Current collimation for thin seed and direct plating
a technology of direct plating and thin seed, which is applied in the field of current collimation of thin seed and direct plating, can solve the problems of high resistance and thin conductive seed layer formed on the substra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
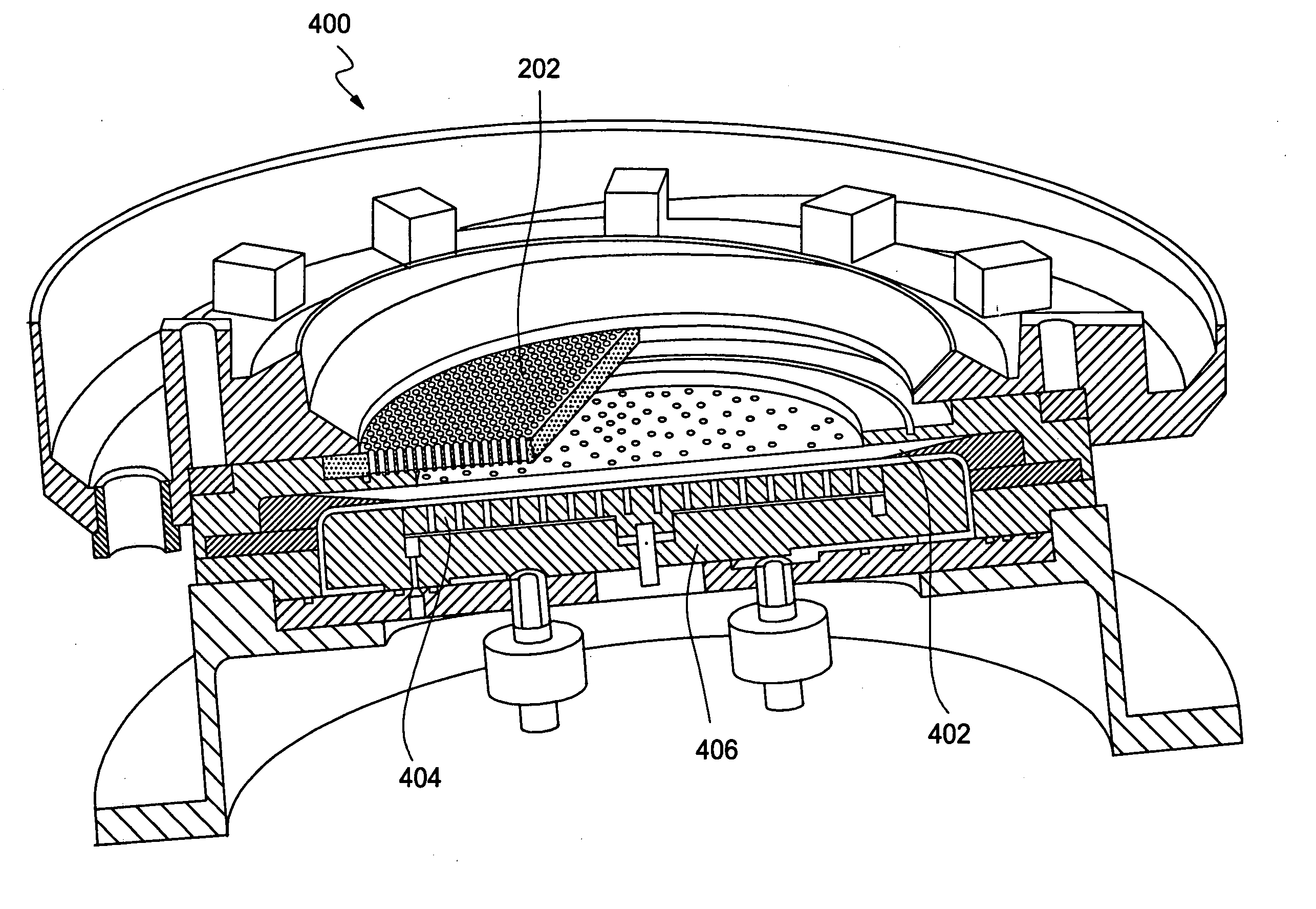
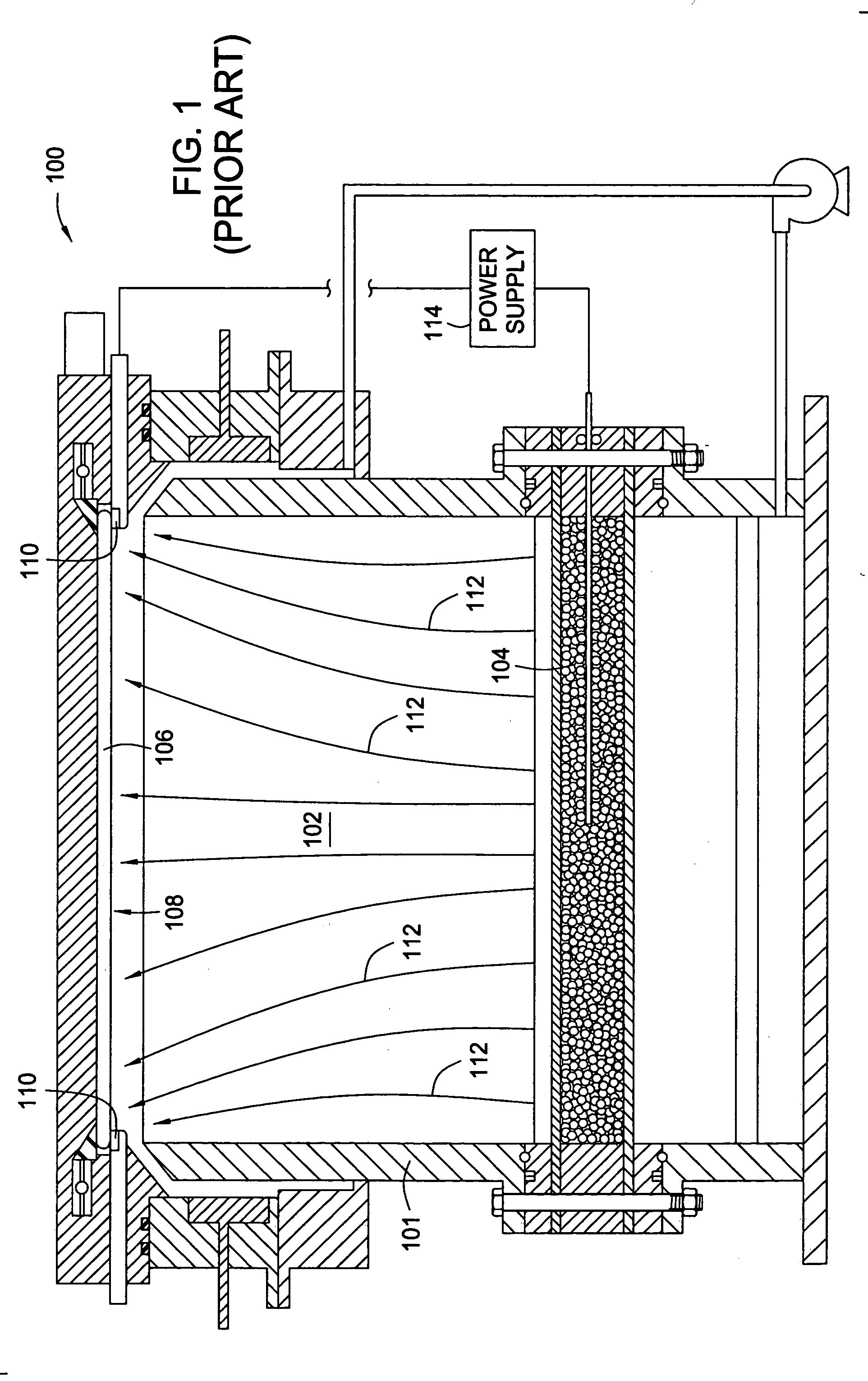
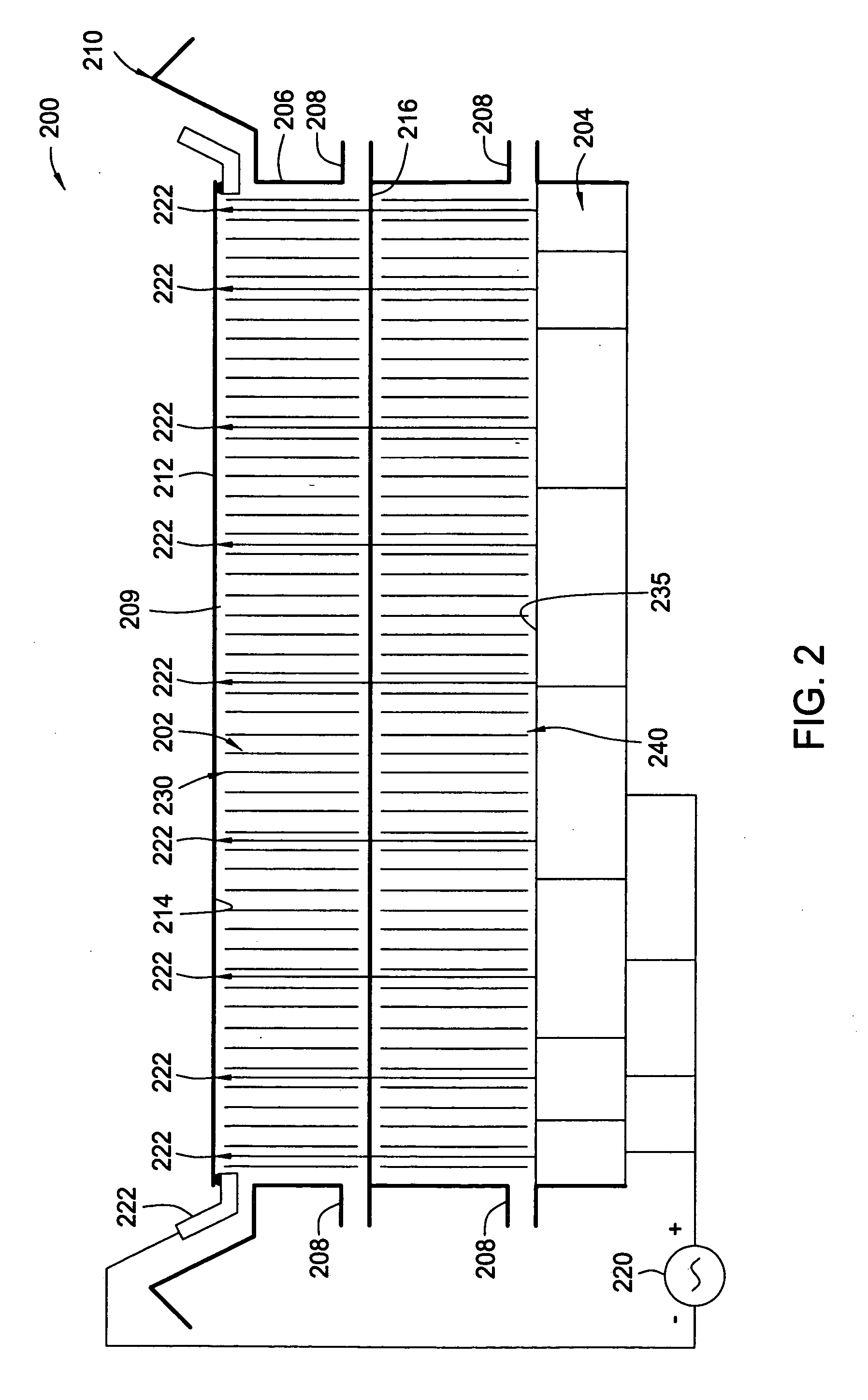
[0027]FIG. 1 illustrates a schematic view of a conventional plating cell 100 and the electric field lines generated therein. The conventional plating cell 100 generally includes a fluid basin 101 configured to contain a fluid volume 102, which is generally an electrolyte plating solution. An anode 104 is positioned in a lower portion of the fluid basin 101 and a substrate 106 that is to be plated is generally positioned across an upper open portion of the cell 100. The substrate 106 is supported by a contact ring that is configured to electrically contact the plating surface 108 of the substrate 106 near the perimeter of the substrate 106 via one or more electric contact elements 110. The electric contact elements 110 are in electrical communication with a cathodic terminal of a power supply 114, while the anodic terminal of the power supply is in electrical communication with the anode 104. Further details of the conventional plating cell 100 may be found in commonly assigned U.S. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| interior diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| interior diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| inner diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com