Method and apparatus for non-compressed evaluation of tissue specimens
a tissue specimen and non-compressed technology, applied in the field of tissue specimen non-compressed evaluation, can solve the problems of loss of relative orientation of the sample in the transition, the surgeon's inability to remove the appropriate amount of tissue from the patient, etc., and achieve the effect of ensuring the relative position and angle of the tissue sample, and facilitating the transport of the sampl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
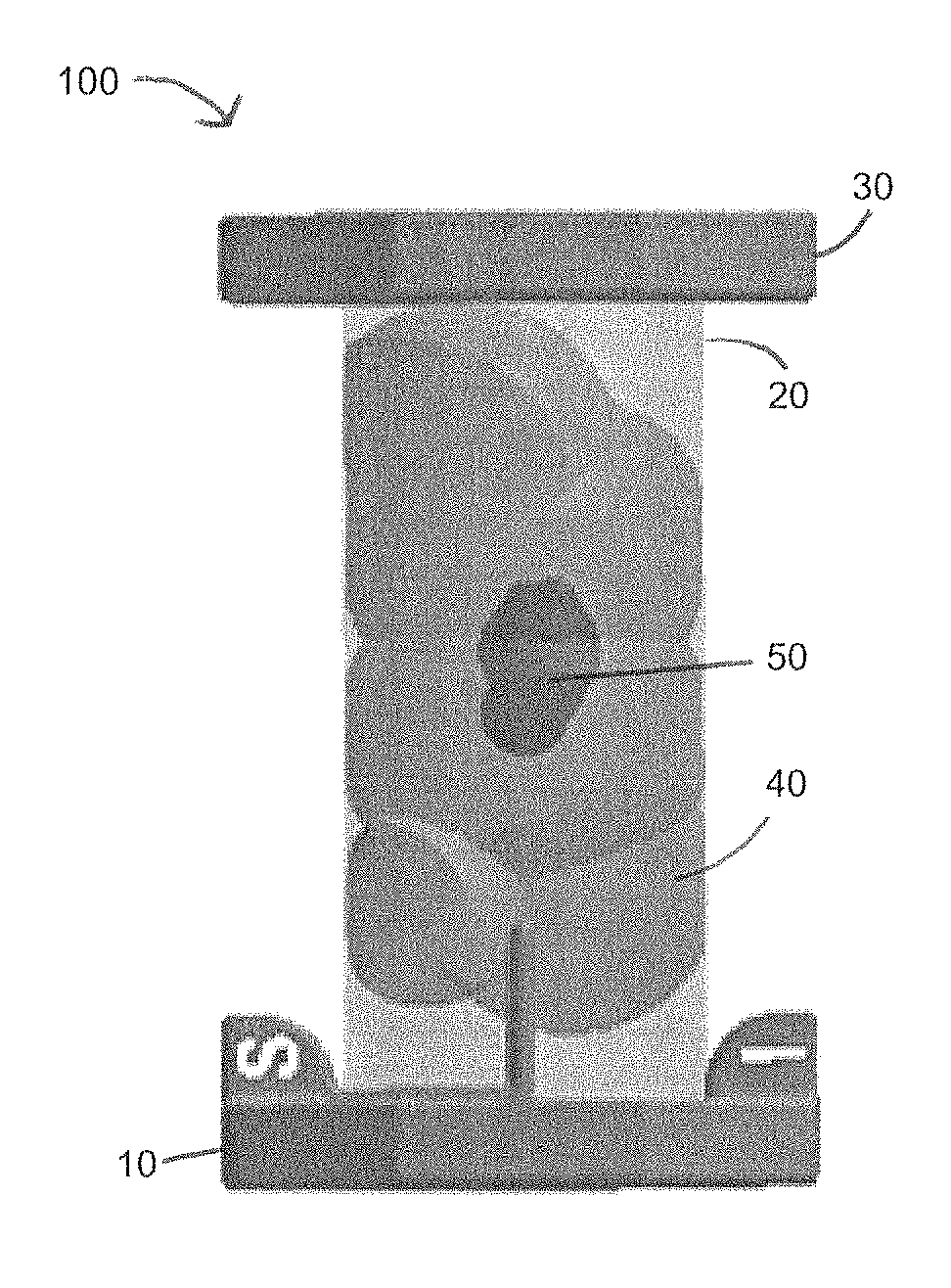
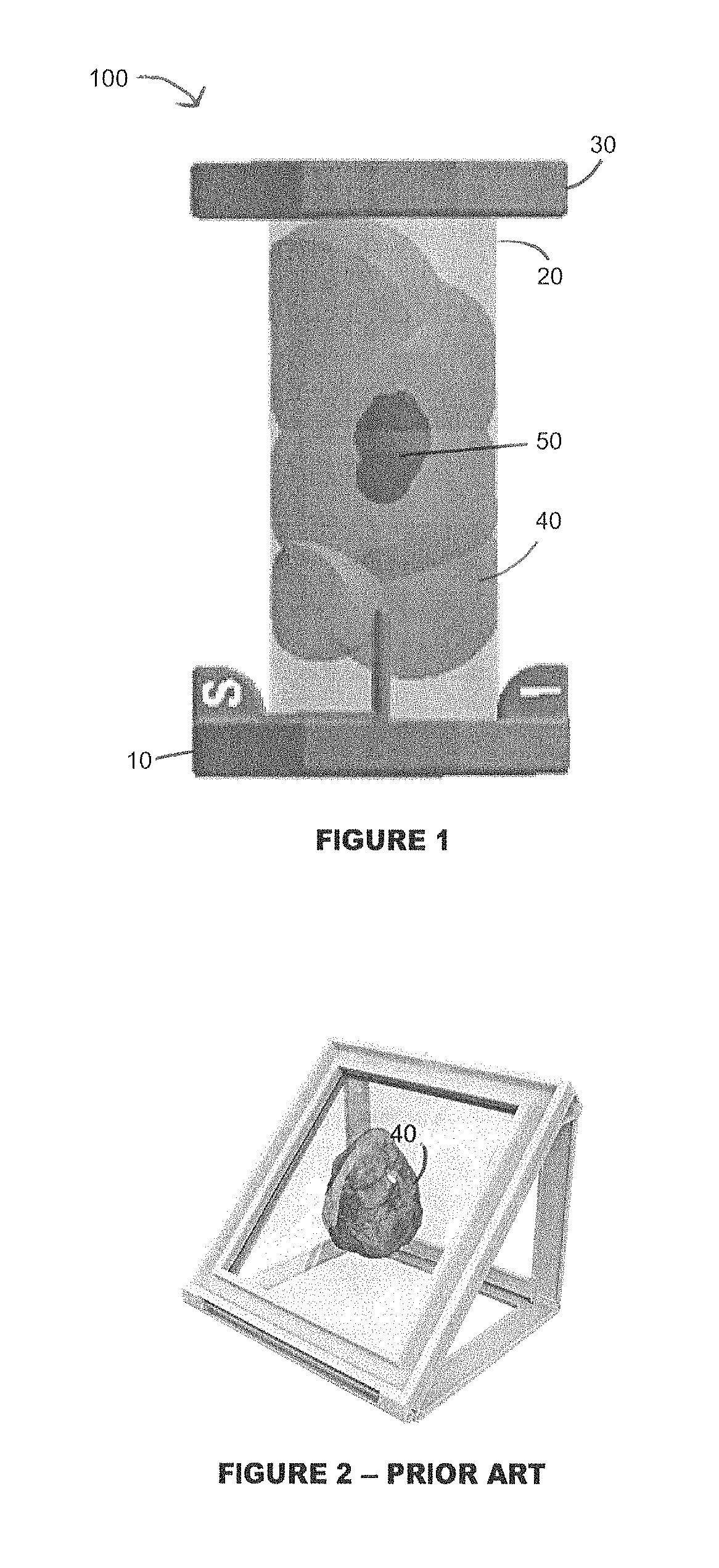
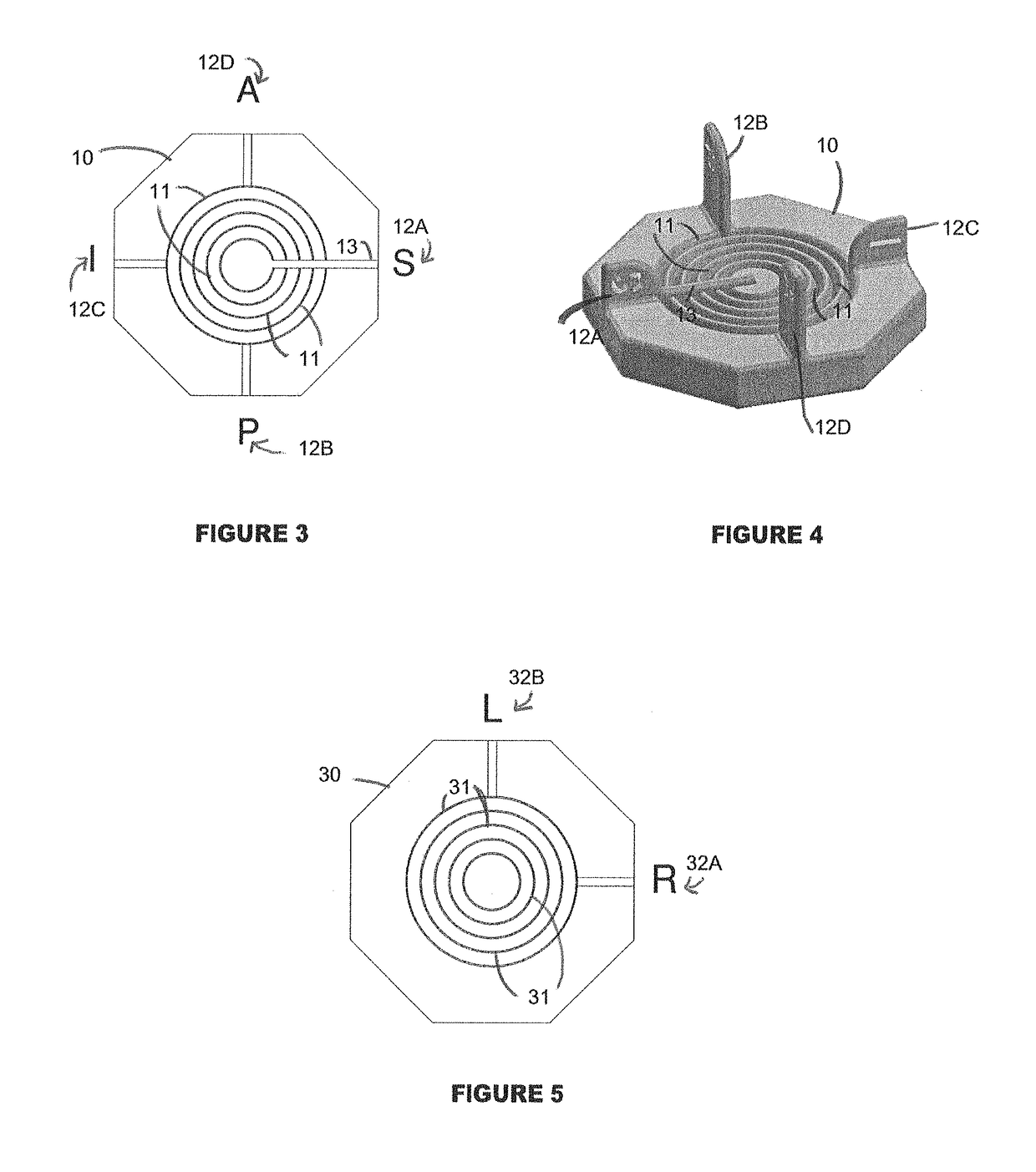
[0031]Referring to FIG. 1 generally, the present invention provides for an apparatus 100 featuring an end cap 10, a flexible plastic sheet 20, and top cap 30. The end cap 10 features a series of lined grooves embedded in the end cap. The flexible plastic sheet 20, when rolled into a round or spherical configuration, may be fitted into one of lined grooves embedded in the end cap 10. After being placed in the appropriate circular groove, the top cap 30, which also features a series of lined grooves embedded into one side of the top cap 30, is placed on the top end of the rolled plastic sheet 20 and the plastic sheet 20 fit into the appropriate lined groove of the top cap 30. Upon placement of the top cap 30 and end cap 10 on the rolled plastic sheet 20, the tissue specimen 40, which may include cancerous cells 50, contained within the sheet 20 will remain suspended and ready for examination by the handler of the apparatus 10.
[0032]FIG. 2 is an example of the conventional manner of en...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com