Control system for driving fluids through an extracorporeal blood circuit
a control system and blood circuit technology, applied in the field of systems for driving fluids through an extracorporeal blood circuit, can solve the problems of difficult manufacturing or operation of valve systems, difficult to manufacture or operate systems, and difficulty in obtaining sufficient supply, etc., to reduce treatment time, less complex, and easy to manufacture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
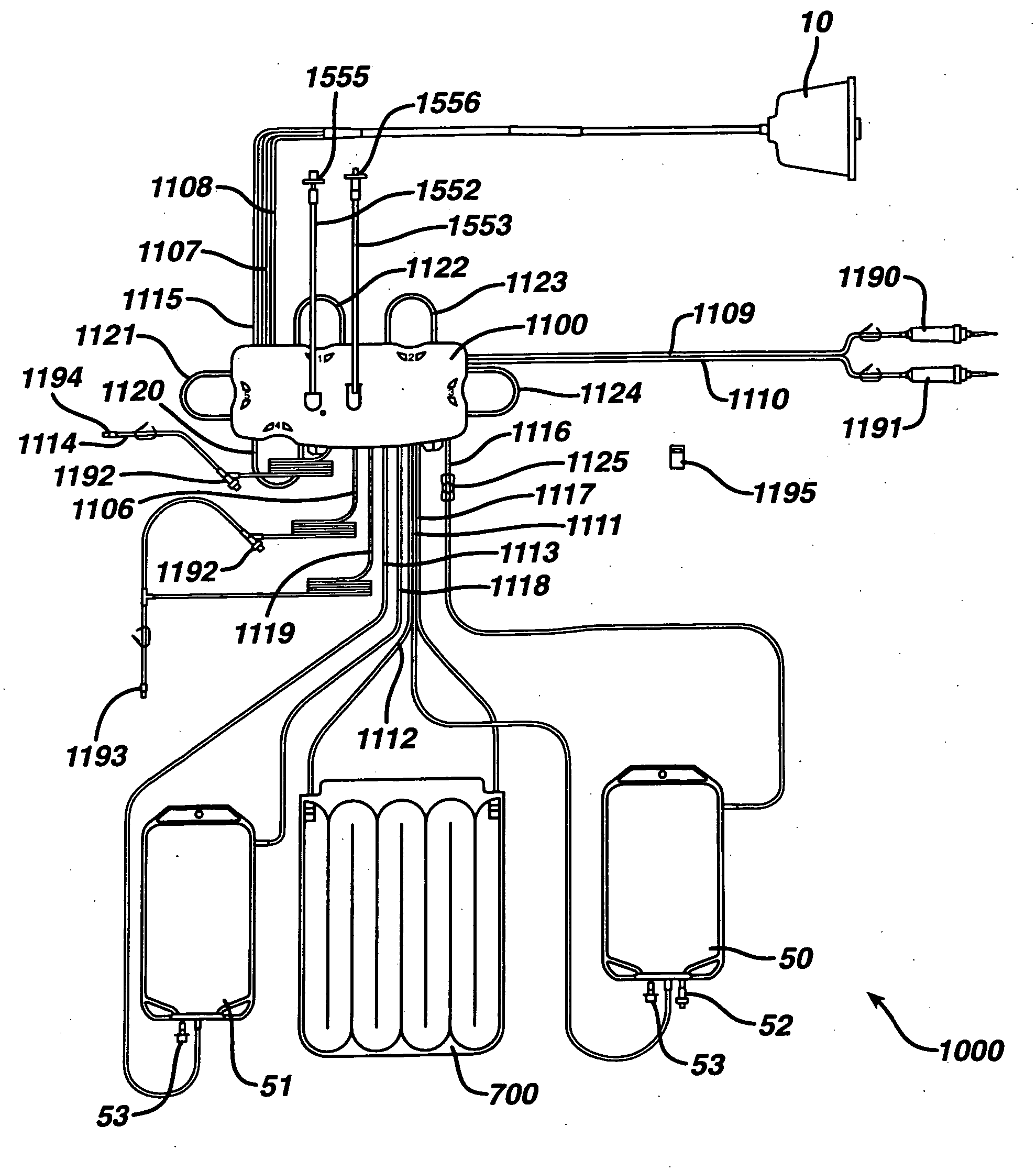
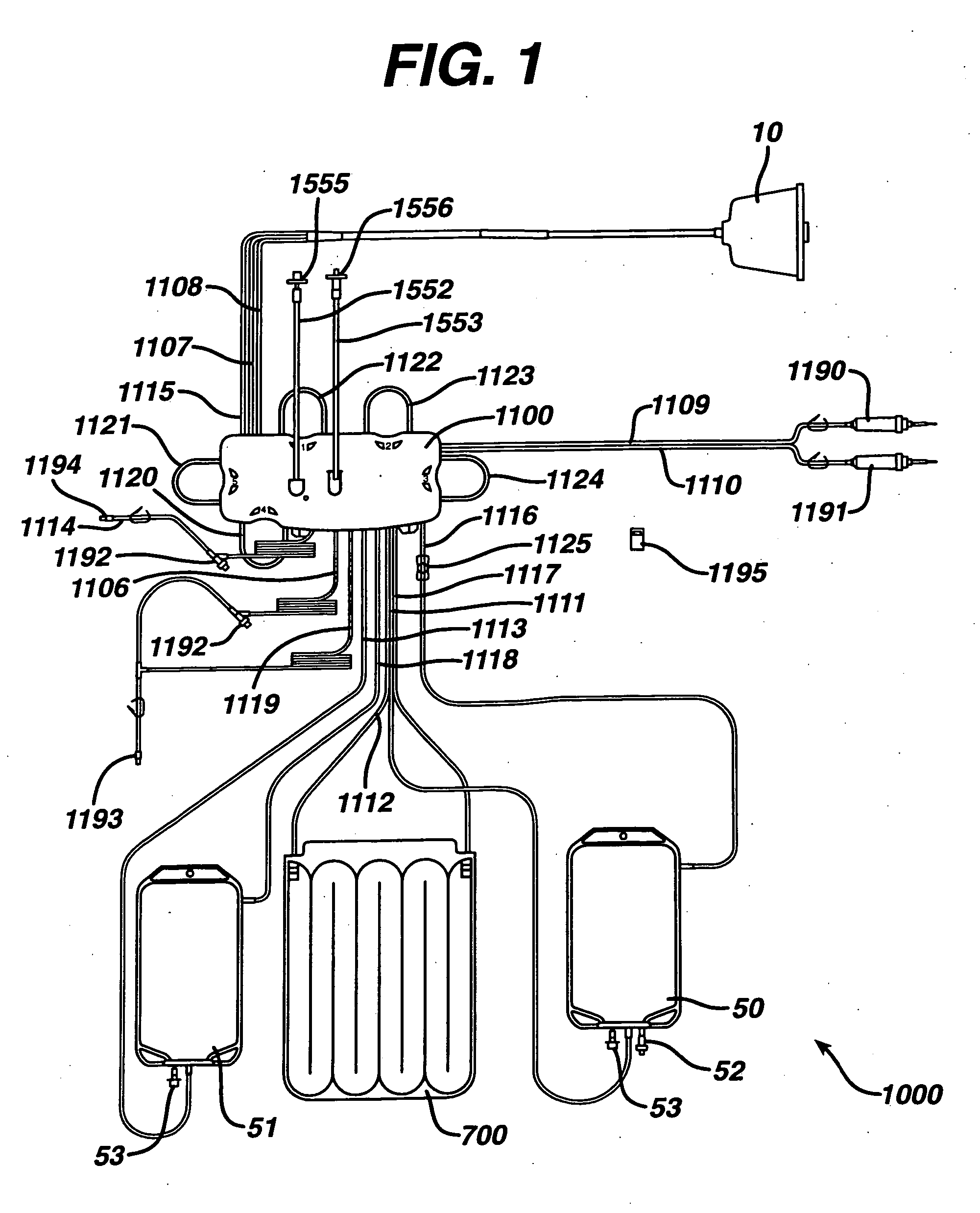
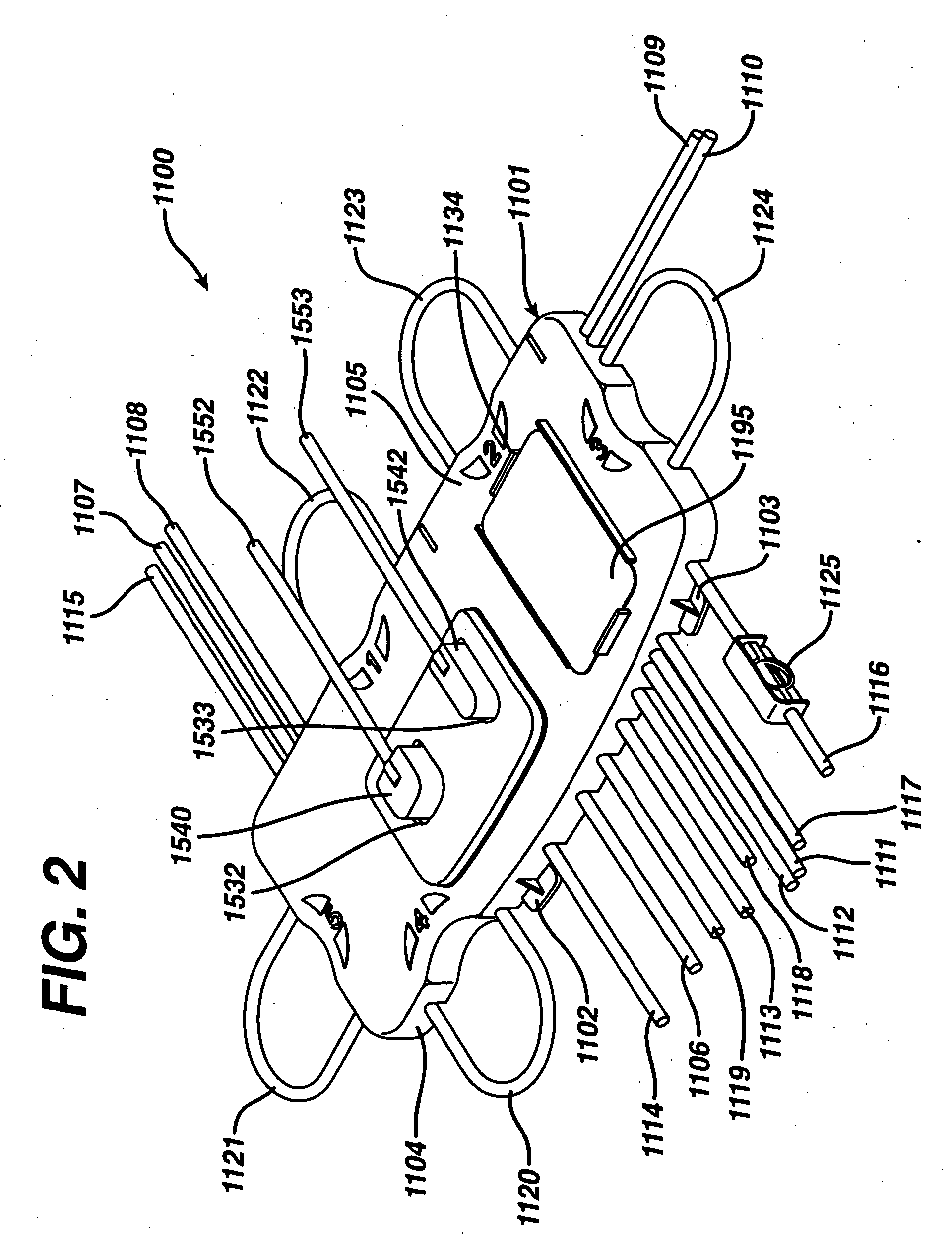
[0085] Features of the present invention are embodied in the permanent blood driving equipment, the disposable photopheresis kit, the various devices which make up the disposable kit, and the corresponding treatment process. The following written description is outlined as follows:
[0086] I. Disposable Photopheresis Kit [0087] A. Cassette for Controlling Fluid Flow [0088] 1. Filter Assembly [0089] B. Irradiation Chamber [0090] C. Centrifuge Bowl [0091] 1. Drive Tube
[0092] II. Permanent Tower System [0093] A Photoactivation Chamber [0094] B. Centrifuge Chamber [0095] C. Fluid Flow Control Deck [0096] 1. Cassette Clamping Mechanism [0097] 2. Self-Loading Peristaltic Pumps [0098] D. Infra-Red Communication
[0099] III. Photopheresis Treatment Process
[0100] The above-outline is included to facilitate understanding of the features of the present invention. The outline is not limiting of the present invention and is not intended to categorize or limit any aspect of the invention. The inv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com