Method and device for controlling the passage of radiant energy into architectural structures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The following examples further illustrate the invention but should not be construed as in any way limiting its scope.
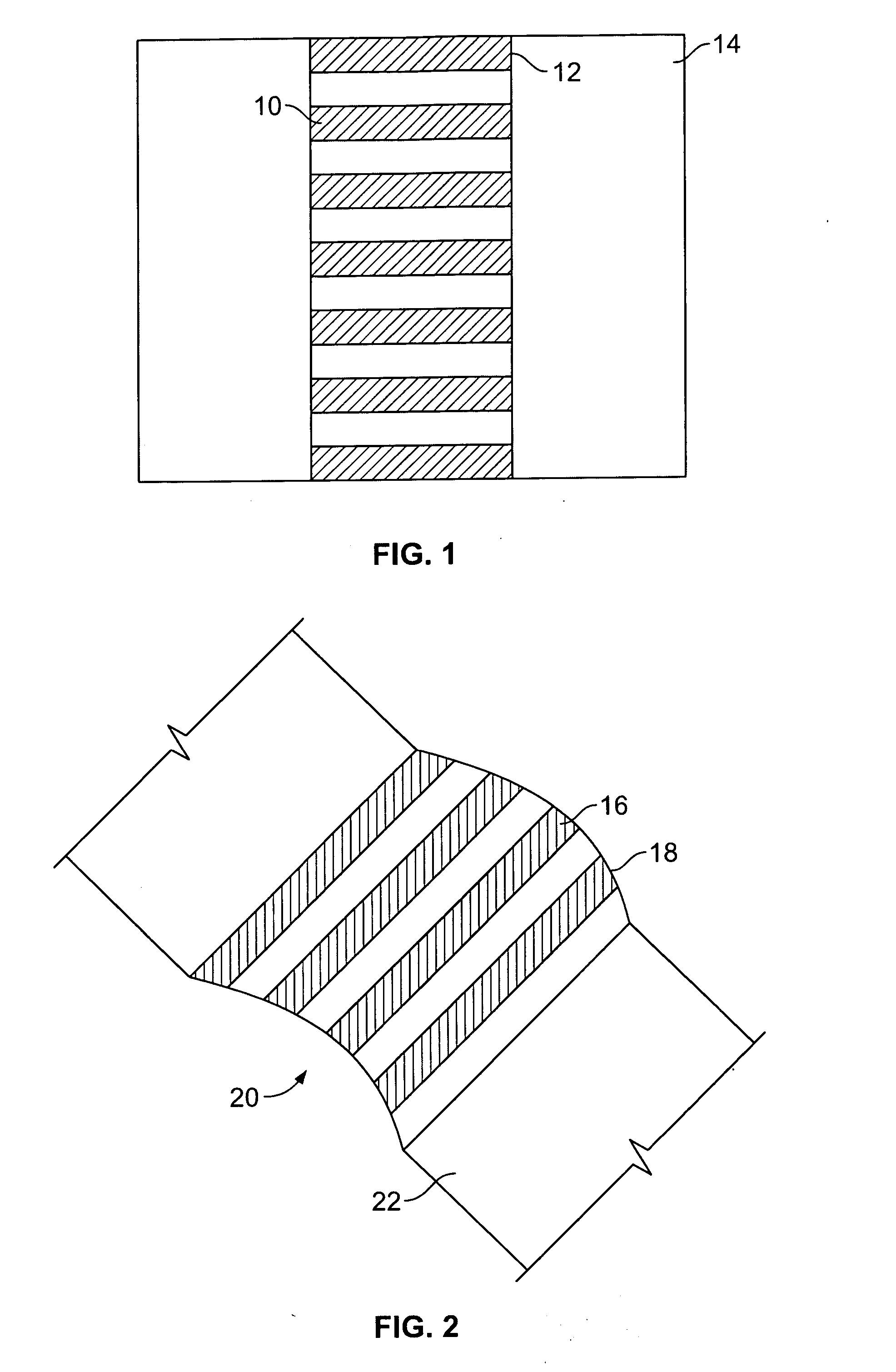
[0035] In one embodiment of the invention, as illustrated in FIG. 1, a control assembly 10 is shown mounted in a defined region 12 in a roof 14 to control the passage of radiant energy through the defined region. Although this embodiment illustrates the mounting of the control assembly across a generally planar defined region, a curved control assembly 16 may also be mounted across a curved defined region 18, such as the curved skylight 20 of roof 22 as illustrated in FIG. 2.
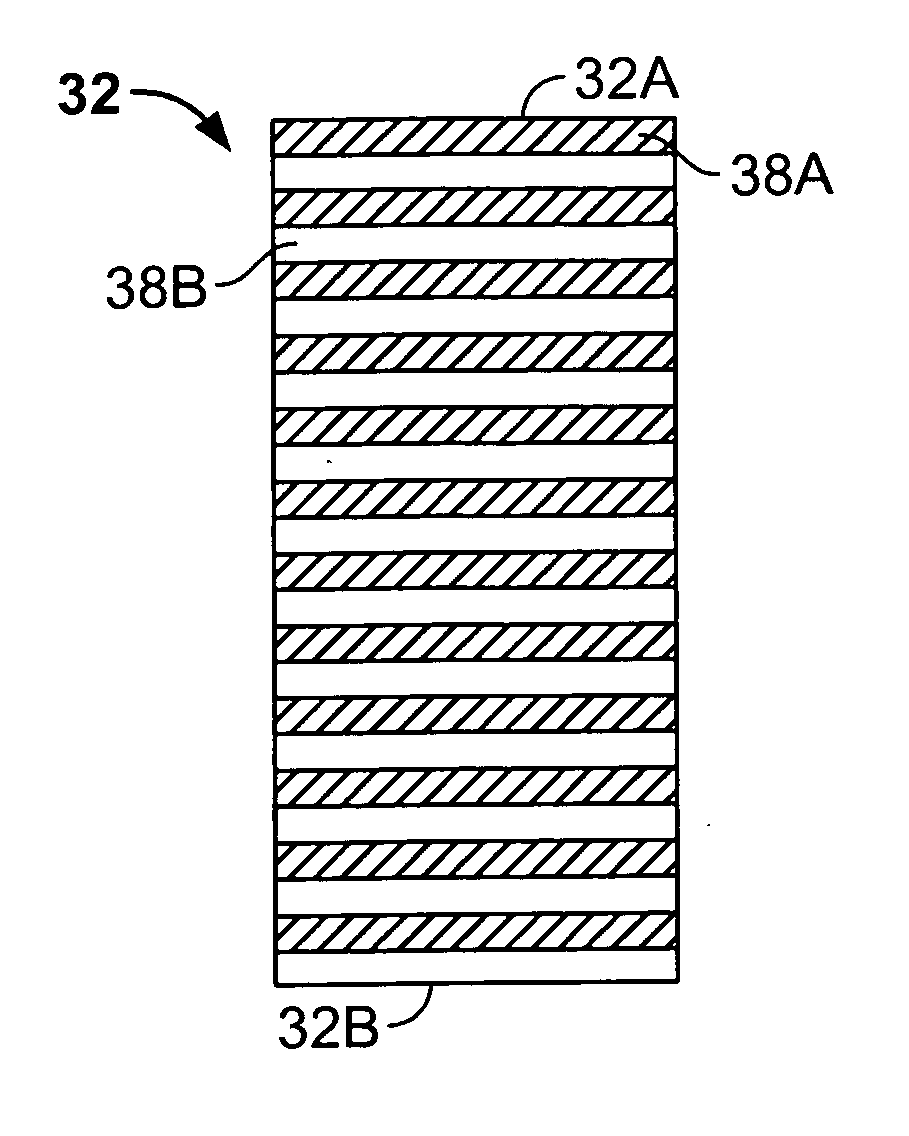
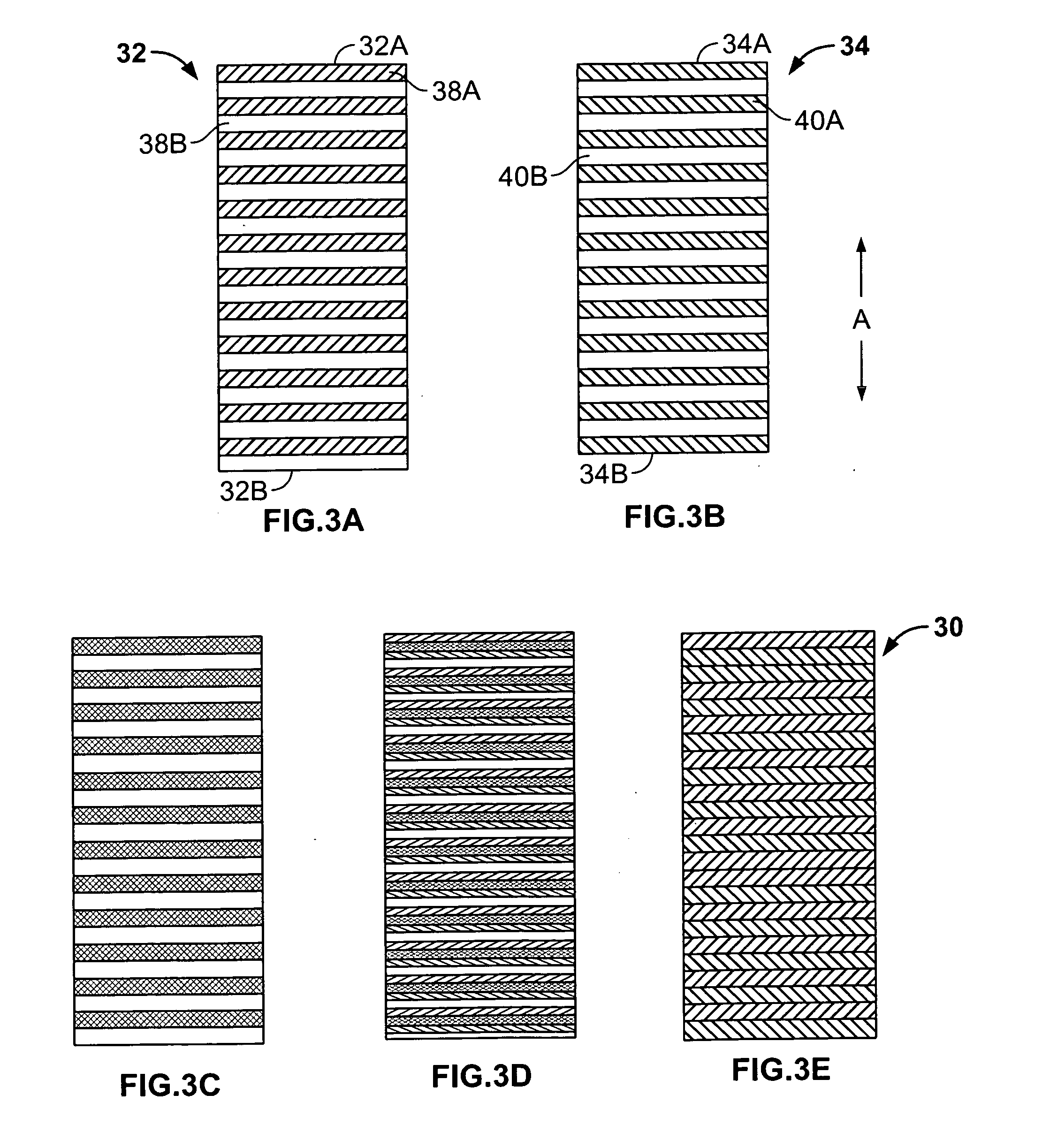
[0036] Turning now to FIGS. 3A-3E, on assembly 30 in accordance with the invention is illustrated in an embodiment including two control members in the form of planar rigid rectangular panels 32 and 34 of generally the same shape and dimensions. These panels are mounted for generally parallel movement relative to each other (in direction A) between a fully closed position (FIG. 3E) and a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com