Plant defense signal peptides
a plant defense and signal peptide technology, applied in the field of plant defense signal peptides, can solve the problems of many interactions that are harmful to plants, damage to plants, and decimation of ornamental plants, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing disease symptoms, enhancing plant defenses, and improving plant product yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Isolation and Analysis of AtPep1 and Paralogs and Orthologs Thereof
[0214]Innate immunity is initiated in animals and plants through the recognition of a variety of pathogen associated molecules that in animals are called “pathogen-associated molecular patterns,” or PAMPS, and in plants are called elicitors. Peptides derived from pathogens can be powerful elicitors of plant defense responses (Hahlbrock et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:4150-4157, 1995; van den Askerveken et al., Plant Physiol. 103:91-96, 1993; Kammpren, Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 4:295-300, 2001; Kunze et al., Plant Cell, 16:3496-3507, 2004; Navarro et al., Plant Physiol. 135:1113-1128, 2004; Fellbrich et al., Plant J. 32:375-390, 2002; He et al., Cell 73:1255-1266, 1993), but plant-derived peptides have not been identified previously that are elicitors of immune responses directed against pathogens.
[0215]We have isolated and characterized a 23 amino acid peptide, called AtPep1, that is a signaling component of the ...
example 2
An LRR Receptor Kinase is a Component of AtPep1 Amplification of Innate Immunity in Arabidopsis
[0251]Over 200 LRR receptor kinases are present in the Arabidopsis genome. Only a few LRR receptor kinases have been identified that interact with the peptide signals in plants. This includes the receptor for the defense peptide signal, systemin (Scheer and Ryan, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99:9585-9590, 2002) and receptors for the developmental peptide signals CLAVATA1 (Clark and Meyerowitz, Cell 89:575-585, 1997), phytosulfokine-alpha (Matsubayashi et al., Science 296:1470-1472, 2002) and the pathogen-derived peptide flg22 (Gomez-Gomez and Boller, Trends Plant Sci. 7:251-256, 2000).
[0252]The discovery that the AtPep family of endogenous peptides from Arabidopsis leaf extracts cause an alkalinization of the medium of Arabidopsis suspension cultured cells indicates that the peptide plays a role in plant cells by interacting with a cell surface receptor. Investigations of the biological role of...
example 3
Shorter Peptides from the C-Terminus of AtPep1 Possess Substantial Defense Signal Peptide Activity
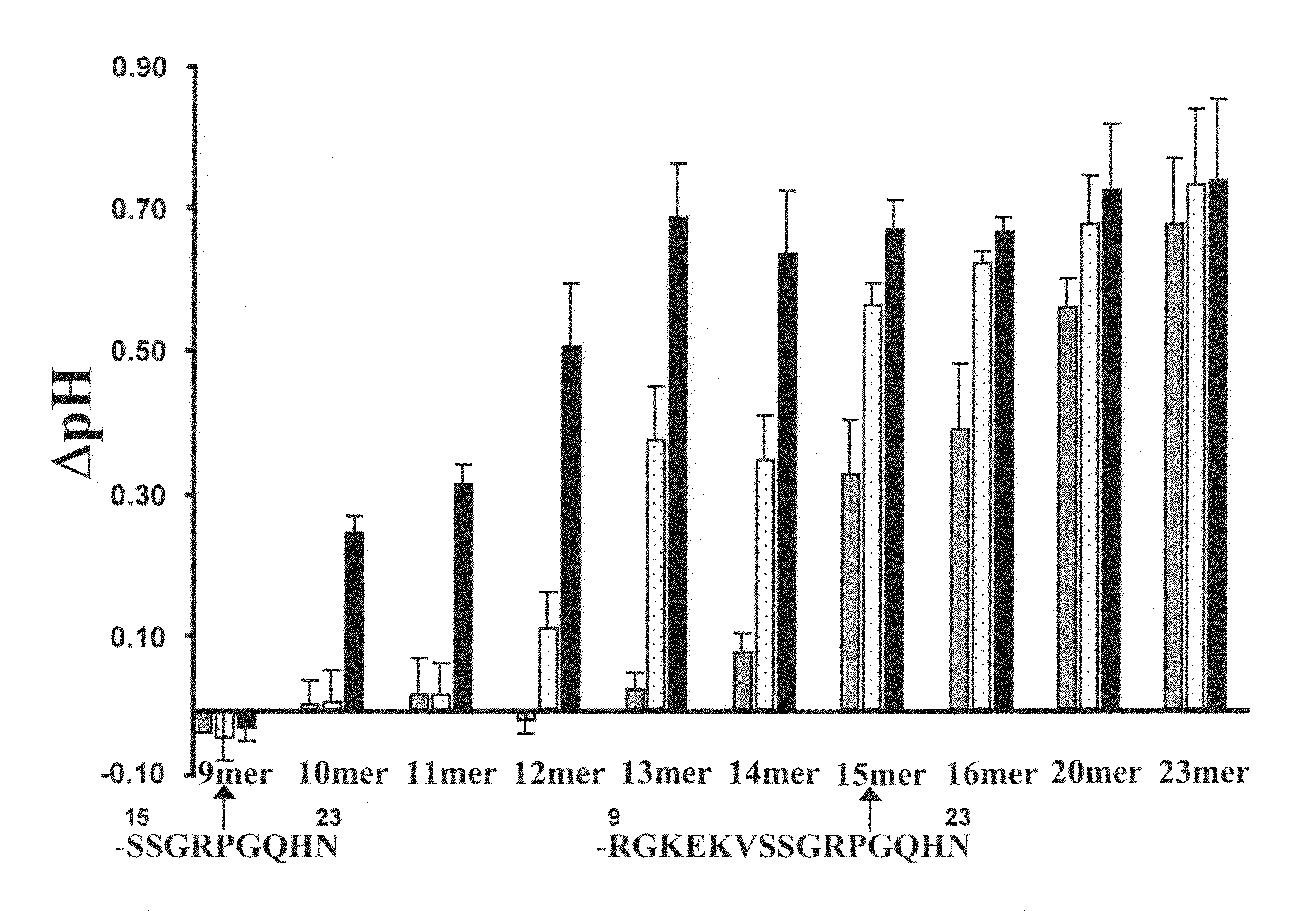
[0268]Analogs of AtPep1 from the C-terminus of AtPep1 were synthesized and assayed in the alkalinization assay. One mL aliquots of 4 day old Arabidopsis cells were allowed to equilibrate on an orbital shaker at 180 rpm for one hour. A 10 μL aliquot of each peptide solution was added to the cells. Peptide concentrations of 0.25 nM, 2.5 nM, and 25 nM were tested. After 20 min, the pH of the media was recorded. The results are shown in FIG. 5. An analog of AtPep1 missing the carboxy-terminal amino acid was completely inactive, whereas deletions from the amino-terminus of the peptide resulted in a sequential reduction in activity, until peptides with 9 carboxy-terminal amino acids remaining (SSGRPGQHN (SEQ ID NO: 75)) were inactive. A peptide with 10 carboxy-terminal amino acids remaining had substantial defense signal peptide activity at the 25 nM peptide concentration, causing a change in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com