Nasal Delivery Devices
a nasal mucosa and nasal tube technology, applied in the field of nasal tube delivery devices, can solve the problems of significant obstacles to reliable and cost-effective delivery, snoring and sleep disturbance, and the effect of liver effect is significant, so as to reduce the chance of inhalation of the substance, prevent the effect of inhalation and low production cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
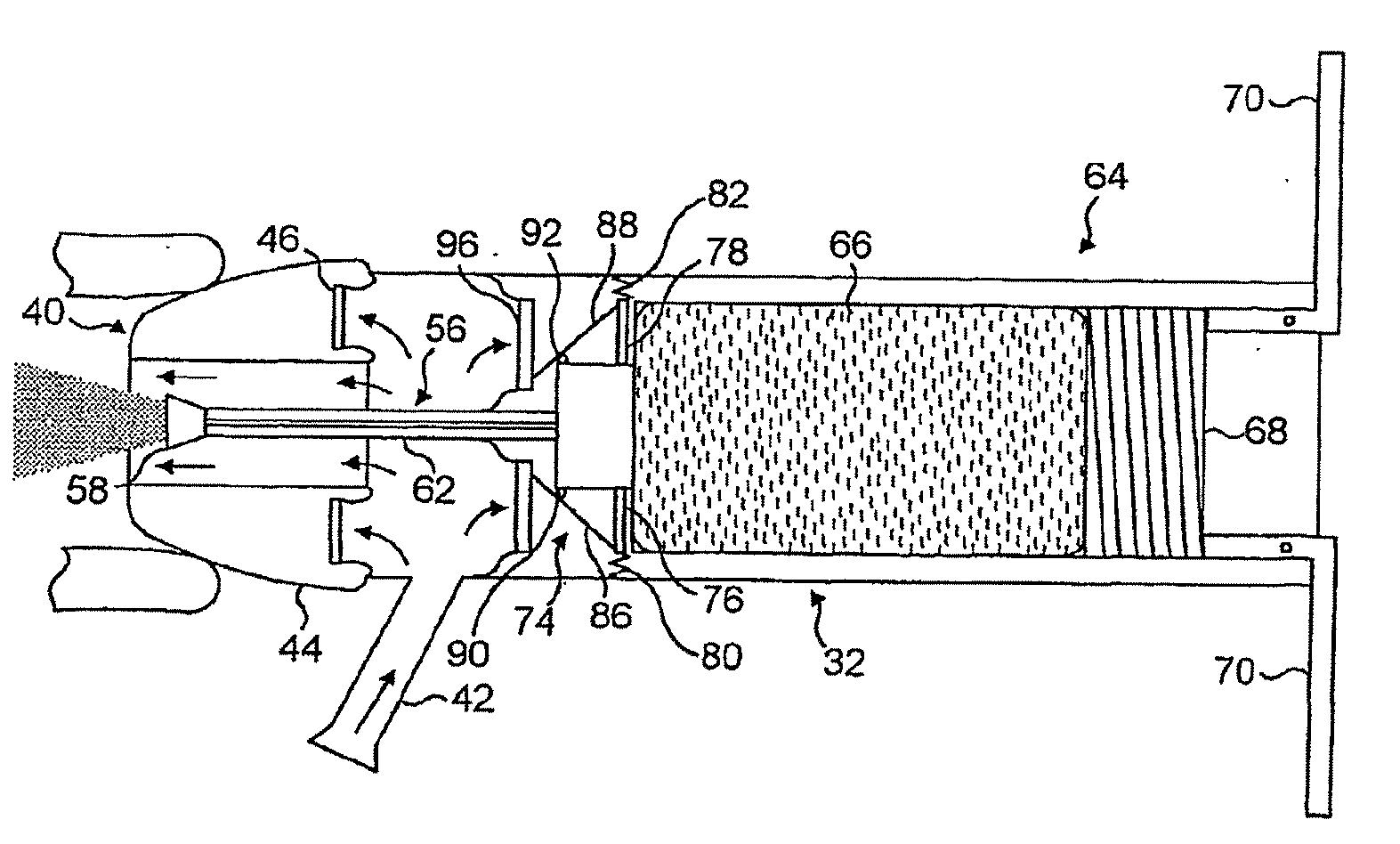
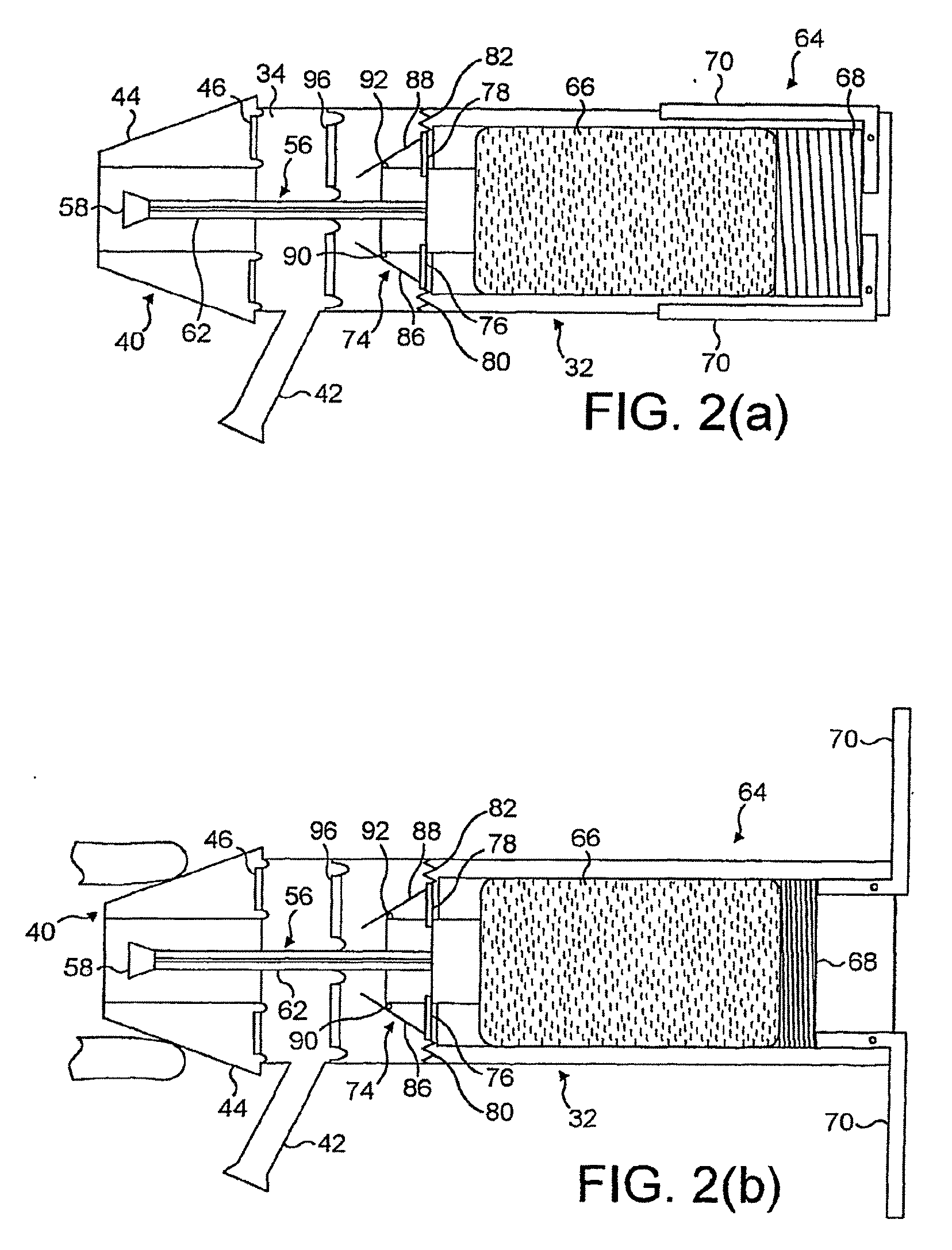
[0083]FIGS. 2(a) to (d) illustrate an oral exhalation breath-actuated nasal delivery device in accordance with the present invention.
[0084]The delivery device comprises a housing 32 which includes a chamber 34 for receiving the exhalation breath of a subject, a nosepiece 40 for fitting in a nostril of the subject which is in fluid communication with the chamber 34 in the housing 32 and disposed to one, the distal, end of the housing 32, and a mouthpiece 42 through which the subject exhales and which is in fluid communication with the chamber 34 in the housing 32.
[0085]The nosepiece 40 is an expandable member which is configured to expand on exhalation through the mouthpiece 42 such as to promote a sealing fit between the nosepiece 40 and a nostril of a subject, with such a sealing fit only being achievable on the nosepiece 40 firstly being sufficiently inserted into the nostril of the subject for effective operation of the delivery device. Where the nosepiece 40 is not sufficiently ...
second embodiment
[0098]FIGS. 3(a) to (d) illustrate an oral exhalation breath-actuated nasal delivery device in accordance with the present invention.
[0099]The delivery device of this embodiment is very similar to the delivery device of the above-described first embodiment, and thus, in order to avoid unnecessary duplication of description, only the differences will be described in detail, with like reference signs designating like parts.
[0100]The delivery device of this embodiment differs from that of the above-described first embodiment in further comprising an oral exhalation breath-actuatable gas supply unit 98 for delivering a gas flow to the chamber 34 in the housing 32 in response to exhalation by a subject, and in that the mouthpiece 42 is in fluid communication with the gas supply unit 98 and not the chamber 34 in the housing 32, whereby a controlled gas flow is delivered to the chamber 34 in the housing 32, and hence the nasal airway of a subject, from the gas supply unit 98 in response to...
third embodiment
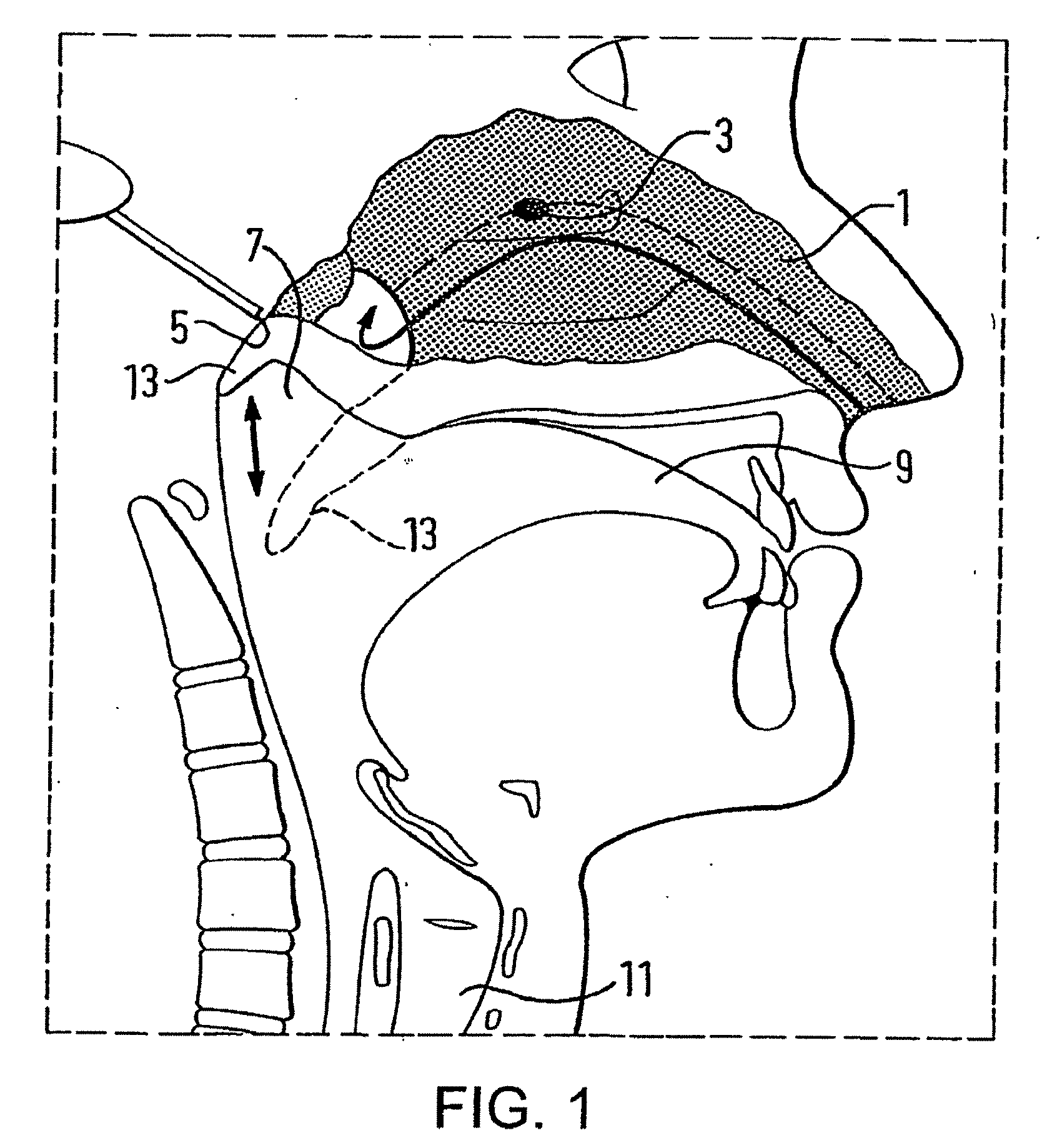
[0102]FIG. 4 illustrates an oral exhalation breath-actuated nasal delivery device in accordance with the present invention.
[0103]The delivery device comprises a nosepiece 101 for fitting in one nostril of a subject to provide a fluid-tight seal therewith, a mouthpiece 103 through which the subject exhales, and a flow channel 105 which fluidly connects the nosepiece 101 and the mouthpiece 103. With this configuration, exhaled air from an exhalation breath of a subject is delivered through the nasal airway of the subject.
[0104]In this embodiment the delivery device further comprises a filter unit 107 which is disposed at the inlet end of the flow channel 105, here including a moisture filter. In a preferred embodiment the filter unit 107 could include an anti-microbial filter.
[0105]The delivery device further comprises a pressure detector 109, in this embodiment an electronic pressure detector, which is disposed in the flow channel 105, in this embodiment downstream of the filter unit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com