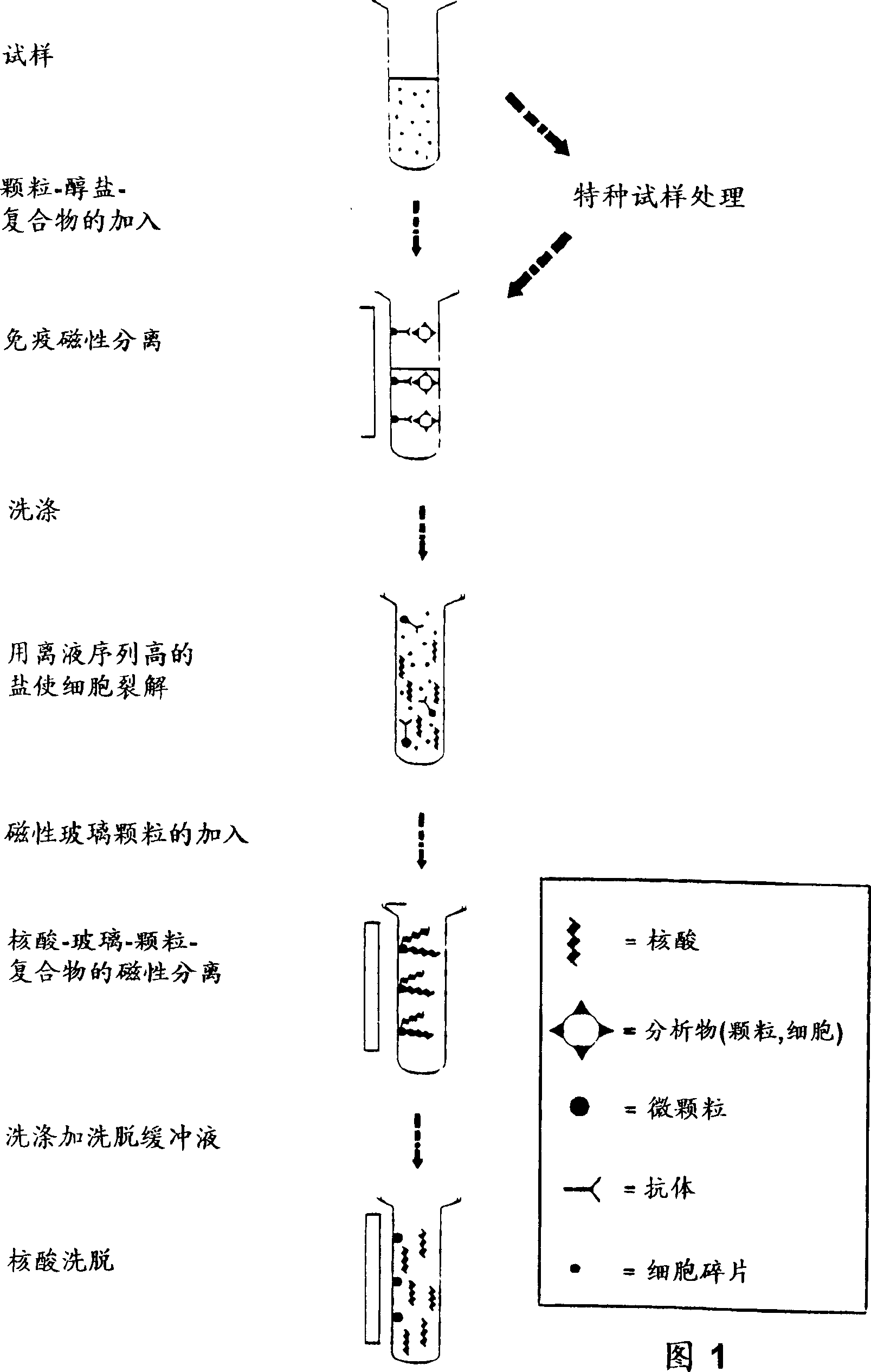
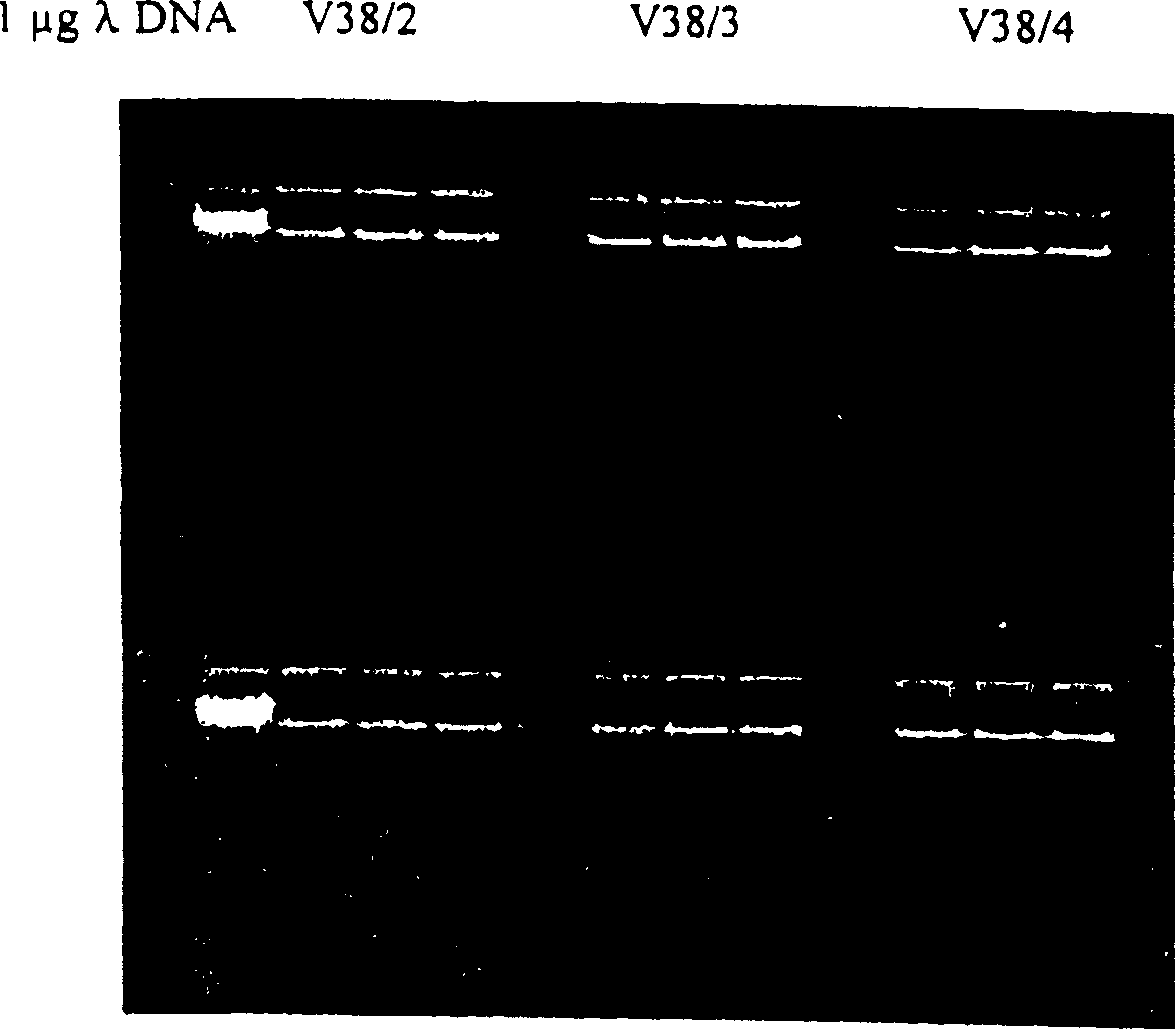
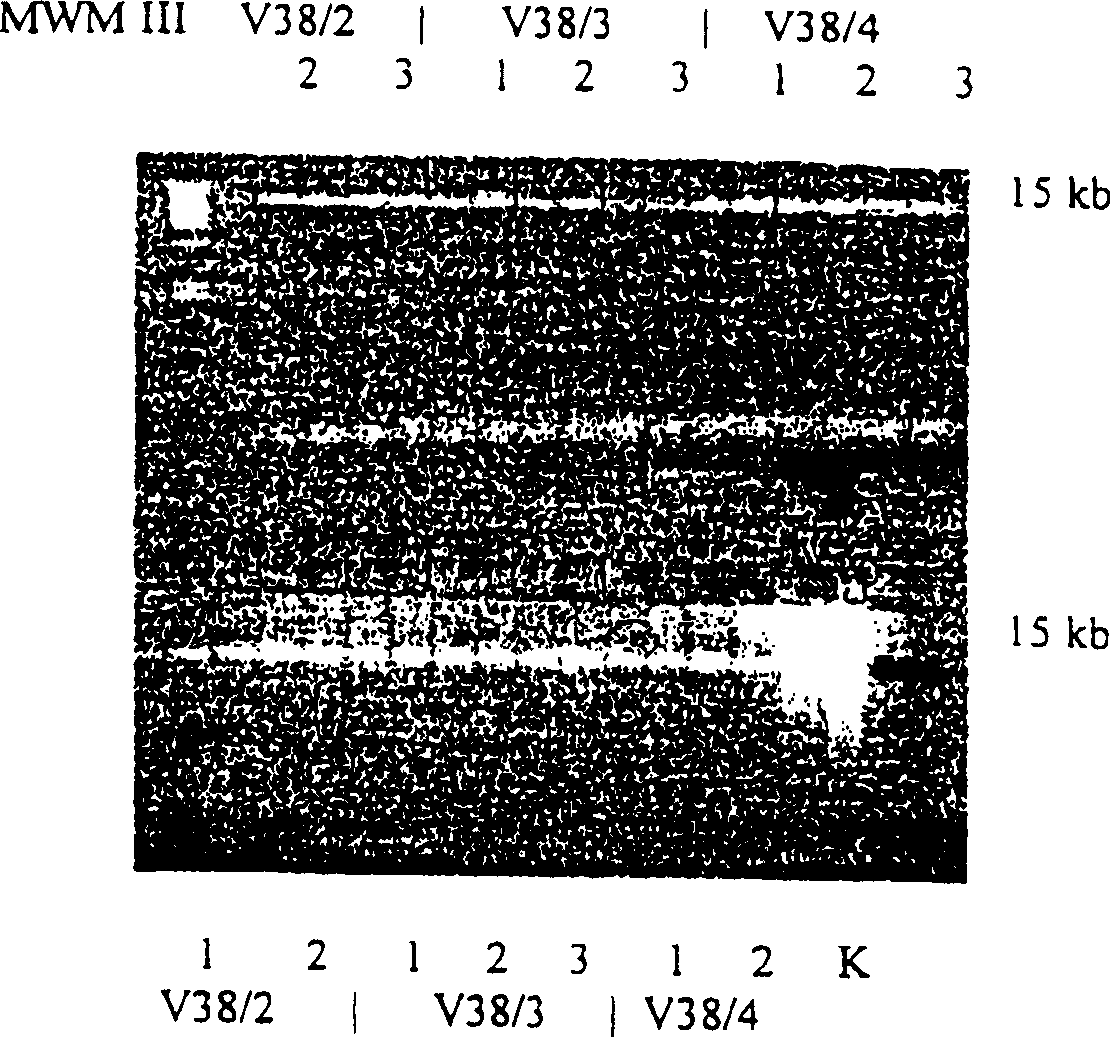
Enzyme reaction method for nucleic acid and composition for separating nucleic acid
An enzymatic reaction and nucleic acid technology, applied in the direction of alkali metal compounds, chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems that cannot be used to remove inhibitors, and achieve the effect of easy preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0070] Preparation of magnetic particles of the present invention
[0071] Six sols were used. The sols were prepared as follows:
[0072] Sol 1 (SiO 2 :B 2 0 3 =7:3):
[0073] Synthesis was carried out in a 250ml round flask with constant agitation.
[0074] 86.6ml tetraethylorthosilicate
[0075] +7ml absolute non-denatured ethanol
[0076] +14.1ml0.15M HCl
[0077] A two-phase mixture was produced. Stir at room temperature until single phase. add drop by drop
[0078] +37.8ml trimethyl borate
[0079] The sol was then left at 50°C for 2 hours. join in
[0080] +14.1ml0.15M HCl
[0081] Sol 2 (SiO 2 :B 2 0 3 =4:1):
[0082] Synthesis was carried out in a 250ml round flask with constant agitation.
[0083] 100.5ml tetraethylorthosilicate
[0084] +7ml absolute non-denatured ethanol
[0085] +16.3ml0.15M HCl
[0086] A two-phase mixture was produced. Stir at room temperature until single phase. add drop by drop
[0087] +25.6ml trimethyl borate
[008...
example 2
[0132] Preparation of GMP1, GMP2, GMP3 and GMP4
[0133] GMP1, GMP2, GMP3 and GMP4 are different batches of pigments prepared under the following conditions from sol 1 (example 1) by the process described in example 1:
[0134] parameter GMP1 GMP2 GMP3 GMP4 Sol aging (h) (30℃) 36 36 36 36 Pigment percentage in sol (g / 100ml) 5 15 8 20 Nozzle Airflow (%) 100 100 100 100 air pressure(bar) 6 6 6 3 Nozzle temperature (℃) 135 120 130 143 Densification temperature (°C) 534 534 534 615 Immediate oxygen treatment time (1 hour) (300℃) (300℃) (300℃) (400℃) Pigment yield Low high middle high DNA yield Low high high high
example 3
[0136] Pretreatment of human whole blood PCR samples using magnetic glass particles
[0137] nucleic acid isolation
[0138] 3 parts of glass magnetic particles (GMP2-4), 10 mg per part were put into micro test tubes. The exact sample weights are given in Table 1. Three repeated measurements were carried out.
[0139]Pipette 40 μl proteinase K (20 mg / ml, made by lyophilization) into 200 μl thawed whole blood and mix immediately. Next add 200 μl binding buffer (6M guanidine-HCl, 10 mM trimethylaminomethane -HCl, 10 mM urea, 30% Triton X-100, pH 4.4) and mixed, then incubated at 70°C for 10 minutes. 200 μl of isopropanol was added and the preparation was mixed in a vortex mixer for 10 seconds. The sample was left at room temperature for 20 minutes and then mixed again for 10 seconds. Magnetic separation was performed on a Boehringer Mannheim (ID# 1641794) Magnetic Particle Separator for at least 30 seconds. Remove the supernatant and analyze as described below.
[0140] Mag...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com