Bat speed sensing device and methods
a speed sensing device and bat technology, applied in the direction of sports apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable use in ordinary play, unsuitable for making measurements during ordinary play, and requiring attachment to the bat, so as to facilitate the use of the system, avoid interference, and facilitate the effect of us
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
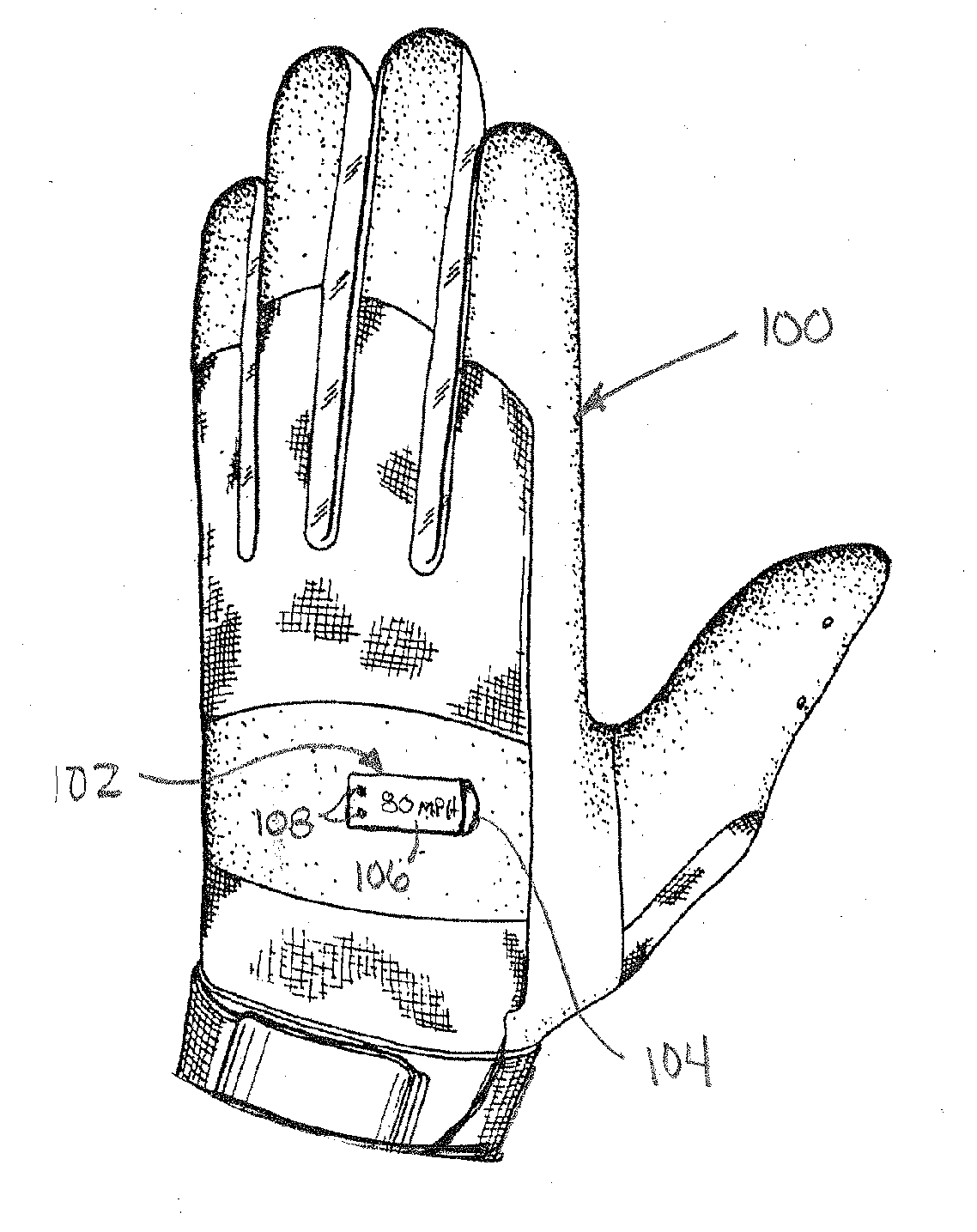
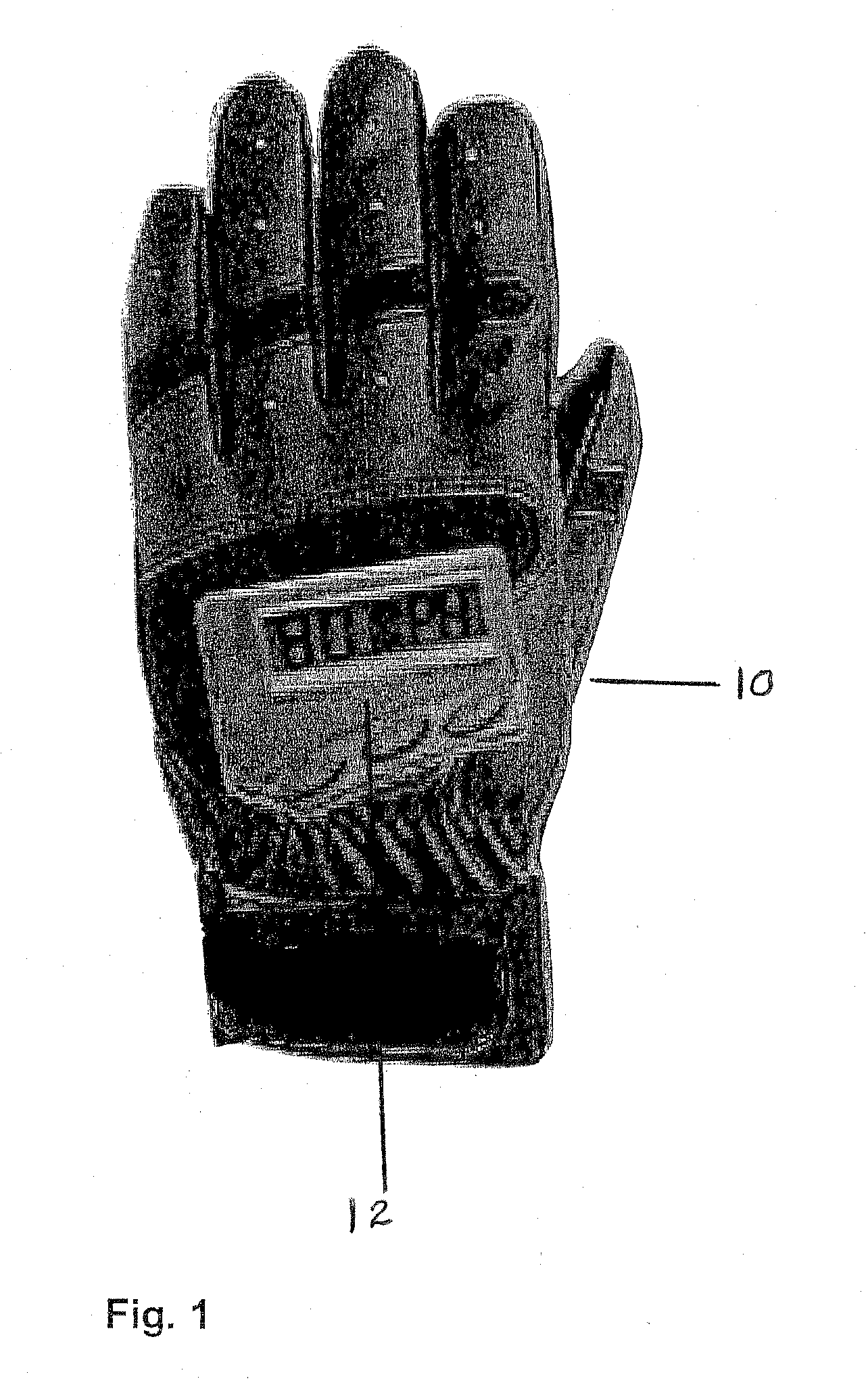
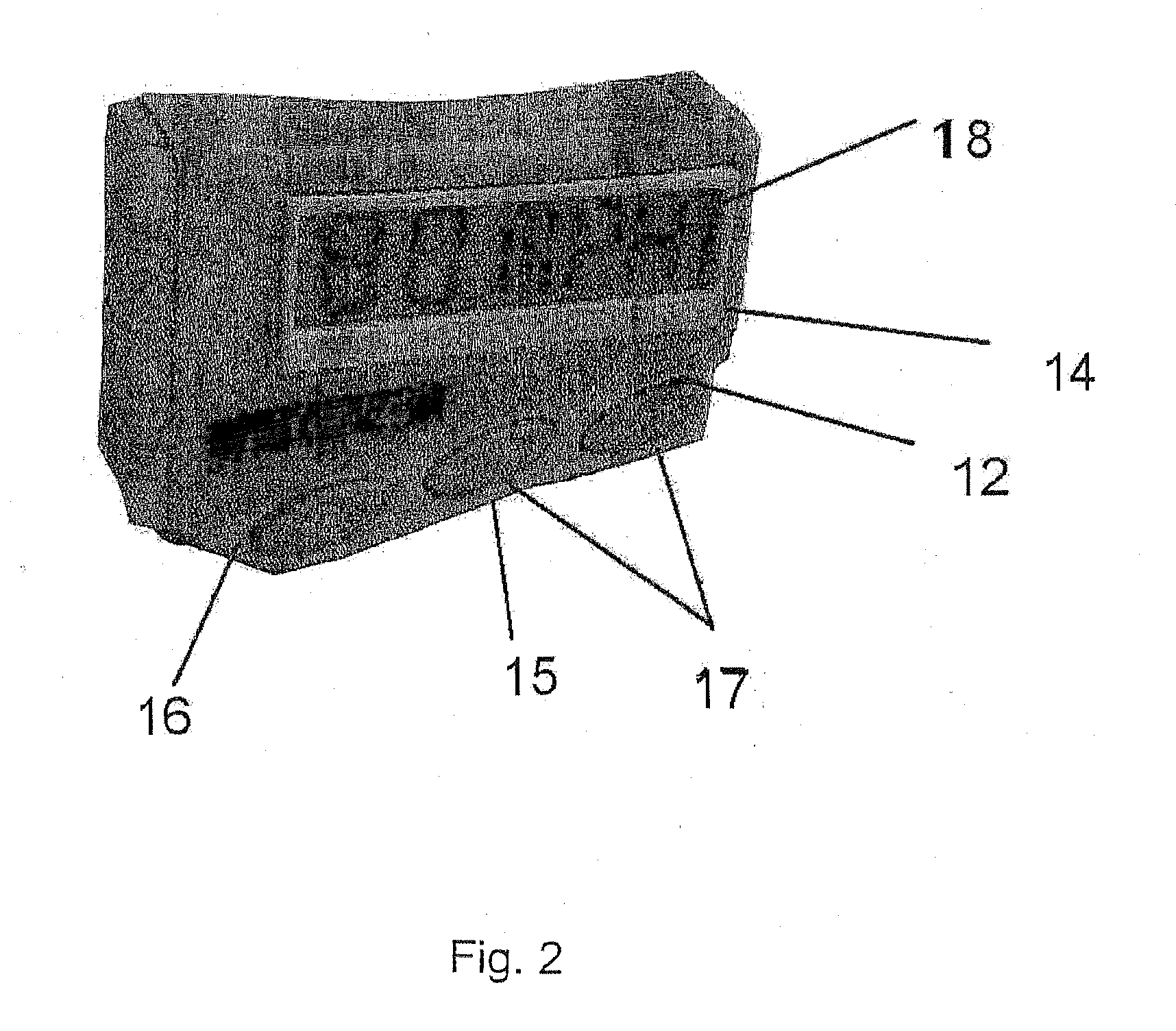
[0020] When a bat is swung, it follows a curved path about two connected centers of rotation. A first center of rotation is located generally between the batter's shoulders. A second center of rotation is formed by the batter's wrists. At the time when the bat strikes the ball, as the batter moves his wrist, the bat is generally aligned with the centers of rotation, and the direction of motion of the batter's hands is generally parallel to the direction of motion of the bat.
[0021] A motion sensor disposed between the centers of rotation, e.g., between the shoulders and wrists, will not respond to motion about the second center of rotation. A sensor disposed between the second center of rotation and the bat will respond to motions about both centers of rotation. A bat-mounted sensor will experience the greatest motion if mounted on the bat's face, and this location will provide a given sensor with the largest signal output and measurement accuracy. However, there are problems, such ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com