Toposcopic methods and devices for delivering a sleeve having axially compressed and elongate configurations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
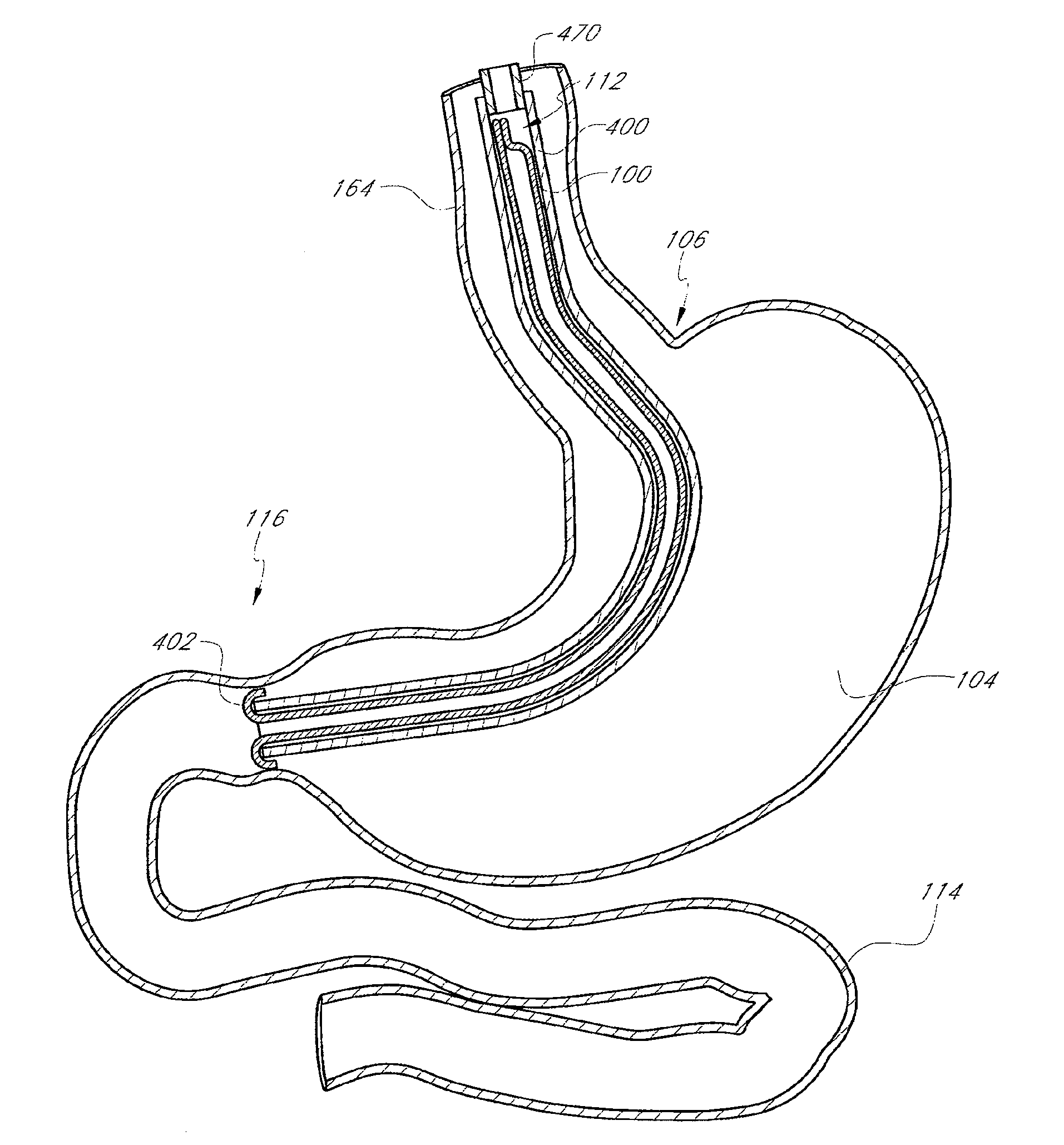
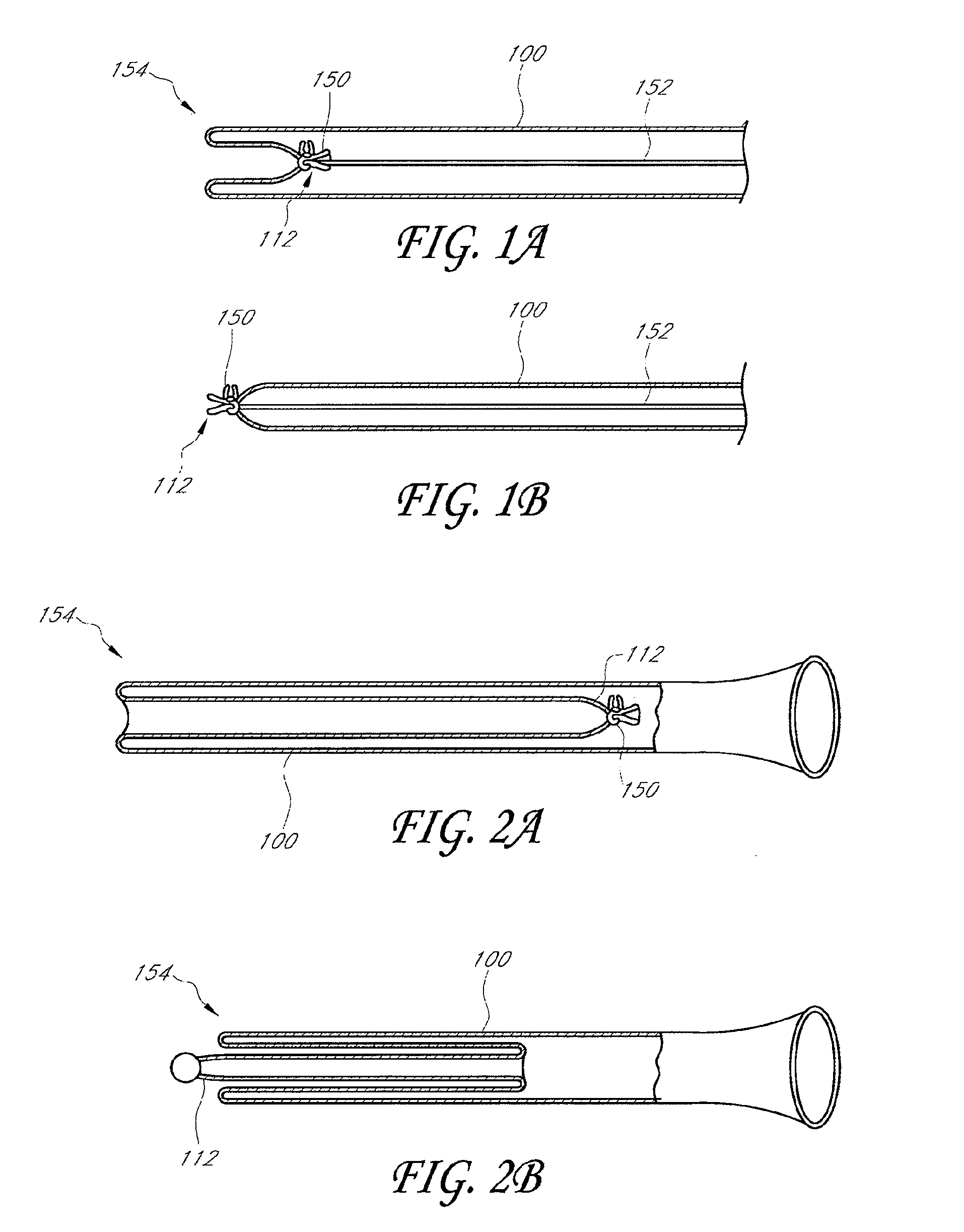
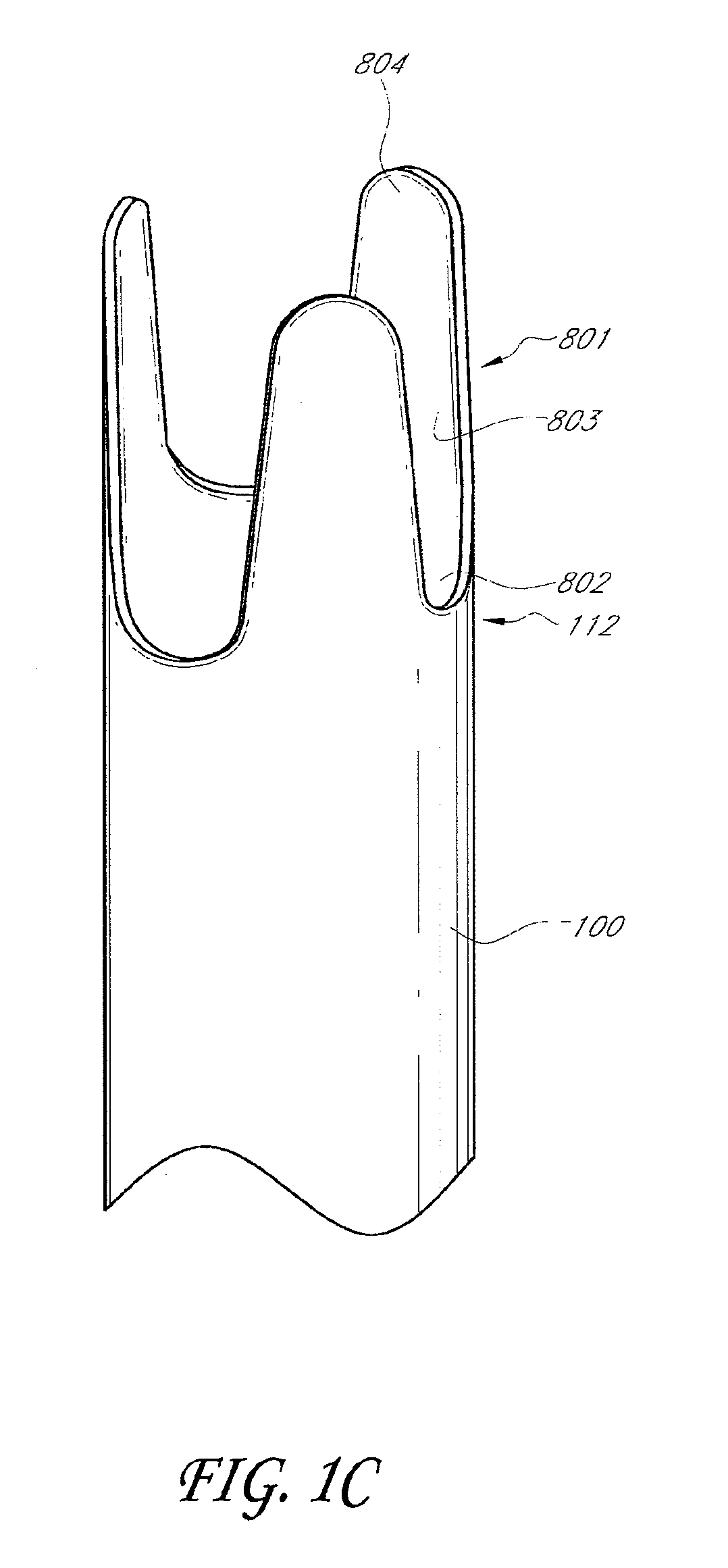
[0045]The present invention relates to elongate flexible medical devices which are capable of axial elongation through the mechanism of eversion or toposcopic expansion. In general, this may be accomplished by providing a flexible tubular device having a proximal end and a distal end. Retraction of the distal end in a proximal direction through the tubular body inverts the tube upon itself, causing an axial shortening of the overall length of the device. The original length of the device can be restored by coupling a pressurized media to the proximal end of the sleeve. If the distal end of the sleeve is temporarily restricted or closed, the pressurized media causes the distal end of the sleeve to travel distally until the full length of the sleeve has been restored. The general topic of toposcopic deployment is understood in the art.
[0046]In general, the toposcopic devices in accordance with the present invention may be utilized for any of a variety of purposes, some of which are ex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com