Tubular baseball bats with variable stiffened barrels
a baseball bat and variable stiffening technology, applied in the field of baseball bats, can solve the problems of increasing radial stiffness, reducing performance, and reducing performance, so as to reduce bat performance, reduce bat performance, and achieve the highest radial stiffness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
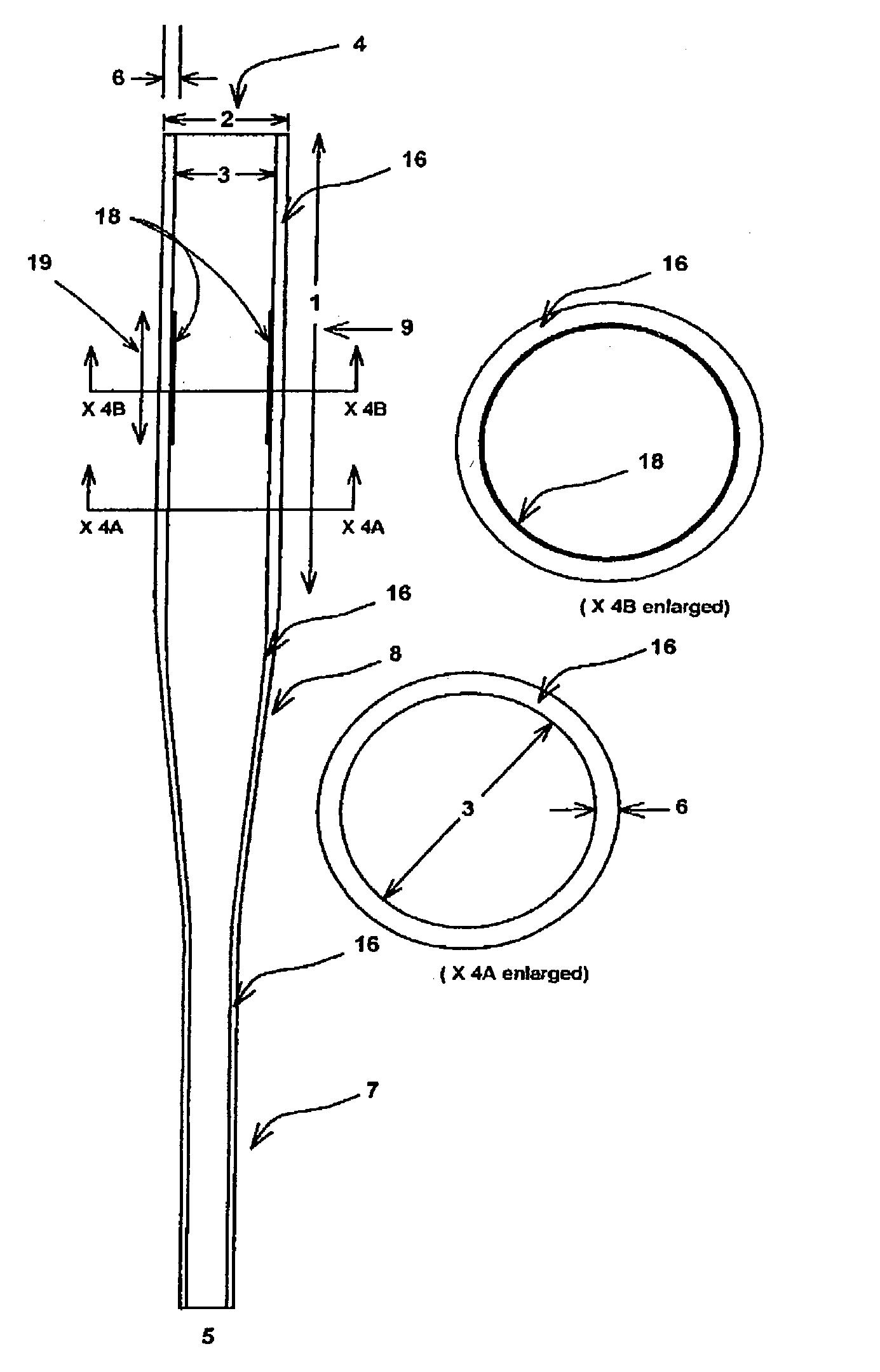
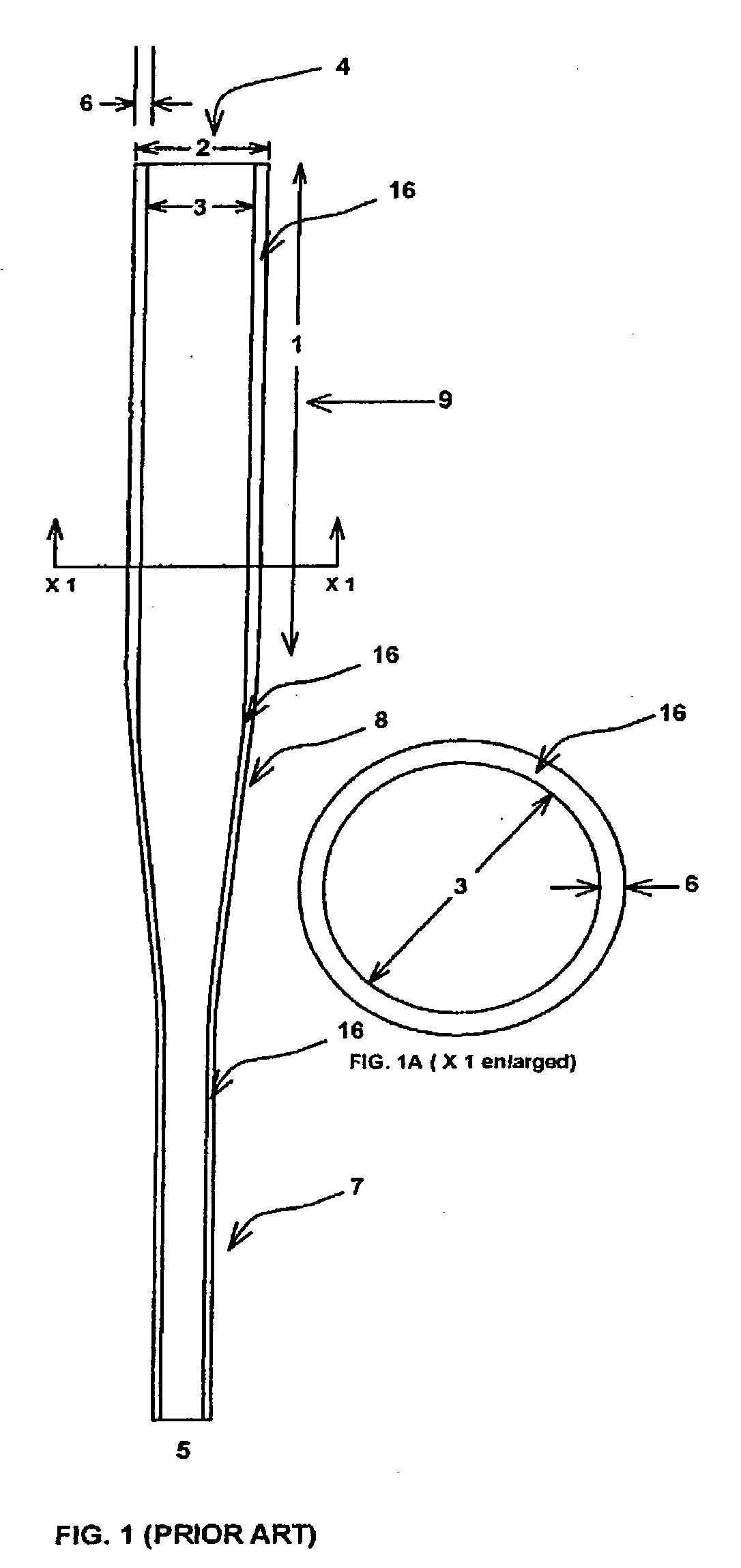
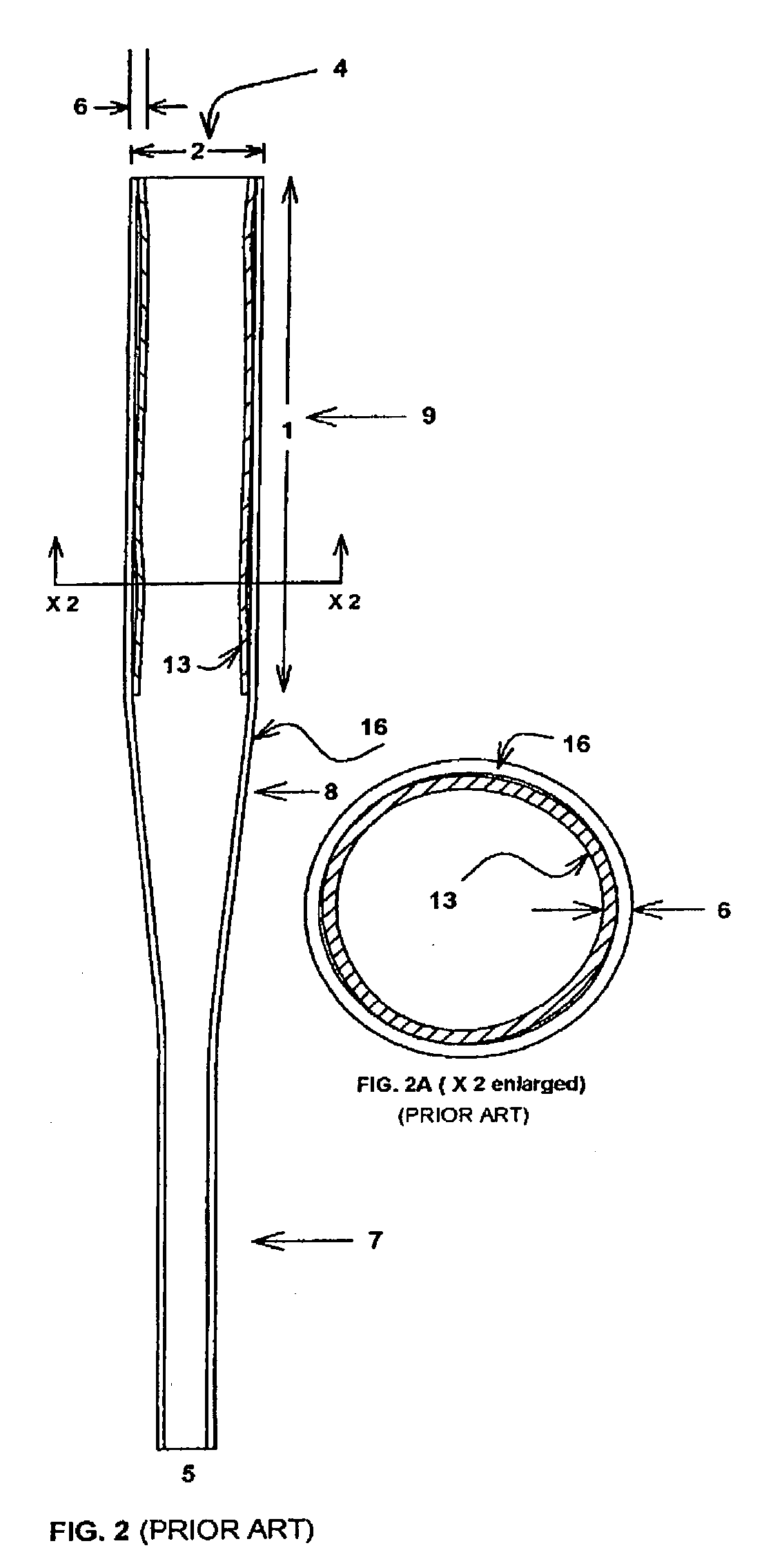
[0051] the present invention FIG. 4 is a single wall tubular baseball bat consisting of a cylindrical handle portion 7 for gripping, a cylindrical tubular barrel portion 9 for striking or hitting, and a tapered mid-section 8 connecting the handle 7 and barrel 9 portions, with a thin polymer composite stiffener 18 located internally within the barrel portion 9 and extending longitudinally in the sweetspot area 19 of the barrel length 1.
[0052] A polymer composite is a non-homogenous material consisting of continuous fibers embedded in, and wetted by, a polymeric resin matrix whereby the properties of the material are superior to those of its constituent fibers and resin taken separately. Such polymer composites are anistropic materials since they exhibit different responses to stresses applied in different directions depending on how the fibers are aligned or angled within the matrix.
[0053] Other materials commonly used in bat constructions such as aluminum, wood and plastics are not...
second embodiment
[0063] the present invention FIG. 5 is a single wall tubular baseball bat which in accordance with the present invention has a thin polymer composite stiffener 18 located externally to the barrel portion 9 generally in the sweetspot area 19 located in proximity to the middle area of the barrel length 1. The resultant stiffened bat results in a calculated lower performance, with a bigger (longer) sweetspot 19, as previously explained.
third embodiment
[0064] the present invention FIG. 6 is a single wall tubular polymer composite baseball bat which in accordance with the present invention has a localized area of fiber type and / or angle change 20 resulting in increased radial stiffness generally in the sweetspot area 19 located in proximity to the middle area of the barrel length 1. Though not shown, this embodiment applies equally well to double-wall and multi-wall (more than two walls) tubular all polymer composite baseball bats and is limited to newly designed polymer composite single wall, double-wall, and multi-walled new bats as opposed to field returned bats. Though not shown, the fiber types, and / or fiber angles, and / or fiber sizes, and / or composite thickness can be designed such as to graduate the radial stiffness of the barrel portion 1 along its entire length. That is, the radial stiffness could be highest in the peak performance area (generally the sweetspot area 19) and gradually changing in uniform increments towards ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com