Method and apparatus for processing hard material
a technology of hard material and processing method, which is applied in the field of processing hard material, can solve the problems of less optimal processing efficiency, normal difficulty in hydrating and cleaning tissue or other hard material during treatment, and achieve the effect of preventing radiation energy loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
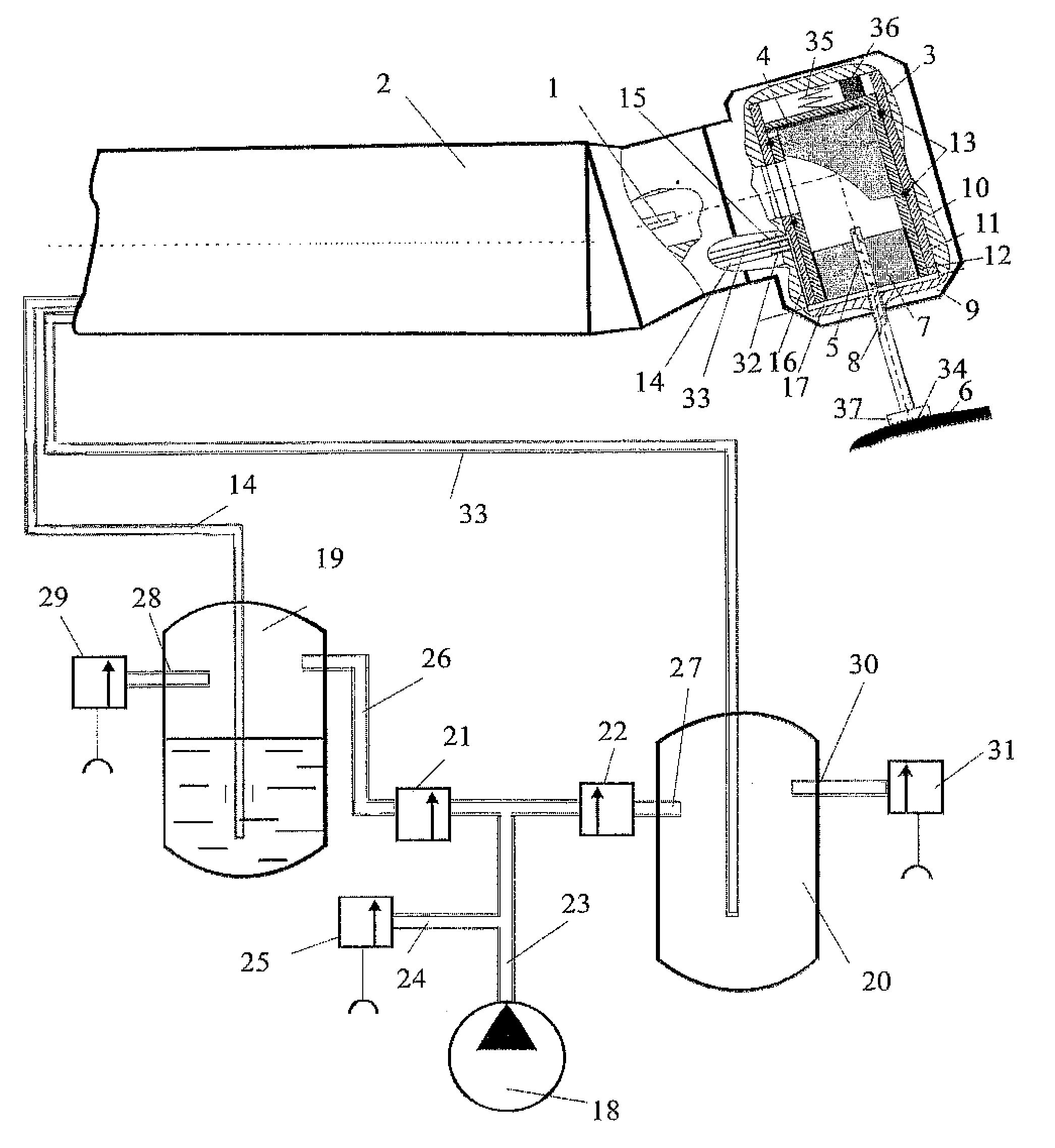
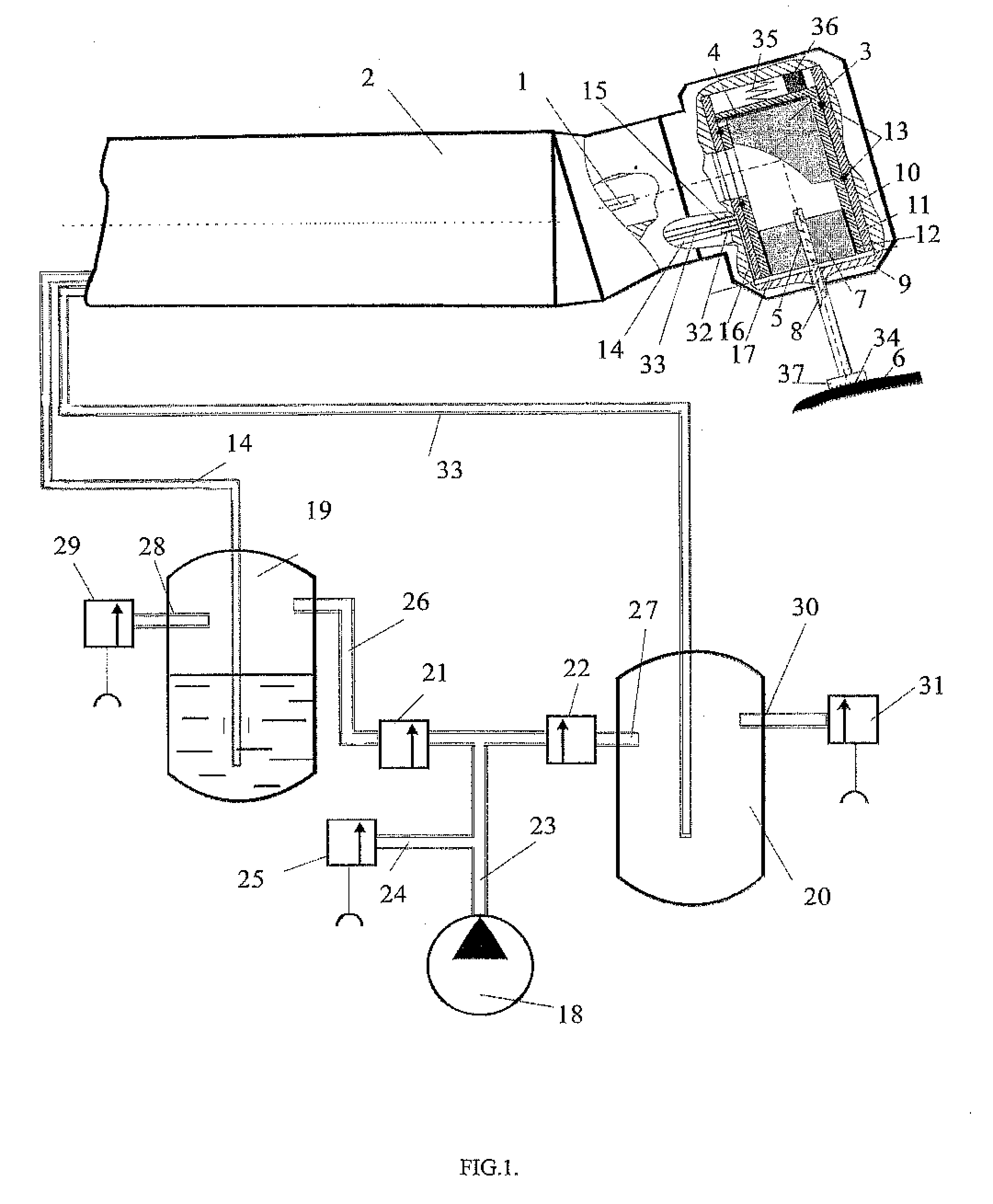
[0024] In general, the invention involves selectively providing hydration, cleaning and / or recycling of energy resulting from ablation to enhance ablation efficiency and providing a small gap between the tip of an optical light guide used to direct radiation to the material surface, at least during periods when hydration of the surface being treated is occurring and during cleaning of the surface. For some embodiments, the gap may also be provided during irradiation to facilitate the recycling of ablation products / energy to the material. For other embodiments, the tip is in contact with the treated surface during irradiation and recycling may be primarily of energy. The improved efficiency of the ablation permits the process to be performed using smaller and less expensive laser radiation sources, and in particular diode laser or diode / fiber laser pumped radiation sources which may be small enough to fit in a treatment hand-piece.
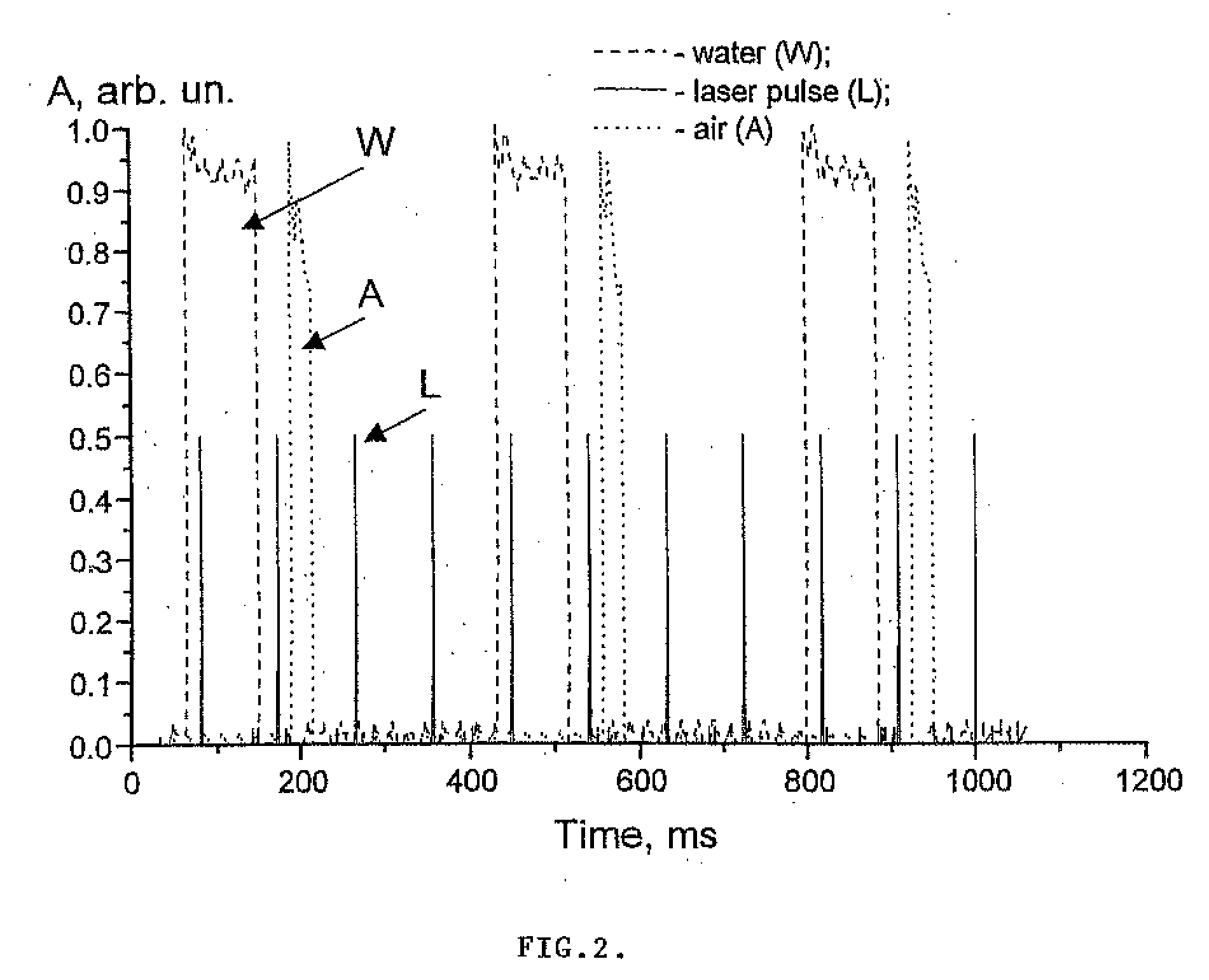
[0025]FIG. 8 illustrates the general concept of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com