Method and device for threading needles
a needle threading and needle threading technology, applied in the field of domestic sewing, can solve the problems of linear strength, breakage, and thin wire forming the loop is subject to rapid metal fatigue, and achieve the effects of long durability, improved threading efficiency, and improved threading efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
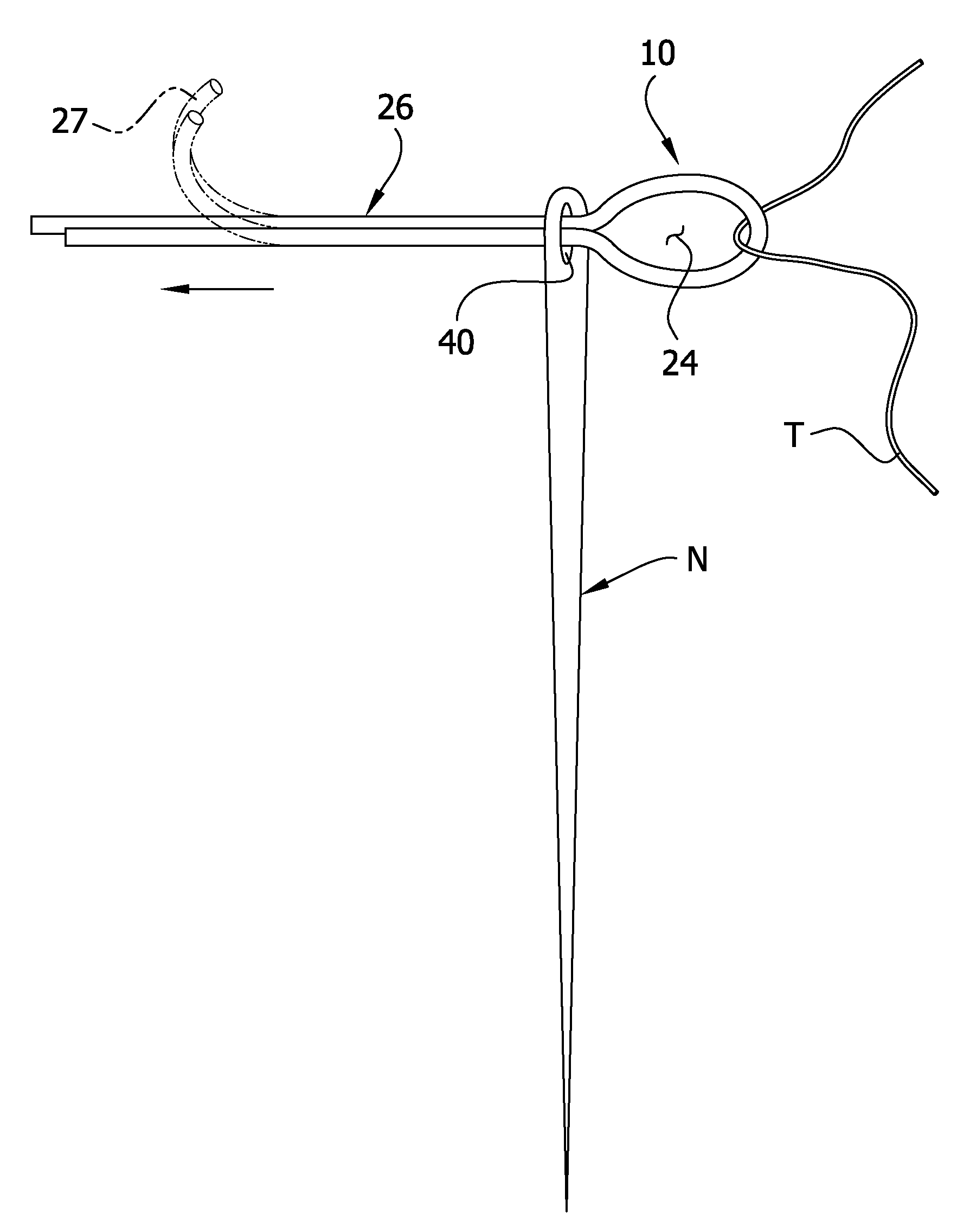
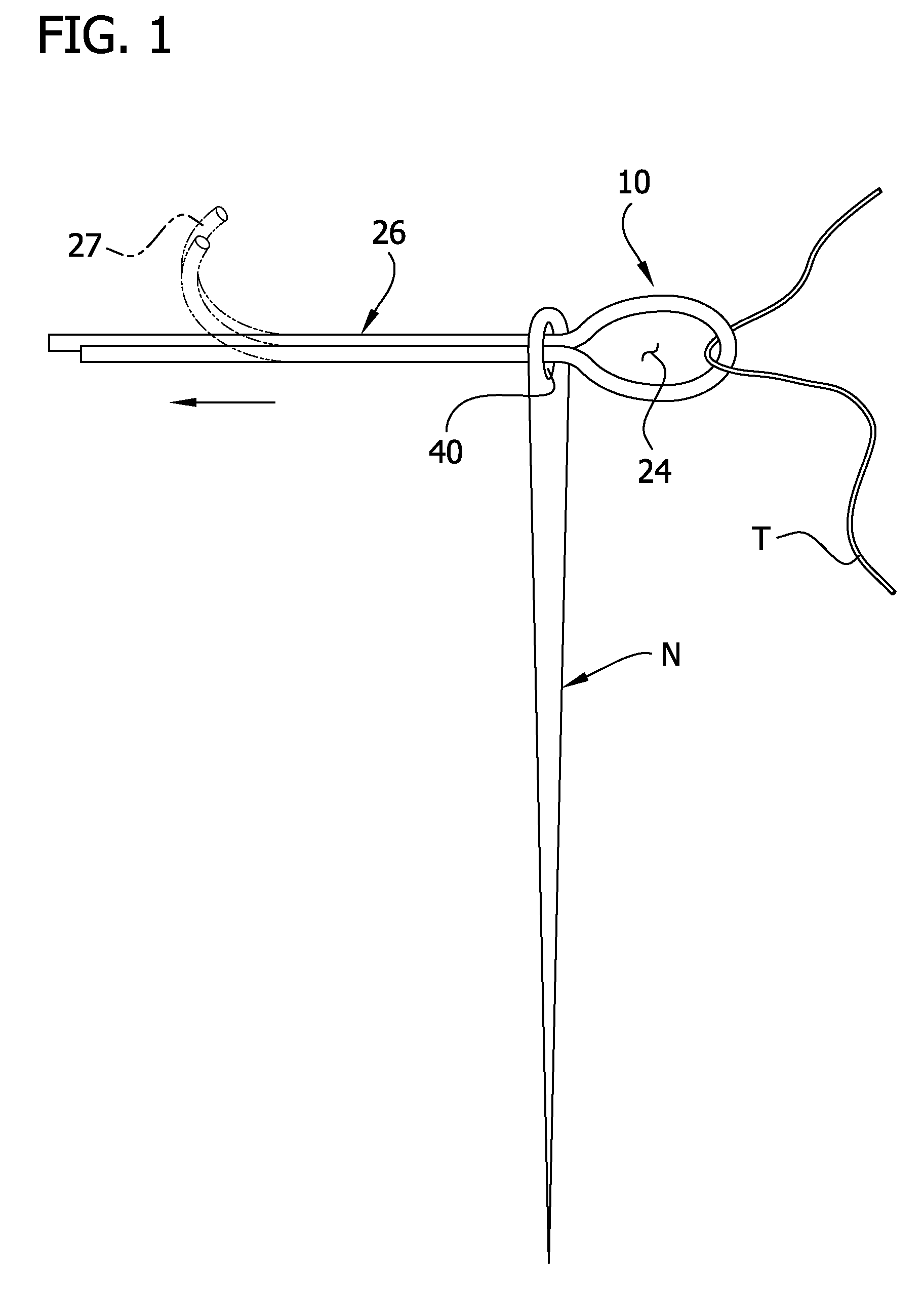
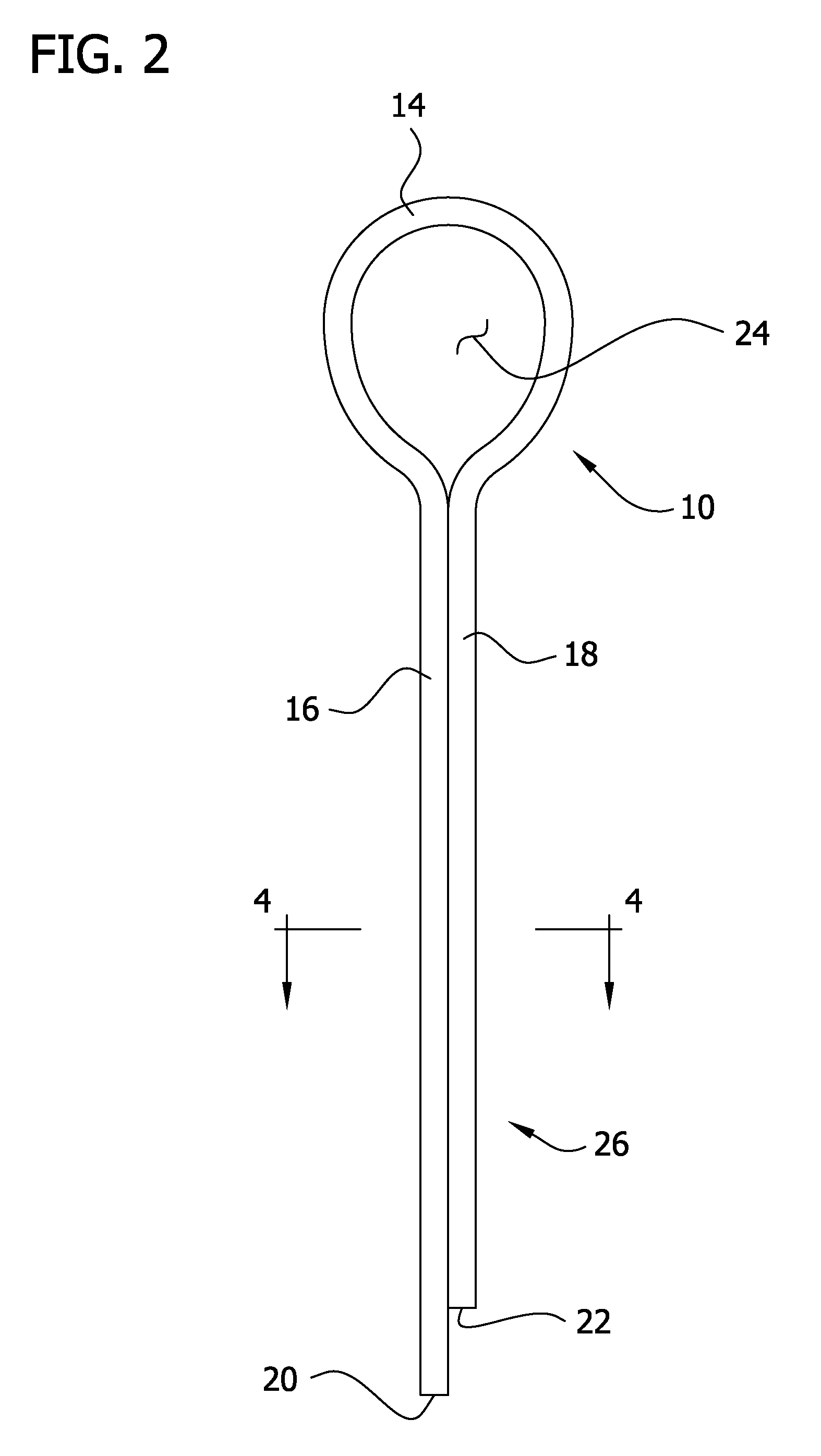
[0017]Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2 of the drawings, the invention in its simplest form is embodied in a needle threading device 10 (FIG. 2) formed from a single non-metallic length of microfilament 12 (FIGS. 3a and 3b) of a selected plastic material. The monofilament 12 has a central loop-forming zone 14 and outer first and second end zones 16, 18 with free ends 20, 22 respectively. The flexible monofilament 12 is bent or folded to form the central zone 14 into a closed loop or loophole or snare 24 (FIGS. 1, 2) with the end zones or portions 16, 18 extending outwardly in a side by side or parallel and abutting relationship to form a threading spike, spine or stem (shown generally at 26).
[0018]FIG. 1 also illustrates the method of the invention in which the device 10 is used to thread the elongate eyelet 40 of a typical needle N; and it should be noted that the device and method is also applicable to needles having round eyelets although the smaller eyelet will of course reduce the app...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com