Method and apparatus for measuring parameters of a stratified flow
a stratified flow and measurement method technology, applied in the direction of liquid/fluent solid measurement, volume/mass flow by differential pressure, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high pipe wear, high process downtime costs, and high energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
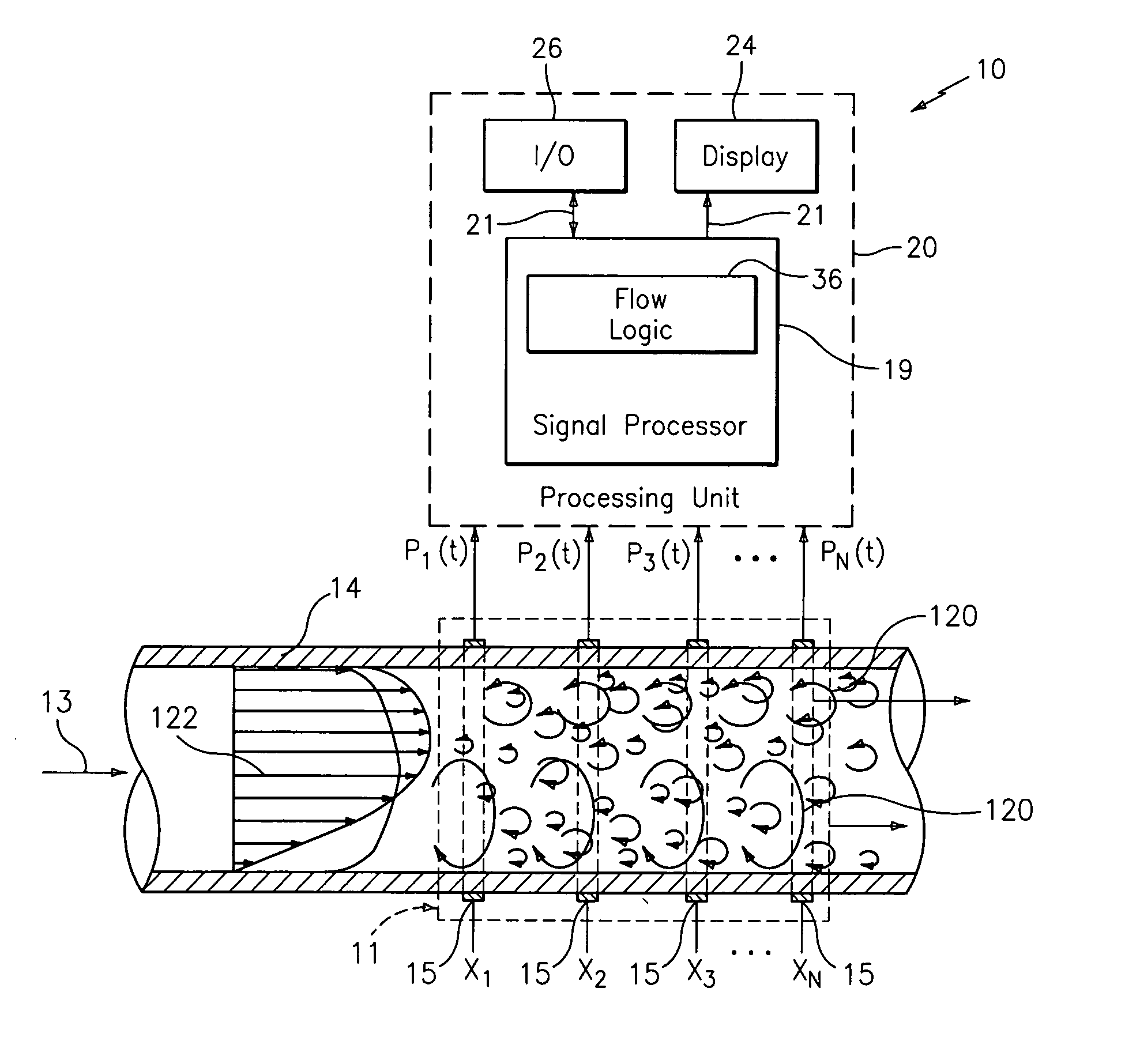
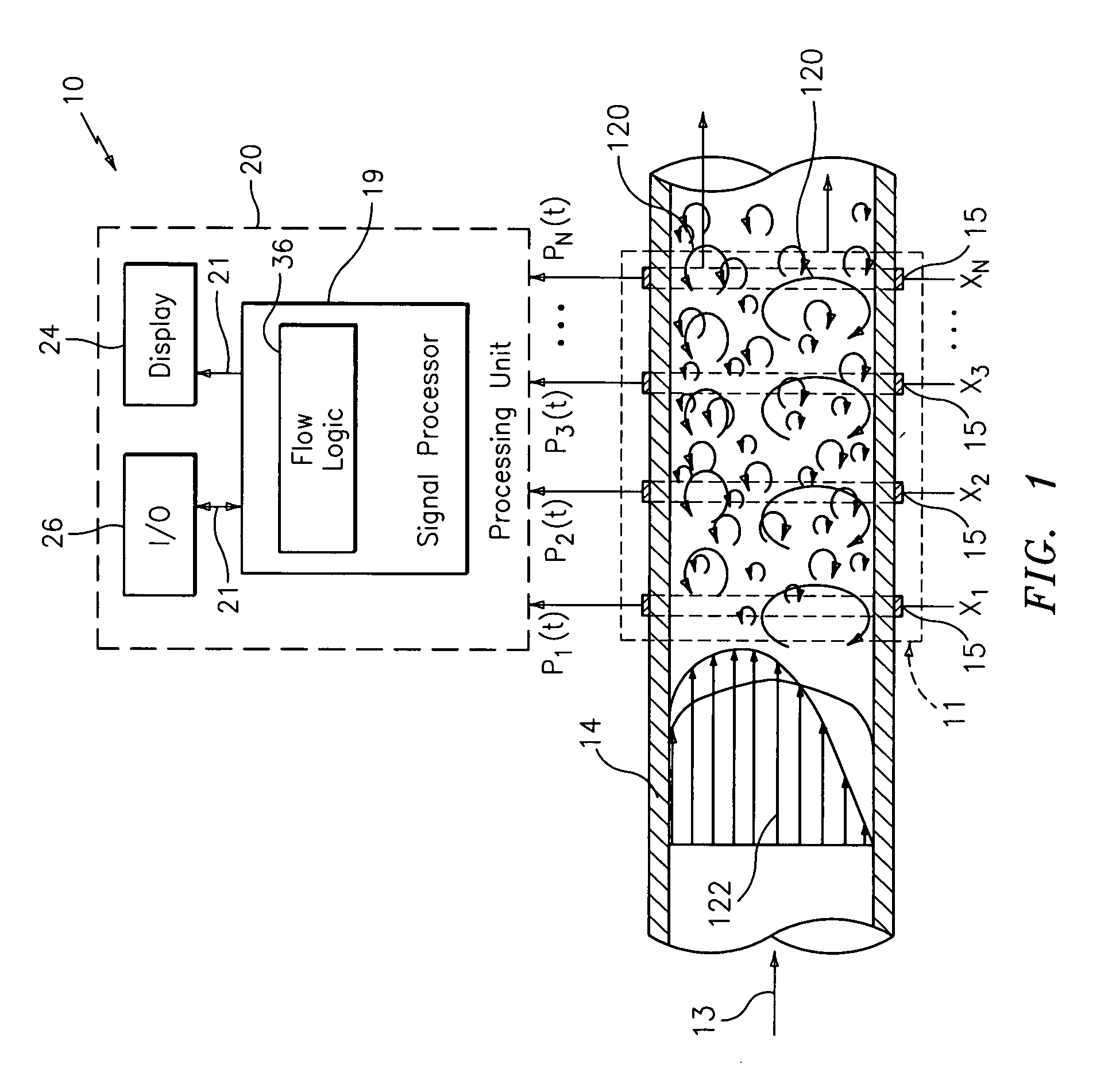
[0043] As described in commonly-owned U.S. Pat. No. 6,609,069 to Gysling, entitled “Method and Apparatus for Determining the Flow Velocity Within a Pipe”, and U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10 / 007,736, filed on Nov. 11, 2001, which are incorporated herein by reference in their entirety, unsteady pressures along a pipe caused by coherent structures (e.g., turbulent eddies and vortical disturbances) that convect with a fluid flowing in the pipe, contain useful information regarding parameters of the fluid. The present invention provides various means for using this information to measure parameters of a stratified flow, such as, for example, velocity, level / degree of stratification, and volumetric flow rate.
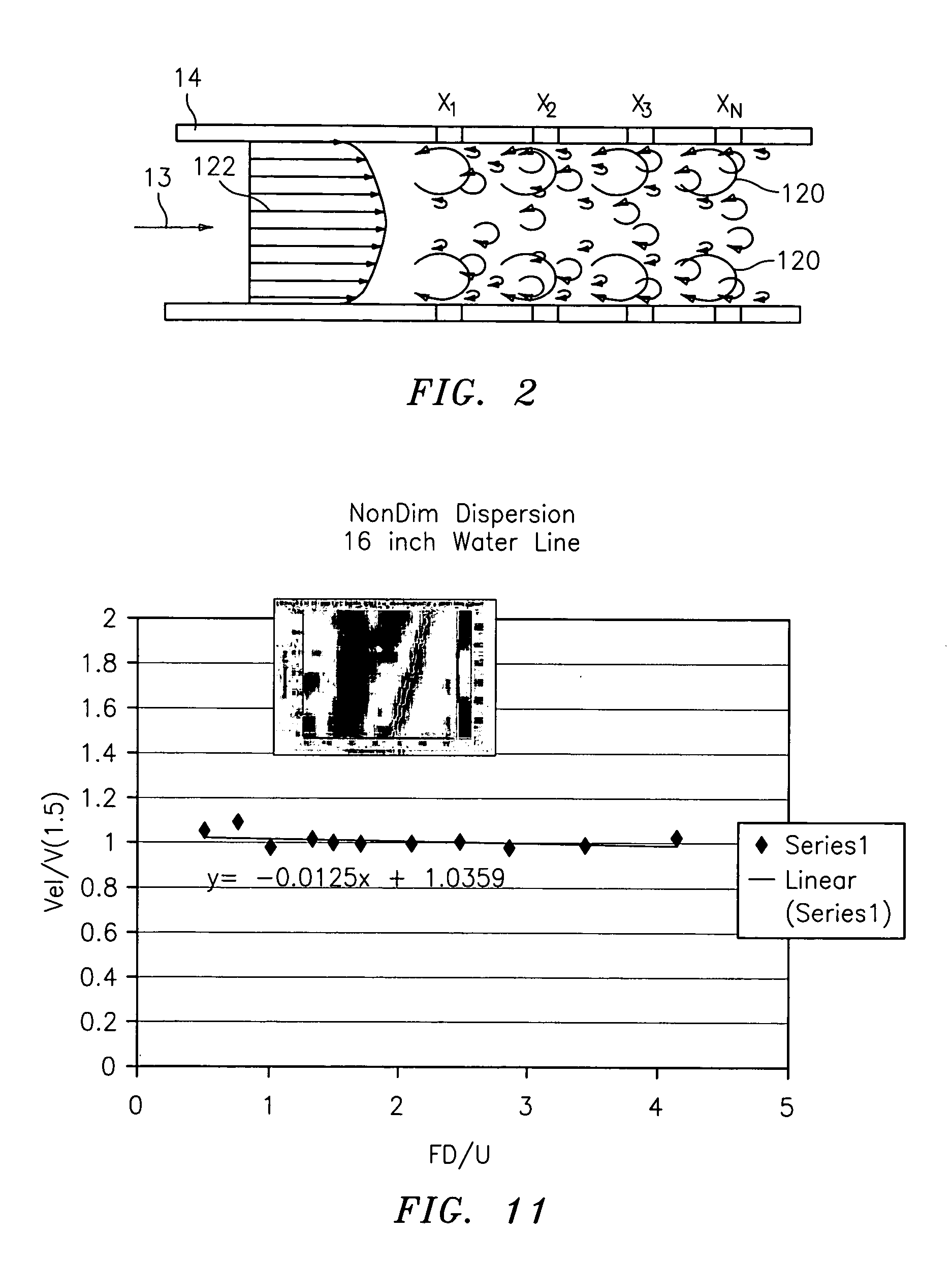
[0044] Referring to FIG. 1, an apparatus 10 for measuring at least one parameter associated with a flow 13 flowing within a duct, conduit or other form of pipe 14, is shown. The parameter of the flow 13 may include, for example, at least one of: velocity of the flow 13, volumetr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com