Certificate validity checking
a certificate and validity technology, applied in the field of certificate validity checking, can solve the problems of unauthorized terminal devices being inserted into the local network, failing to obtain public keys, and affecting the validity of certificates, etc., and achieving the effect of preventing the certificate from being disabled sooner
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0093]FIG. 7 illustrates an example of a method for checking a validity of a certificate according to the present invention. The certificate is associated to a network device in a network.
[0094] An encrypted content is received at the network. An encrypted validity index associated to the encrypted content is received at the network (box 71). The received validity index is decrypted at decrypting means of the network (box 72).
[0095] Alternatively, the validity index VI is integrity protected such that a hacker cannot alter a value of the validity index VI without visible consequences. For example, an index signature is associated to the validity index, the index signature having a value that is computed from a value of the validity index and from a secret key stored at a secure device of the network. The secure device, e.g. a content receiver, comprises checking means, e.g. a portable security module, allowing to check an integrity of the validity index from the index signature. Th...
second embodiment
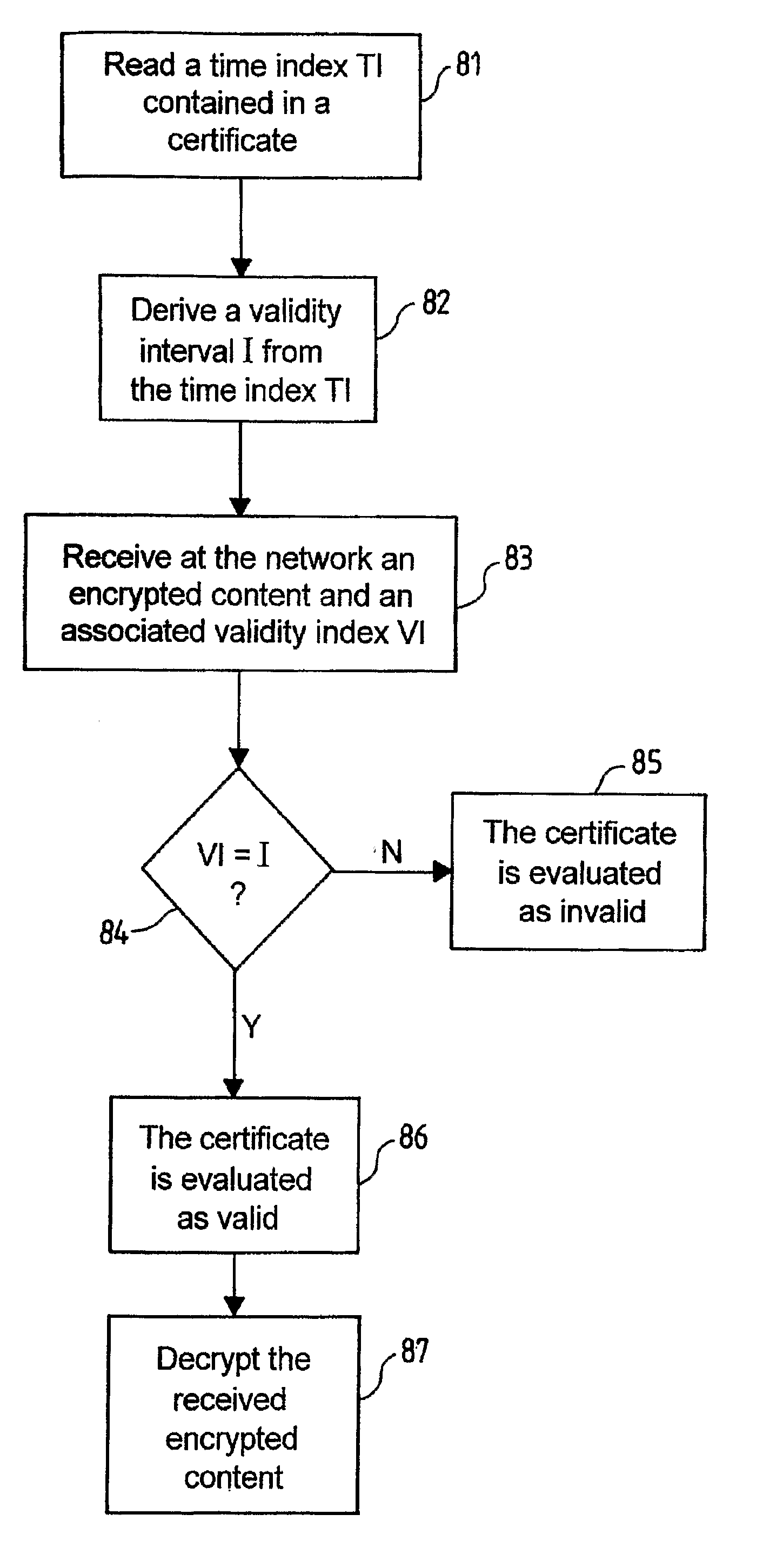
[0100]FIG. 8 illustrates an example of a method for checking a validity of a certificate according to the present invention.
[0101] The certificate comprises a time index TI that has a value corresponding to a time of issue of the certificate, e.g. a date of a manufacturing of a hardware support of the certificate. The time index TI is read (box 81).
[0102] A validity interval I is derived from the read value of the time index TI (box 82).
[0103] The time index TI may be contained in an encrypted form within the certificate. In this latter case (not represented), the time index TI is decrypted before the deriving of the validity interval I.
[0104] When an encrypted content and an associated validity index VI are received at the network (box 83), the validity of the certificate is evaluated: the certificate is evaluated as valid if the received validity index VI belongs to the time interval I (box 86). If the received validity index VI is outside the time interval I, the certificate i...
third embodiment
[0108]FIG. 9 illustrates an example of a method for checking a validity of a certificate according to the present invention. The certificate is associated to a network device of a network.
[0109] An encrypted content and an associated validity index VI are received at a network (box 91). The received validity index is used to update a comparison index CI (box 92). The comparison index is stored within a determined network device of the network, e.g. the network device to which the certificate is associated.
[0110] The updated comparison index is compared to a time index TI contained within the certificate (box 93). The time index has a value that corresponds to a time of issue of the certificate. The validity of the certificate is thus evaluated from the time index TI and from the validity index VI, the validity index VI only allowing to update a comparison index CI.
[0111] The certificate is evaluated as invalid if the time index TI is smaller than the updated comparison index (box ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com