 Fiber with refractive index profile shown.
[0075] attached Figure 5 Design values of the refractive index profile in the general NZ-DSF dispersion region are shown. attached Image 6Design values of the refractive index distribution are shown when the dispersion is set to about +9 ps / nm / km higher than the dispersion of the ordinary NZ-DSF. This optical fiber is manufactured by using chemical vapor deposition (hereinafter referred to as CVD) method to produce figure 2 The region (a) in the optical fiber with the shown refractive index profile, this region (a) contains the core; figure 2 The region (b) in the fiber of the shown refractive index profile, this region (b) contains the cladding. attached here figure 2 As shown in , the outer diameter of the cladding in the fiber was produced to be 125 μm.
[0076] In this fiber example, the MRIP can be reduced from 0.50 to 0.43 by increasing the dispersion to about +9 ps / nm / km. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com