Data quality management using business process modeling
a business process and data quality technology, applied in the field of data quality management using business process modeling, can solve problems such as affecting the overall quality of sales data, and achieve the effect of minimizing the cost of operating these controls
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Process Model
[0031] A business process model represents the flow of physical items or informational artifacts through a sequence of tasks and sub-processes that operate on them. The flow may be controlled by different types of “gateways” that can diverge or converge flows using constructs such as branches, forks, merges, and joins. These elements form a directed graph with the tasks and gateways as nodes. The graphs may be cyclic (with the probability of a cycle being less than one) as well as hierarchical, where one of the nodes could be a sub-process containing its own directed graph.
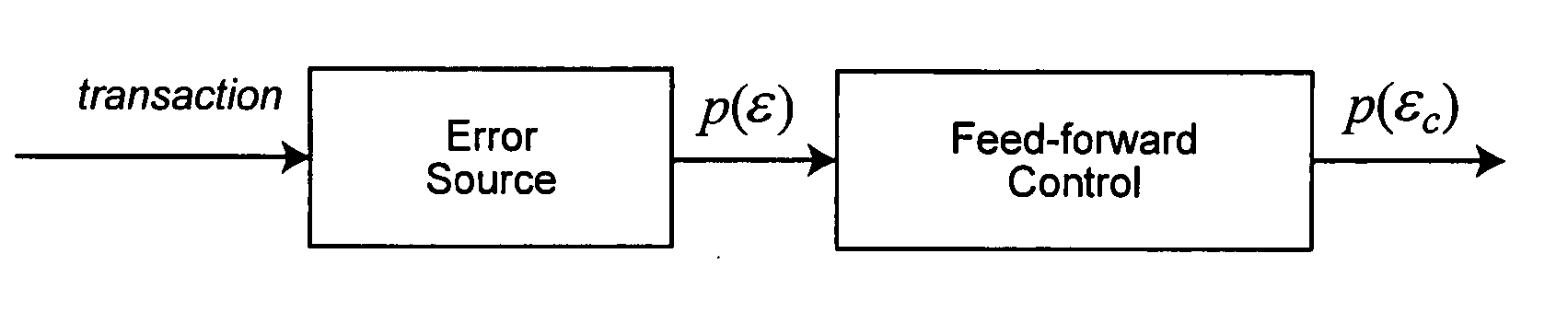
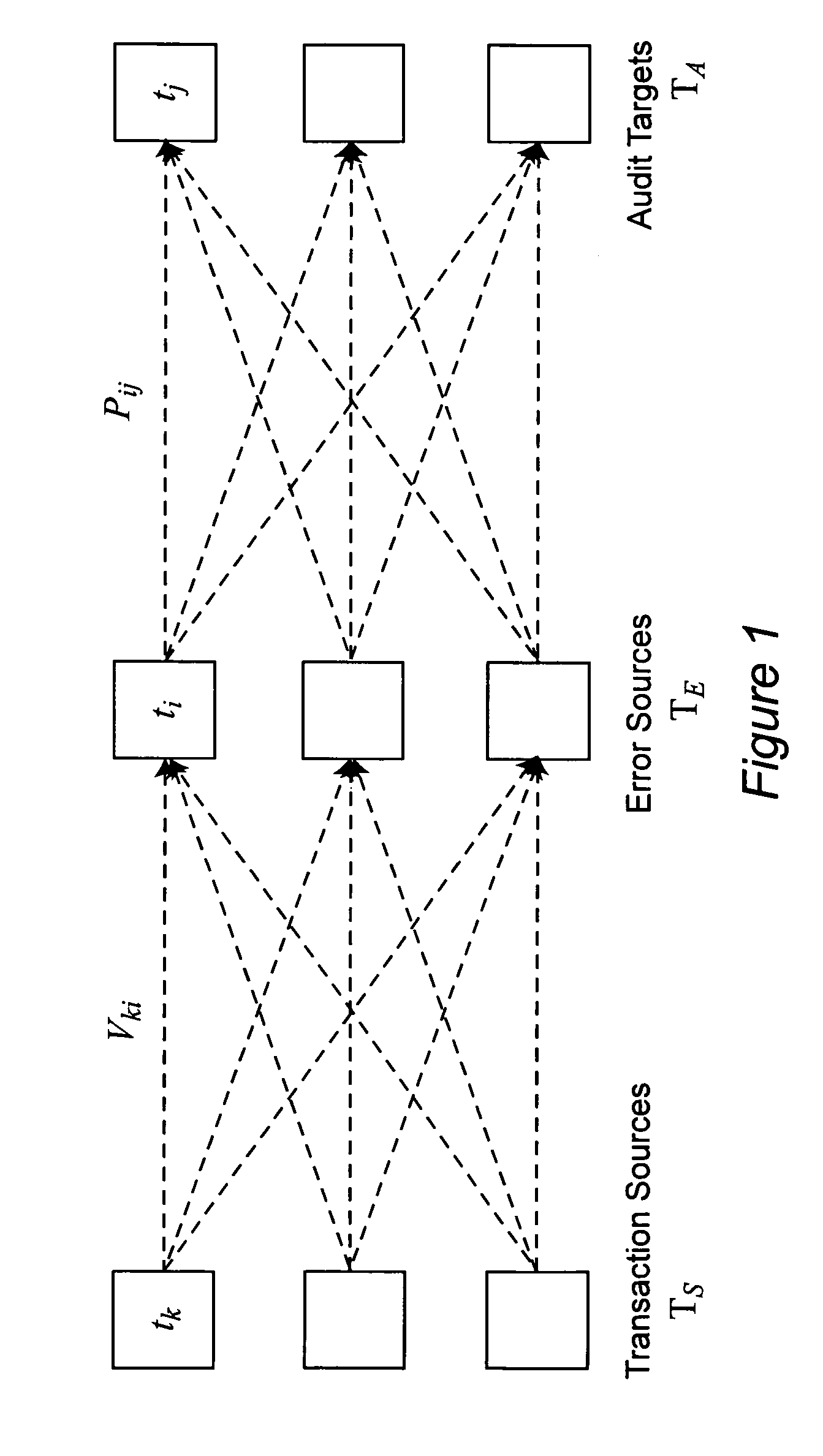
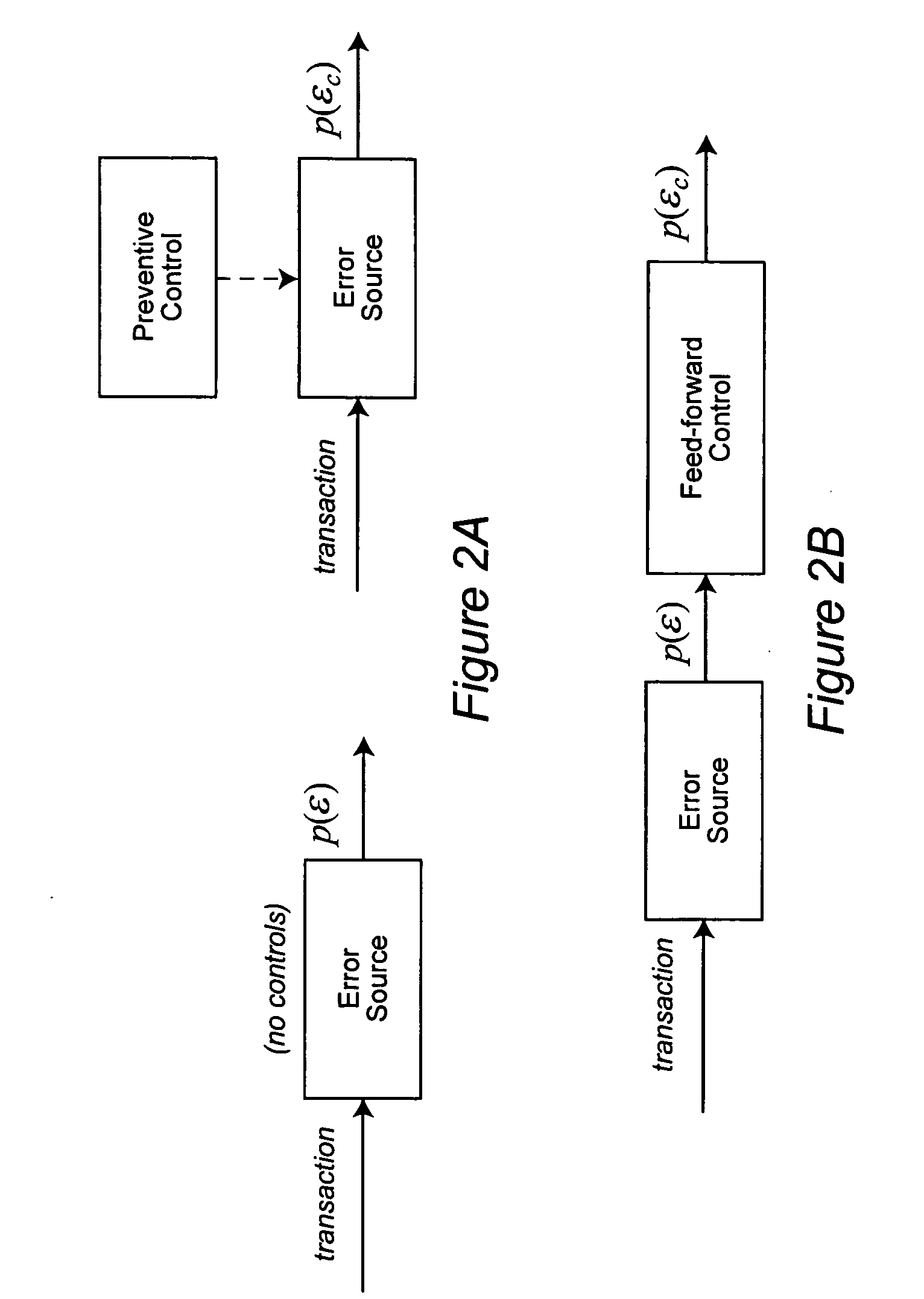
[0032] We extend the business process modeling framework by adding the following attributes relevant to modeling data quality. Consider a business process with T tasks, including all the tasks in its sub-processes. We assign some of these tasks to be transaction sources, error sources, and audit targets as defined next.
[0033] A start event or initial task in a process may be assigned to be a transa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com