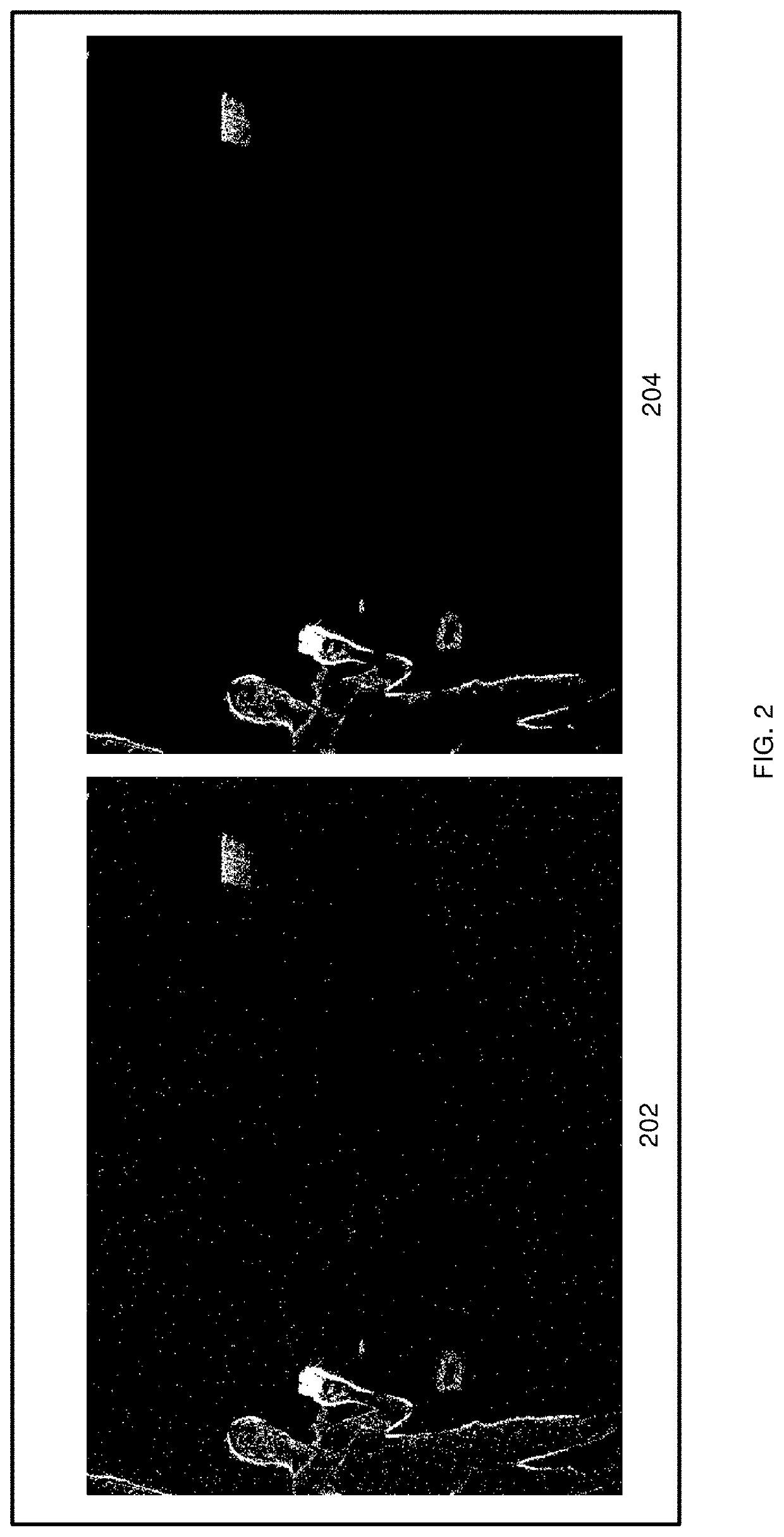
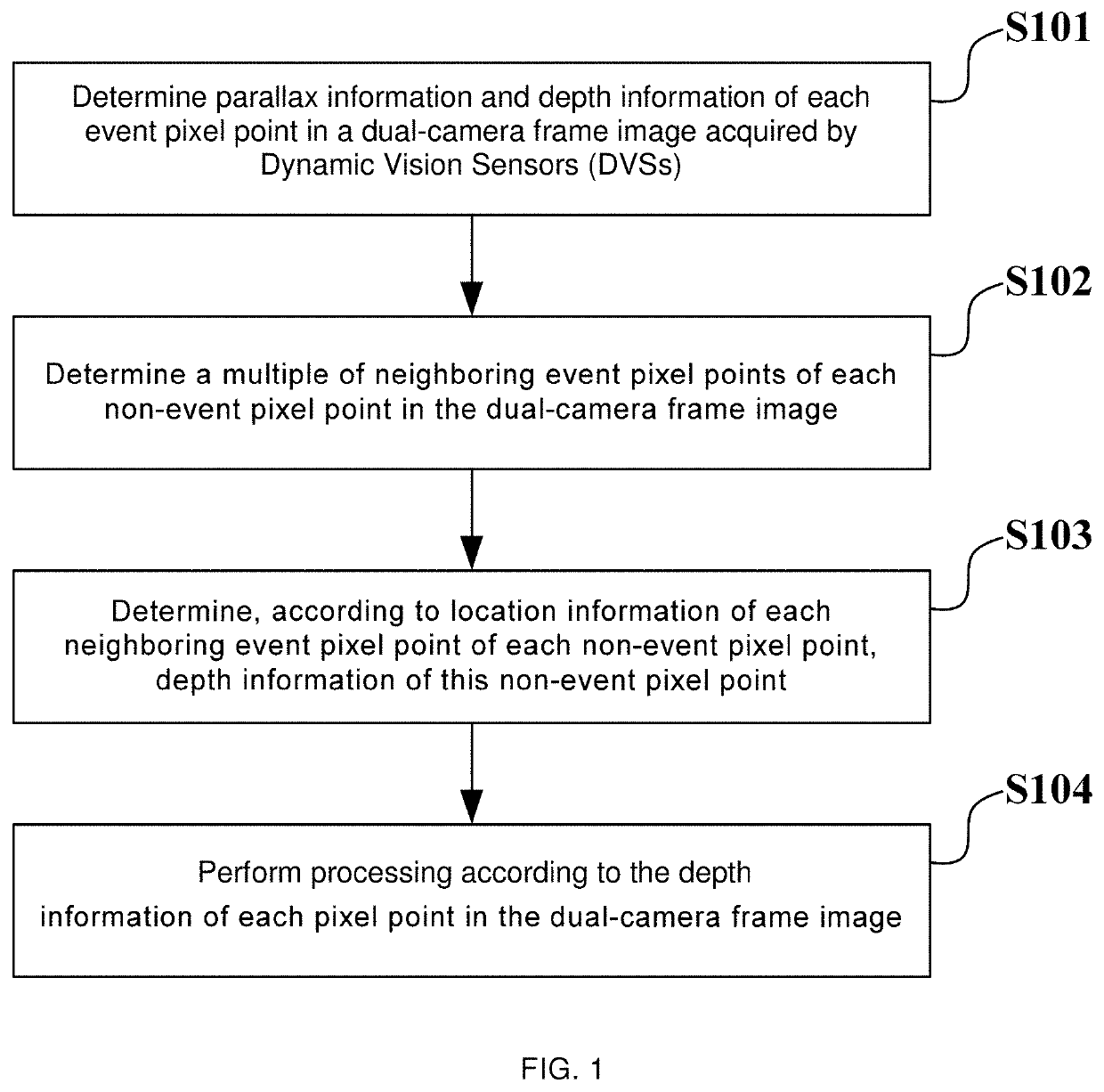
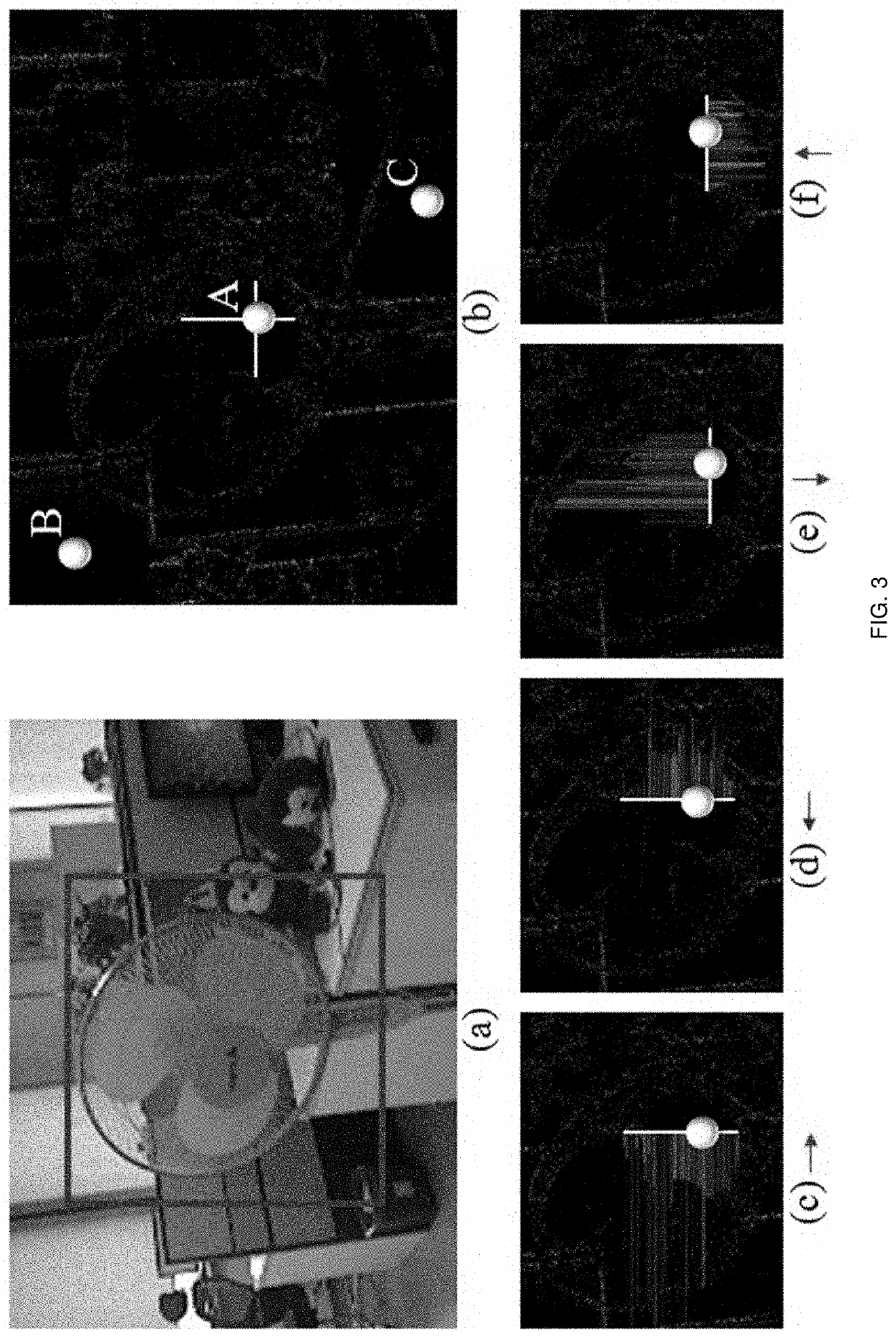
Image vision processing method, device and equipment
a processing method and image technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as information determination, pixel points are wrong, and it is difficult to distinguish between non-event pixel points,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024]Exemplary embodiments will be described in detail hereinafter. The examples of these exemplary embodiments have been illustrated in the accompanying drawings throughout which same or similar reference numerals refer to same or similar elements or elements having same or similar functions. The embodiments described with reference to the accompanying drawings are illustrative, merely used for explaining the present invention and should not be regarded as any limitations thereto.
[0025]It should be understood by one person of ordinary skill in the art that singular forms “a”, “an”, “the”, and “said” may be intended to include plural forms as well, unless otherwise stated. It should be further understood that terms “comprise / comprising” used in this specification specify the presence of the stated features, integers, steps, operations, elements and / or components, but not exclusive of the presence or addition of one or more other features, integers, steps, operations, elements, comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com