Brake device for elevator
A braking device and elevator technology, which is applied to elevators, transportation and packaging, elevators, etc. in buildings, can solve problems such as increasing the current flowing into the coil, and achieve the effect of reducing braking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
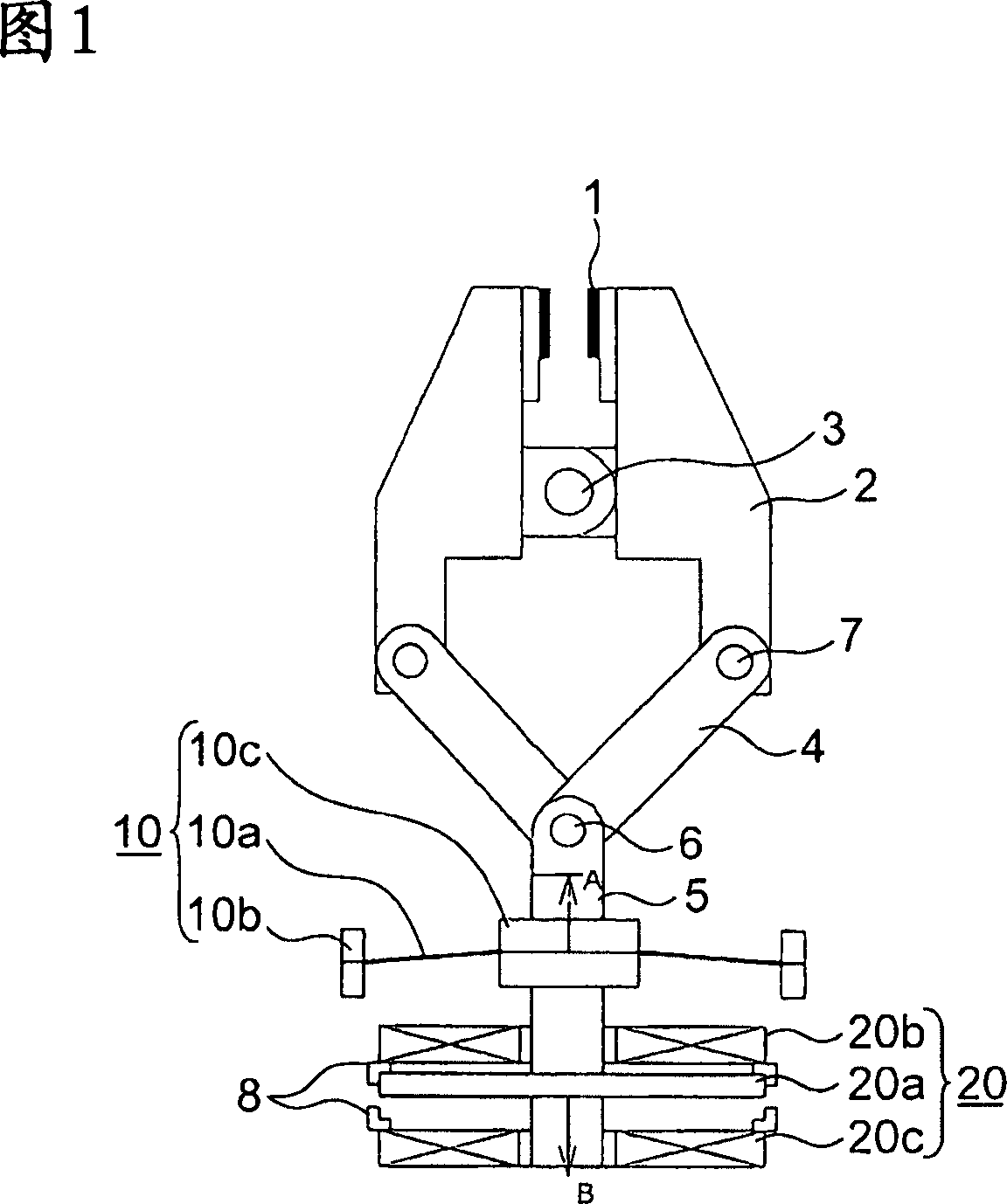
[0024] Fig. 1 is a block diagram showing an elevator braking device according to a first embodiment of the present invention. The outer edge portion of the disc spring 10a is supported by the fixing portion by the support portion 10b. And the inner edge portion (central portion) of the disc spring is fixed to the movable plunger 5 by the support portion 10c. One end of the movable inserting rod 5 is connected with one end of the connecting rod 4 through the supporting shaft 6 , and the connecting rod 4 can rotate relative to the supporting shaft 6 . The other end of the link 4 is connected to the end of the arm 2 through a support shaft 7 so that it can freely rotate relative to the support shaft 7 . The arm 2 is rotatably fixed on a fixed shaft 3 . Attached to the front end of the arm 2 is a slide member 1 that is in direct contact with a disk member, a guide rail (not shown), or the like. At the other end of the movable plunger 5, a drive unit 20 for the movable plunger i...
no. 2 approach
[0031] Fig. 5 is a block diagram showing a braking device for an elevator according to a second embodiment of the present invention. The magnet spring 40 is composed of a permanent magnet 40a, a movable iron core 40b integrally fixed to the movable plunger 5 and operated, and a yoke 40c provided to surround these components. Other structures are the same as those of the first embodiment. In addition, 1 to 4, 6, and 7 constitute a brake mechanism, 40 constitutes a first drive mechanism, and 20 constitutes a second drive mechanism.
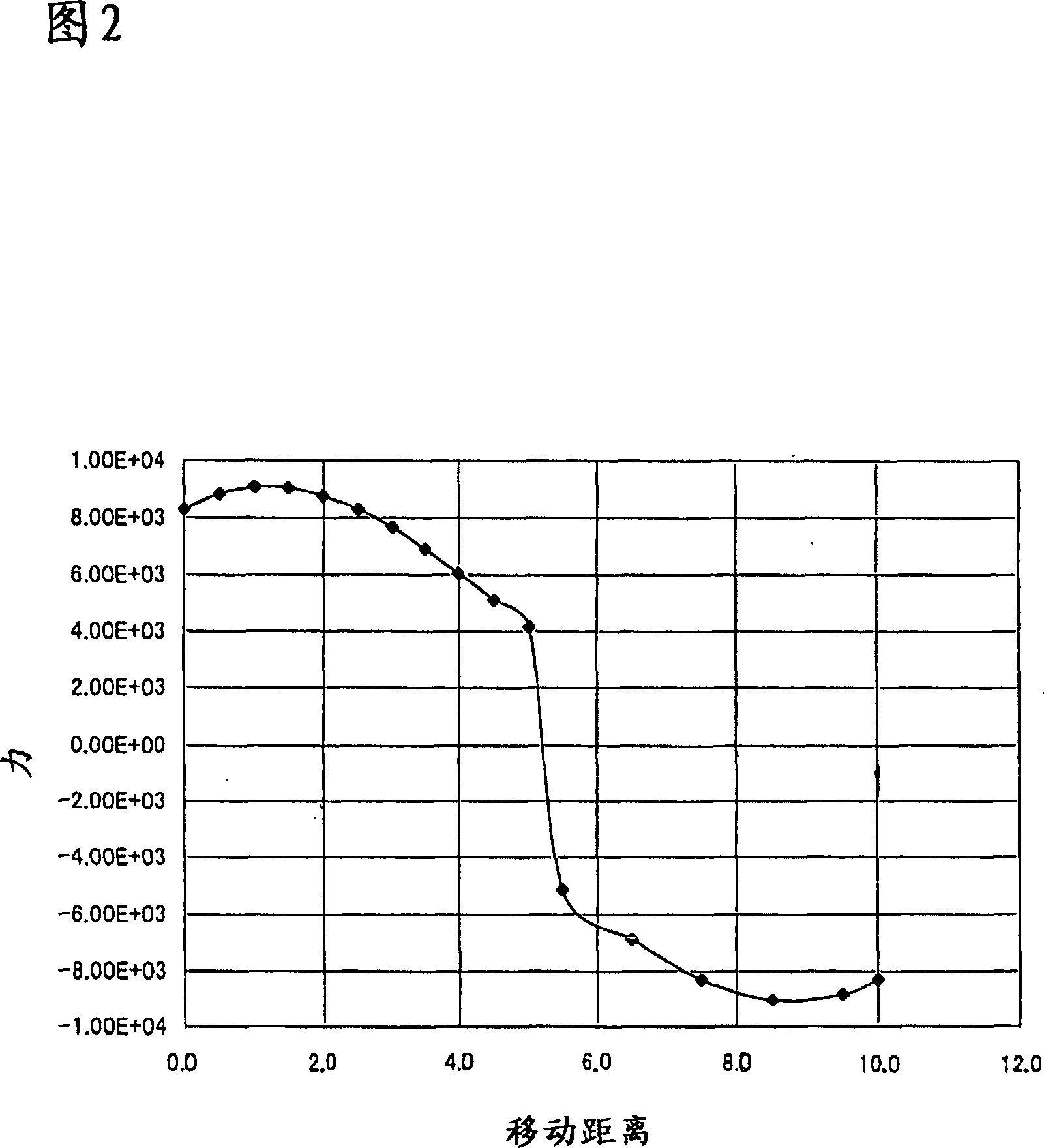
[0032] The operation will be described below. FIG. 5 shows a state in which a disc member or a guide rail is gripped between slide members 1 and a braking force is exerted. At this time, the movable iron core 40b is pressed in the arrow A direction by the magnetic flux in the arrow C direction of the permanent magnet 40a. Like this, movable inserting rod 5 is also stressed in the direction of arrow A, and the supporting shaft 7 of connecting rod ...
no. 3 approach
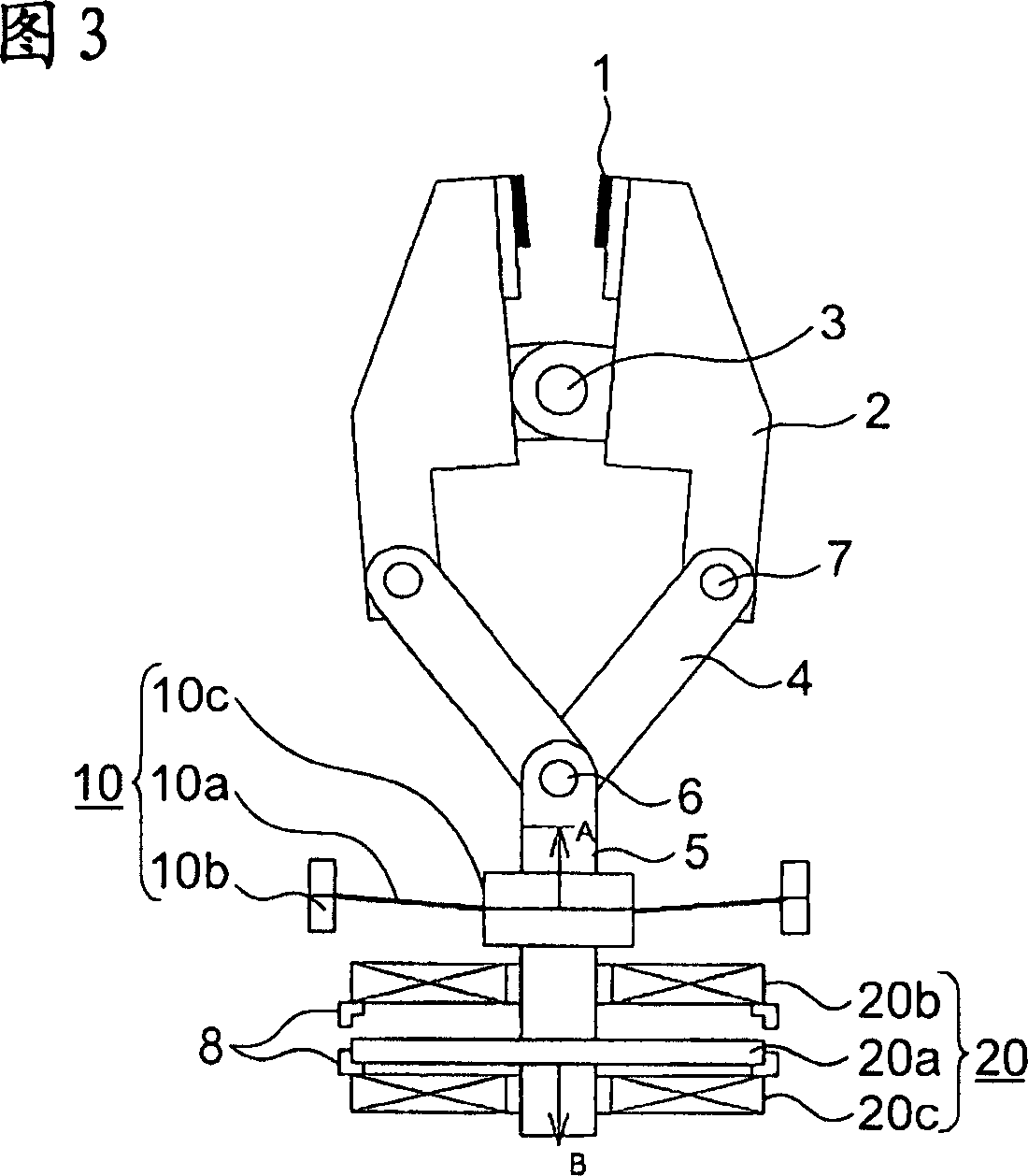
[0037] Fig. 8 is a configuration diagram showing an elevator braking device according to a third embodiment of the present invention. The electromagnetic attraction device 50 is fixed on the movable plunger 5 by a permanent magnet 50a and forms a movable iron core 50b that moves integrally, and the braking coils are respectively arranged on the opposite sides (mutually opposite) of the permanent magnet 50a both sides. 51a, a release coil 51b, and a yoke 50c provided to surround the coils 51a, 51b, the permanent magnet 50a, and the movable iron core 50b. Other structures are the same as those of the first embodiment. In addition, 1 to 4, 6, and 7 constitute a brake device, 50 constitutes a first drive mechanism, and 51a, 51b constitute a second drive mechanism.
[0038] The operation will be described below. FIG. 8 shows a state in which a disc member or a guide rail is gripped between the slide members 1 and a braking force is exerted. At this time, neither the brake coil 5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com