Methods of modulating hvem, btla and cd160 cis complex response or signaling activity with soluble light polypeptide sequences
a cis complex and soluble light polypeptide technology, applied in the field of hvem cis complexes, can solve the problems of unsafe application and poorly understood cosignaling pathway, and achieve the effects of inhibiting or preventing spontaneous multimerization of hvem, preventing recruitment, and inhibiting trans activation of hvem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
This Example Describes Materials and Methods Used in Examples 2 to 12
Reagents and Cell Lines
[0153]Antibodies used included: mouse anti-BTLA mAb (J168, IgG1κ; BD Bioscience, San Diego, Calif.), mouse anti-HVEM mAb (clone 94801, R&D System, Emeryville, Calif.), mouse anti-mouse BTLA mAb (6F7), Armenian Hamster anti-HVEM mAb (LH1), mouse anti-human HVEM (eBioHVEM-122), and mouse anti-human BTLA (MIH26) (eBioscience, San Diego, Calif.); mouse anti-FLAG mAb (M2 clone, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mo.), rabbit-anti-RelA / p65 Ab (C-20), anti-RelB (C-19) and anti-TRAF3 Ab (H-122) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and rat anti-TRAF2 mAb (6F8 clone, MBL, Nagoya, Japan). Rat anti-BTLA mAb (6F4, IgG1κ), goat anti-HVEM and anti-LTβR IgG were made in-house against purified receptor Fc proteins as described (Rooney, et al., Methods Enzymol 322:345 (2000)). Purified Fc fusion proteins: HVEM-Fc, BTLA-Fc and LTβR-Fc, of mouse or human origin, were produced and purified as described (Cheung, et al., Proc Natl Ac...
example 2
This Example Includes Studies Showing Expression Patterns of Intrinsic BTLA and HVEM Complex in T cells
[0164]The possibility that HVEM and BTLA act in cis, implicated T cells may coexpress HVEM and BTLA. The expression patterns of HVEM and BTLA in mouse and human naïve T cells isolated from spleen or peripheral blood, respectively using specific mAb were studied. Indeed, the vast majority of CD3+T cells obtained from human and mouse coexpressed HVEM and BTLA, suggesting a pattern of expression conserved across species. Both major subsets of mouse T lymphocytes coexpressed HVEM and BTLA with CD4 T cells expressing relatively more BTLA than CD8 T cells.
example 3
This Example Includes Studies Showing Cis-Interaction Between HVEM and BTLA
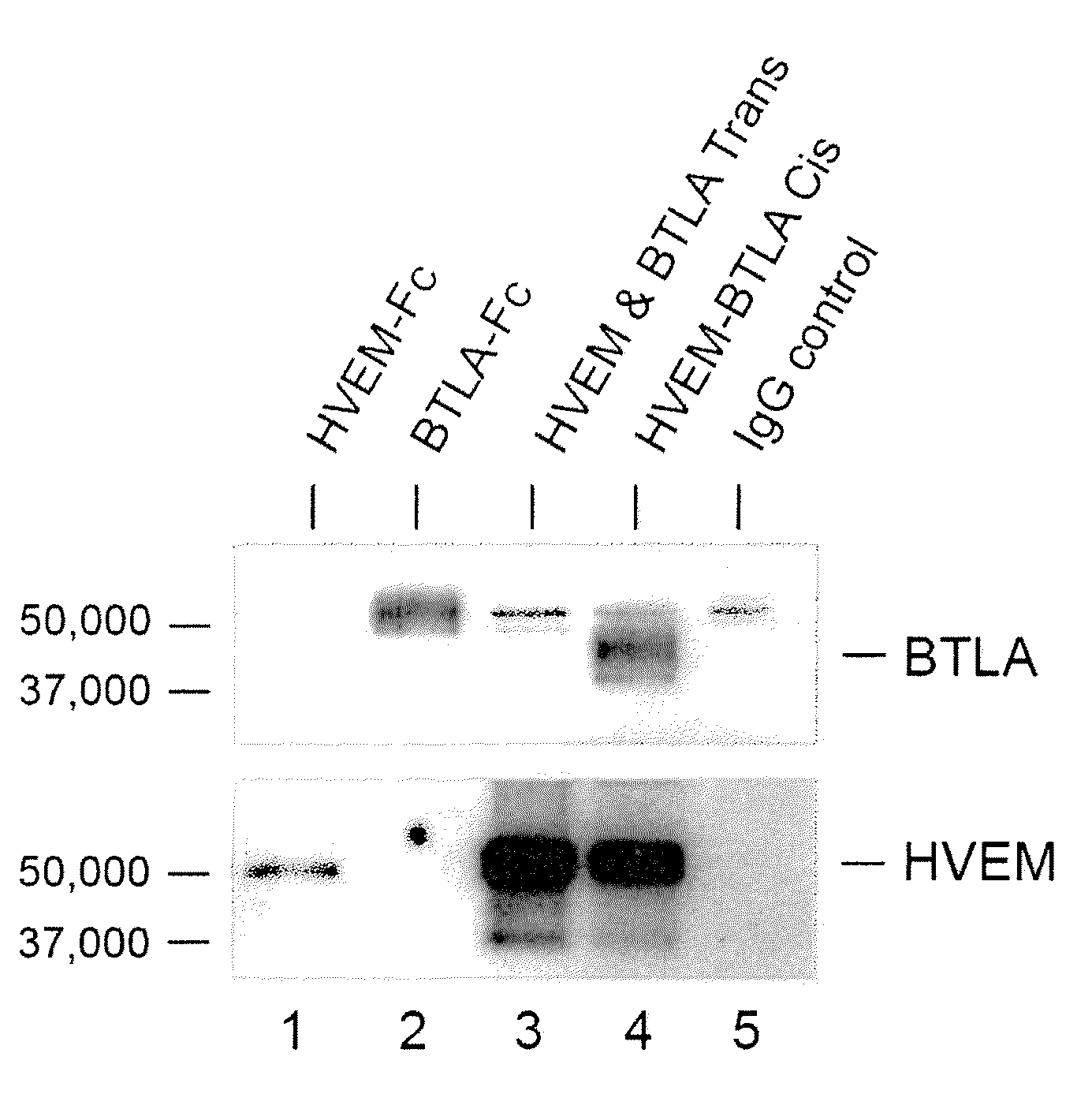
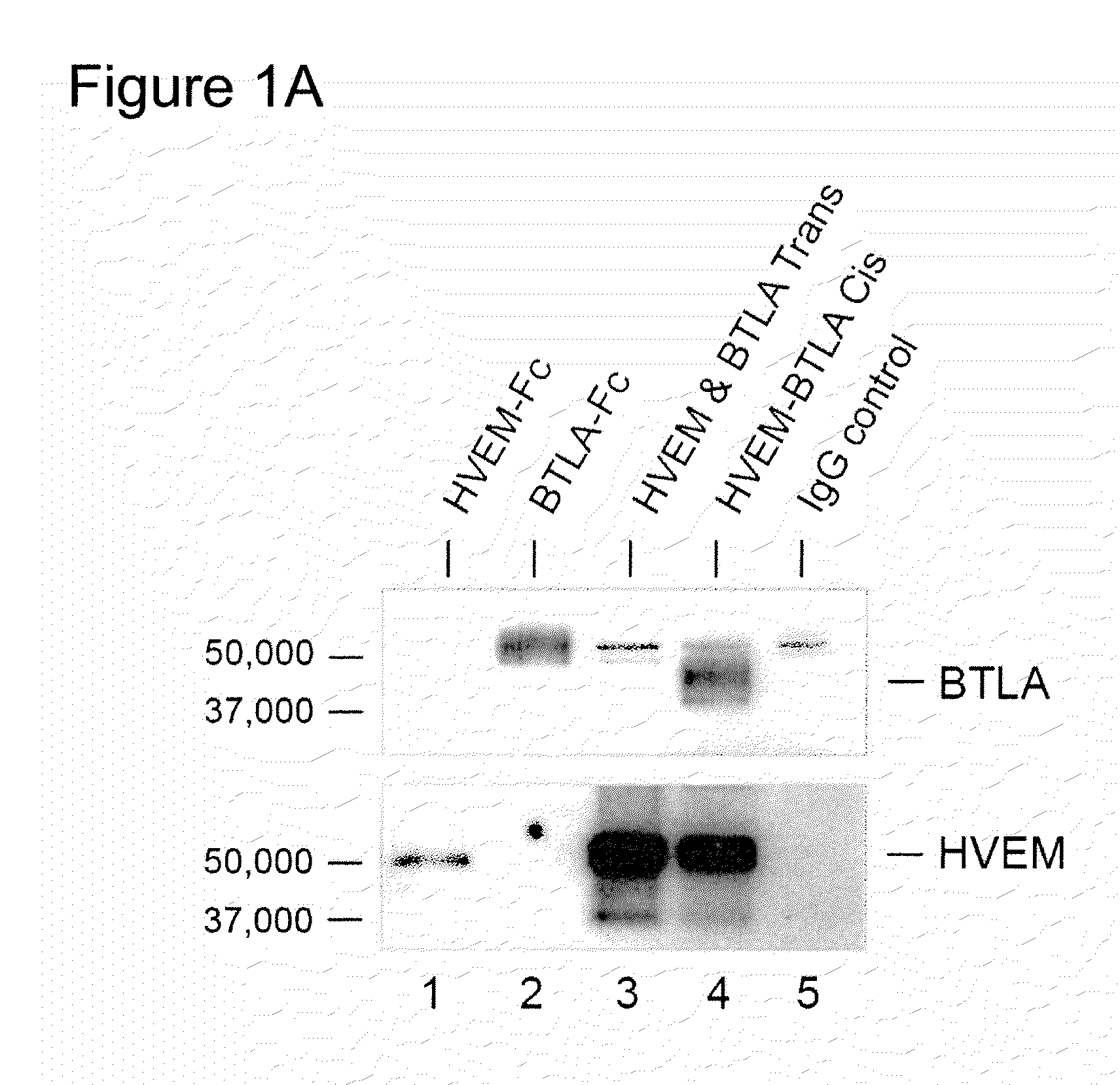
[0165]Dendritic cells, and T and B lymphocytes depending on their state of activation, coexpress HVEM and BTLA (De Trez, et al., J Immunol (2008) 180:238; Sedy, et al., Nat Rev Immunol (2005) 8:861) indicating the potential for ligand receptor complex formation in cis. To determine whether HVEM and BTLA form a complex when coexpressed in the same cells, 293T cells were transfected with BTLA, HVEM or both, and HVEM immunoprecipitated from lysates with aid of a Flag-epitope tag (HVEM-Flag). BTLA specifically coimmunoprecipitated with HVEM-Flag in cells coexpressing HVEM and BTLA (FIG. 1A, lane 4). In contrast, BTLA did not associate with HVEM when immunoprecipitated from a mixture of HVEM expressing 293T cells (293T-HVEM) and BTLA expressing 293T cells (293T-BTLA) (FIG. 1A, lane 3). This result indicated HVEM-BTLA forms a stable complex in cis, but not in trans.
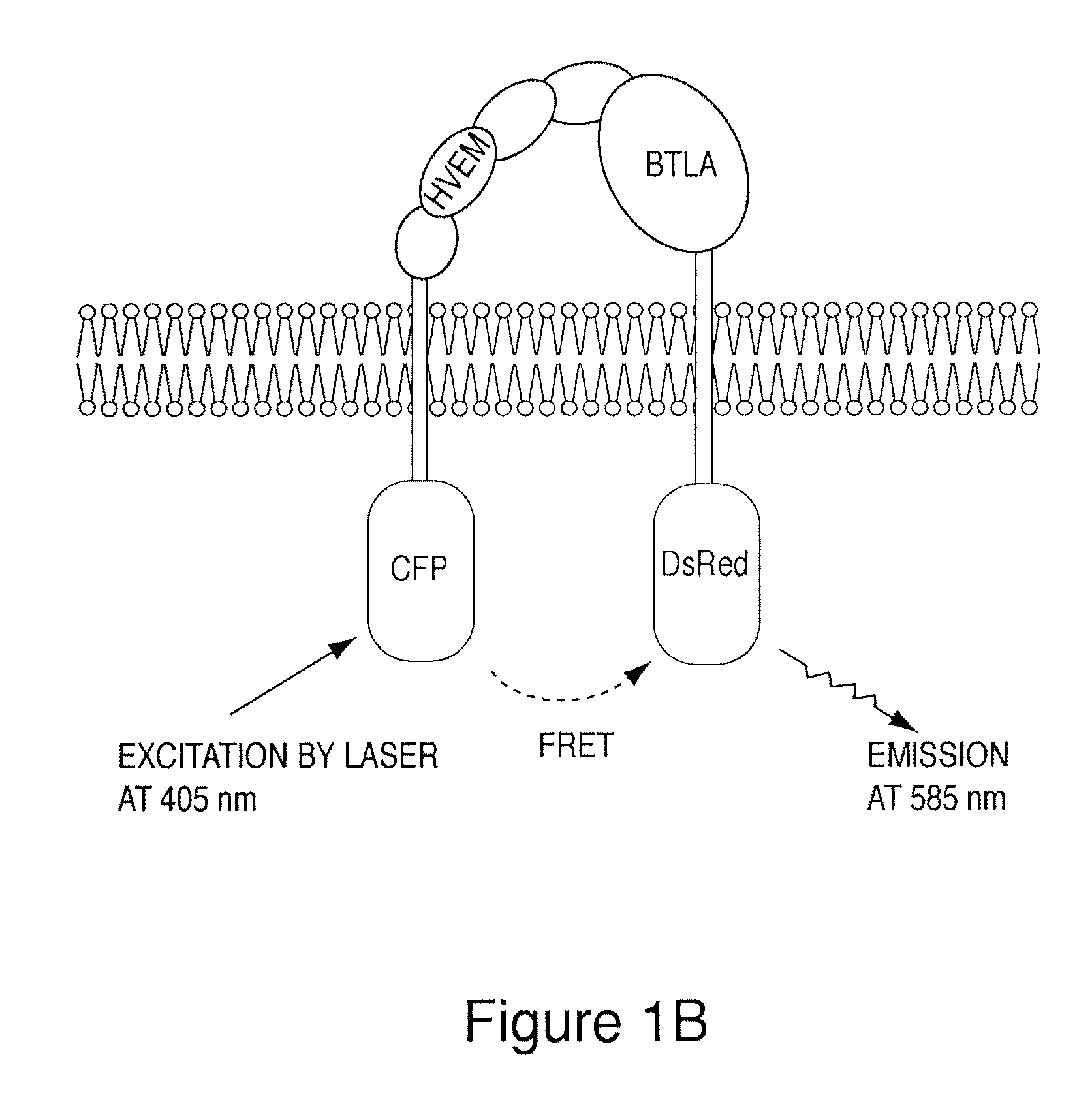
[0166]To measure HVEM and BTLA interactions in nat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Solubility (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Immunogenicity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Cytotoxicity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com