Neutron and gamma-ray detection system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
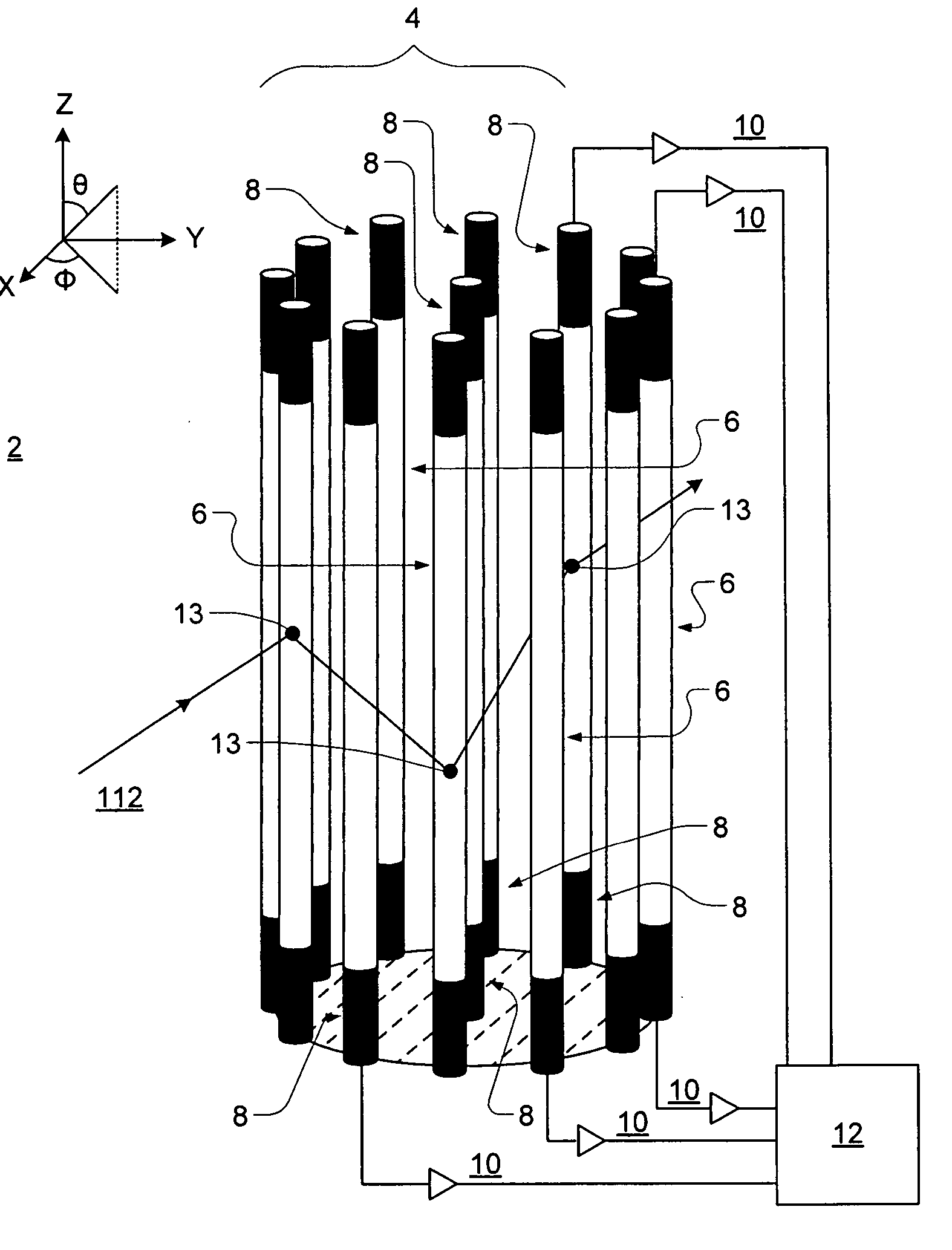
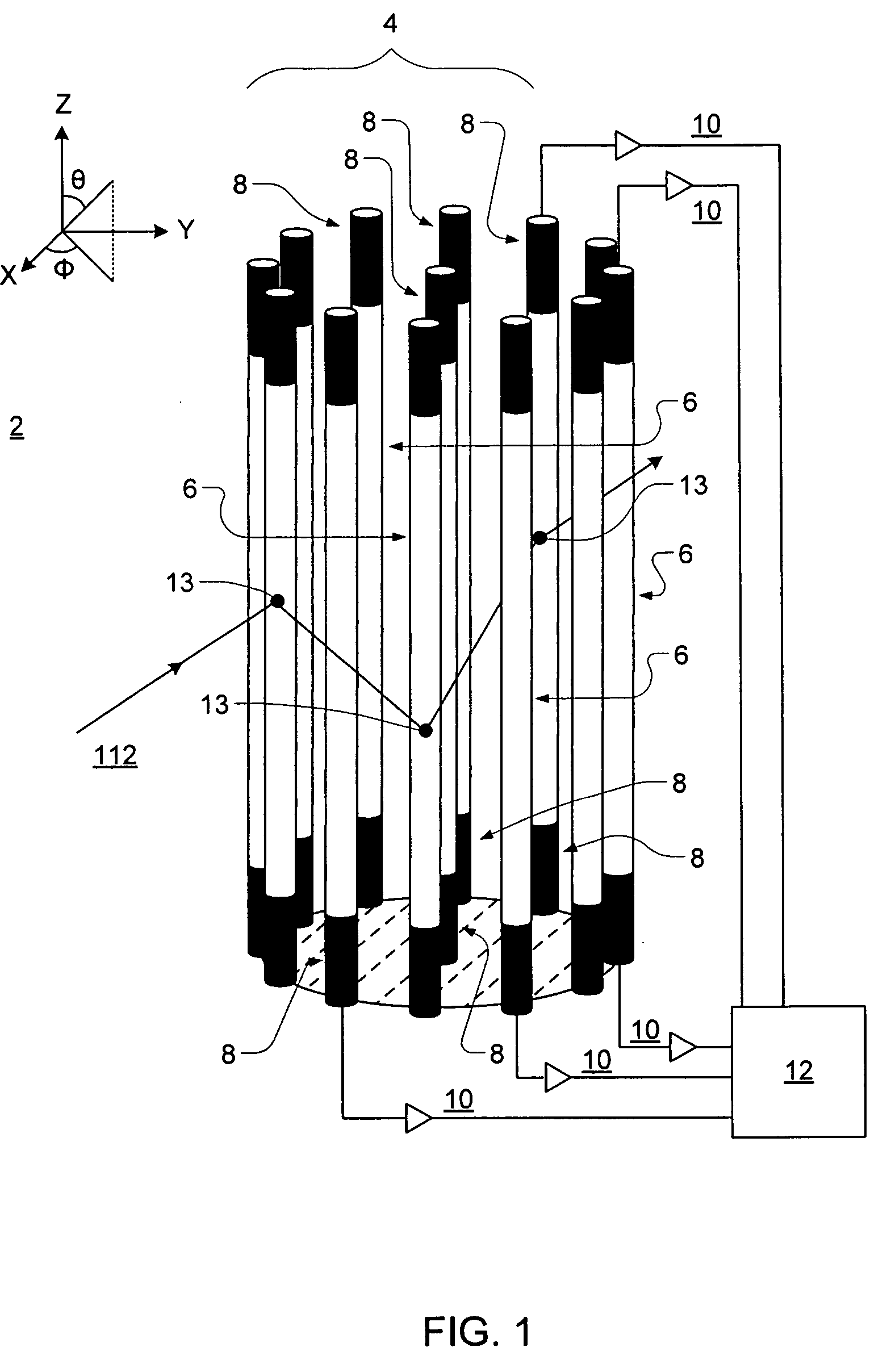
[0016] The present invention relates to a radially symmetric imaging detection system for neutrons or gamma-rays.
[0017] With respect to neutrons, the present invention measures the energy of an incident neutron, and through scattering kinematics determines the point or extended sources of the neutron. This technique is based on a known detection mechanism—fast neutron scattering off ambient hydrogen (n-p scattering). Such a detection system is configured to locate n-p scatter sites within its volume using the scintillation light generated by recoil protons, highly ionizing particles. For the neutrons that undergo at least two successive n-p scatters, an image revealing the location of a source can be constructed.
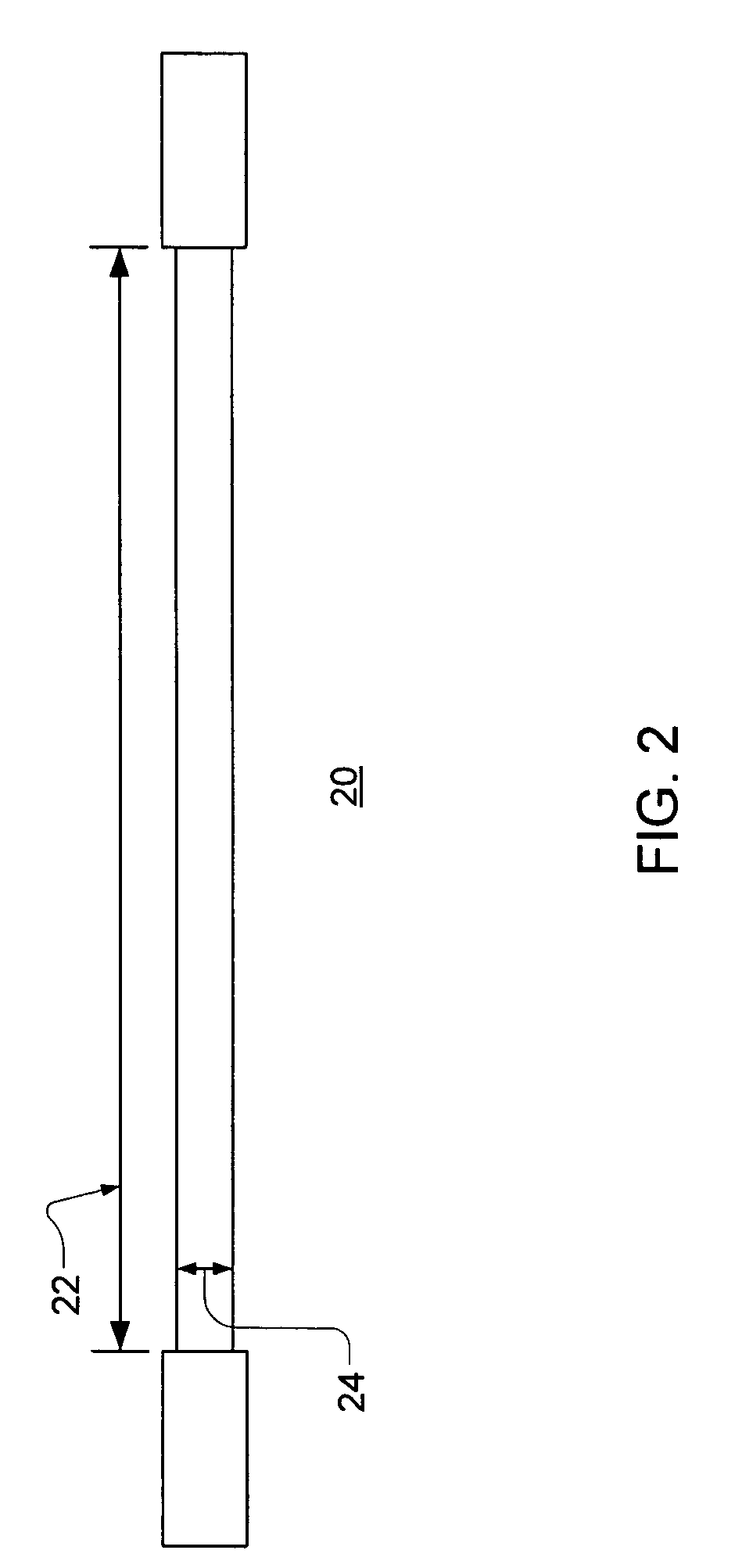
[0018]FIG. 1 shows one preferred embodiment of the imaging detection system 2 of the present invention. The design consists of a radially symmetric array 4 of multiple (in this embodiment 13) parallel scintillator bars 6. The scintillator bars 6 are preferably organic scin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com