Hydroentangling process
a technology of water entanglement and process, applied in the field of water entanglement process, can solve the problems of reduced process efficiency of cellulosic pulp, short fibers that remain, dust from the formed product, etc., and achieves the effect of less fiber loss, efficient process and more efficient process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
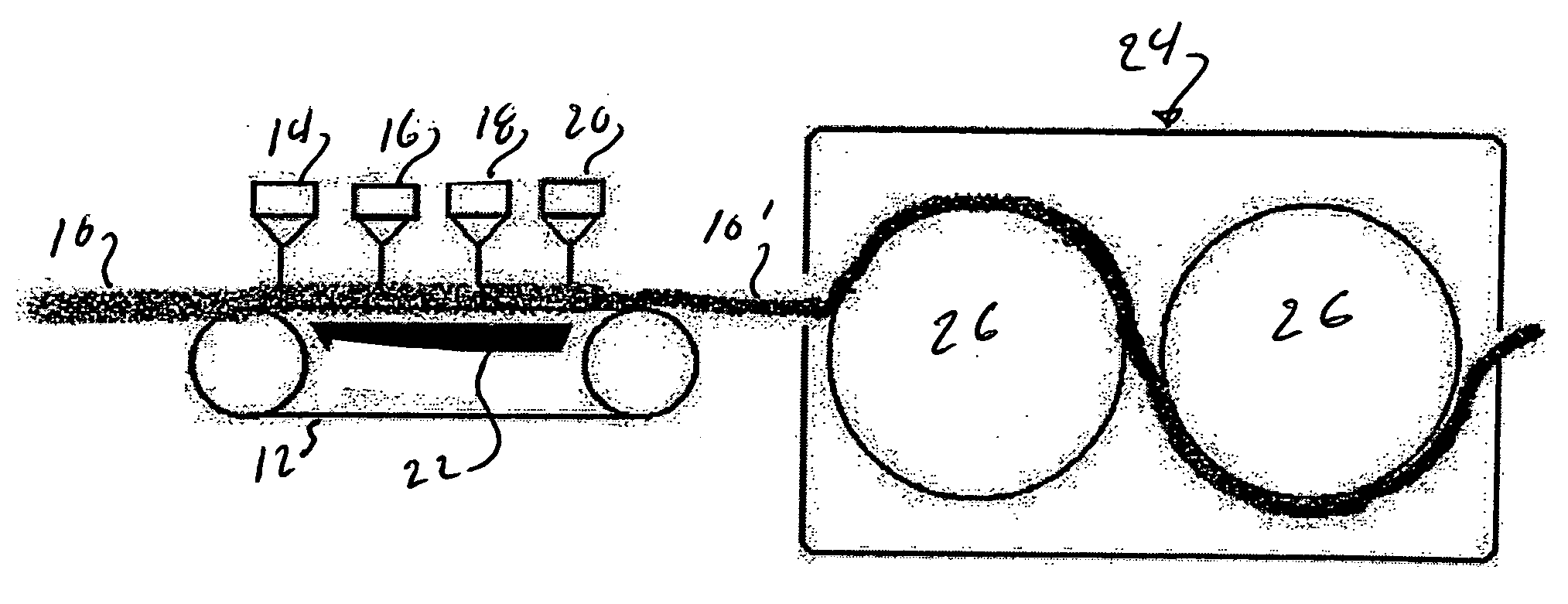
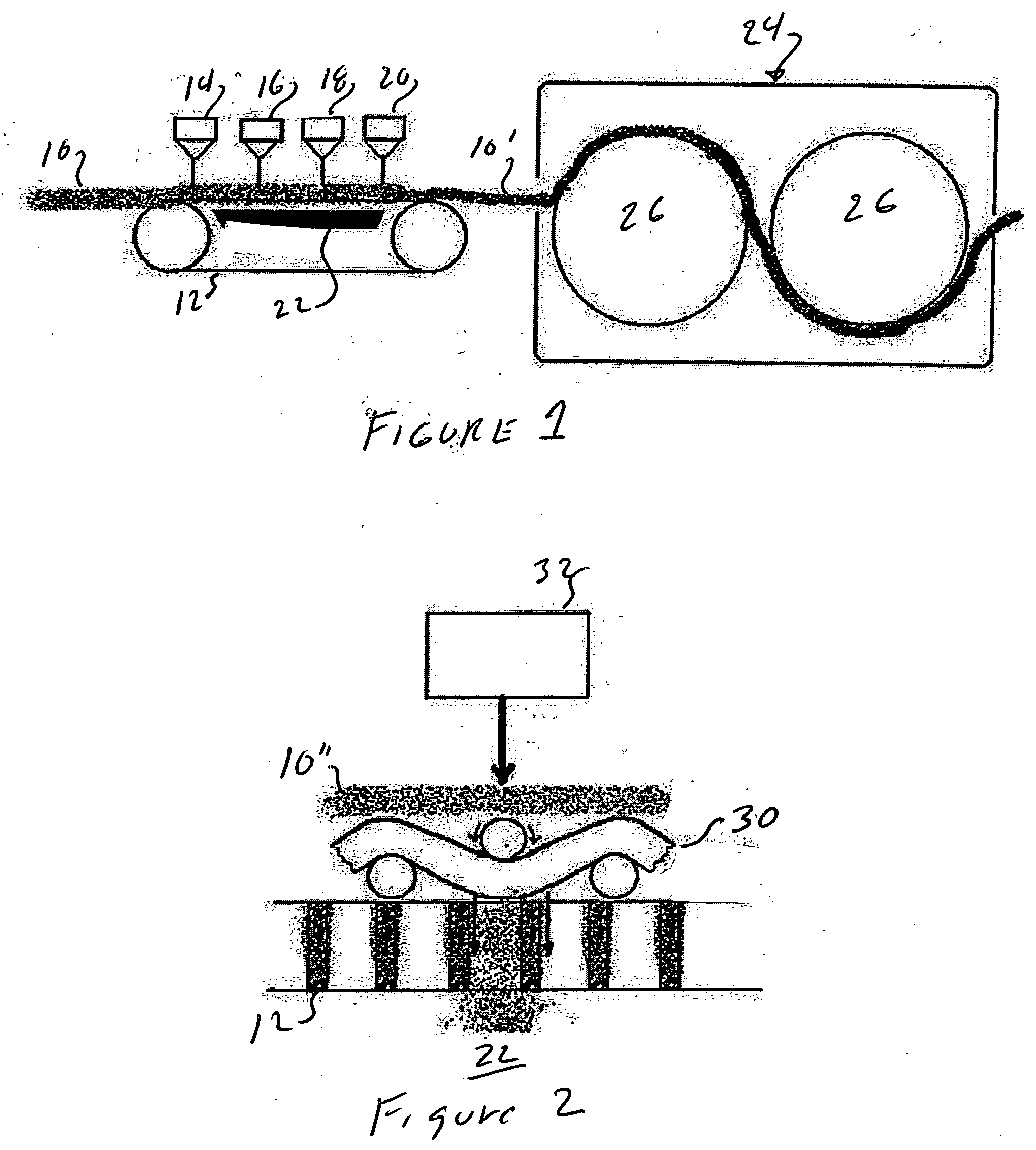
[0015]FIG. 1 shows an apparatus for spunlacing a mat of fibers. The mat 10 is carried onto a conveyor 12 and passes under a series of water jets 14, 16, 18 and 20. The water jets are usually at increasing water pressure. There is a vacuum chamber 22 underneath the conveyor 12. The water from the jets 14, 16, 18 and 20 pass through the mat 10 entangling the fibers. The water is pulled from the mat by the vacuum in chamber 22. The mat of entangled fibers 10′ is transported into the dryer section 24 and dried. Dryer cans 26 are shown. The mat is then rolled up or boxed for shipment.
[0016]FIG. 2 shows airlacing. The apparatus would be the same as the apparatus in FIG. 1. The difference between FIGS. 1 and 2 is the web 30. The water jet 32, which is one of a series of water jets, displaces the fibers in the mat 10″ downwardly and entangles the fibers with the web 30. The composite web is then dried as shown in FIG. 1.
[0017] The pulp fibers that may be used are mechanical pulp fibers, t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length weighted average length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com