Method for operating redox flow battery and redox flow battery cell stack
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example
TEST EXAMPLE 1
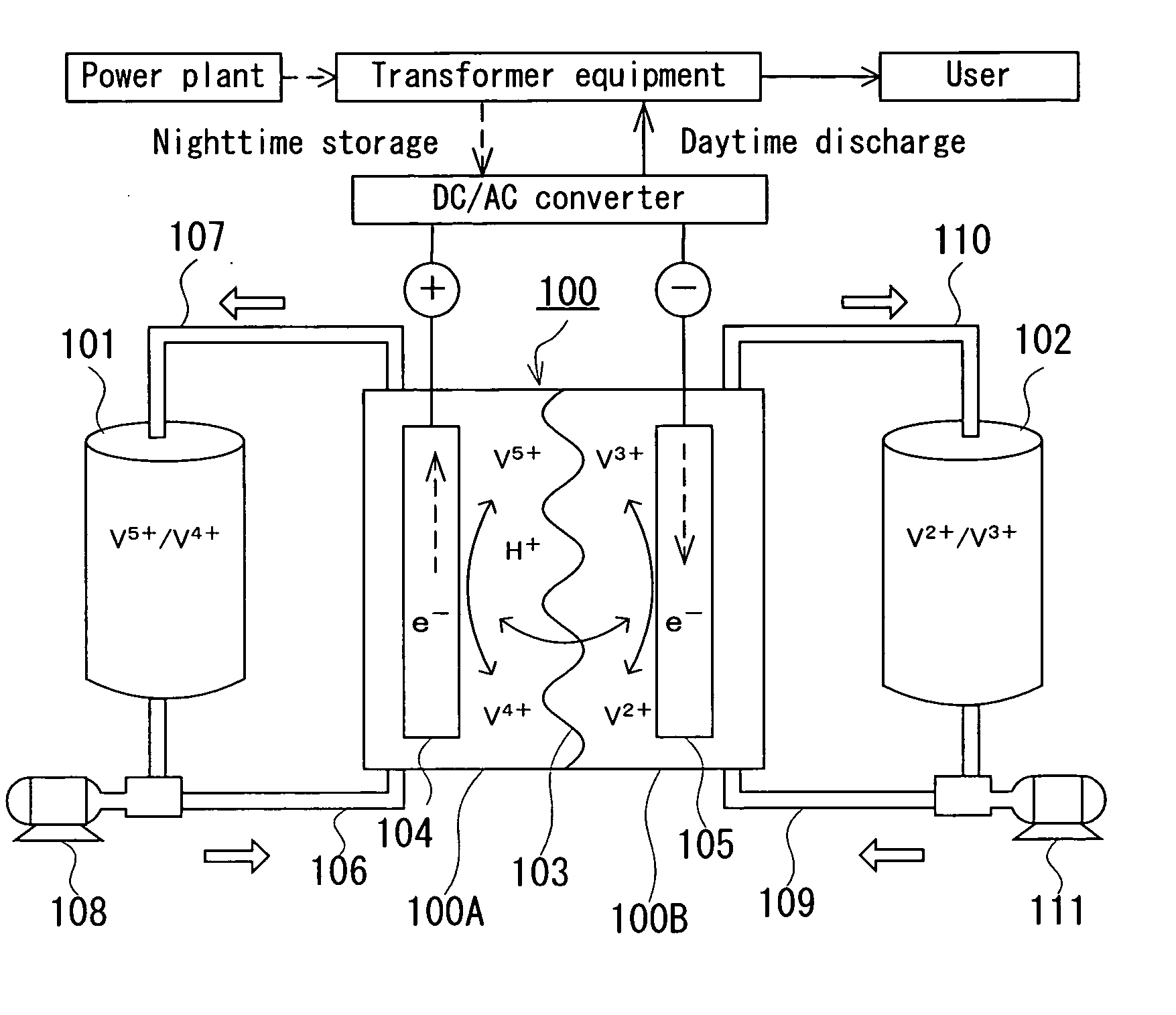
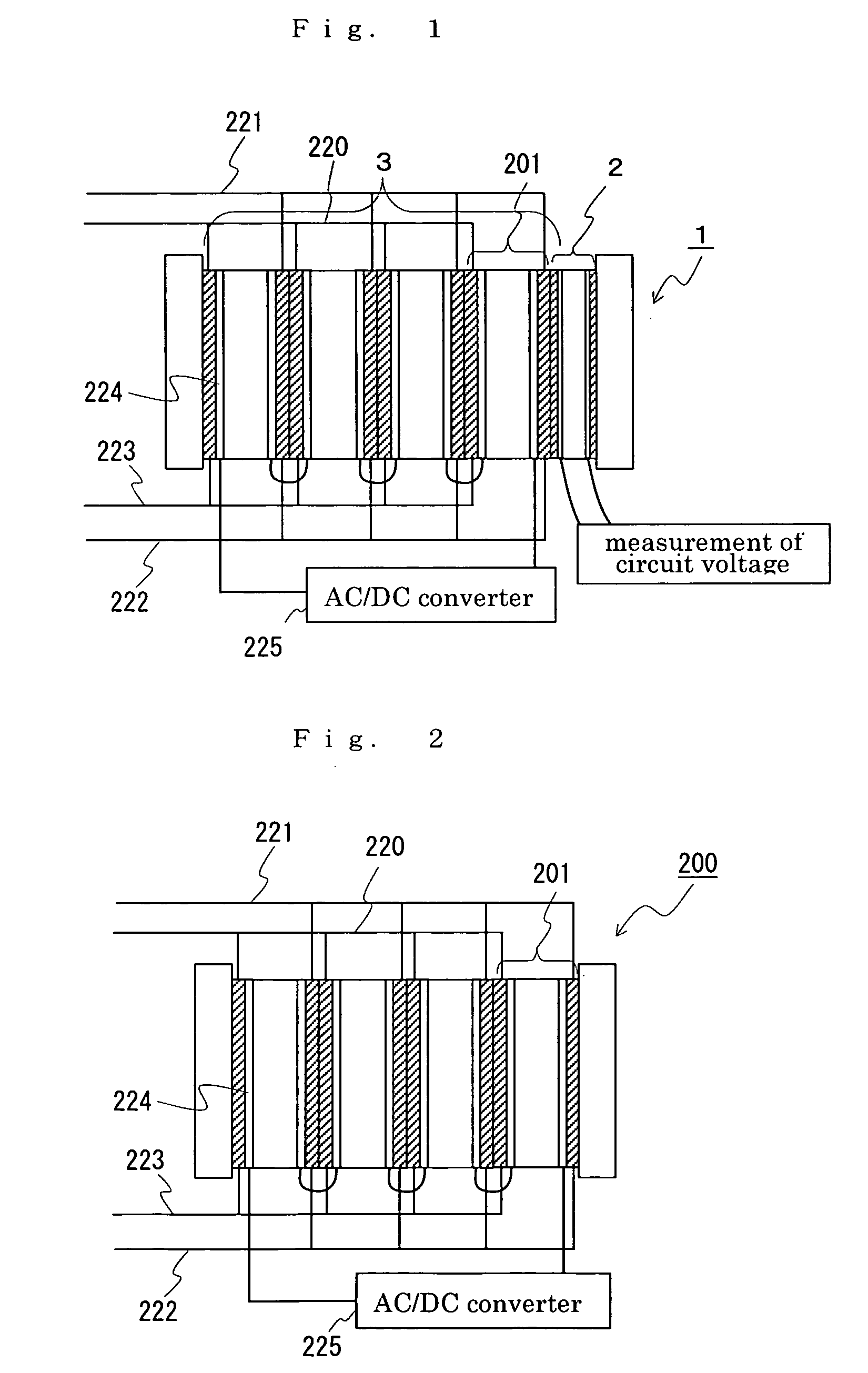
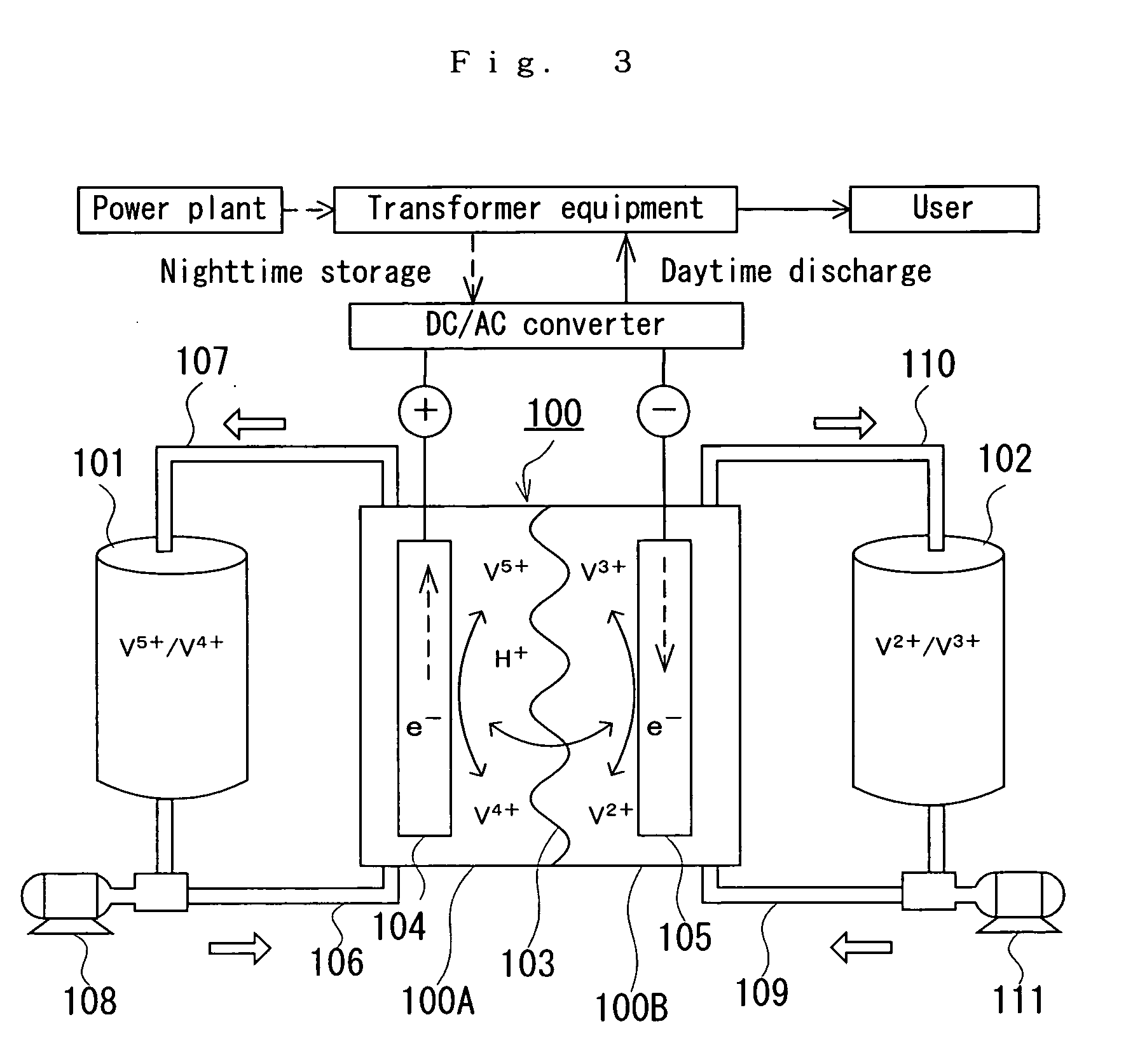
[0031] A redox flow battery of AC170 kW×8 hrs. was produced and the changes of the battery capacity with variation of temperature was monitored. For the test, the redox flow battery system as shown in FIGS. 3 and 4 was fabricated. Taken as the test sample No. 1-1 was a redox flow battery using the cell stack 1 comprising a total of five sets of cells, namely, four sets of sub-stacks 201 (main cell 3), each comprising twenty-five cells stacked in layers, not shown, and one set of auxiliary cell 2 comprising the same cell 1, as shown in FIG. 1. Taken as the test sample No. 1-2 was a redox flow battery using the cell stack 200 comprising four sets of sub-stacks 201 and having no auxiliary cell (the cell stack comprising the main cell only), as shown in FIG. 2. The operating conditions for the test are shown below. The test results are shown in TABLE 1.
[0032] Test Sample No. 1-1: The circuit voltage is constantly measured by the auxiliary cell so that the stop of charge ...
Example
TEST EXAMPLE 2
[0036] A redox flow battery of AC170 kW×6 hrs. was produced. When the charging rate of the main cell decreased, the auxiliary cell was charged. The basic configuration of the battery used in this example was the same as that of the redox flow battery taken as the test sample No. 1-1 used in the Test Example 1. The test was carried out in the following manner. When the circuit voltage as measured by the auxiliary cell reached 1.35V / cell, a direct-current power source additionally provided on the auxiliary cell was turned on to start the charging and discharging operation of the auxiliary cell.
[0037] It was found from the test results that when about 100 kWh was charged by the auxiliary cell in a constant current operation, the decreased charging rate of the main cell could be increased by the auxiliary cell, so that the main cell could keep on discharging to an extent corresponding to the electricity charged by the auxiliary cell. Then, the output capacity was nearly ...
Example
TEST EXAMPLE 3
[0039] Combination of the redox flow battery (AC170 kW×6 hrs.) produced in Test Example 2 with a wind generator was produced. When reduction occurred in charging rate of the main cell, a total output of the wind generator plus the redox flow battery was decreased. This test was carried out in the following manner. When the circuit voltage as measured by the auxiliary cell reached 1.37V / cell, the total output was decreased and the operation was continued until the circuit voltage reached 1.35V / cell. The specification of the wind generator used is given below.
(Specification of Wind Generator)
[0040] Type: Dielectric generator [0041] Rated output: 275 kW [0042] Rated voltage: 400V [0043] Rated speed: 1,500 rpm
[0044] It was found from the test results that the charging rate of the main cell could be increased by decreasing the total output, whereby the main cell could keep on discharging. Then, the output capacity was nearly 1,120 kWh. For comparison, the total output ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com