Optical disc and optical disc address reading apparatus and method
一种光盘、地址的技术,应用在读取装置领域,能够解决串扰等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
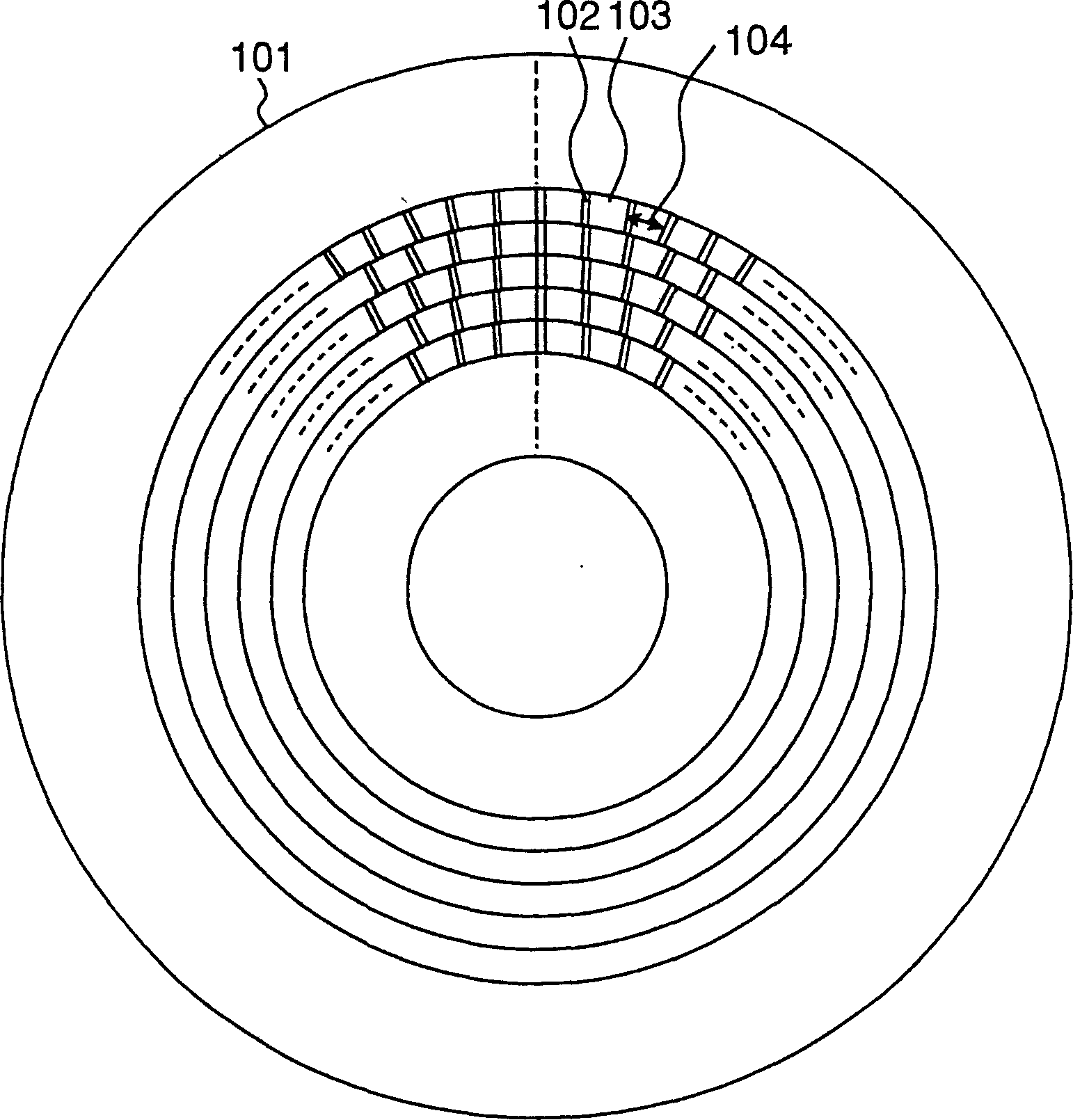
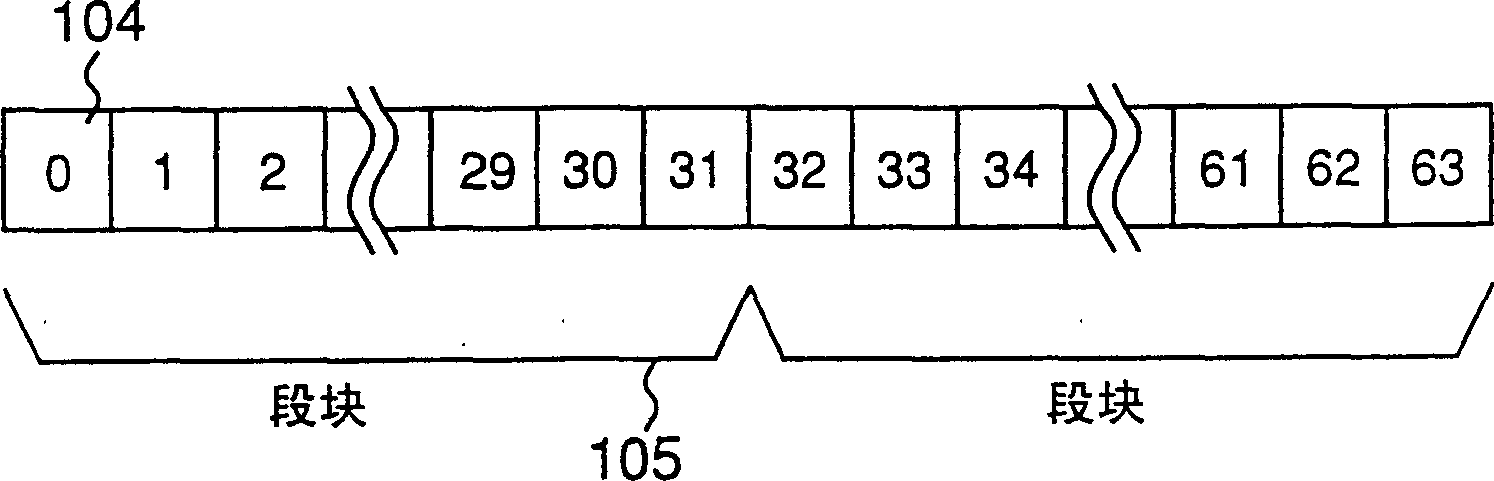
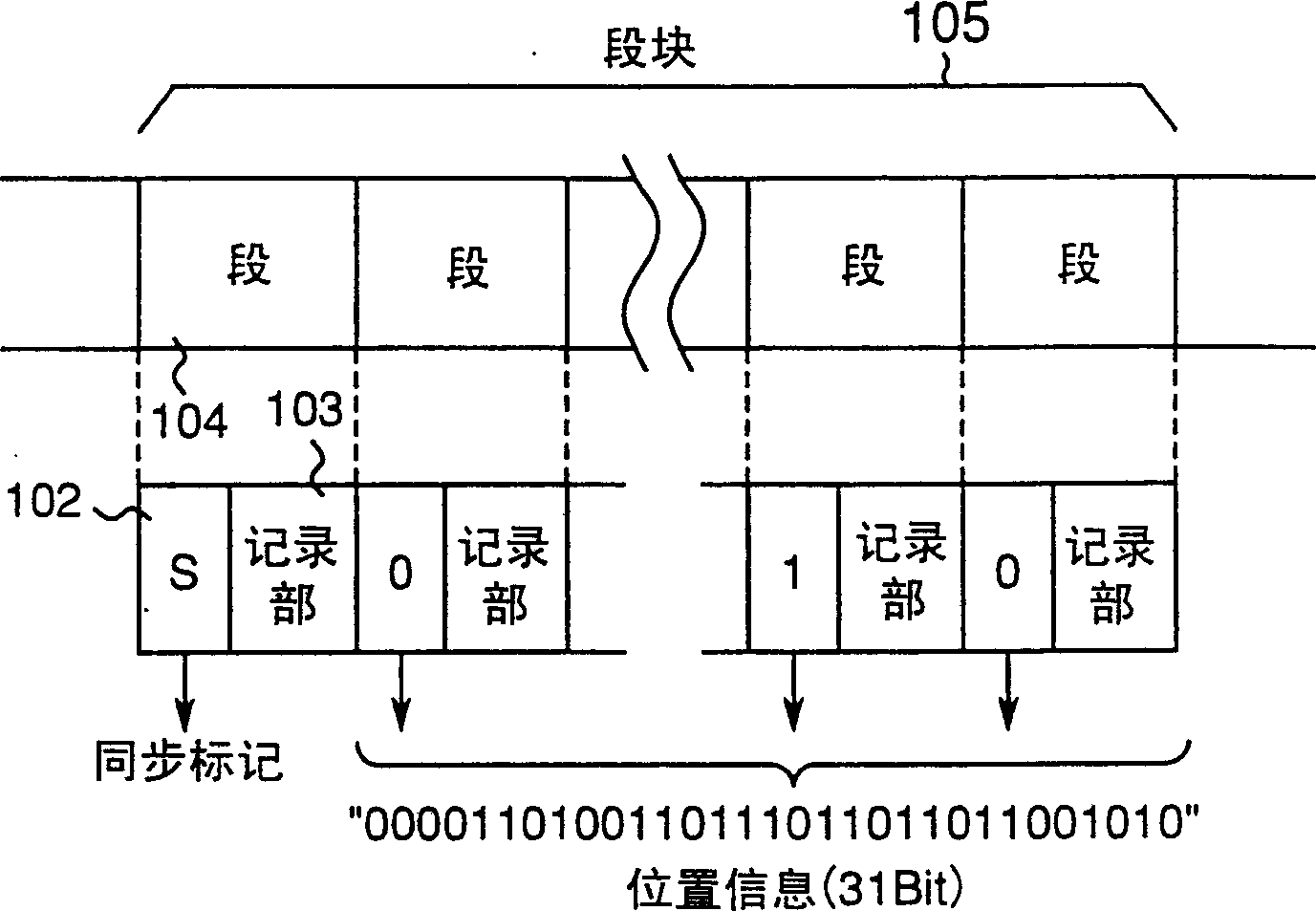
[0170] Figure 1A 1B is a structural diagram of an optical disc according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and 1B is an explanatory diagram showing the arrangement of segments. exist Figure 1A Among them, 101 is an optical disc substrate, 102 is a header portion formed in advance when manufacturing an optical disc, 103 is a recording portion where information can be recorded, and 104 is a segment which is an information unit of data. exist Figure 1B Among them, 105 means a segment block with a given number, for example, 32 as a unit.
[0171] On the optical disk substrate 101, a phase change film is formed in advance which optically changes the phase state like amorphous or crystalline, and reads a signal based on the difference in reflectance during recording and reproduction.
[0172] Below, refer to Figure 2A , detailing the relationship between segment 104 and segment block 105 .
[0173] In the optical disk of this embodiment, a track is formed by continuou...
Embodiment 2
[0218] In Example 2, instead of image 3 Groove discontinuities of varying widths shown, such as Figure 10 As shown, the discrete address is provided by utilizing the groove deformations, namely the groove lower offset 65 , the groove upper offset 66 , and their combination 67 . Such as Figure 10 As shown, the positive mark "1" is represented by the upper groove offset 66 alone, and the synchronization is represented by the combination 67 of the lower groove offset 65 and the upper groove offset 66 occurring in the following given time. The notation "S", if the groove lower excursion 65, and the groove upper excursion 66 does not occur within the following given time, represents a negative notation "0". The groove lower offset and the groove upper offset are collectively referred to as the groove offset. Any one of the part 65, the part 66, and the combination part 67 may be used as the synchronization mark, the positive mark, or the negative mark, but it is preferable to...
Deformed example 1
[0240] From Figure 15 to Figure 20 A first modification example of the groove deformation portion of the second embodiment is shown.
[0241] exist Figure 10 In, although the groove lower offset part 65 and the groove upper offset part 66 are used, but in Figure 17 In the first modified example, the groove descending phase inversion part 74 and the groove rising phase inverting part 75 are respectively changed. The groove falling inverting portion 74 is the descending portion of the groove that oscillates in a sinusoidal wave from the peak to the valley Even if the phase of about 1 / 4 of the swing cycle from the peak of the groove is reversed up and down, the groove rising inverting portion 75 is the rising portion from the valley to the peak of the groove even if the phase is reversed up and down for about 1 / 4 of the wobble period from the valley of the groove. The groove falling phase inverter and the groove rising phase inverter are collectively referred to as the groo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com