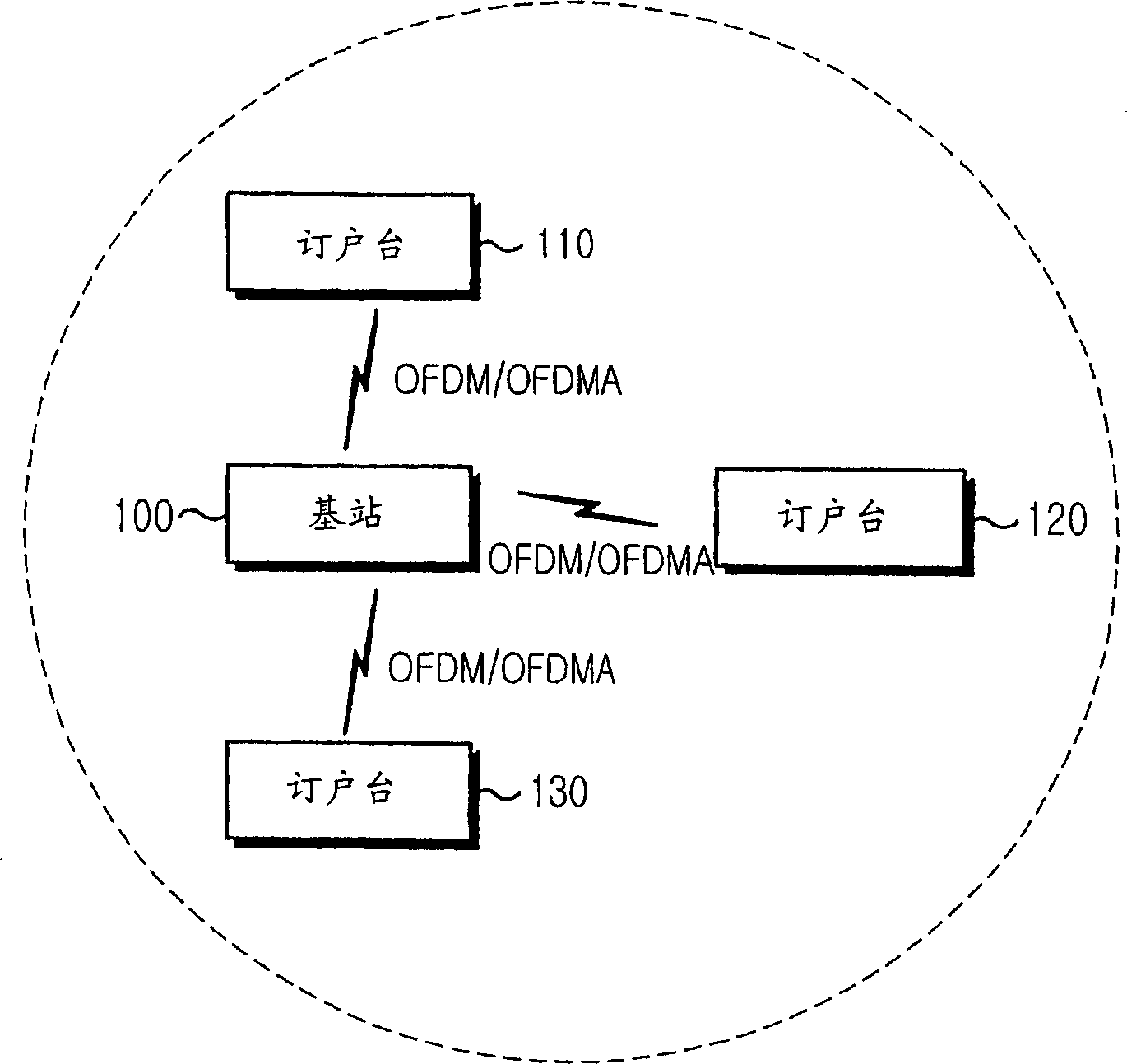
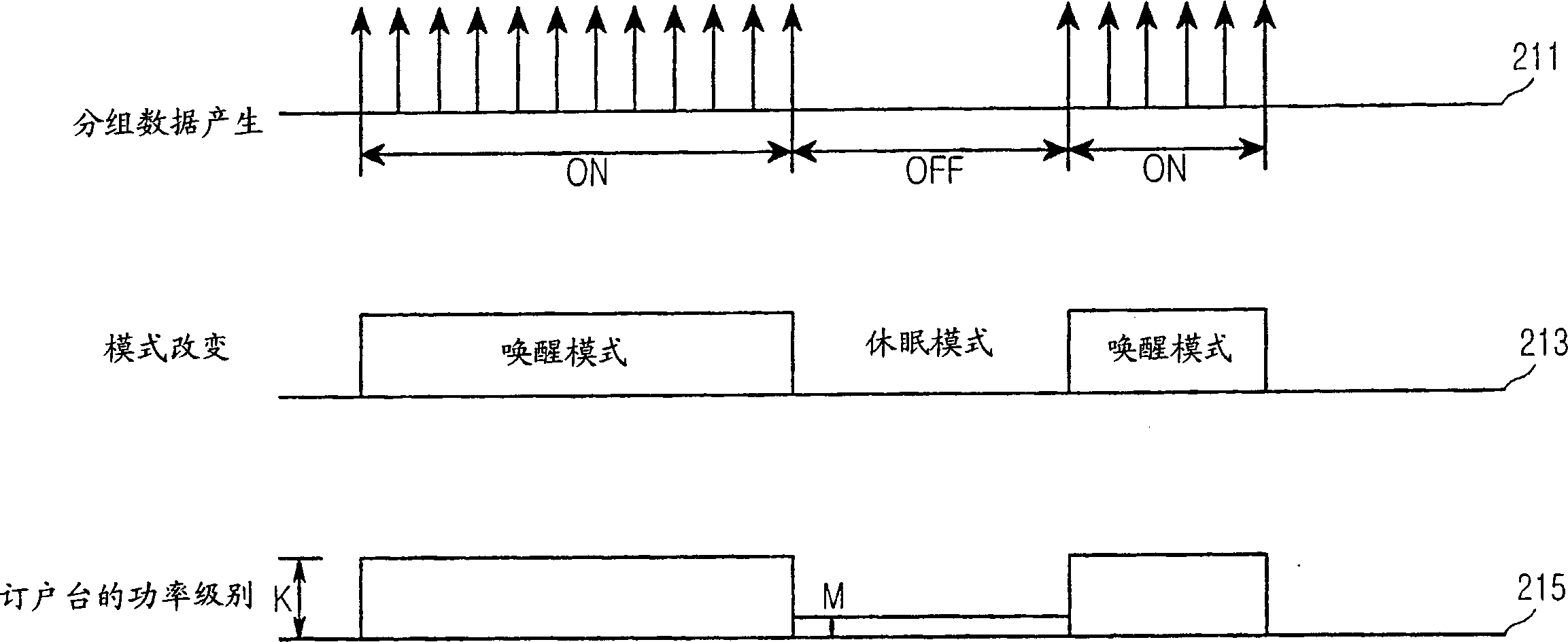
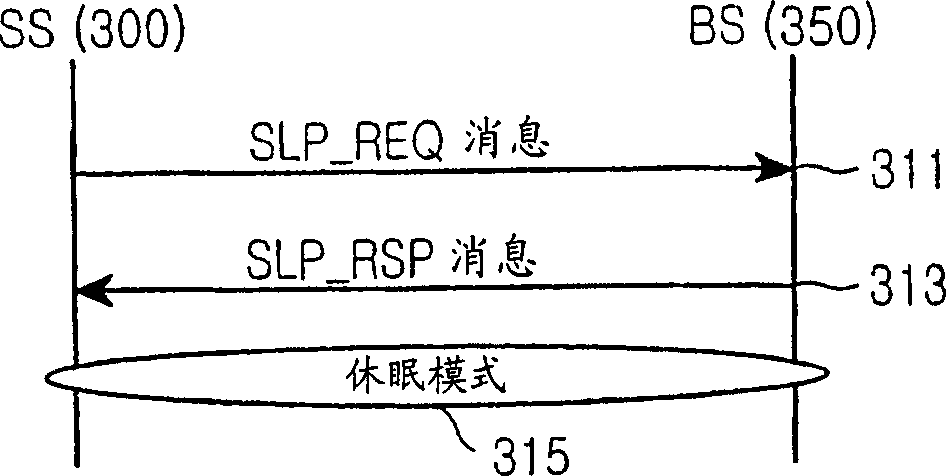
Method for setting sleep interval in a broadband wireless access communications system
A broadband wireless and communication system technology, applied in the field of controlling sleep mode and wake-up mode, can solve the problems of packet data transmission performance degradation, packet data loss, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0116] As the first embodiment of the present invention, the following will refer to Figure 7 and Figure 8 To illustrate the method of keeping the sleep interval value at the maximum window (MAX-WINDOW) value.
[0117] Typically, after the sleep interval has expired and transitioned to the awake mode in sleep mode, the subscriber station transitions back to sleep mode if it receives a negative signal in the traffic indication message during the listen interval.
[0118] After the subscriber station is woken up from the sleep mode, if the subscriber station transitions back to the sleep mode without data transmission / reception, there is a high possibility that data is not transmitted for a while. Then, the sleep interval is gradually increased exponentially to reach the maximum window size previously specified by the base station. Therefore, the first embodiment of the present invention provides a method of continuing to maintain the sleep interval at the maximum window val...
no. 2 example
[0137] As a second embodiment of the present invention, the following will refer to Figure 9 and Figure 10 A method for repeating the process of increasing the sleep interval up to the maximum window value after setting the sleep interval to the minimum window (MIN-WINDOW) value will be described.
[0138] If no data is transmitted, the base station sends a traffic indication message containing negative information to the subscriber station, and the subscriber station receiving the message continues to stay in sleep mode. However, since the data to be transmitted by the base station is not real-time data, the data has random characteristics in terms of frequency of occurrence.
[0139] Therefore, it can be considered that when the sleep interval reaches the maximum window, the sleep interval is set back to the minimum window, and then the sleep interval is increased exponentially.
[0140] Figure 9 A process of setting the sleep interval back to the minimum window value ...
no. 3 example
[0156] As a third embodiment of the present invention, the following will refer to Figure 11 12 to illustrate a method of resetting the sleep interval to a new message when the sleep interval reaches the maximum window value.
[0157] Under normal circumstances, when doubling the sleep interval, the sleep interval reaches the maximum window if there is no data to be sent by the base station. In this case, it is preferable to increase the minimum window value and the maximum window value since the frequency at which data is received by the subscriber station can be significantly reduced. That is, a new sleep interval must be set.
[0158] Figure 11 Shown is a procedure for requesting setting of a new sleep interval by a subscriber station by sending a sleep request message when the sleep interval reaches the maximum window value. As explained in the first and second embodiments, after the sleep interval reaches the maximum window value 1117, the subscriber station 1111 tra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com