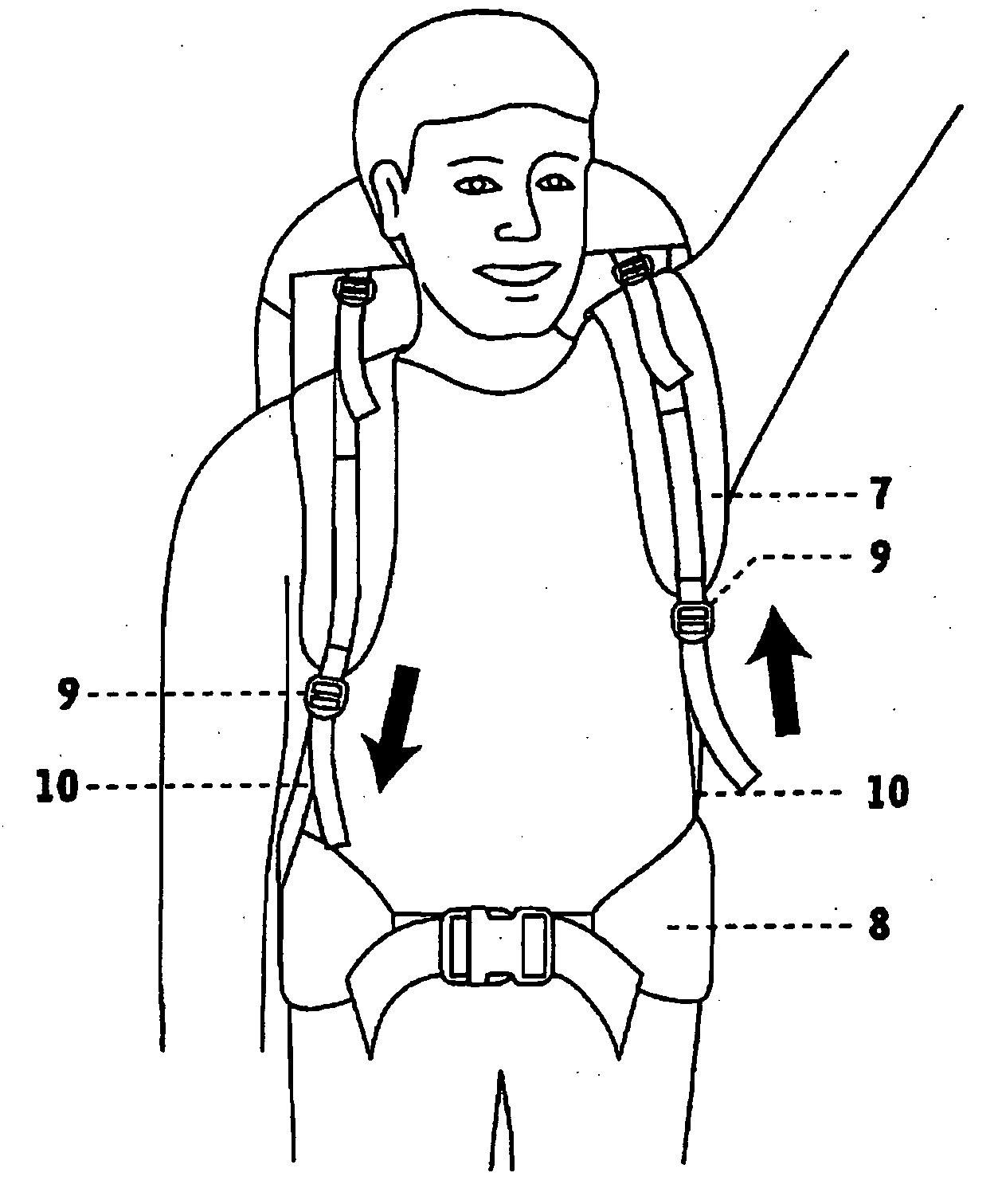
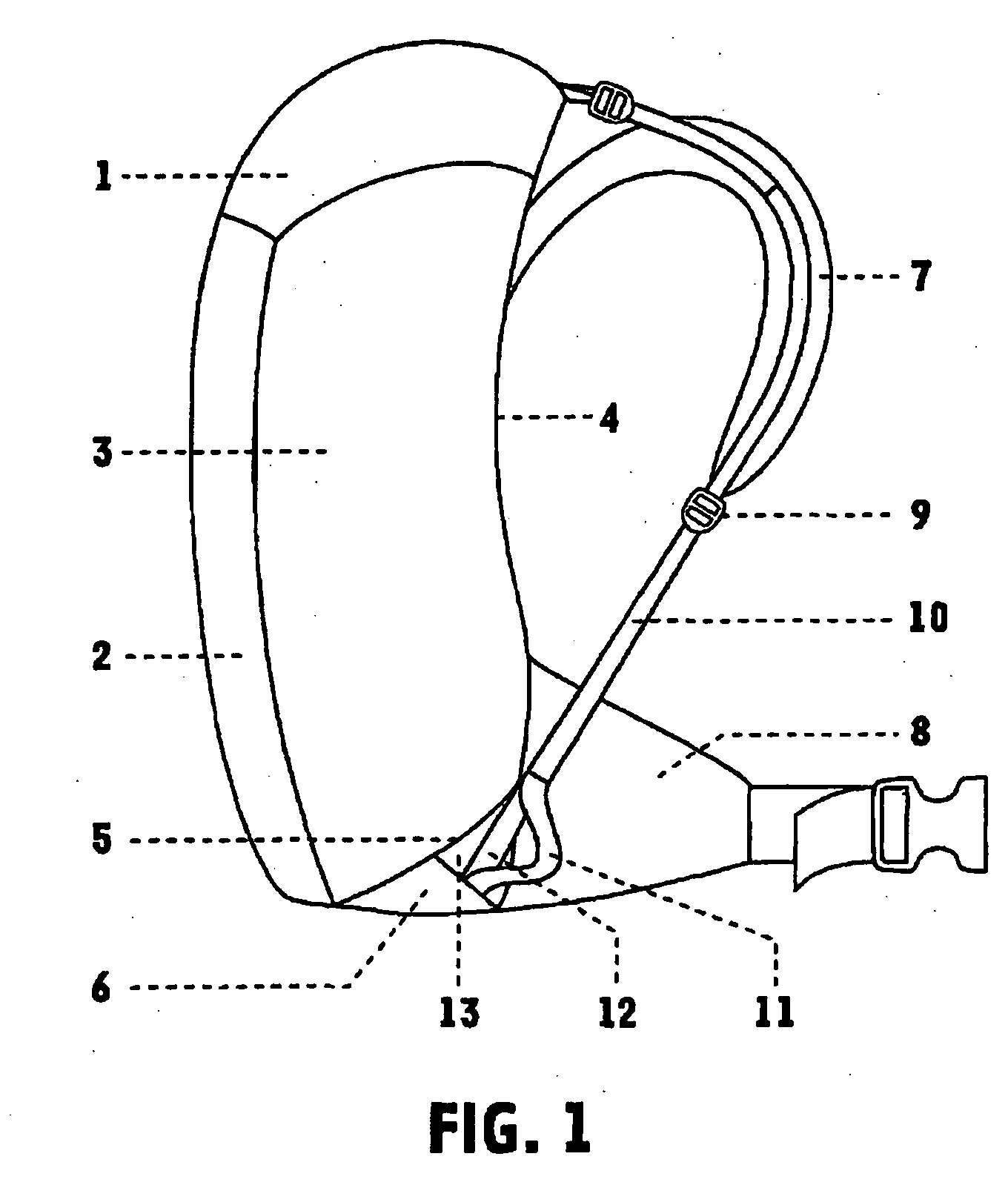
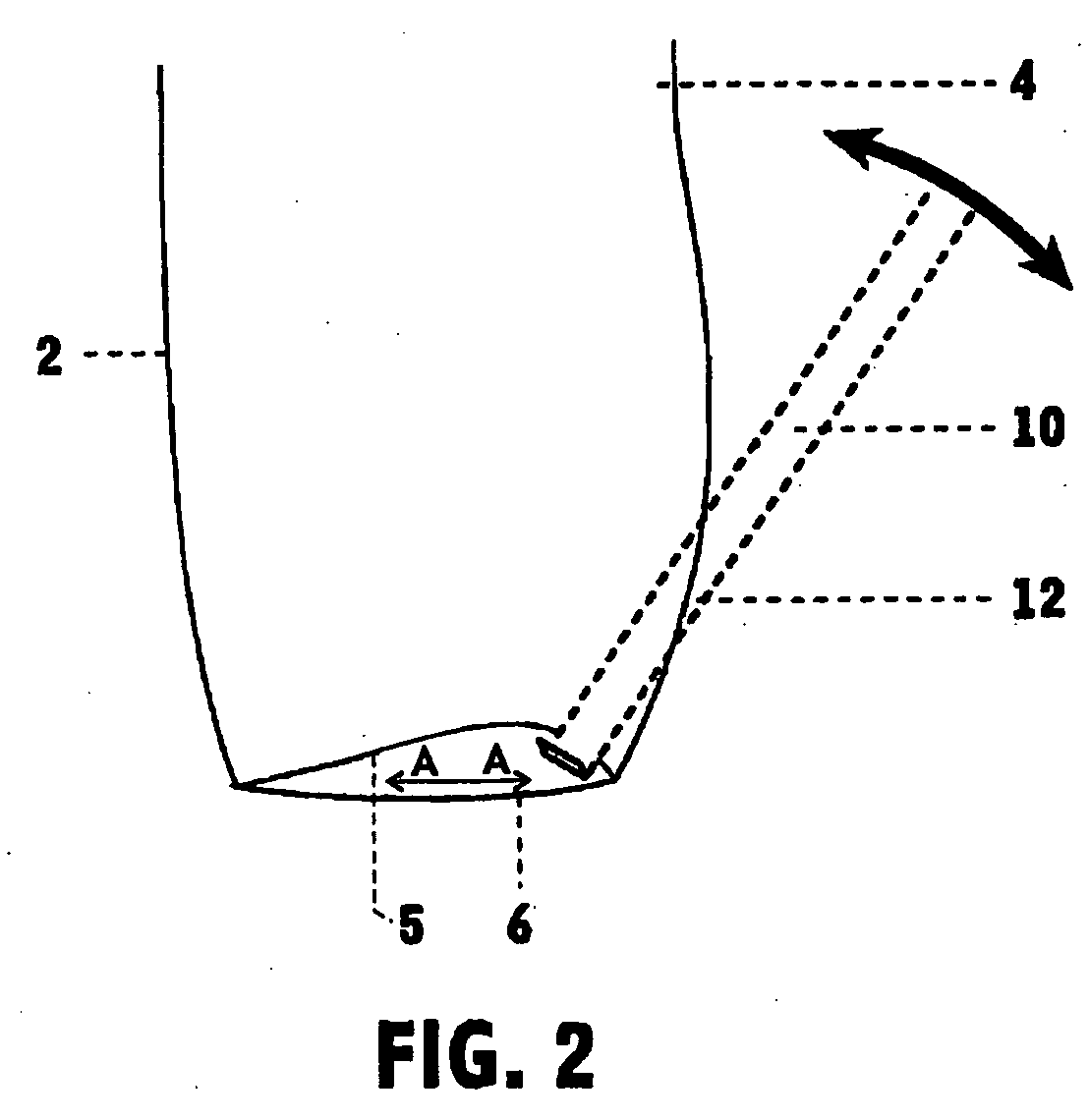
Backpack with shoulder movement harness system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
[0055]FIG. 3 shows a second preferred embodiment of the backpack. Unless described below, the features and operation should be considered to be the same as those described above. In the second embodiment, the flexible member 14 has a substantially circular cross section. Preferably, the flexible member 14 has a smooth surface, and is preferably composed of low friction plastic material. Alternatively, the flexible member 14 may be a cord coated with a friction reducing material such as polytetrafluoroethylene. As outlined above, the flexible member is substantially non-compressible across its width. Preferably, the flexible member is substantially non-compressible along its length, and most preferably the flexible member is substantially non-compressible in every dimension.
[0056] A connector part 15 joins flexible member 14 to both webs 10 and 11. In this embodiment, the inner panel 5 of the base portion may be the same width from front to back as the outer panel 6. In this embodime...
third embodiment
[0058] In this third embodiment, the strapping arrangement has buckles and webs or straps connected to the shoulder harness, and the backpack has a pair of frame stays 16 located in the back panel. The stays are preferably positioned in a tapering generally V-shaped configuration being centrally located at the base of the back panel and laterally located in the upper area. A part of the upper section of each stay is exposed. These frame stays are held in position by fabric or web sleeves in the bottom and middle sections and at the top ends.
[0059] The base of the shoulder harness is fixed to the back panel behind a breathable outer back panel surface 17. The shoulder harness has webs 18 fixed to the central portion. Webs 18 are threaded through each buckle 19. Buckles 19 are linked to connectors 21 via webs 20. Connectors 21 are linked to and substantially free to slide up or down the exposed portion of frames 16 when the backpack is in use. For wearers of different back lengths, th...
fourth embodiment
[0062] In this fourth embodiment, buckles 19 are fixed to opposite ends of web 22. The central section of web or support strap 22 passes through, and is slidable relative to, a support loop 23, folding over as it passes through the loop in a V configuration. The loop 23 is fixed to the top of the pack via a web 24. As the shoulders move, web 22 slides substantially freely through the loop 23. This embodiment allows twisting of the shoulders relative to the hips, as well as sideways bending of the shoulders.
[0063] In the third and fourth embodiments, the webs 18 extend from the shoulder straps of the shoulder harness, and from the general regions of the shoulder straps that will extend over the wearer's shoulders in use. Preferably, the webs 18 extend from the shoulder straps level with or slightly forward of the tops of the wearer's shoulders in use. The configuration is preferably such that the webs 18 extend in a tangent from the top curvature of the shoulders of a wearer.
[0064] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com