Trim paneling with miterless corner joints and related methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
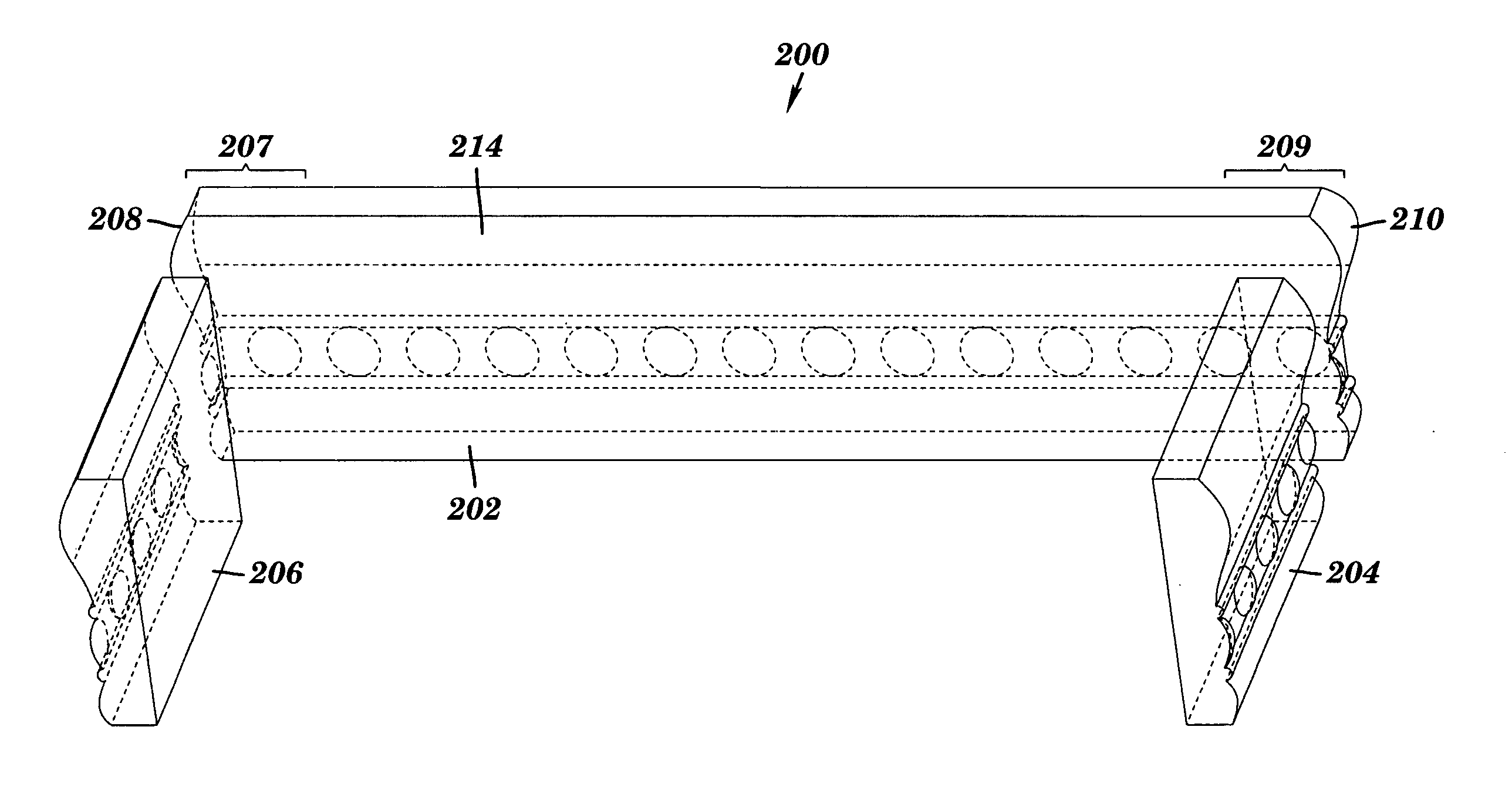
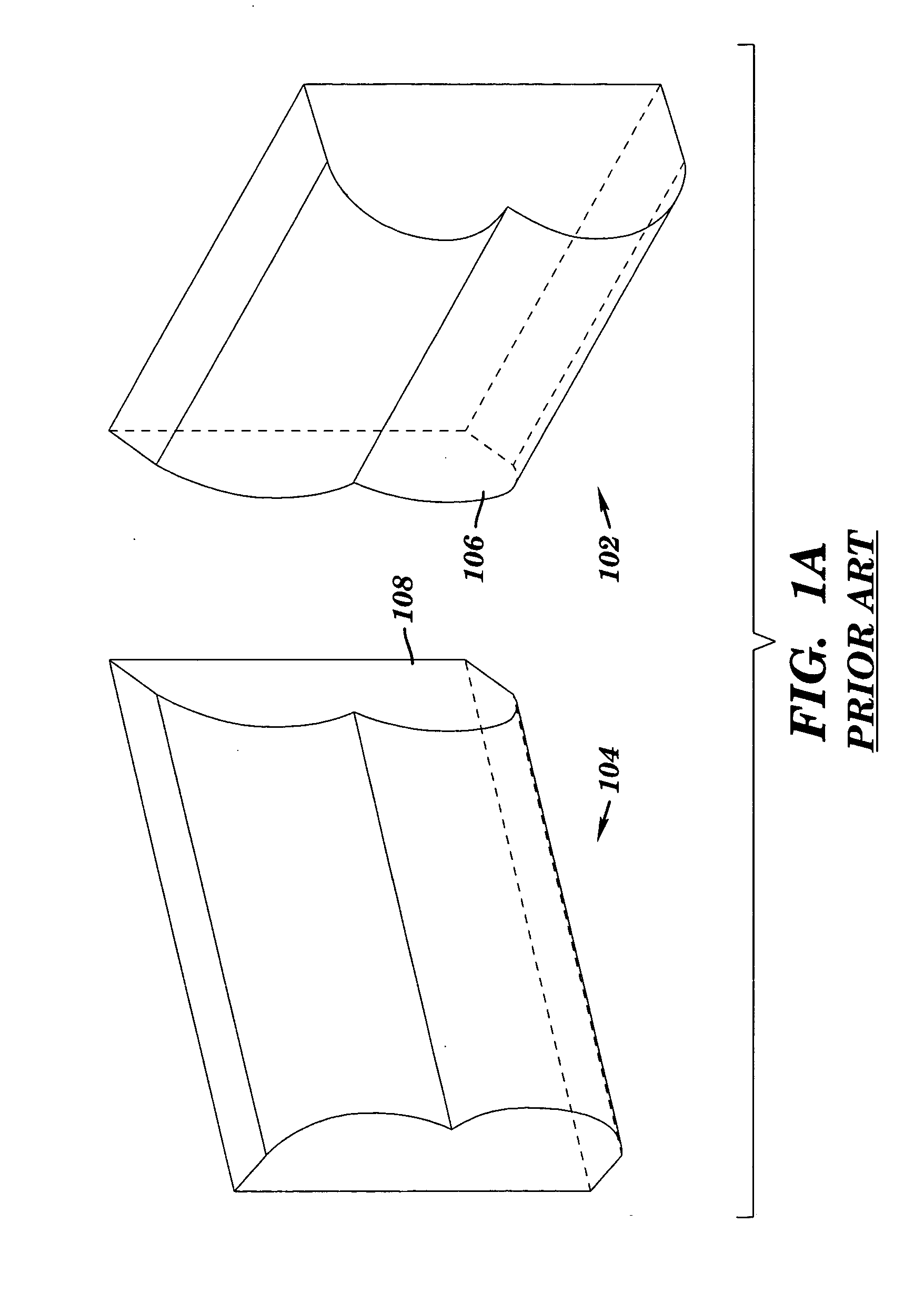
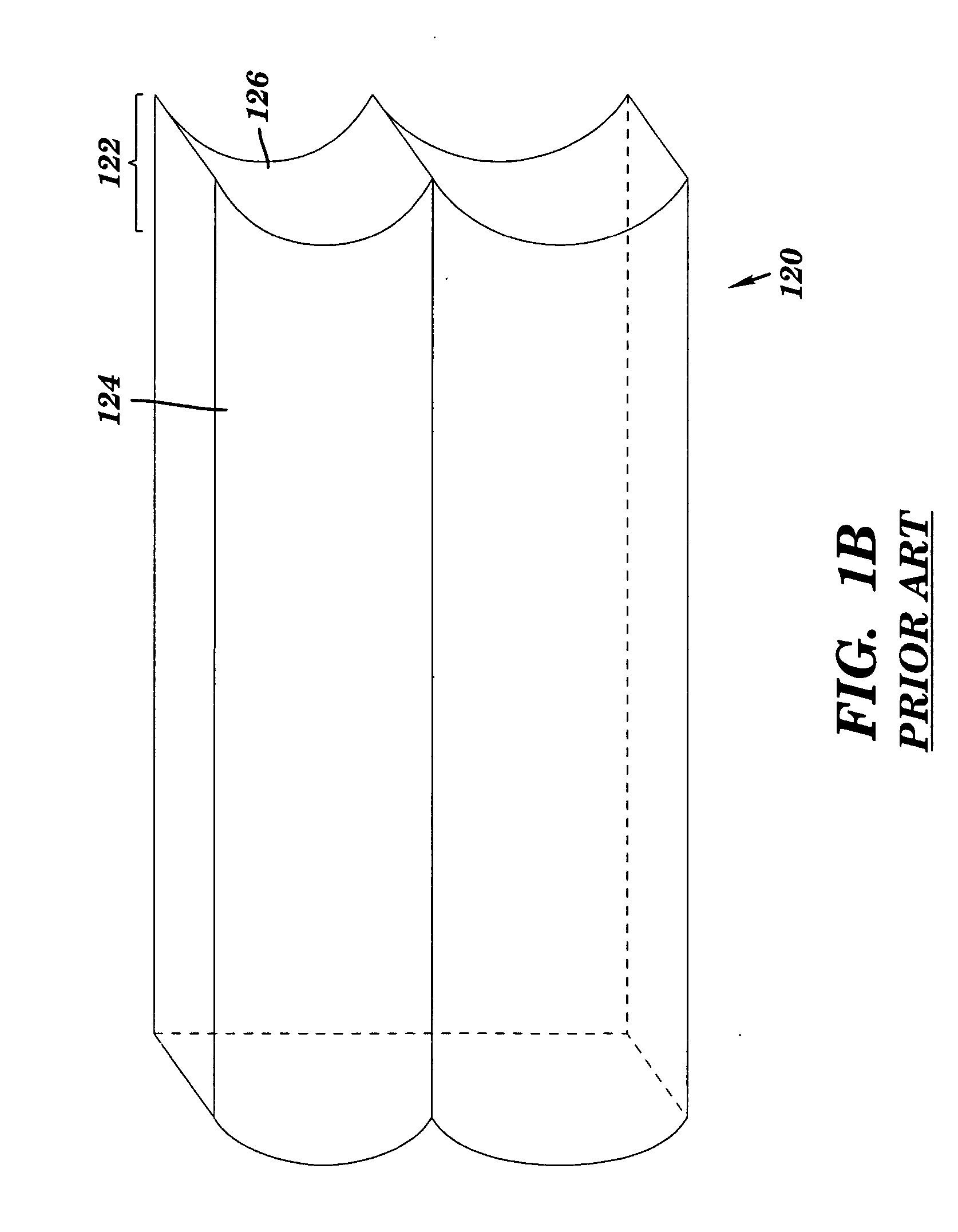
[0025] As mentioned above, various embodiments of the invention feature a paneling set that includes a transition element having two prefabricated coping profiles configured to mate with a span element at each end of the transition element, i.e. a single prefabricated transition element can be used to form two corners.
[0026] Referring to FIGS. 2A-2B, in one embodiment of the invention, a paneling set 200 includes a transition element 202 and span elements 204 and 206, whereby the transition element 202 is positioned to form a first corner with a first span element 204 and a second corner with a second span element 206. The elements of the paneling set have a rear face 214 and a front face 212. In various embodiments of the invention, the front faces 212 of both the span elements 204, 206 and the transition element 202 are designed to be substantially non-planar and decorative, whereas the rear faces are substantially planar, i.e. having a non-rectangular lateral cross-section.
[002...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com