Variable rail safety system
a safety system and variable technology, applied in the field of safety devices, can solve the problems of prior art products, falling objects on the lower level of the construction site, and workers falling and risking injury or death
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
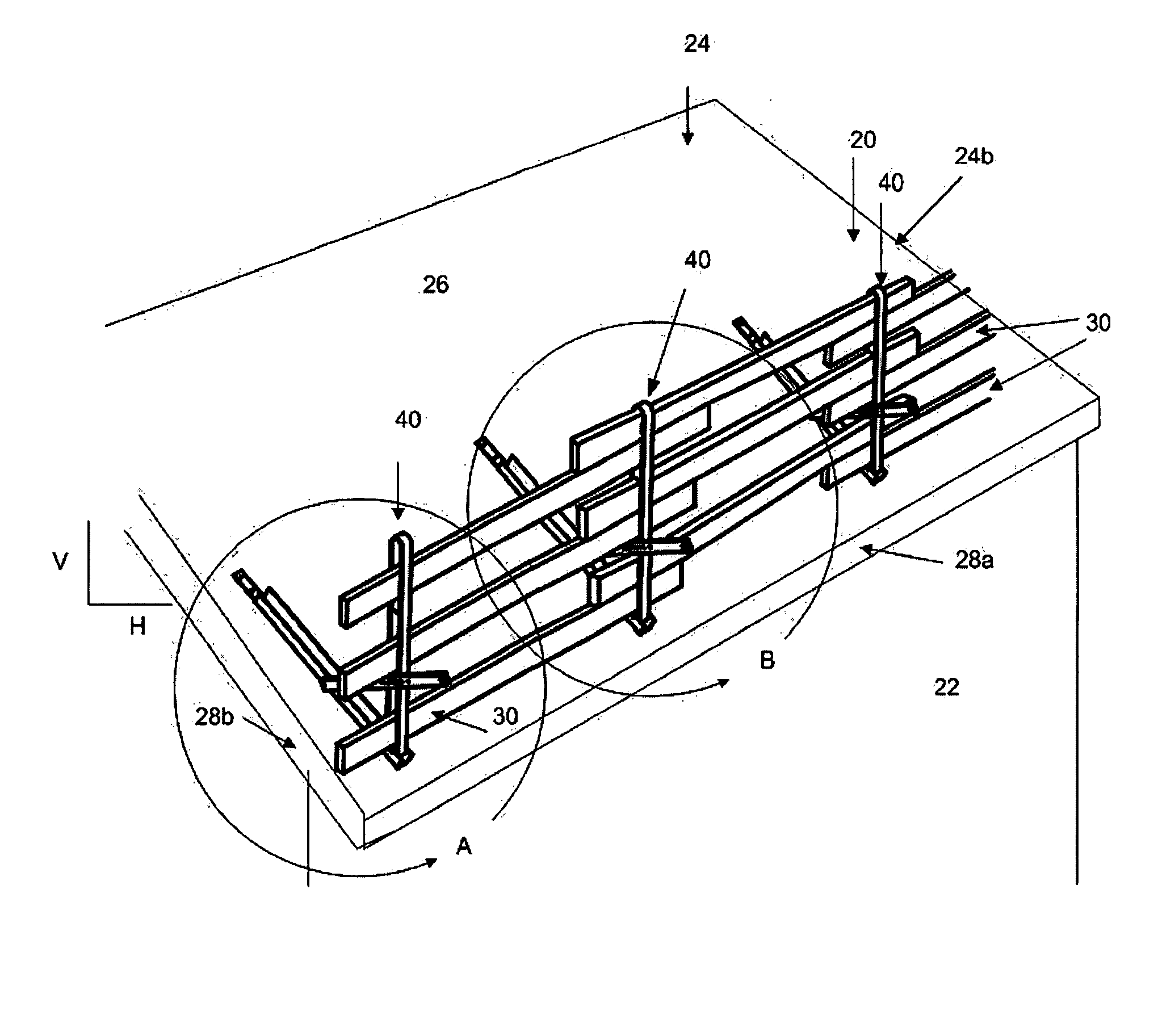
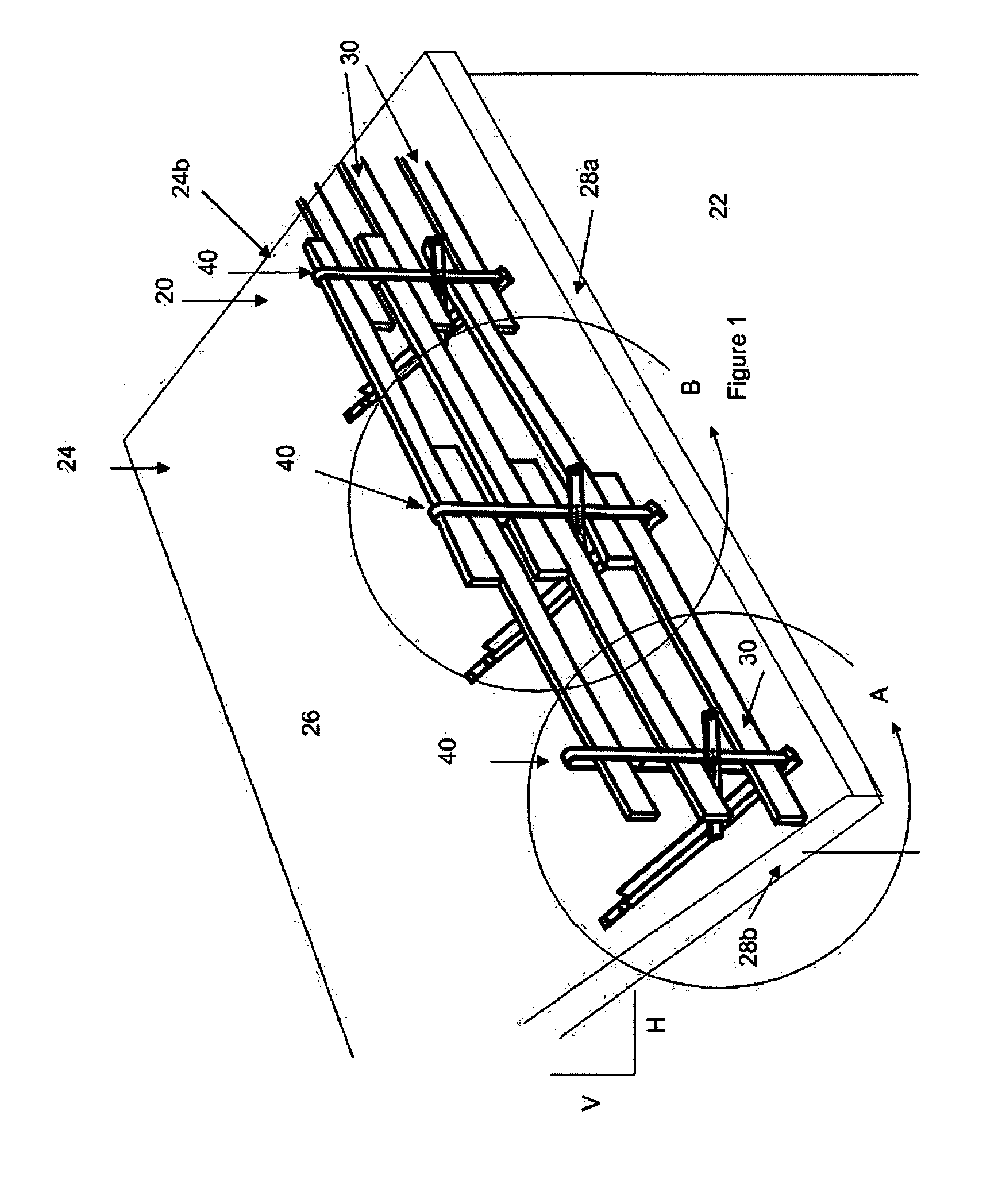
[0048] The figures show a guard rail system and assembly according to the present invention, which is also referred to herein as a variable rail safety system, or simply the “VRS system”. Referring first to FIGS. 1 to 1b, the VRS system is defined by a guard rail fence (generally designated by the reference numeral 20) which is capable of being removably attached to various structures, most commonly to a building 22 under construction, to provide a safe working area. One such structure for illustrative purposes is an inclined or pitched roof 24 having a timber truss sub-structure (not shown) covered by plywood or like sheeting 26. The VRS system should be installed wherever a fall barrier is required, such as along the front and / or side edges 28a, 28b of the roof. Other structures will be shown and discussed later.
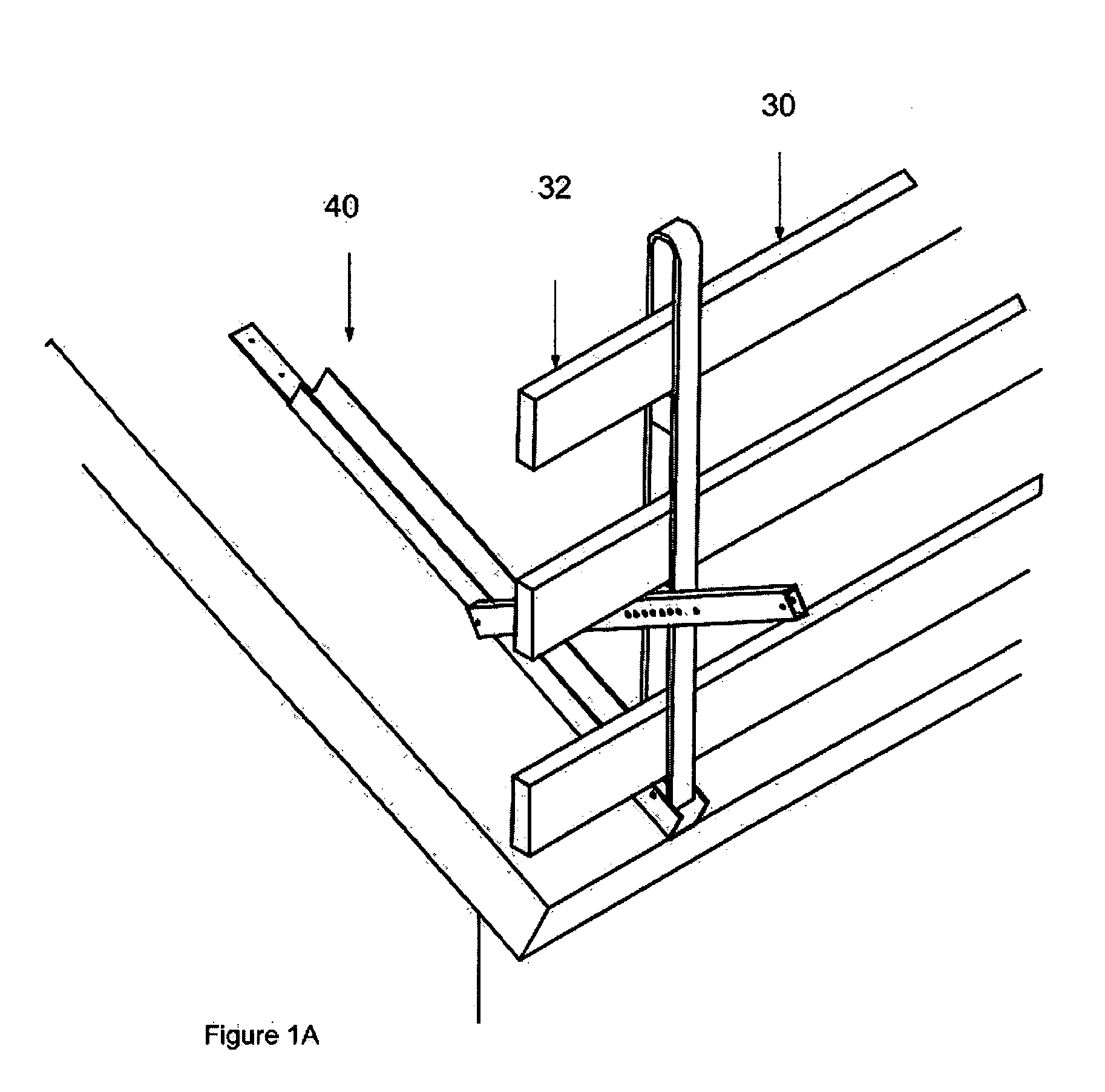
[0049] Referring still to the embodiment shown in FIGS. 1-1b, the guard rail fence 20 is formed by removably attaching several elongate rail supports 40 to the roof at sp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com