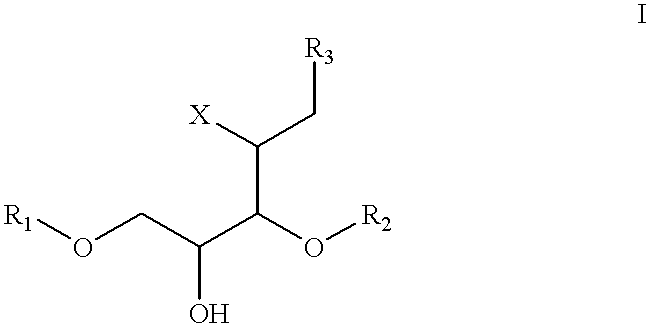
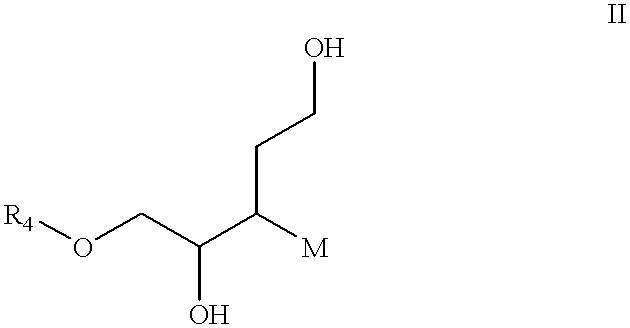
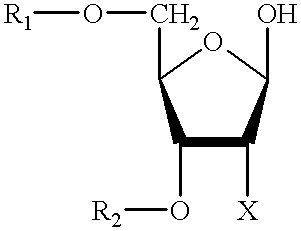
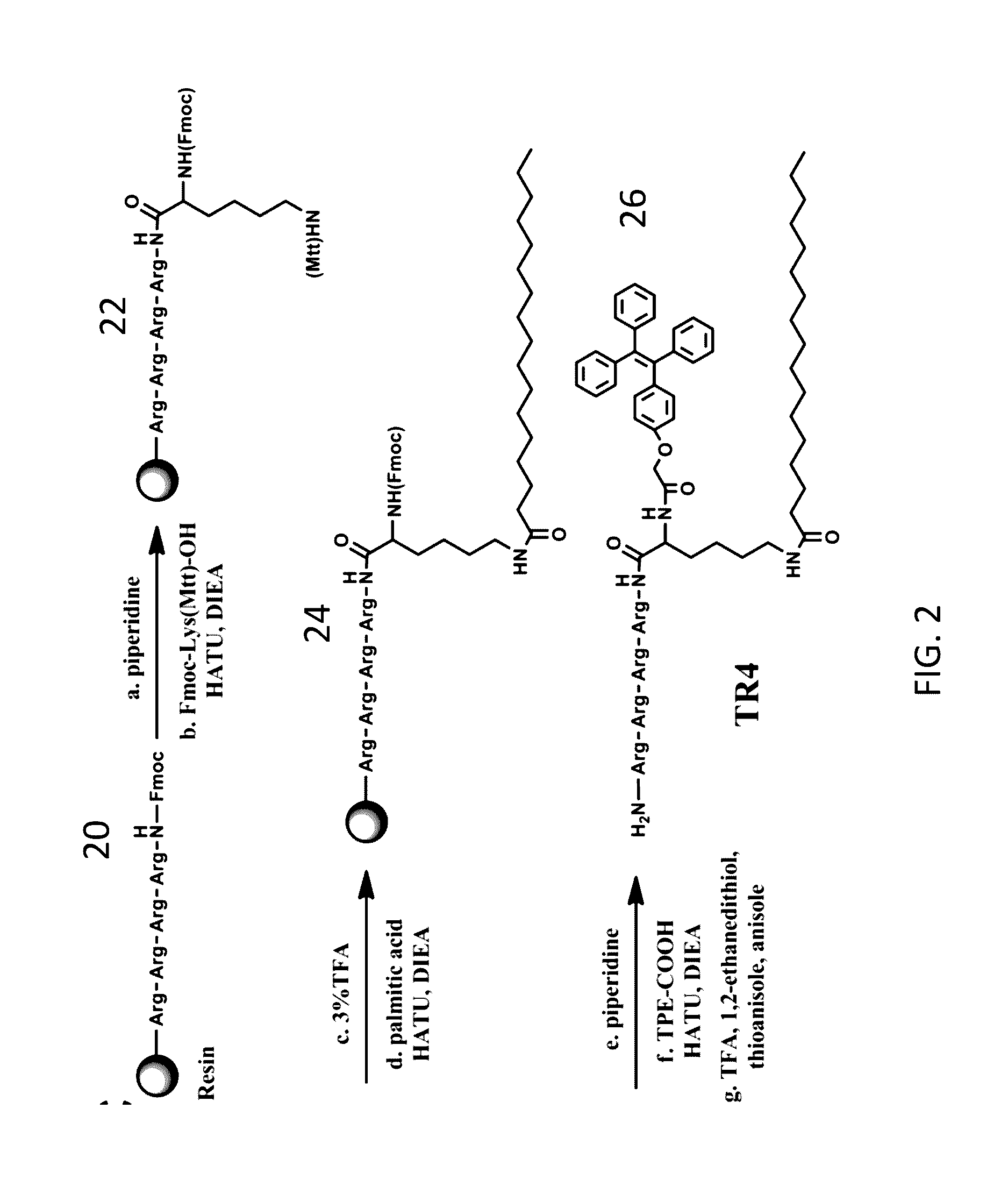
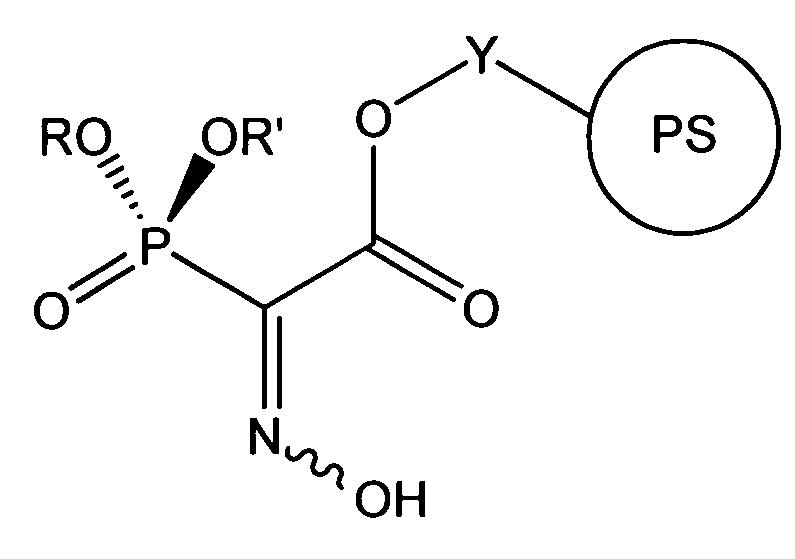
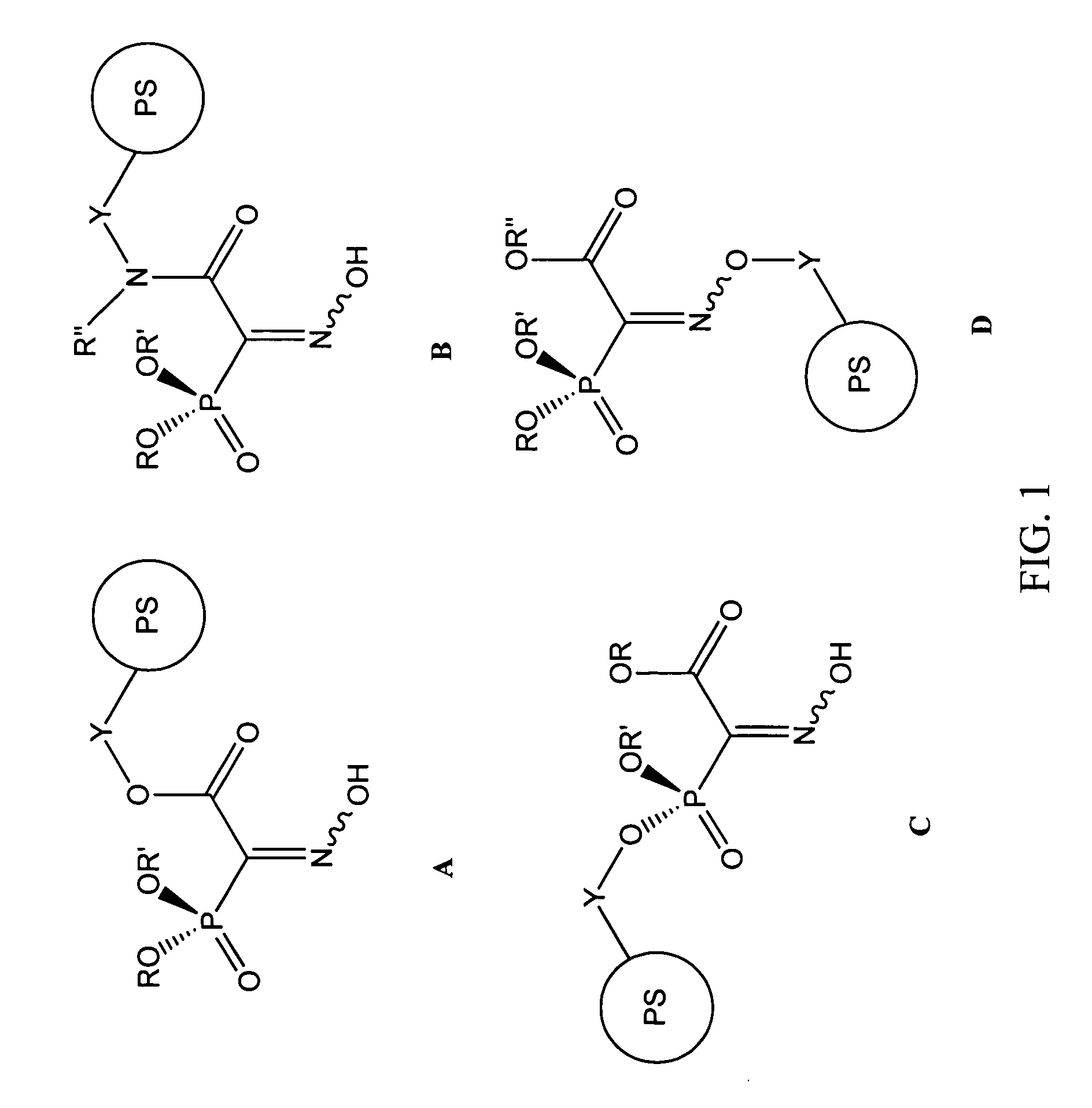
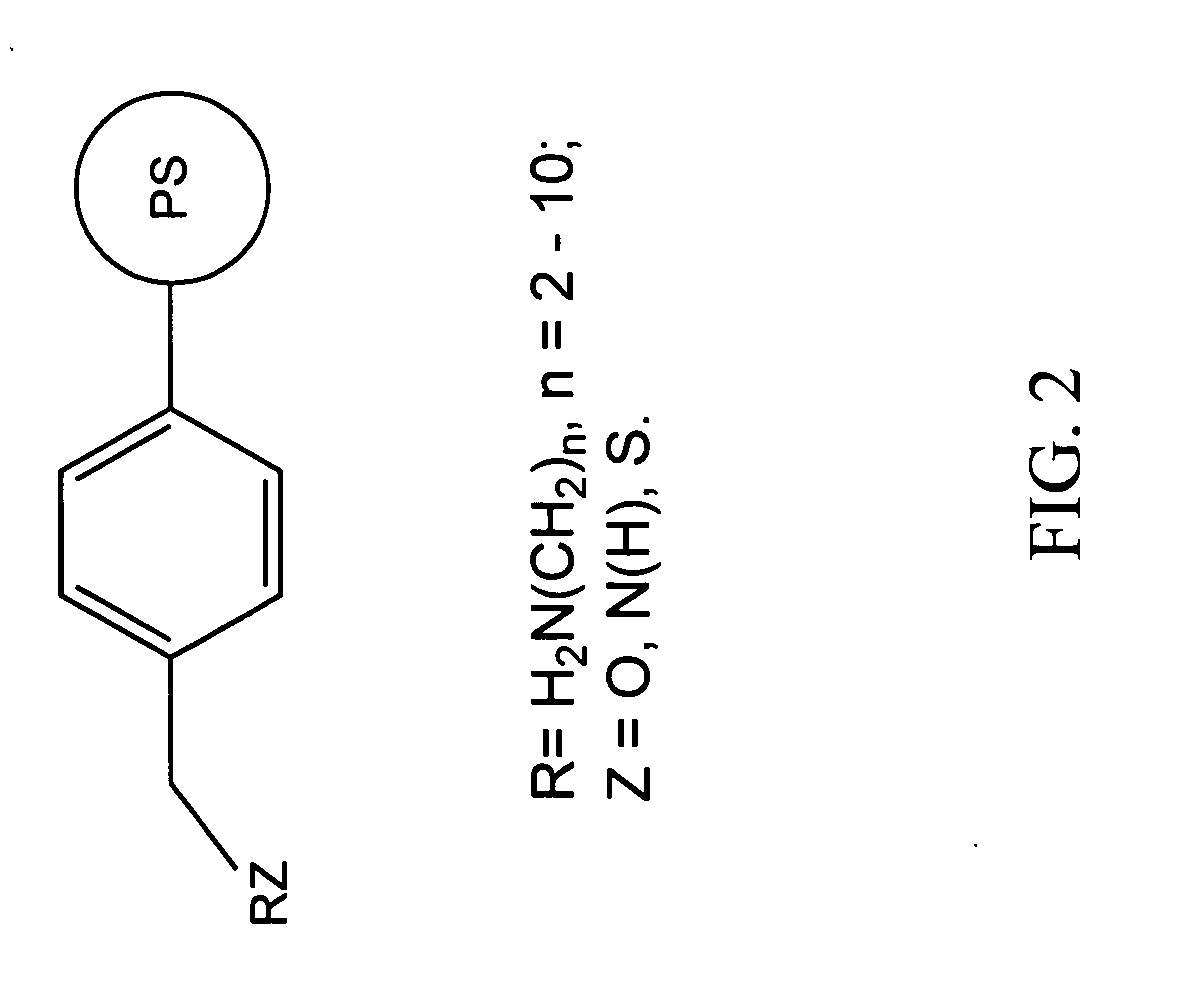
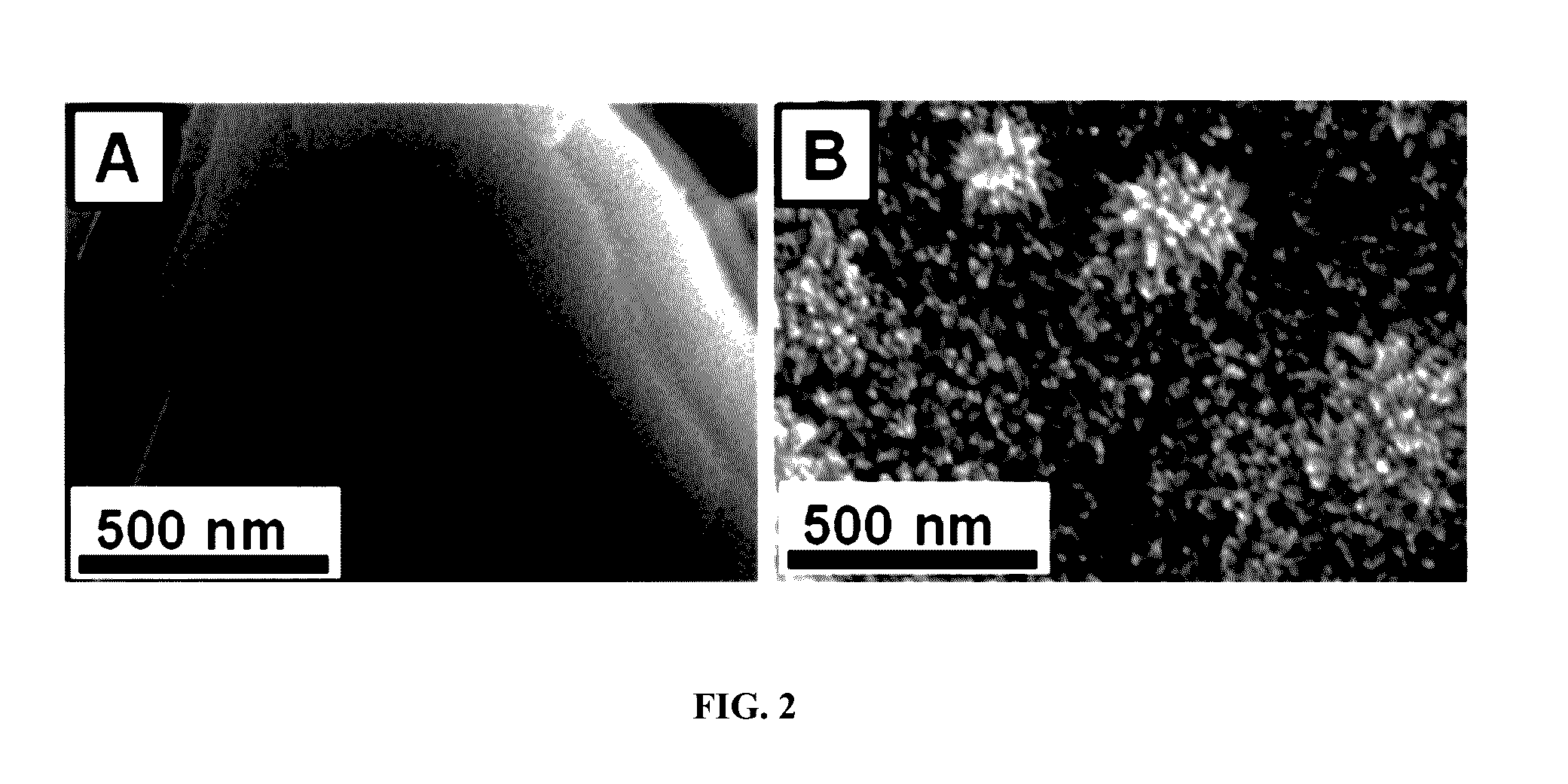
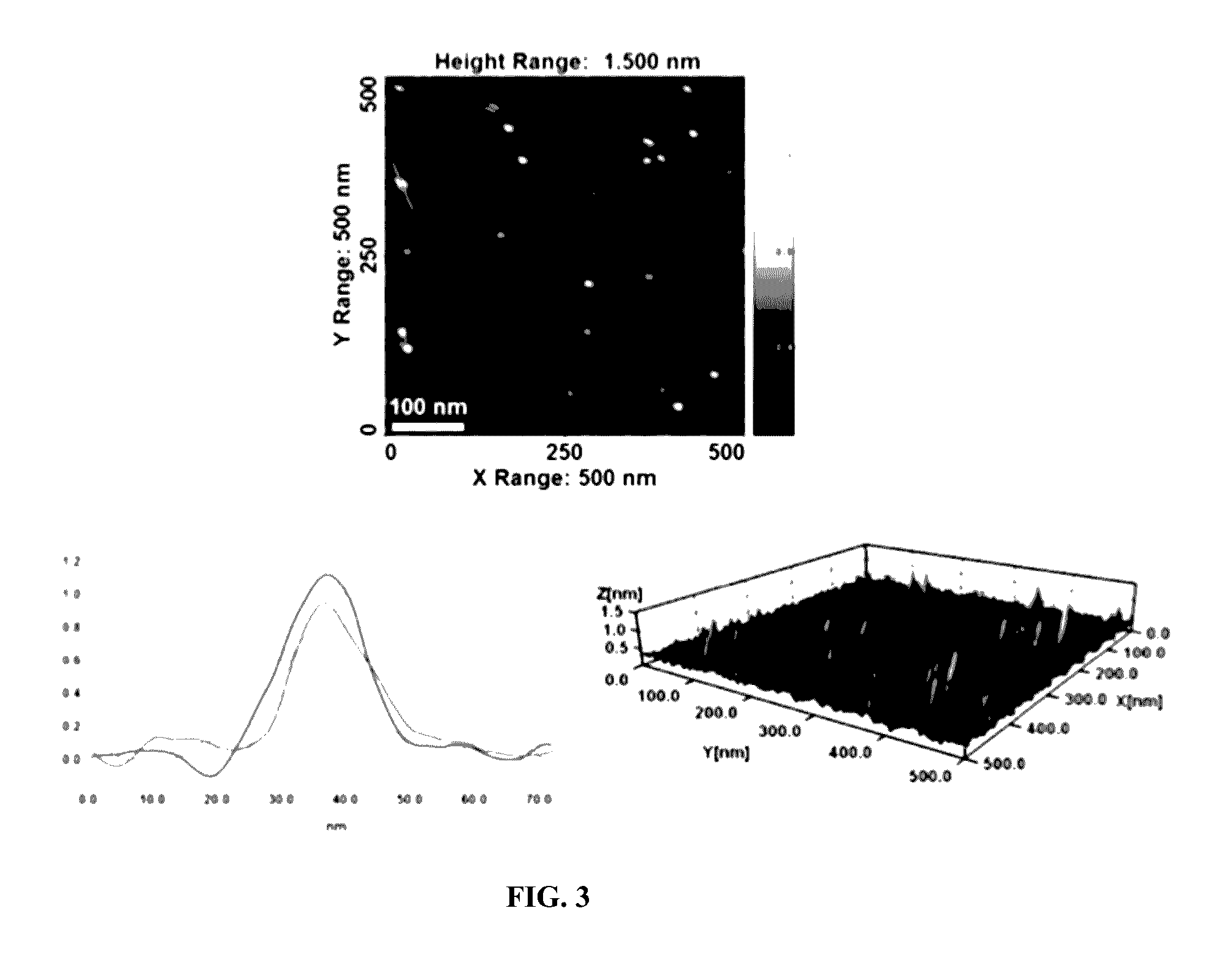
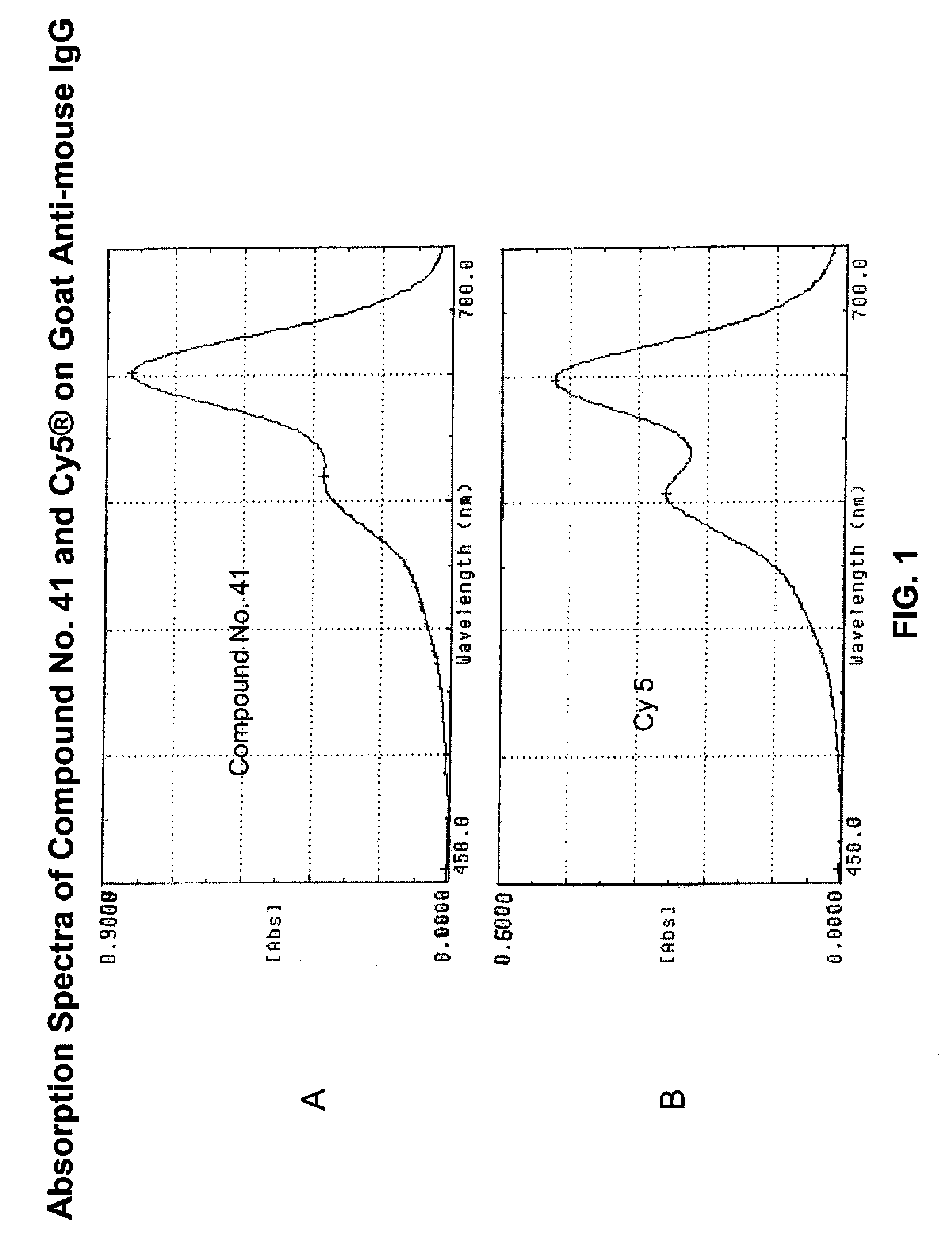
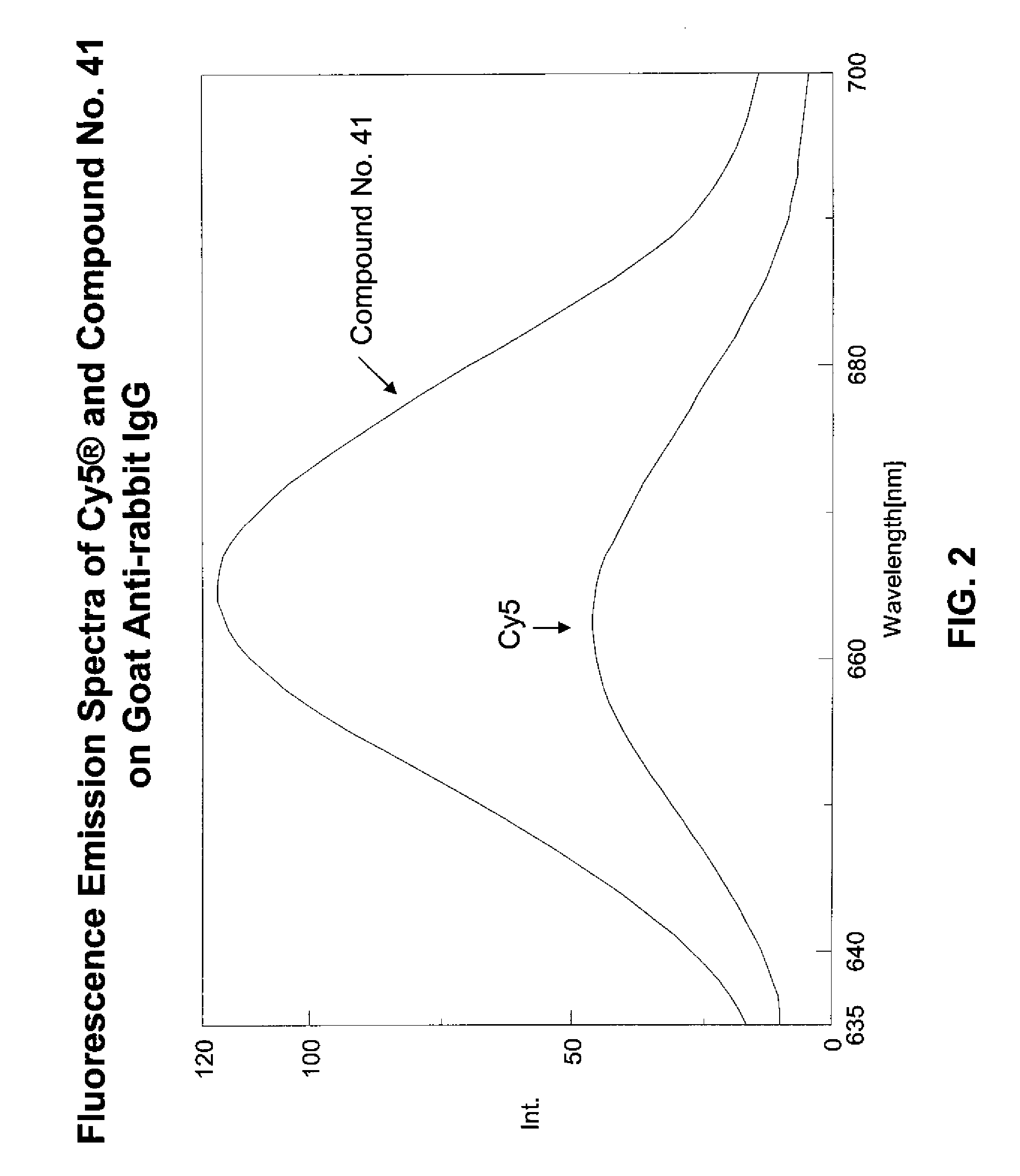
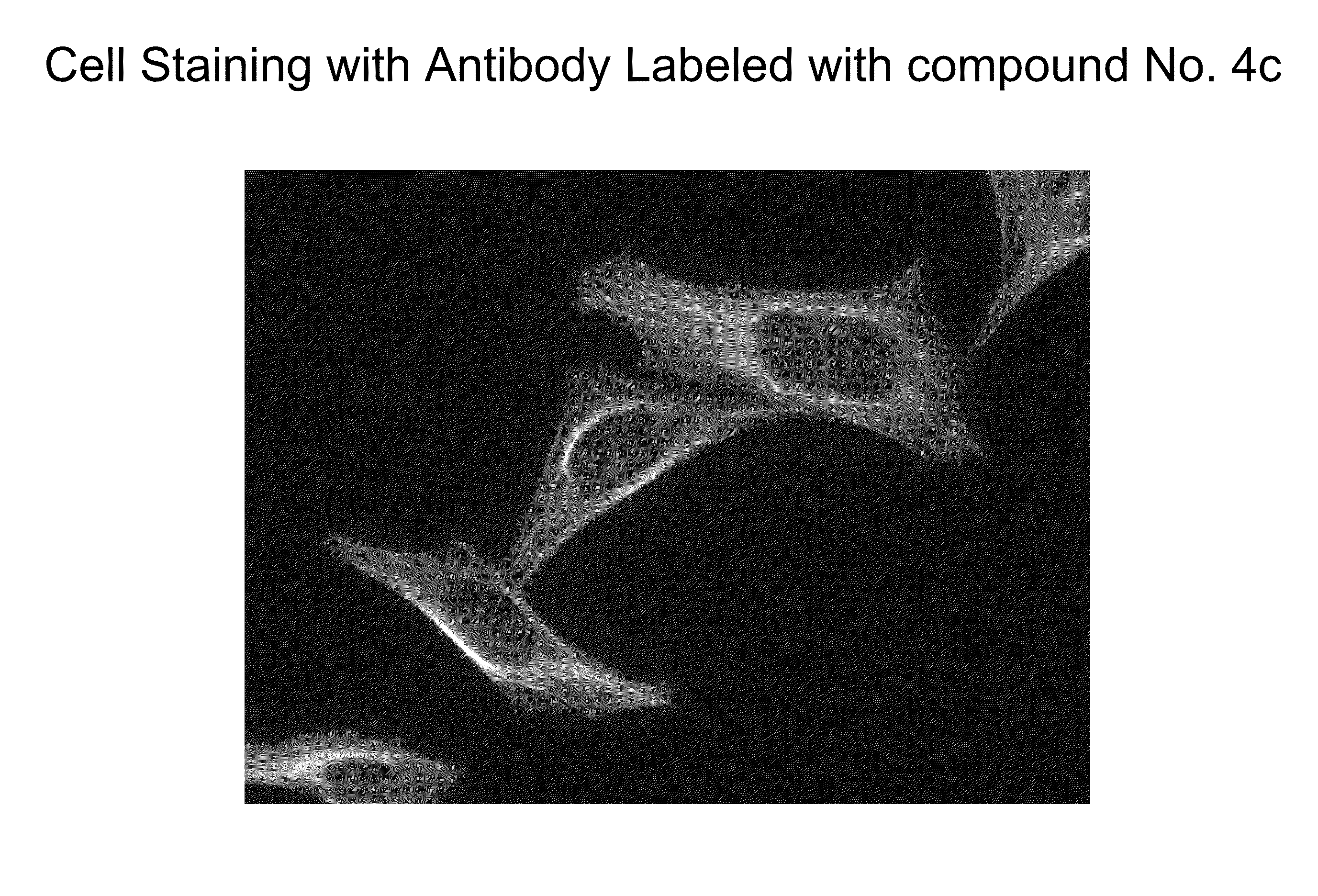
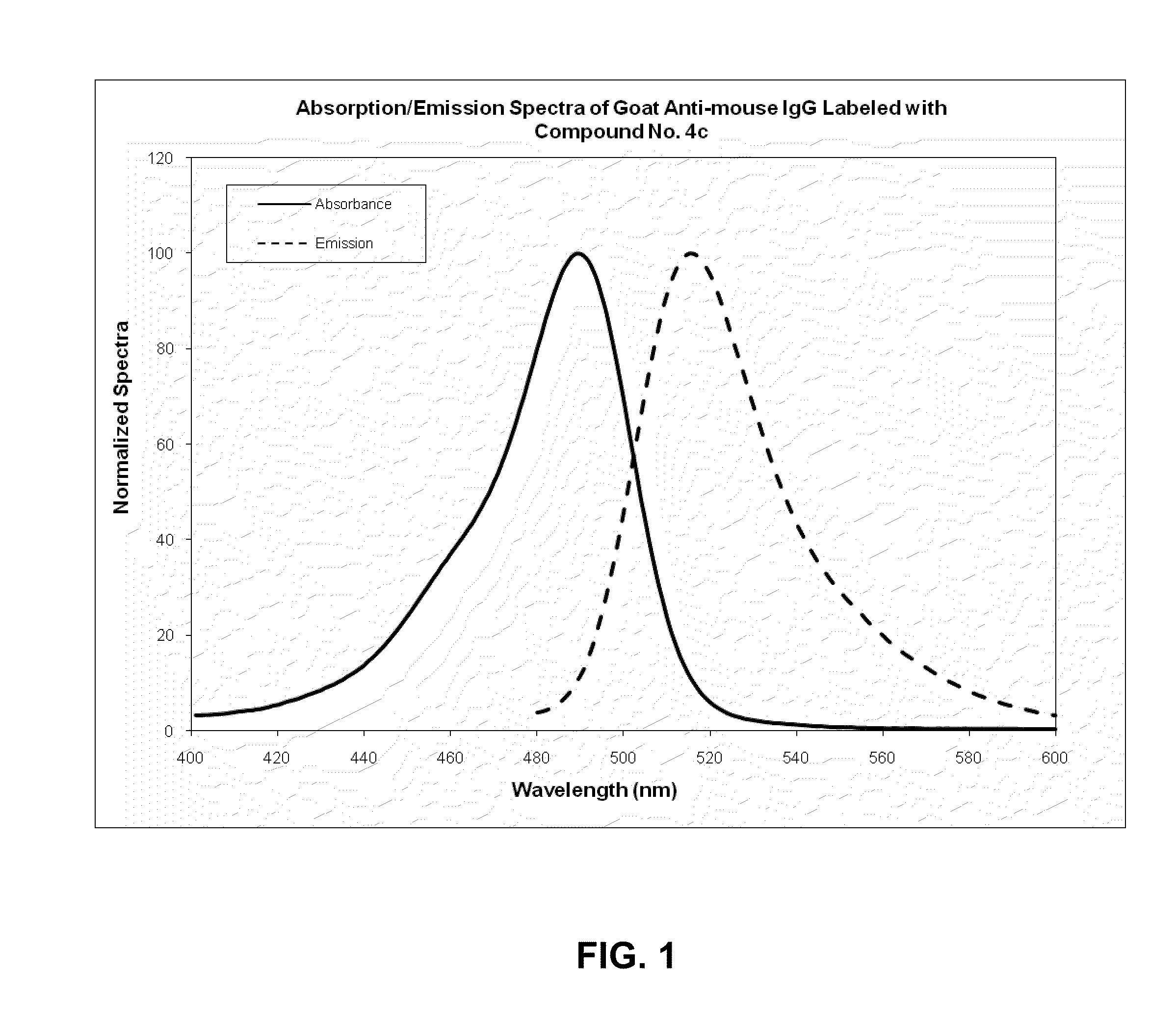
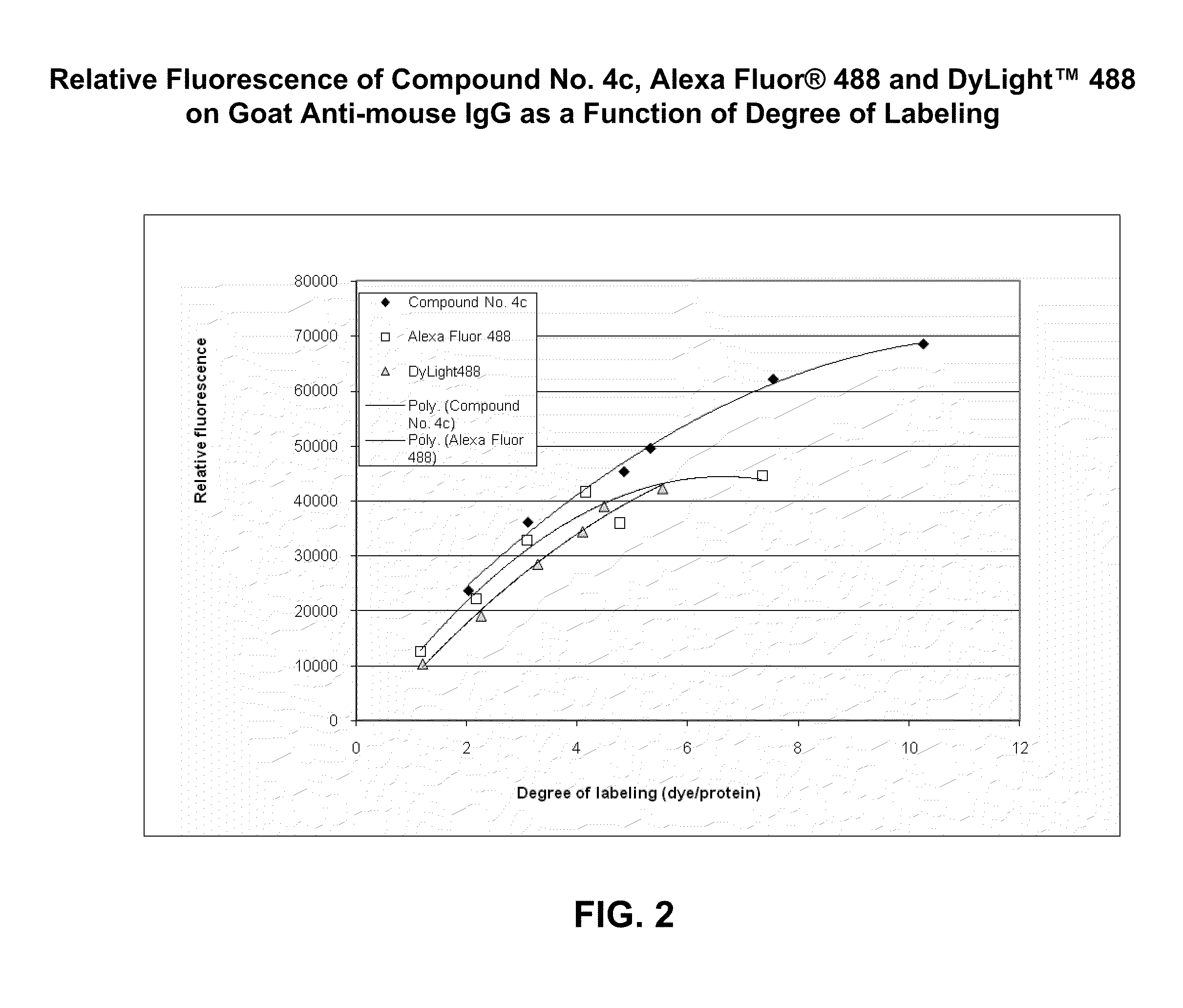
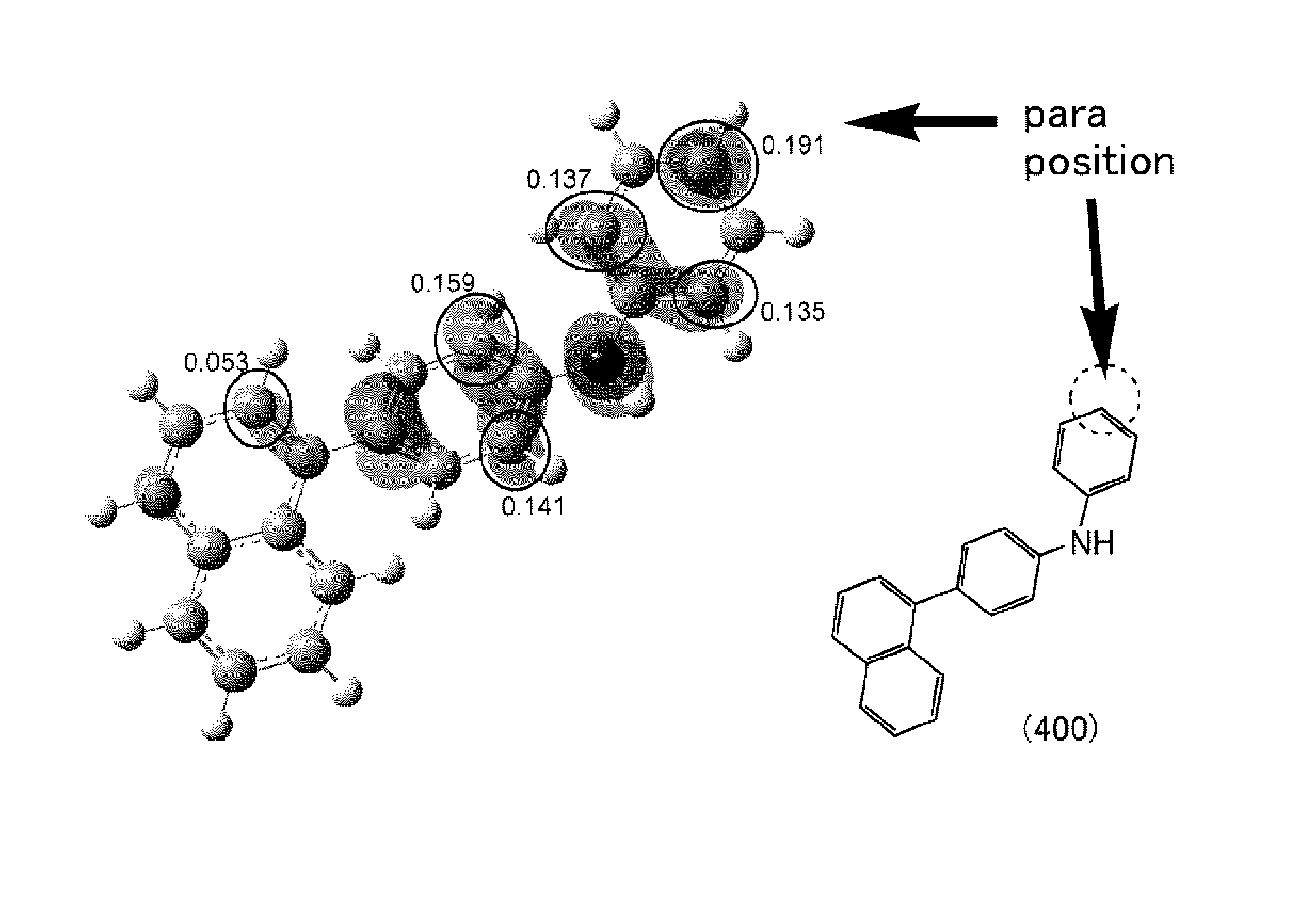
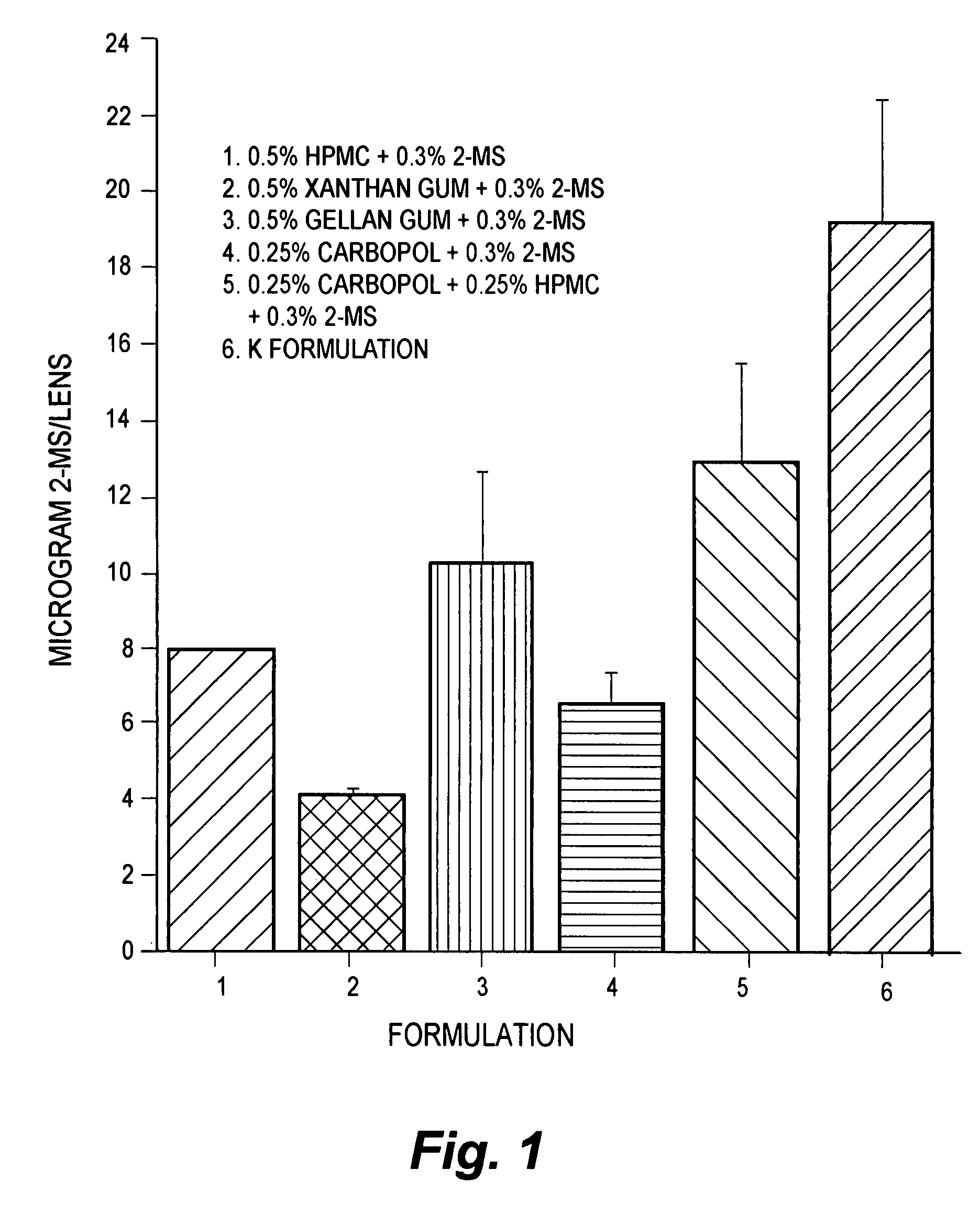
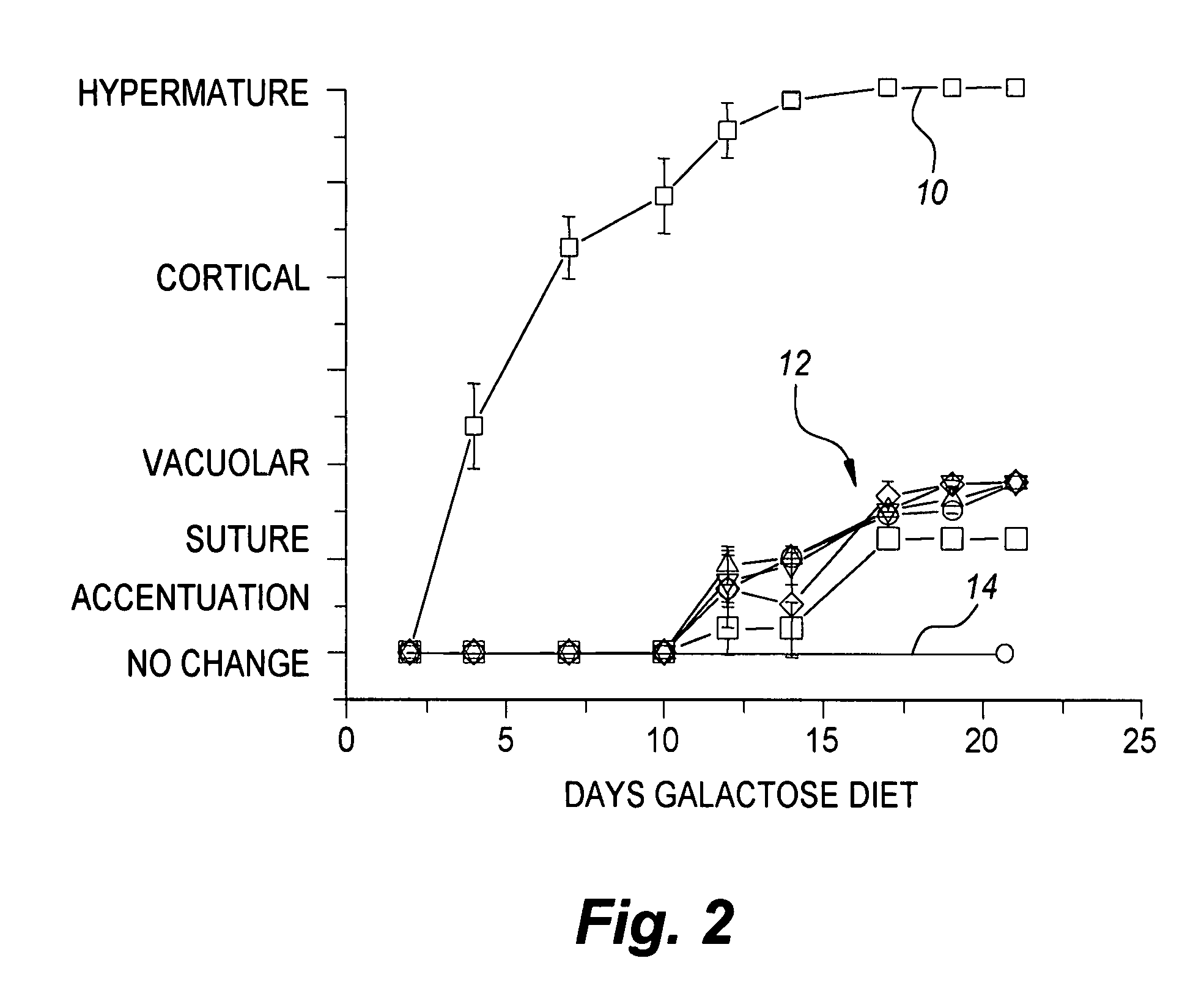
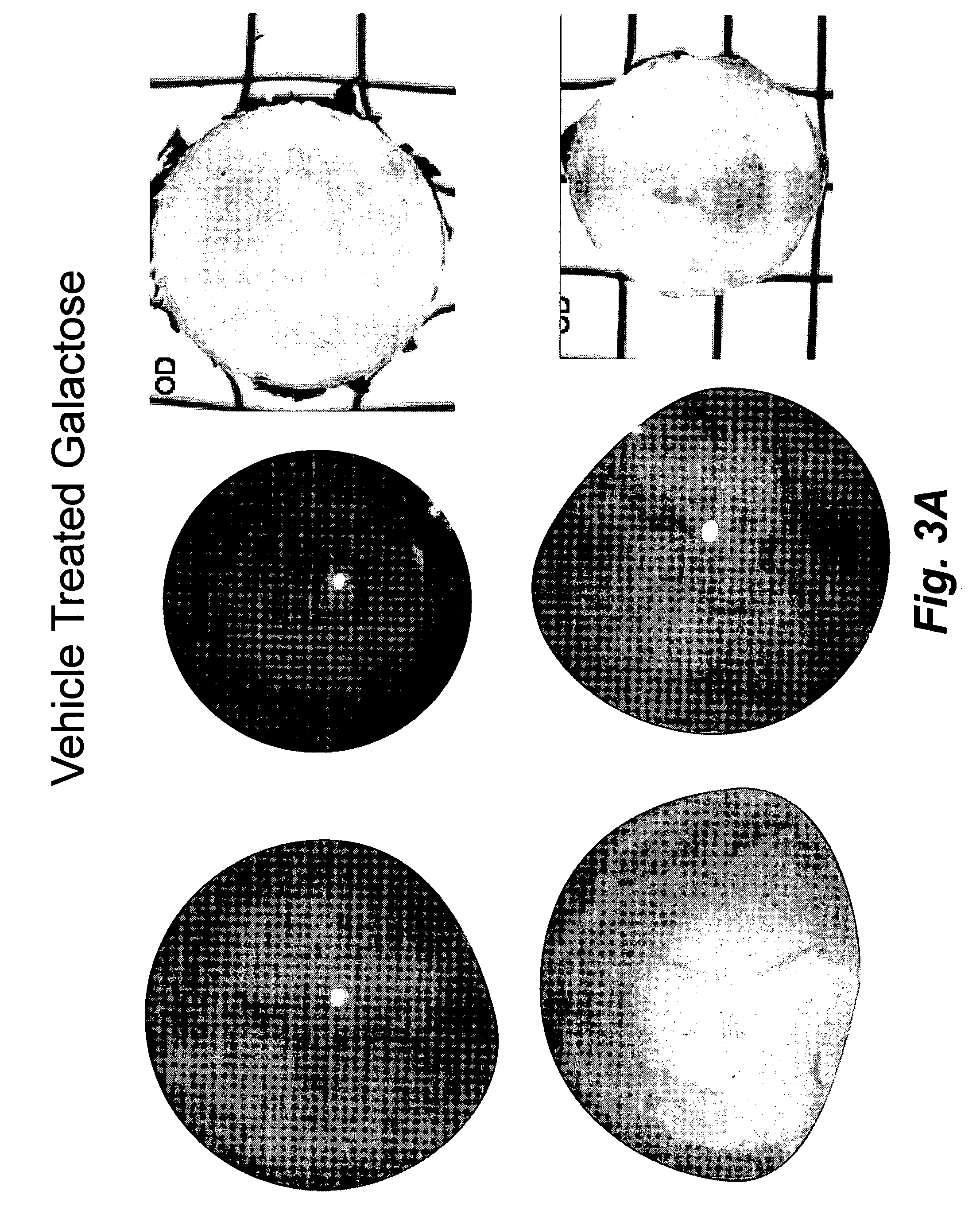
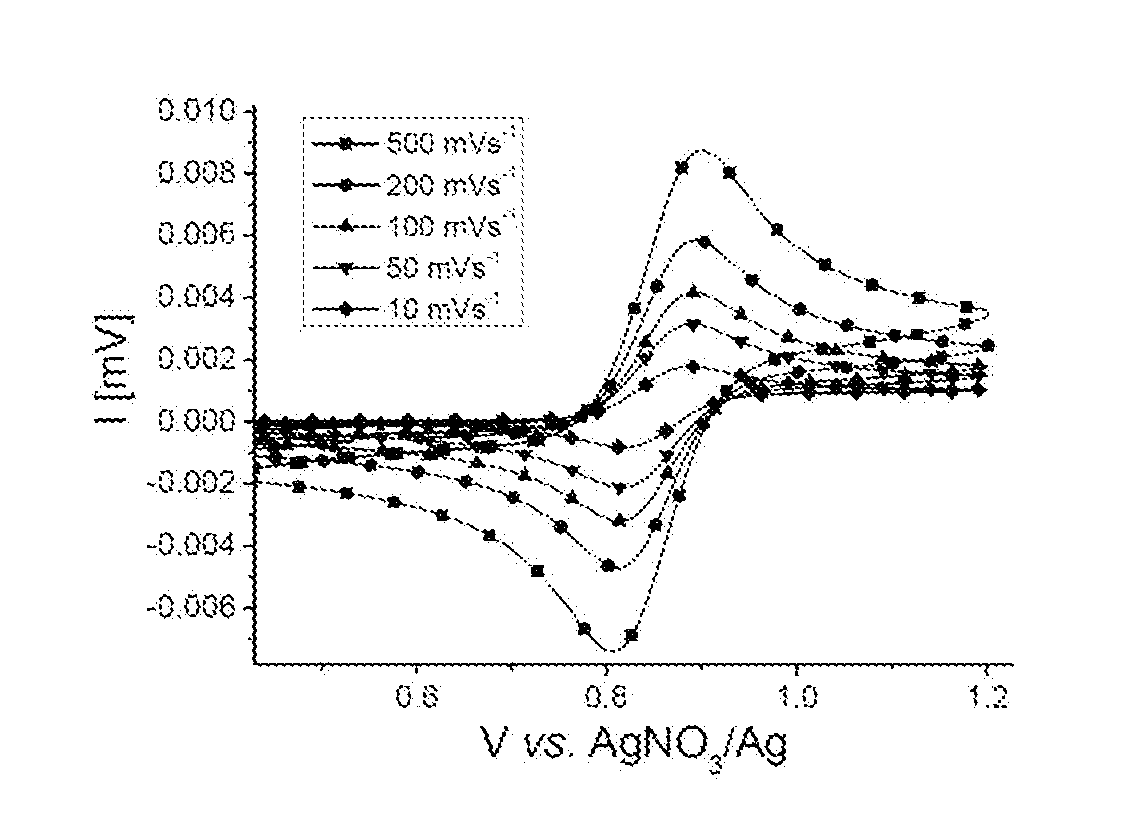
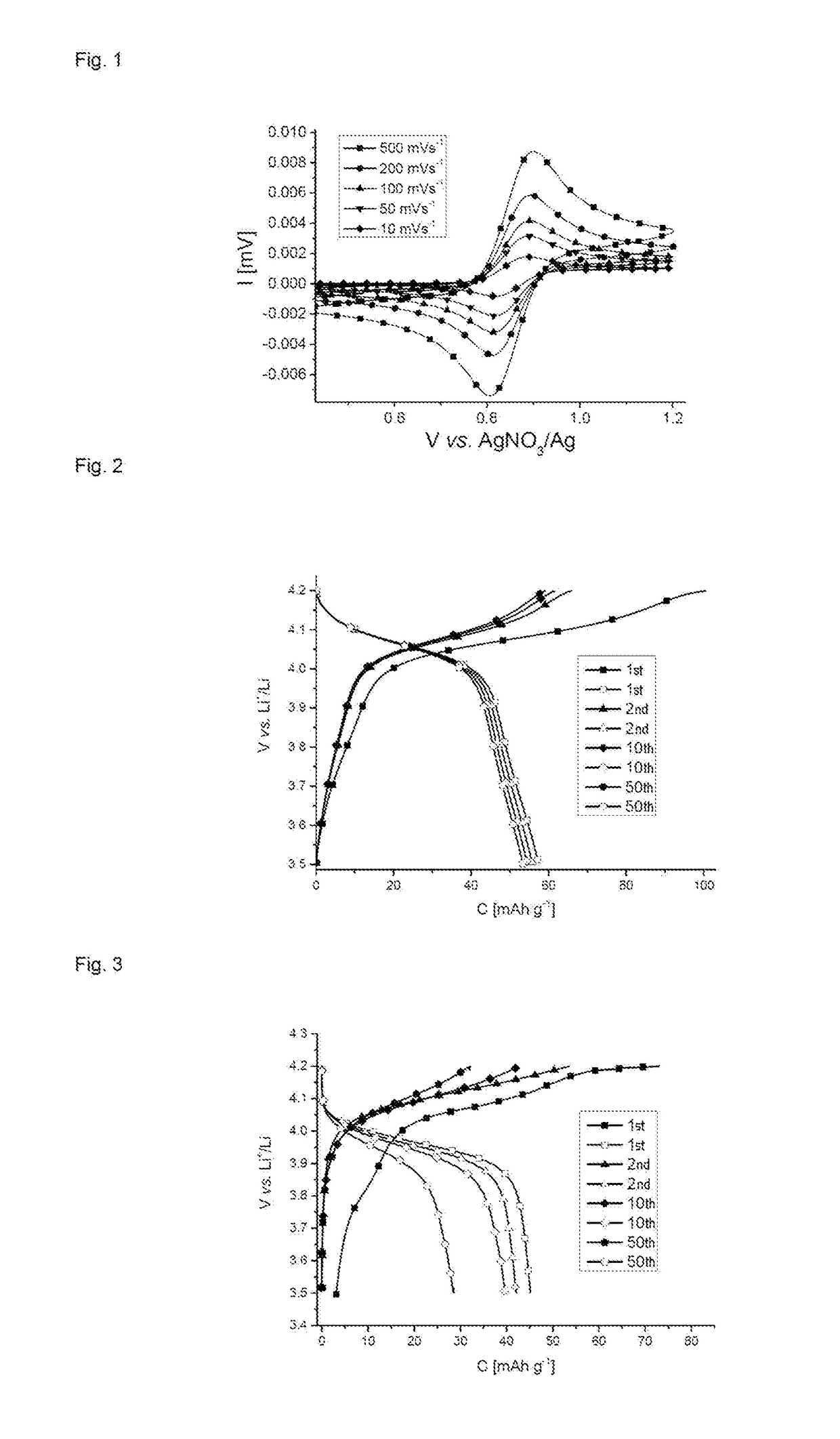
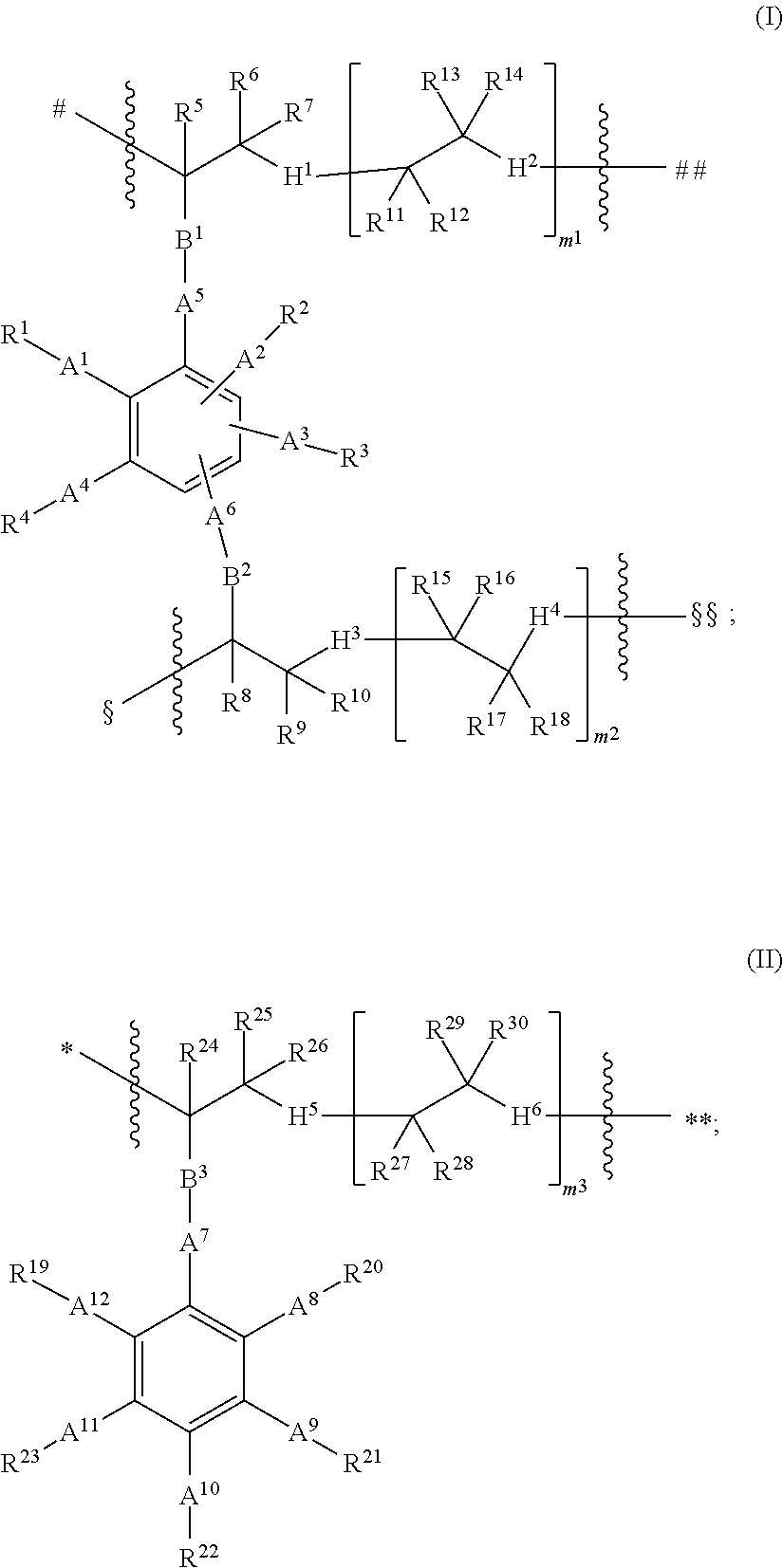
Patents
Literature
149results about How to "Synthetic is simple" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of synthesis and use
InactiveUS6235886B1Increase the number ofGood curative effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideOrganic chemistry
Oligonucleotide and nucleotide amine analogs and methods of preparing and using these compounds are provided by the present invention.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonists, compositions, and methods of treatment
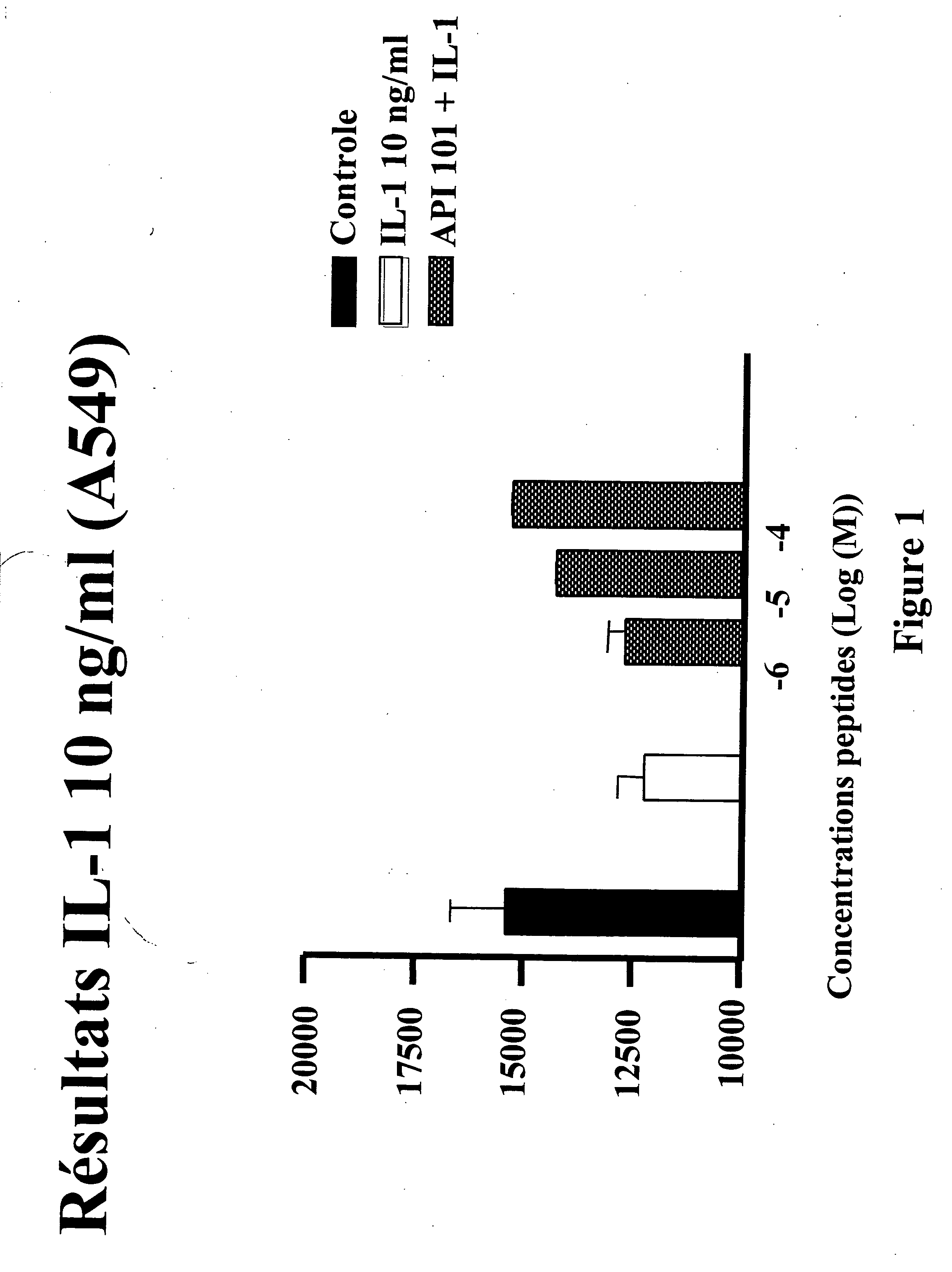
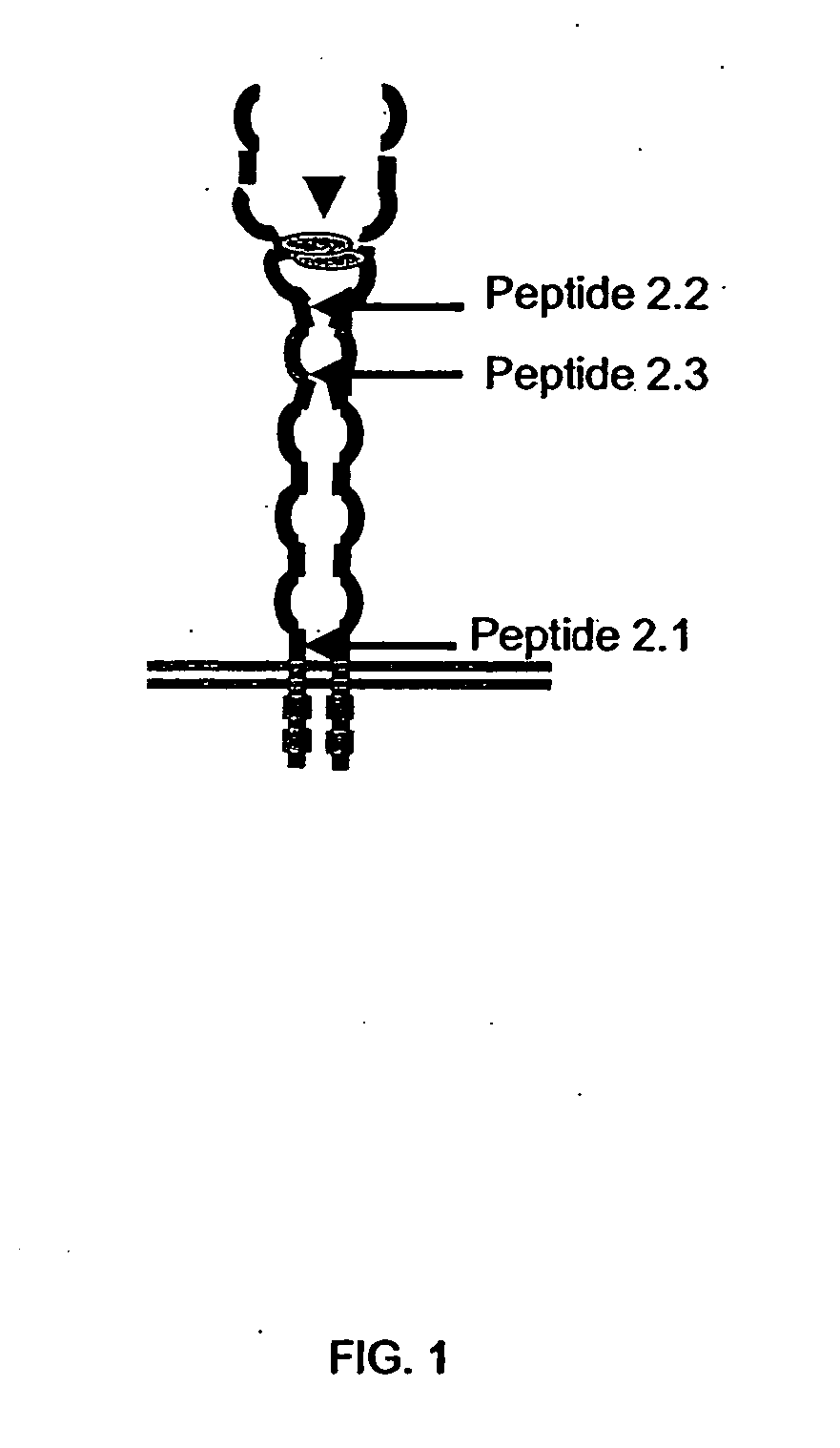
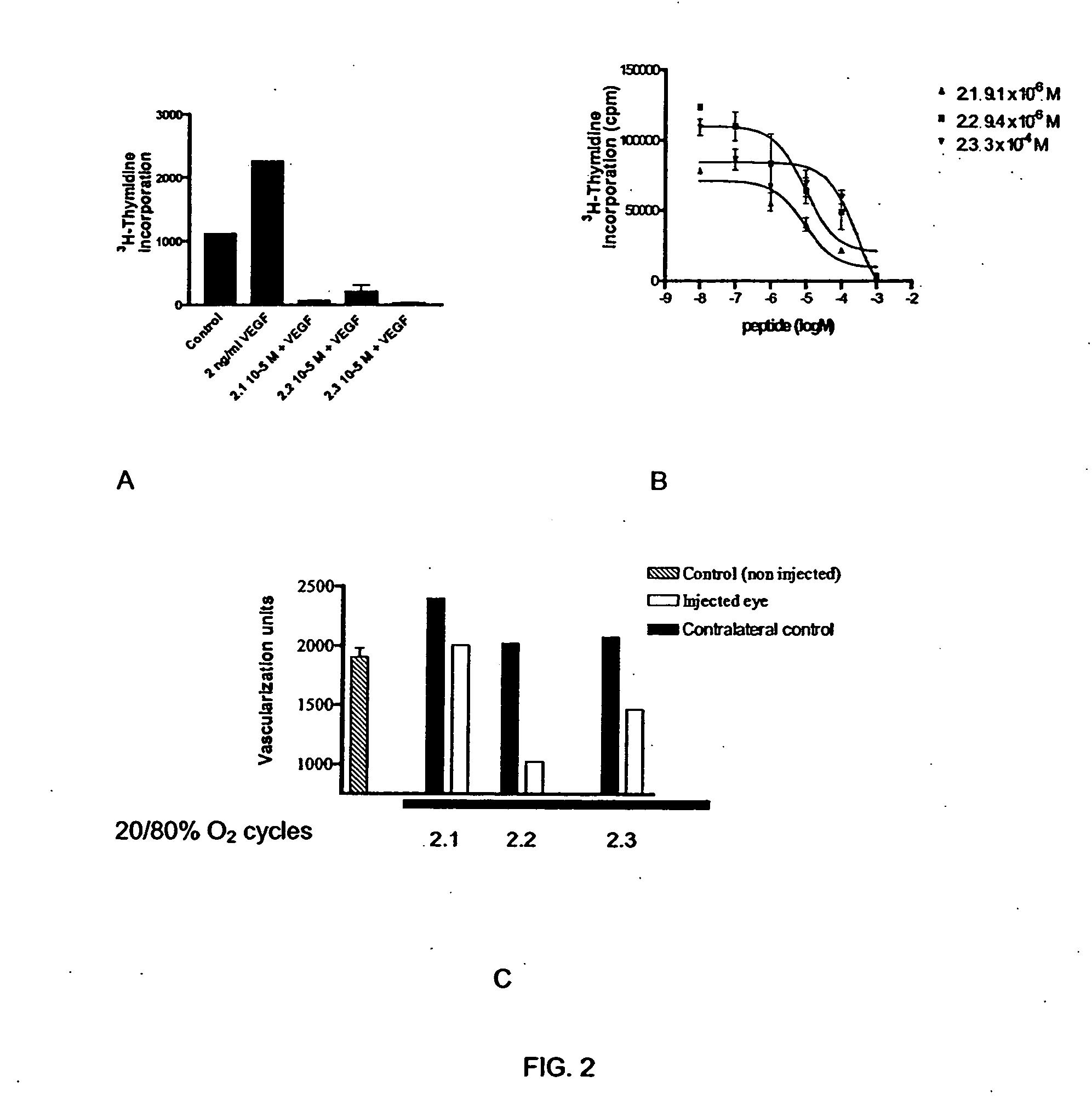
ActiveUS20060094663A1Synthetic is simpleInhibition of activationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsArthritisDrug biological activity
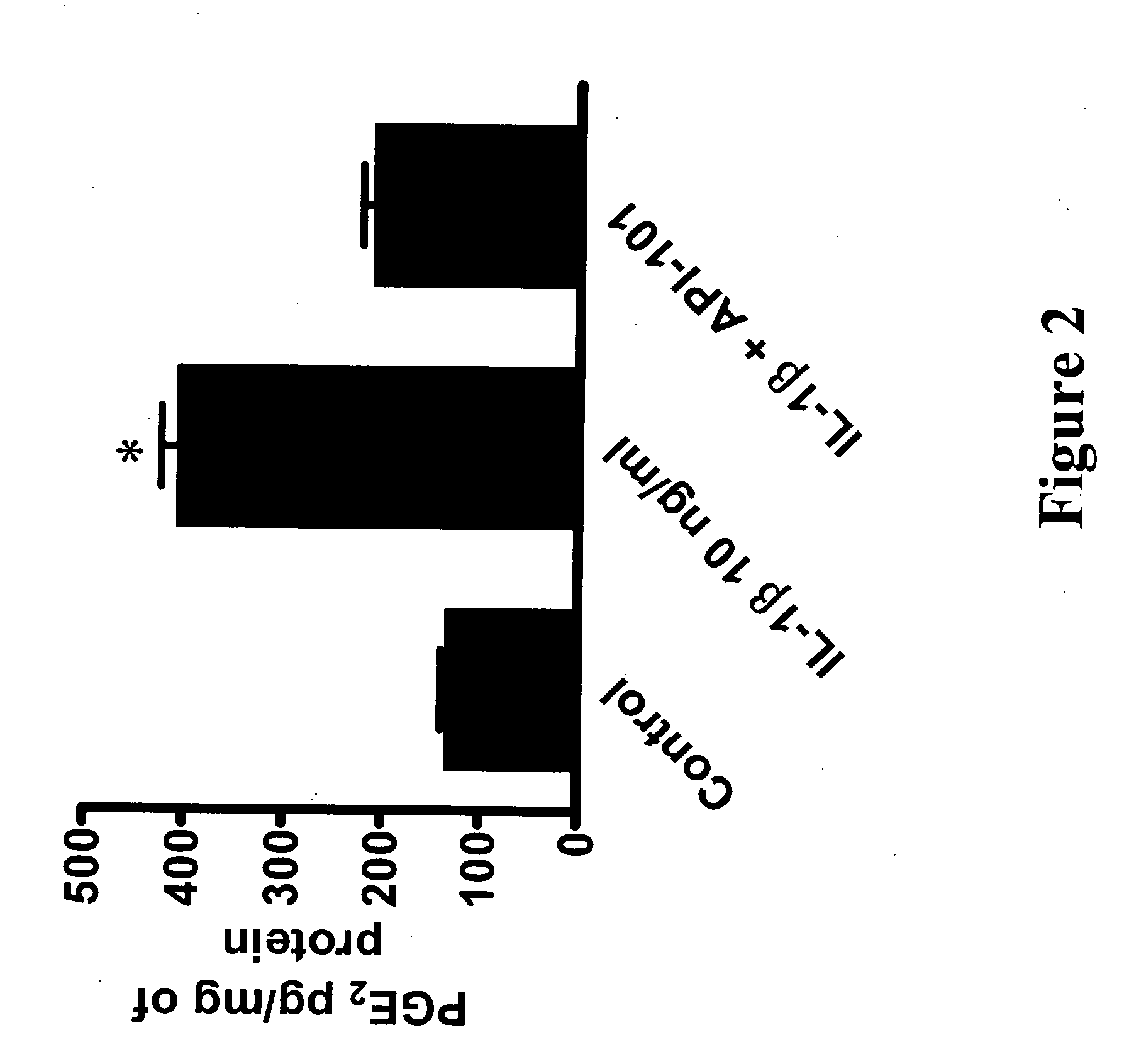
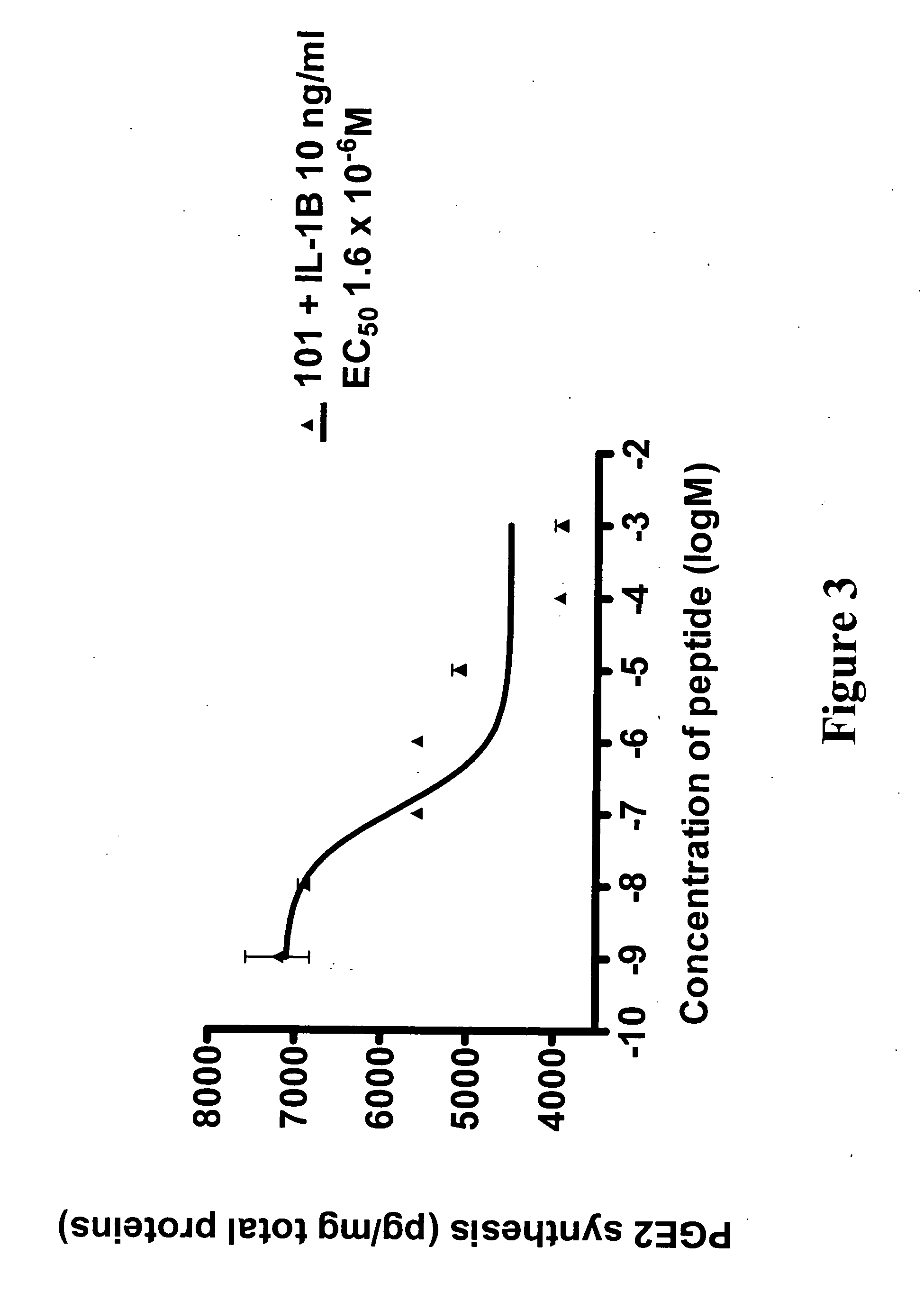
Peptides that are designed to inhibit the biological activity of the IL-1R type 1 receptor and inhibit IL-1R / IL-1RacP related cell signaling and biological activity are disclosed. Compositions comprising IL-1R antagonists of the present invention are useful in the treatment of IL-1 related diseases or conditions such as arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease as well as other chronic or acute inflammatory diseases. This invention also discloses an isolated compound having an IL-1R antagonist activity, said compound being selected from the group consisting of: a peptide comprising the amino acid sequence RYTPELX, wherein R, Y, T, P, E, L, refer to their corresponding amino acids, and X is selected from no amino acid and alanine (A); and a derivative of (a) wherein the derivative incorporates one, two or three amino acid modification selected from an amino acid addition, deletion or substitution in the RYTPEL portion of the peptide, and wherein said derivative maintains its antagonist IL-1R activity.
Owner:VALORISATION HSJ LLP
Benzenesulfonamide inhibitors of PDE-IV and their therapeutic use
InactiveUS6162830ASimple structureSynthetic is simpleBiocideNervous disorderDiseasePhosphodiesterase
PCT No. PCT / US98 / 23482 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 7, 2000 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 7, 2000 PCT Filed Nov. 4, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO99 / 26616 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 3, 1999The present invention provides compounds and pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of using same in the treatment of diseases whose treatment benefits from the inhibition of phosphodiesterase (PDE-IV) or Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) including asthma, allergic diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, septic shock. The compounds provided by this invention have formula (I) wherein R1, R2, R3, R4 are as defined herein.
Owner:WARNER-LAMBERT CO
Method for catalytic polymerization of alpha-olefin monomers using an ultra-high activity non-metallocene pre-catalyst
InactiveUS6596827B2High molecular weightLow molecularGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
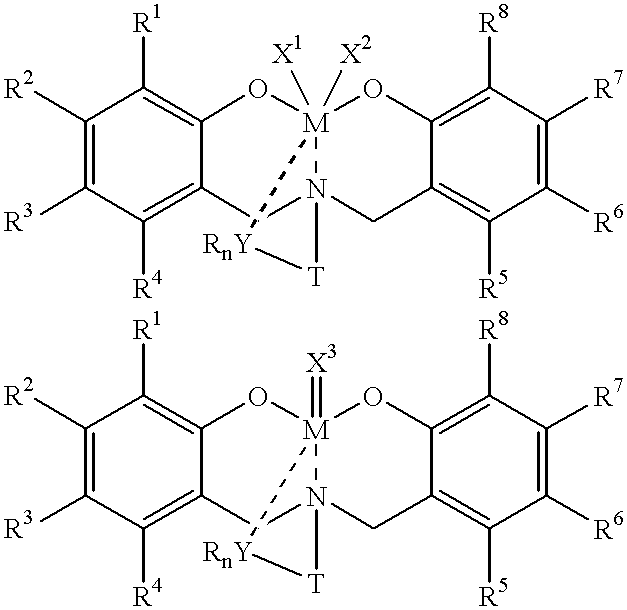
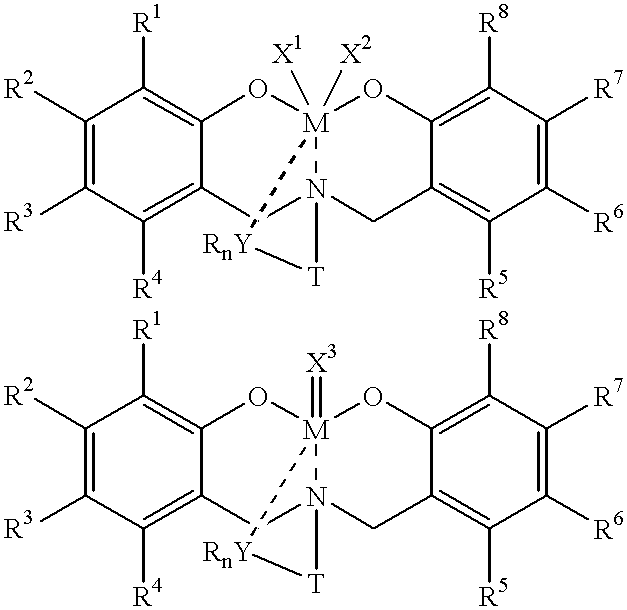
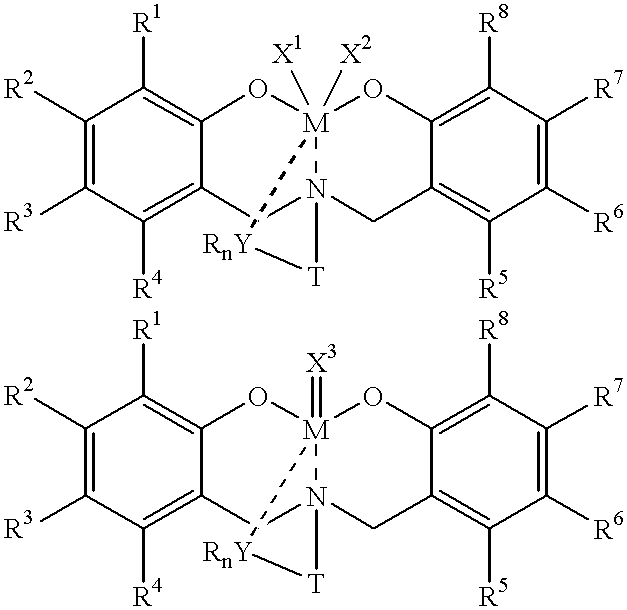
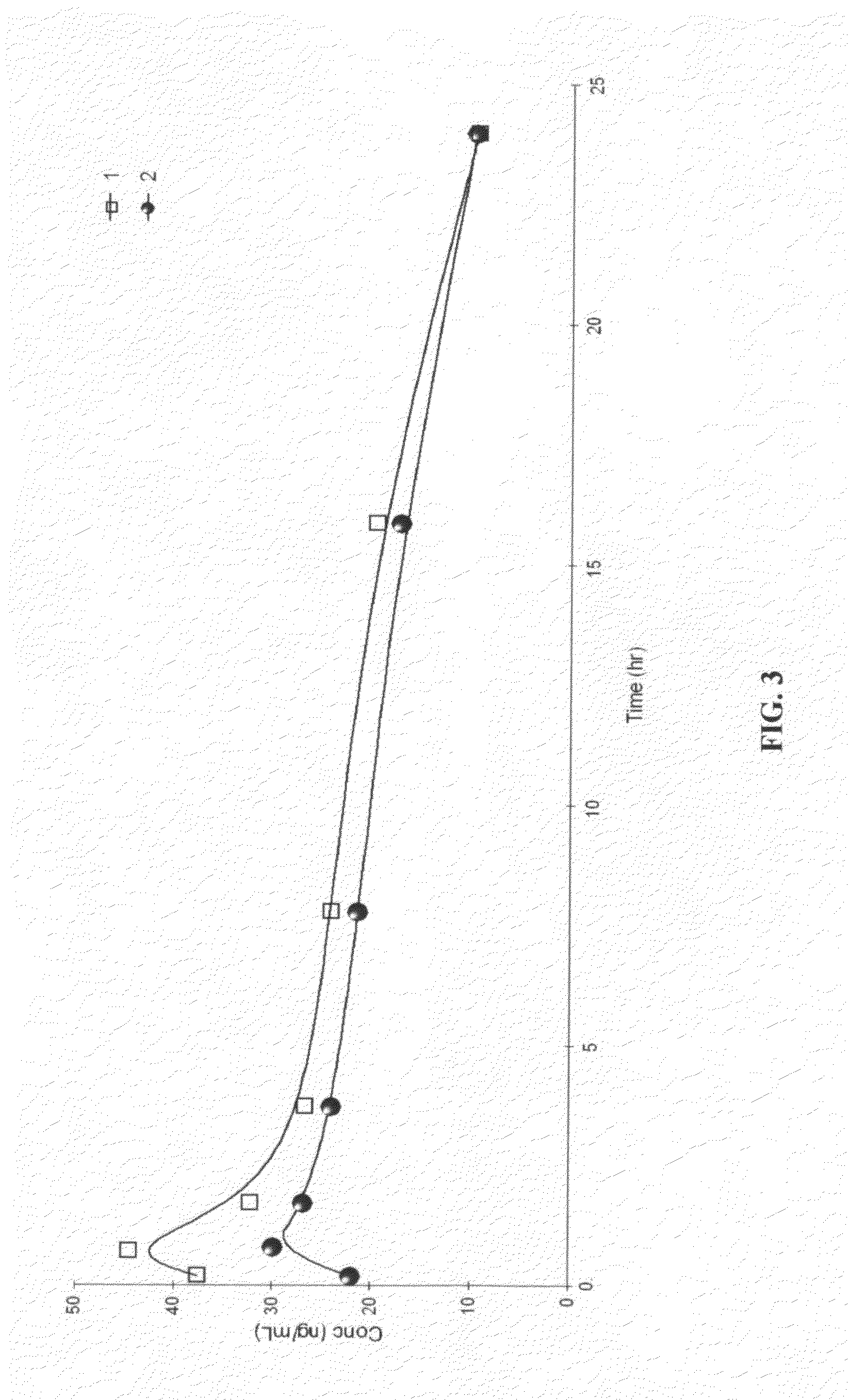
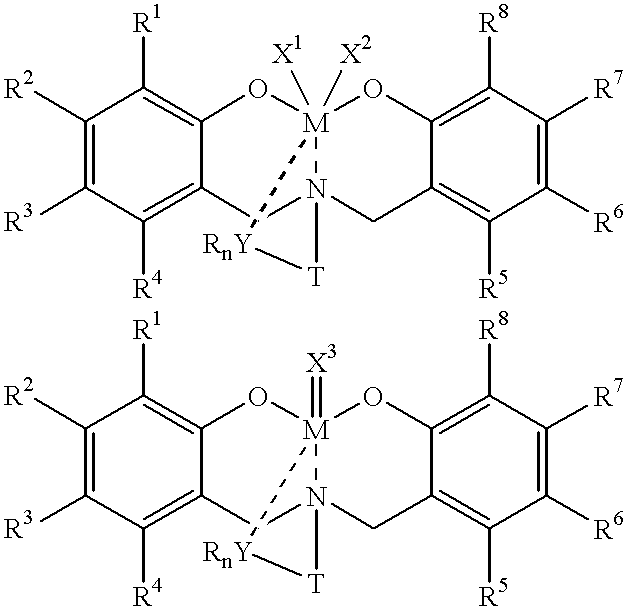
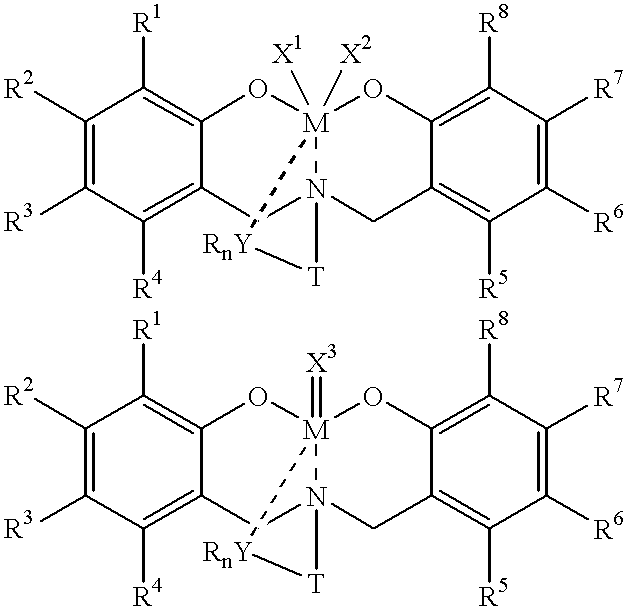
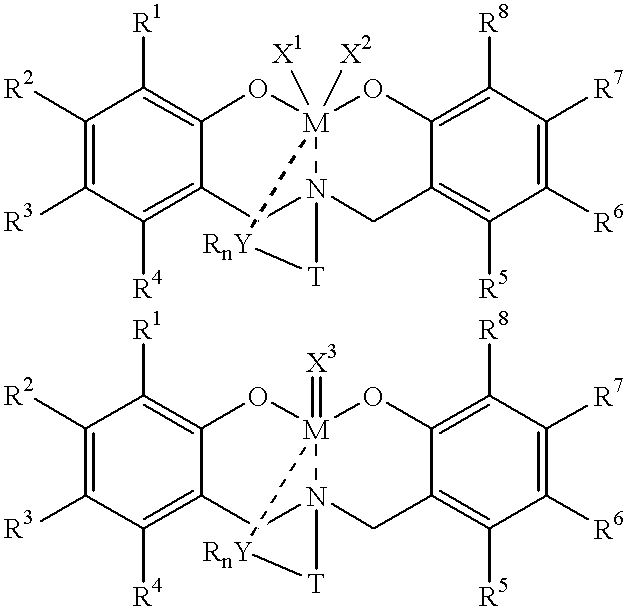
Disclosed are olefin polymerization methods comprising the use of the following compounds:wherein M is a metal atom, R1-R8 are univalent radicals, X1 and X2 are univalent ligands, X3 is a divalent ligand, and (RnY-T) is an optional donor or non-donor group. The relatively stable and simply synthesized pre-catalyst is activated by a co-catalyst under mild reaction conditions, producing exceptionally reactive polymerization of a wide variety of alpha-olefin monomers, and forming a variety of poly(alpha-olefin) products, having high molecular weight and low molecular weight distribution (PDIs close to 1). Living polymerization is performed at or above room temperature, along with achieving block co-polymerization of alpha-olefin monomers at room temperature, and producing polymers and oligomers having a wide range of molecular weights. The catalyst formed during reaction remains "alive' for as long as 31 hours, for producing a polymer with a molecular weight as high as 450,000 grams / mole.
Owner:RAMOT UNIV AUTHORITY FOR APPLIED RES & INDAL DEVMENT
Platinum based nano-size catalysts
InactiveUS7566681B2Synthetic is simpleInvolvement between the nano-particle and the stabilizer, can be minimizedMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst activation/preparationNano catalystCarbon black
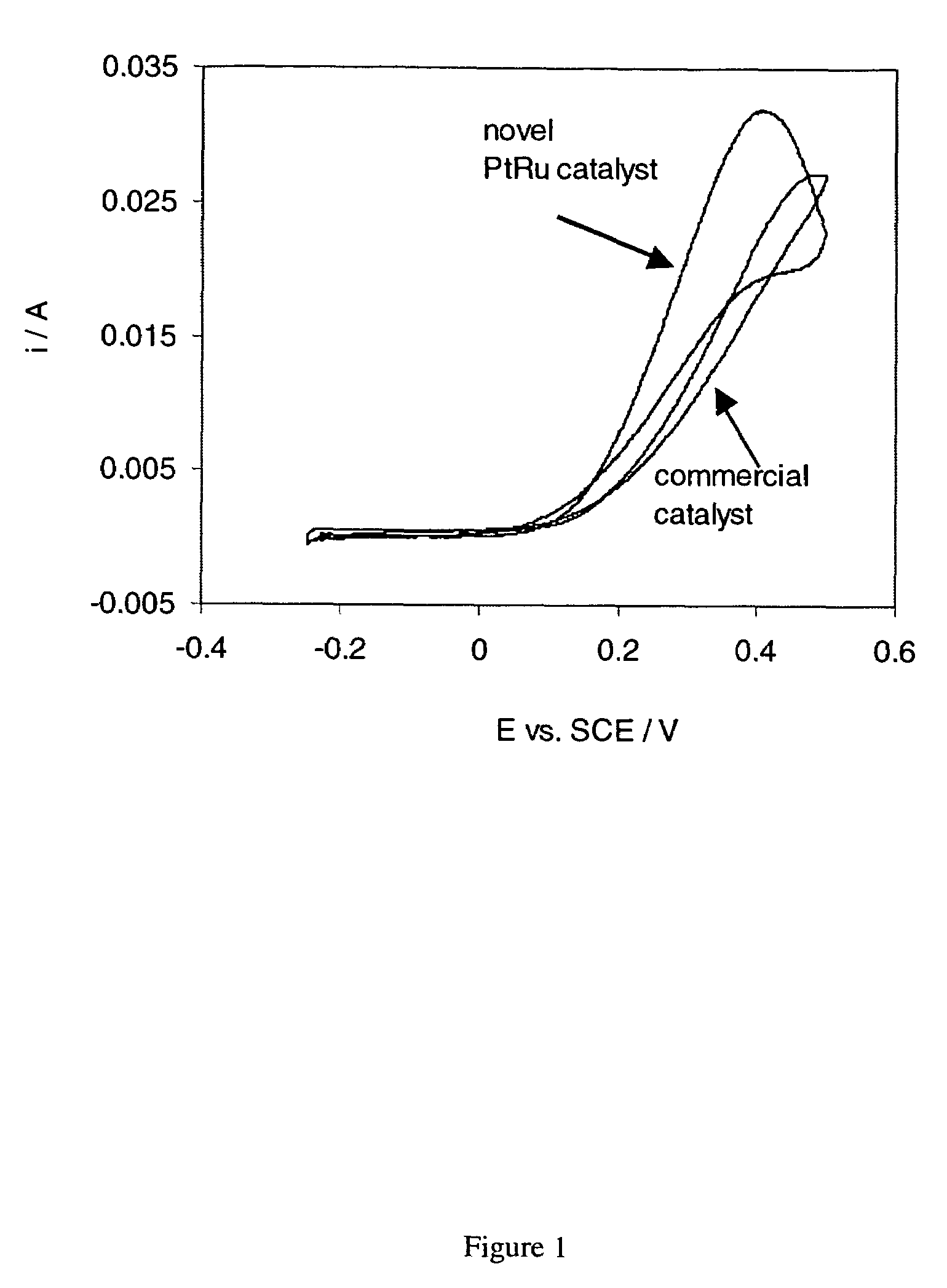
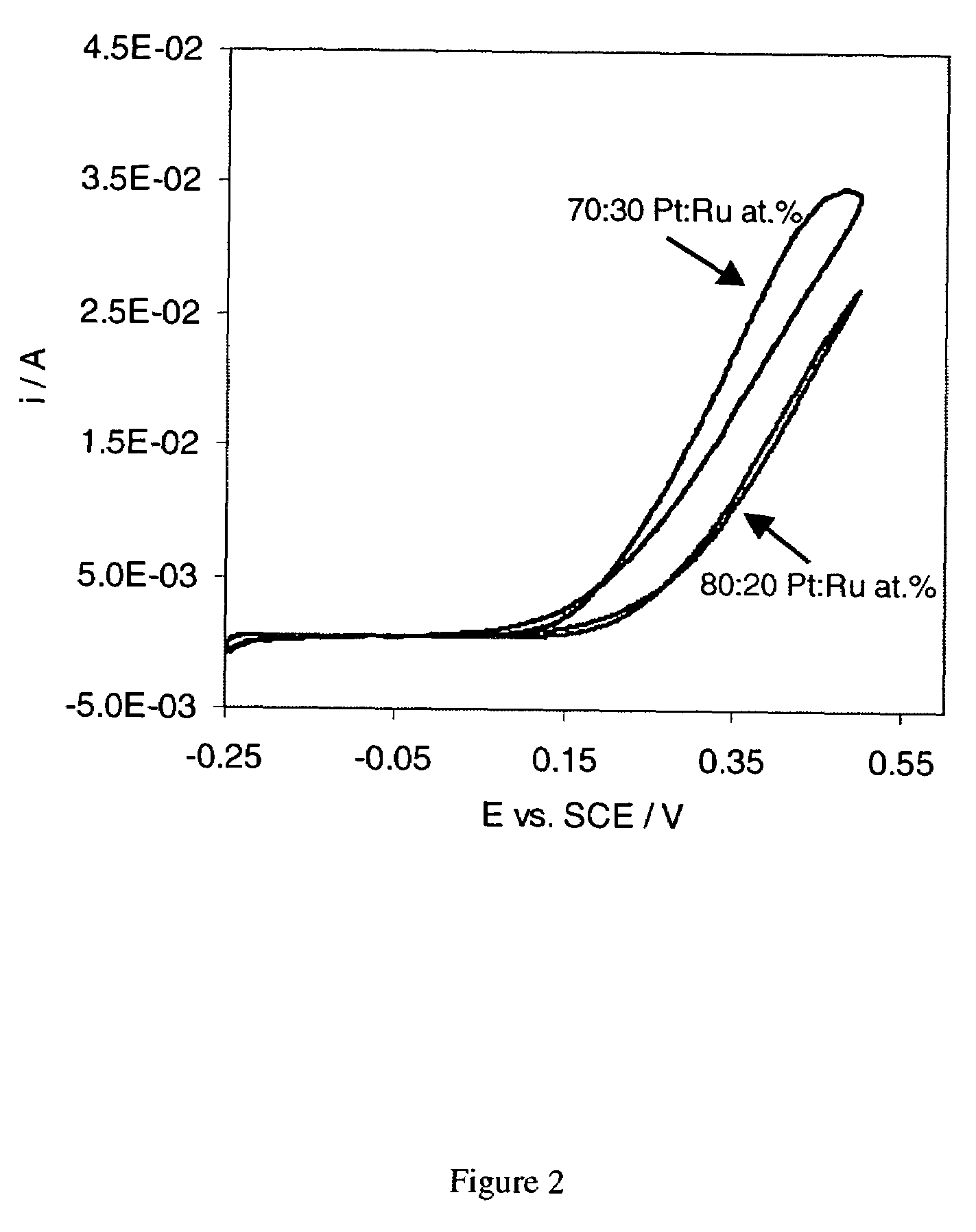
The synthesis of Pt and PtRu and other Pt based nano-particles that catalyze the electrochemical oxidation of methanol, carbon monoxide and hydrogen, as well as oxygen reduction, is described. The Pt based catalysts are synthesized in solution forming particles of 0.8 to 10 nm size (forming a “colloidal” solution) and are subsequently applied to a desired substrate as e.g., carbon black, graphite, metals. The application of the nano-sized catalyst particles on the substrates involves electroless deposition at open-circuit, such as immersing the substrate into the colloidal solution or spraying the catalyst particles on the substrate. The Pt, PtRu and other Pt based catalyst can also be directly deposited on the substrate involving the simultaneous reduction and deposition of the Pt based catalysts onto the substrate surface and into its porous structure. The presently described synthesis and deposition of the resulting Pt based nano-particles on and into a variety of high surface area and preferably electronically conductive substrates results in electrodes of high surface areas, relates directly to the preparation and use of high surface area electrodes, (anodes and cathodes) which could be used in e.g., direct methanol, hydrogen and hydrogen containing carbon monoxide fuel cells.
Owner:RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Graphitic carbon nitride material, and its synthetic method and applications
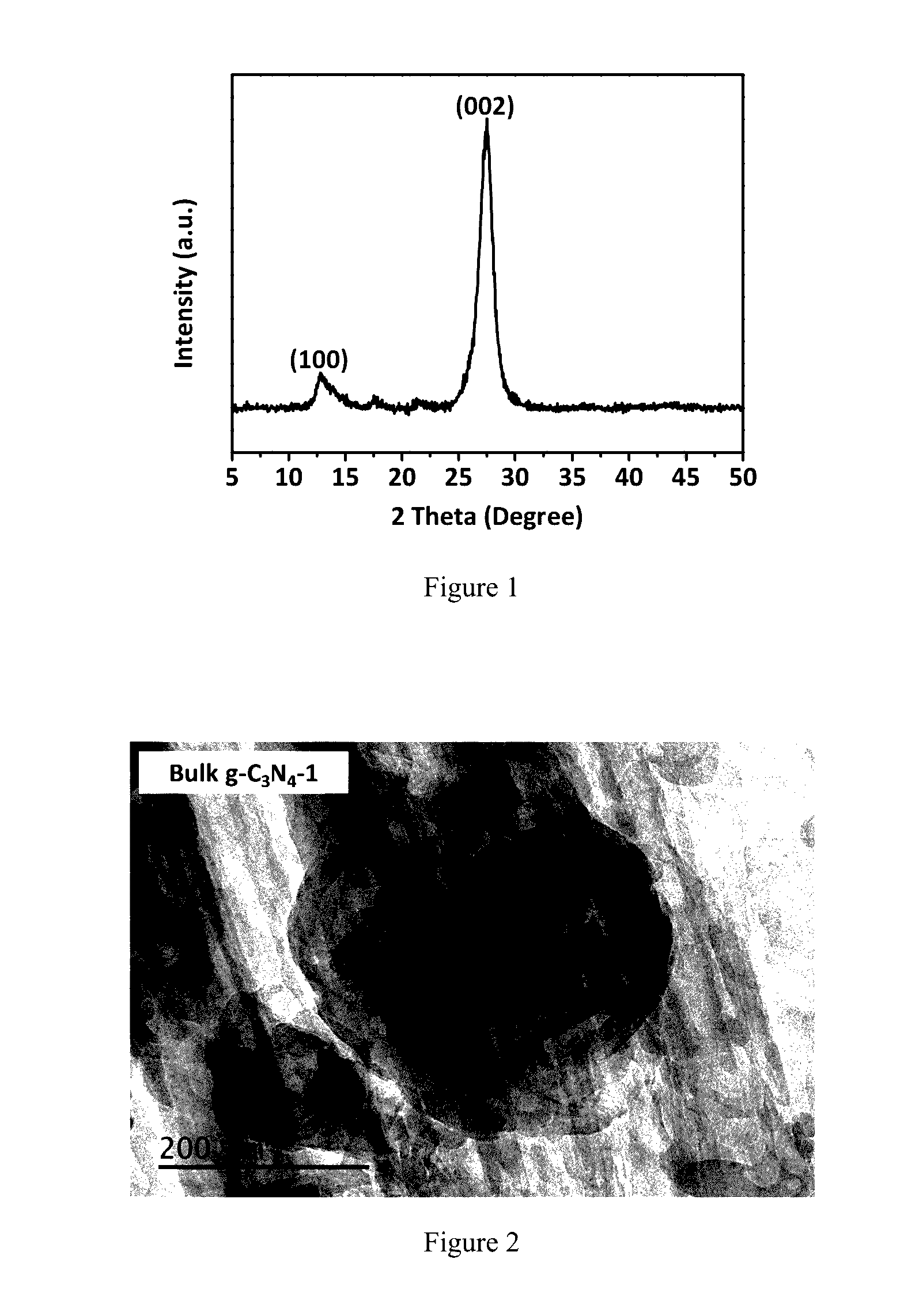
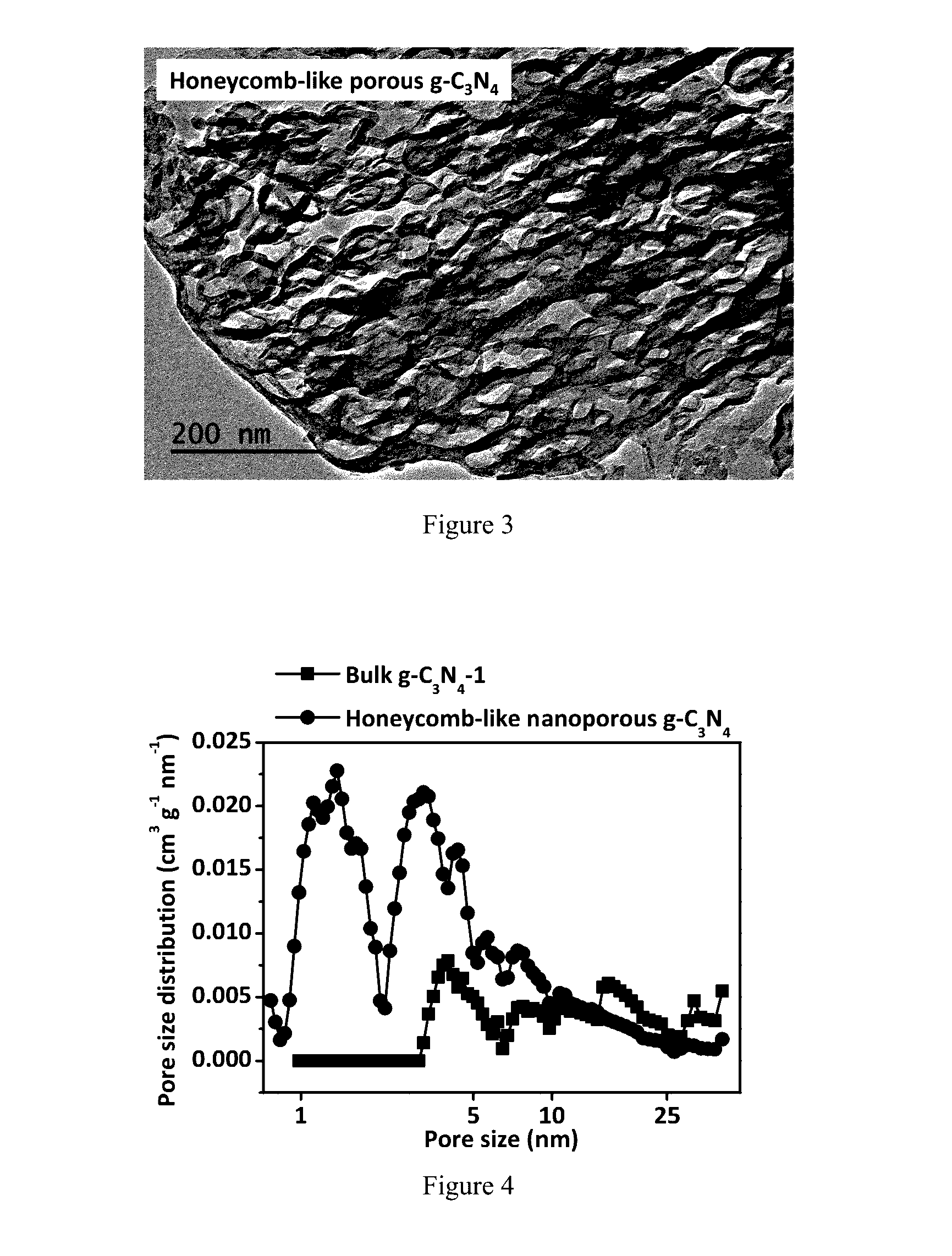
InactiveUS20170057821A1Synthetic is simpleImprove distributionNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsEnergy based wastewater treatmentCarbon nitrideCalcination
The present invention relates to a synthetic method of graphitic carbon nitride material. The method involves a homogenous mixing of carbon nitride precursor and ammonium salt, and calcining the mixture to obtain a porous graphitic carbon nitride material. Wherein, the ammonium salt is any one or a combination of at least two which could release gaseous NH3 during thermolysis. The present invention uses thermolabile ammonium salt as a pore former; the thermolysis of ammonium salt could release soft gas bubbles during the calcination; the later burst of bubbles leads to the formation of nanoporous structure. The proposed method is template-free and environmentally-friendly, and the resultant material exhibits high photocatalytic activity in the field of gas and water decontamination.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pure PEG-lipid conjugates
InactiveUS20110040113A1Low costSynthetic is simpleOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationOligomerSynthesis methods
Syntheses of polyethyleneglycol (PEG)-lipid conjugates are disclosed. Such syntheses involve stepwise addition of small PEG oligomers to a glycerol backbone until the desired chain size is attained. Polymers resulting from the syntheses are highly monodisperse. The present invention provides several advantages such as simplified synthesis, high product yield and low cost for starting materials. The present synthesis method is suitable for preparing a wide range of conjugates.In another aspect, the invention comprises PEG lipid conjugates having a glycerol backbone covalently attached to one or two monodisperse PEG chains and one or two lipids. These conjugates are especially useful for pharmaceutical formulations.
Owner:UKRAINIAN INDEPENDENT INFORMATION AGENCY +1
Method for catalytic polymerization of alpha-olefin monomers using an ultra-high activity non-metallocene pre-catalyst
InactiveUS20020019503A1High molecular weightLow molecularGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMetal chelateAlpha-olefin
A method for catalytic polymerization of alpha-olefin monomers using an ultra-high activity non-metallocene pre-catalyst featuring an amine bis(phenolate) ligand-metal chelate, having general formulas of [{(O)1R1R2R3R4(C6)1(CH2)1(RnY-T)N(CH2)2(C6)2R5R6R7R8(O)2}MX1X2] and [{(O)1R1R2R3R4(C6)1(CH2)1(RnY-T)N(CH2)2(C6)2R5R6R7R8(O)2}MX3], where, M, O, and N, are metal, oxygen, and, nitrogen; X1, X2, and X3, are ligands bonded to M; R1 through R8 are radicals; (RnY-T) is an optional non-donor or donor group bonded to N. The relatively stable and simply synthesized pre-catalyst is activated by a co-catalyst under mild reaction conditions, producing exceptionally reactive polymerization of a wide variety of alpha-olefin monomers, and forming a variety of poly(alpha-olefin) products, having high molecular weight and low molecular weight distribution (PDIs close to 1). Living polymerization is performed at or above room temperature, along with achieving block co-polymerization of alpha-olefin monomers at room temperature, and producing polymers and oligomers having a wide range of molecular weights. The catalyst formed during reaction remains "alive' for as long as 31 hours, for producing a polymer with a molecular weight as high as 450,000 grams / mole.
Owner:RAMOT UNIV AUTHORITY FOR APPLIED RES & INDAL DEVMENT
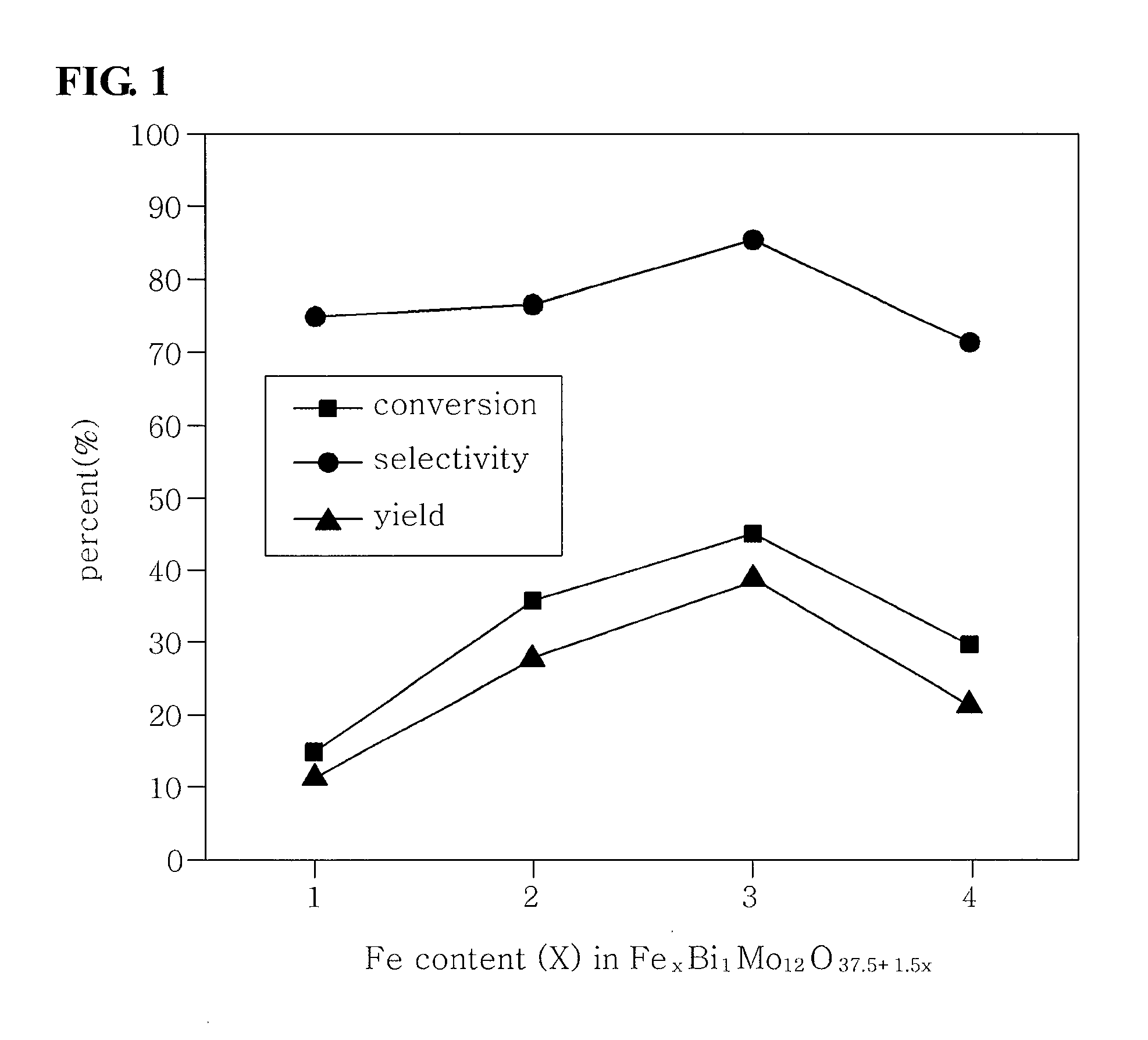
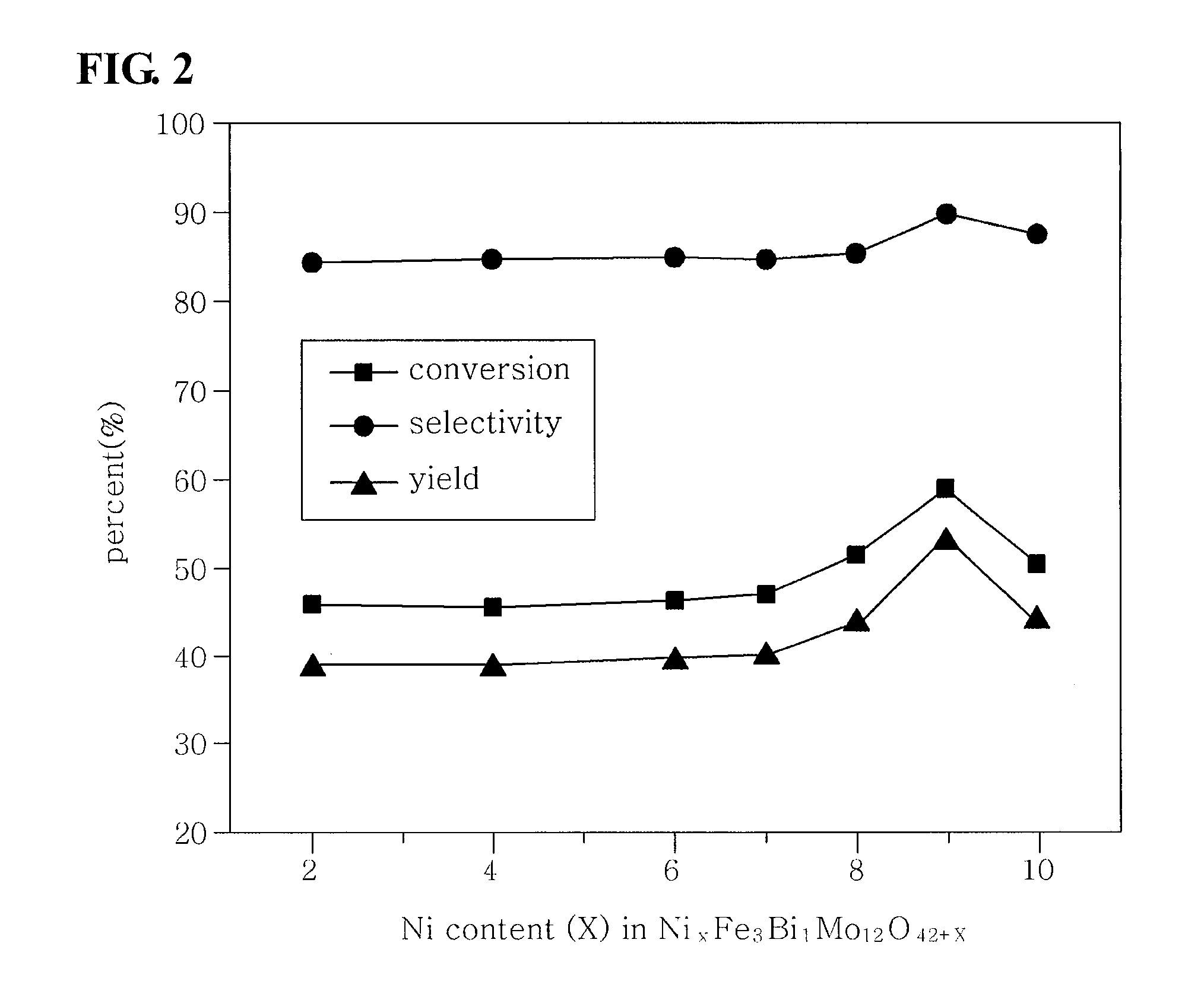
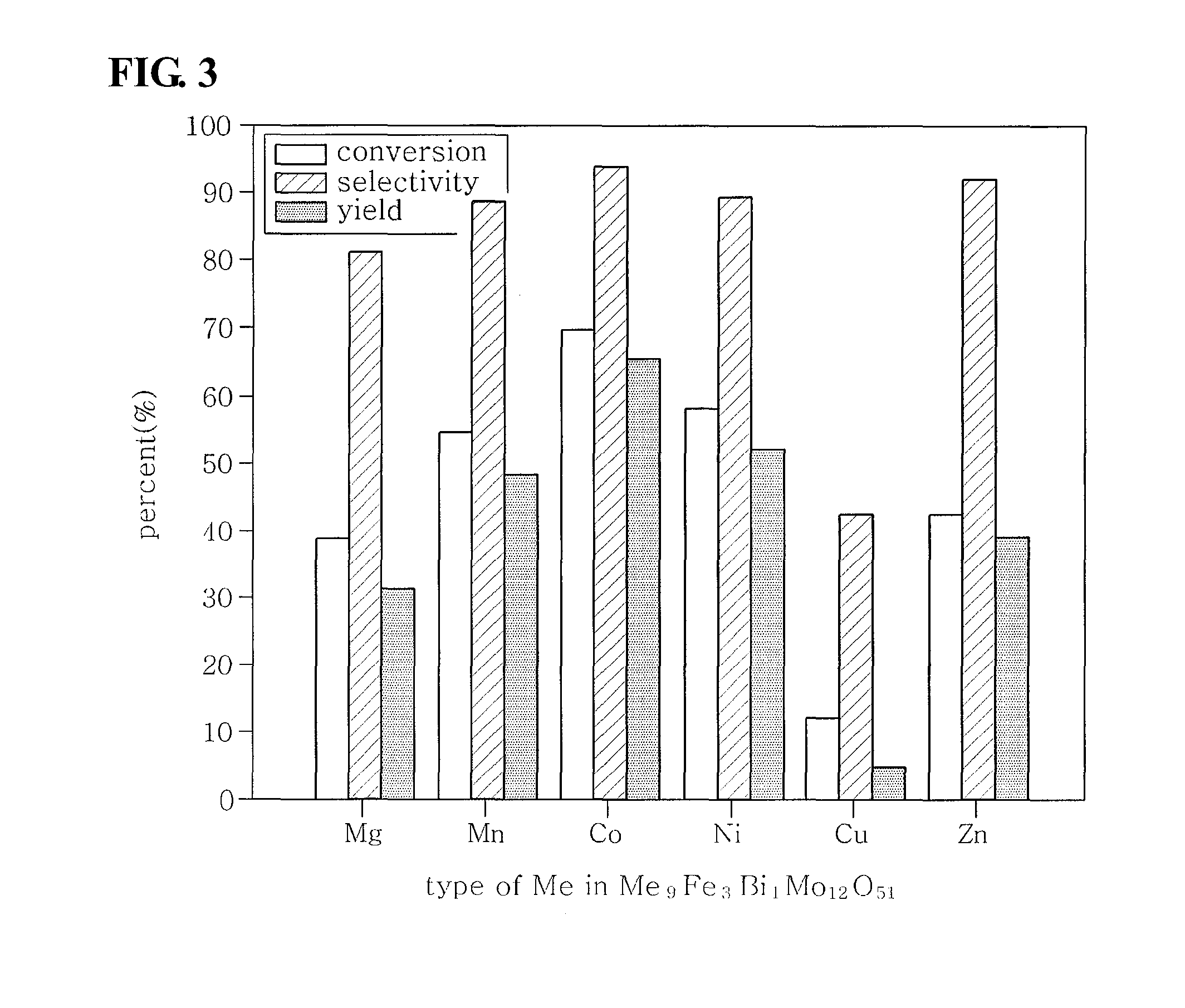
Method of preparing multicomponent bismuth molybdate catalysts comprising four metal components and method of preparing 1,3-butadiene using said catalysts
ActiveUS20100249482A1High activityGood reproducibilityHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsButeneMolybdate
This invention relates to a method of preparing multicomponent bismuth molybdate catalysts composed of four metal components and a method of preparing 1,3-butadiene using the catalyst, and particularly, to multicomponent bismuth molybdate catalysts composed of a divalent cationic metal, a trivalent cationic metal, bismuth and molybdenum, a preparation method thereof, and a method of preparing 1,3-butadiene from a C4 mixture including n-butene and n-butane using oxidative dehydrogenation. According to this invention, it is possible to prepare catalysts having high activity for the preparation process of 1,3-butadiene only using four metal components as shown through systematic investigation of types and ratios of metal components, unlike conventional multicomponent metal oxide catalysts having a complicated composition of metal components.
Owner:SK GEO CENTRIC CO LTD
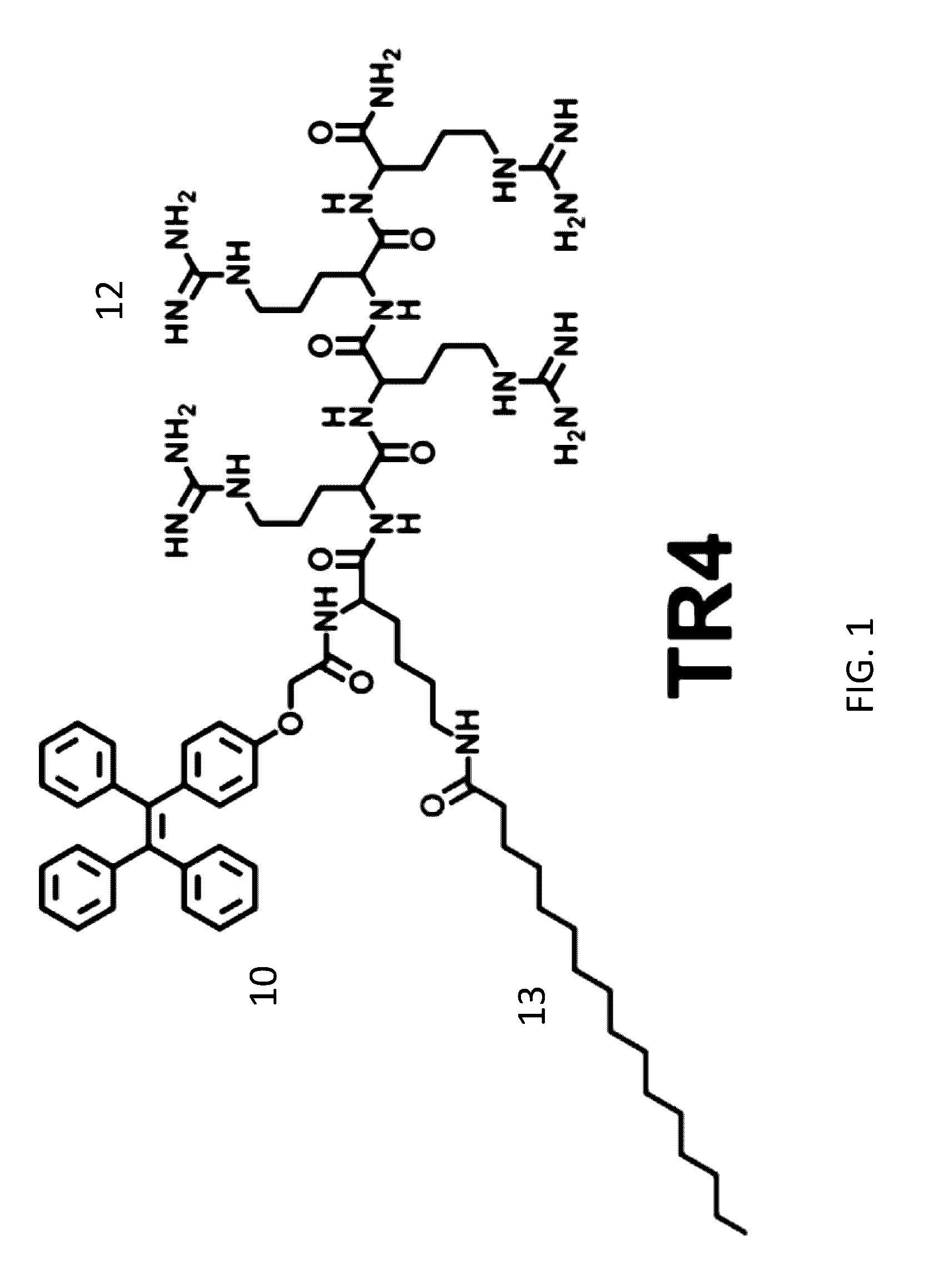
Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen Having An Peptide Sequence And Its Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20160349245A1Low costSynthetic is simpleBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAggregation-induced emissionCell membrane
A fluorescence molecular probe having a hydrophilic polypeptide backbone conjugated with a hydrophobic alkyl chain and a function group with aggregation induced emission is disclosed. The hydrophilic peptide sequence renders DNA binding capacity and the hydrophobic alkyl chain provides capacity for embedding within cell membrane. The aggregation induced emission renders real time tracking for live cell function studies. The synthesis of the probe is simple and easy for purification.
Owner:ZHANG CHUNQIU +1
Chelating agents for heavy metal removal
InactiveUS20060065604A1Easy to separateReduce the total massOther chemical processesComplex ion-exchangersWastewaterAqueous solution
The present invention provides for Troika acids attached to a macroporous resin and Methods of preparing the same, including direct attachment of a Troika acid, and attachment of a Troika acid precursor followed by generation of the Troika acid in situ. Methods of functionalizing a resin to facilitate attachment are also described. Multiple Troika acids, comprising a pair of Troika acids joined together are described. Synthetic routes to both microporous and macroporous resins modified by introduction of a suitable Troika-type acid have been designed and validated. In a preferred embodiment, a macroporous Troika resin removes Cu2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solution with high affinity, and is selective against Mg2+ or Ca2+. The materials of the present invention have advantages for metal removal from power plant waste water.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method for preparing hierarchically porous doped carbon material and its use
ActiveUS20180190996A1Improve stabilityImprove conductivityFuel and primary cellsCell electrodesDopantSupercapacitor
A method for preparing a hierarchically porous doped carbon material includes the steps of heating a mixture including an etching agent precursor and a pore-generating agent. The pore-generating agent is embedded in a matrix including a carbon source and a dopant source for simultaneously carbonizing the carbon source. The method further includes doping with the dopant and etching the pore-generating agent for obtaining the hierarchically porous doped carbon material.The hierarchically porous doped carbon material can form an electrode, and an energy storage device such as a supercapacitor can include such an electrode. The hierarchically porous doped carbon material can also help form an energy storage and conversion device such as a metal-air battery or a regenerative fuel cell.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method for the synthesis of layered luminescent transition metal dichalcogenide quantum dots
InactiveUS20170029962A1Simple and cost-effective approachSynthetic is simpleMaterial nanotechnologyCellsSolar waterSolar cell
The invention discloses a method for the synthesis of monodispersed luminescent quantum dots of transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDC), single- or few-layered, using a single-step electrochemical exfoliation that involves dilute ionic liquid and water. The method disclosed helps to obtain nanoclusters of TMDC of desired size including small sizes ranging up to 6 nm, by varying the concentration of the electrolyte and the applied DC voltage. The invention further discloses a method by which mono- or few-layered luminescent transition metal dichalcogenides can be directly deposited onto conducting substrates in a uniform manner. The monodispersed single- or few-layered luminescent TMDC and electro-deposited substrates exhibit improved electronic conductivity and new active sites, making them suitable as high-performance electrocatalysts in hydrogen evolution reactions in solar water-splitting applications and also as electrodes for solar cell applications.
Owner:INDIAN INST OF SCI EDUCATION & RES THIRUVANANTHAPURAM IISER TVM
Fluorescent compounds
ActiveUS9097667B2Convenient and effective labelingReduce formationMethine/polymethine dyesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMicroorganism
The present invention relates to fluorescent dyes. The present invention provides a wide range of fluorescent dyes and kits containing the same, which are applicable for labeling a variety of biomolecules, cells and microorganisms. In one aspect, the invention provides a compound having a maximal fluorescence excitation wavelength, wherein the compound has a structure of Formula II:F—Y=Ψ Formula IIand wherein Z— is a counterion, Y is a bridge unit permitting electron delocalization between F and Ψ, and F is a moiety having the structure:The present invention also provides various methods of using the fluorescent dyes for research and development, forensic identification, environmental studies, diagnosis, prognosis, and / or treatment of disease conditions.
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
N-aryl-carbamic acid ester-derived and valeric acid ester-derived cross-linkers and conjugates, and methods for their synthesis and use
ActiveUS6887952B1Simplified synthetic routeAbility to monitor synthesisOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistrySolubilityAryl
The present invention describes carbamic acid ester-derived and valeric acid ester-derived polyfunctional cross-linker molecules, and methods for their synthesis and use. The inclusion of polymeric moieties such as poly(alkylene oxide) in the cross-linkers of the present invention can provide advantageous solubility properties in aqueous environments. Such cross-linkers may be used to form conjugates for use in a variety of assay formats.
Owner:BIOSITE DIAGNOSTICS
Xanthene dyes comprising a sulfonamide group
ActiveUS20100197030A1Convenient and effective labelingHigh fluorescence quantum yieldSugar derivativesPeptide preparation methodsDiseaseMicroorganism
The present invention relates to fluorescent dyes in general. The present invention provides a wide range of fluorescent dyes and kits containing the same, which are applicable for labeling a variety of biomolecules, cells and microorganisms. The present invention also provides various methods of using the fluorescent dyes for research and development, forensic identification, environmental studies, diagnosis, prognosis, and / or treatment of disease conditions.
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
Halogenated diarylamine compound and synthesis method thereof
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Chelating agents for heavy metal removal
InactiveUS7527733B2Easy to separateReduce the total massOther chemical processesComplex ion-exchangersWastewaterAqueous solution
The present invention provides for Troika acids attached to a macroporous resin and Methods of preparing the same, including direct attachment of a Troika acid, and attachment of a Troika acid precursor followed by generation of the Troika acid in situ. Methods of functionalizing a resin to facilitate attachment are also described. Multiple Troika acids, comprising a pair of Troika acids joined together are described. Synthetic routes to both microporous and macroporous resins modified by introduction of a suitable Troika-type acid have been designed and validated. In a preferred embodiment, a macroporous Troika resin removes Cu2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solution with high affinity, and is selective against Mg2+ or Ca2+. The materials of the present invention have advantages for metal removal from power plant waste water.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
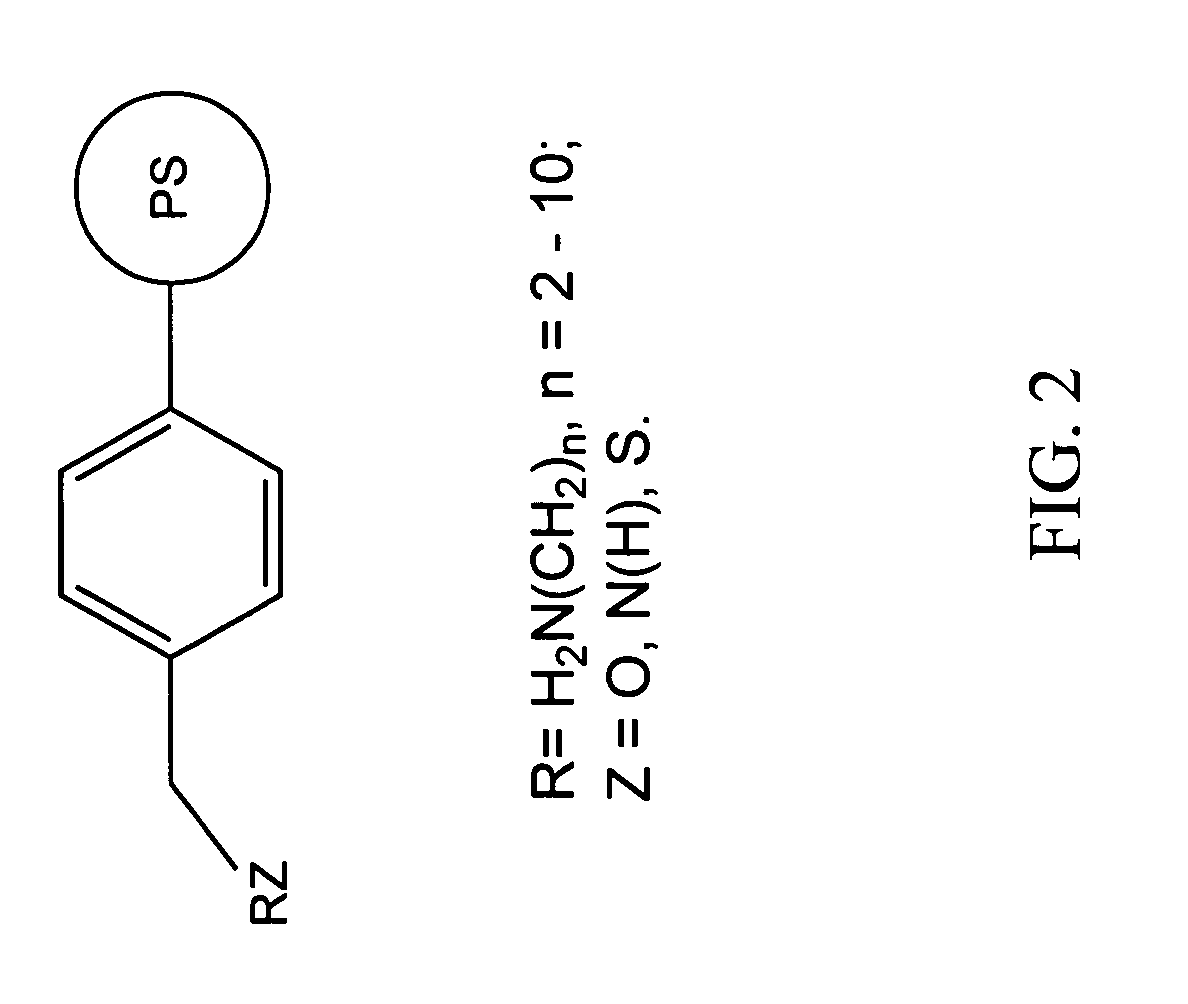
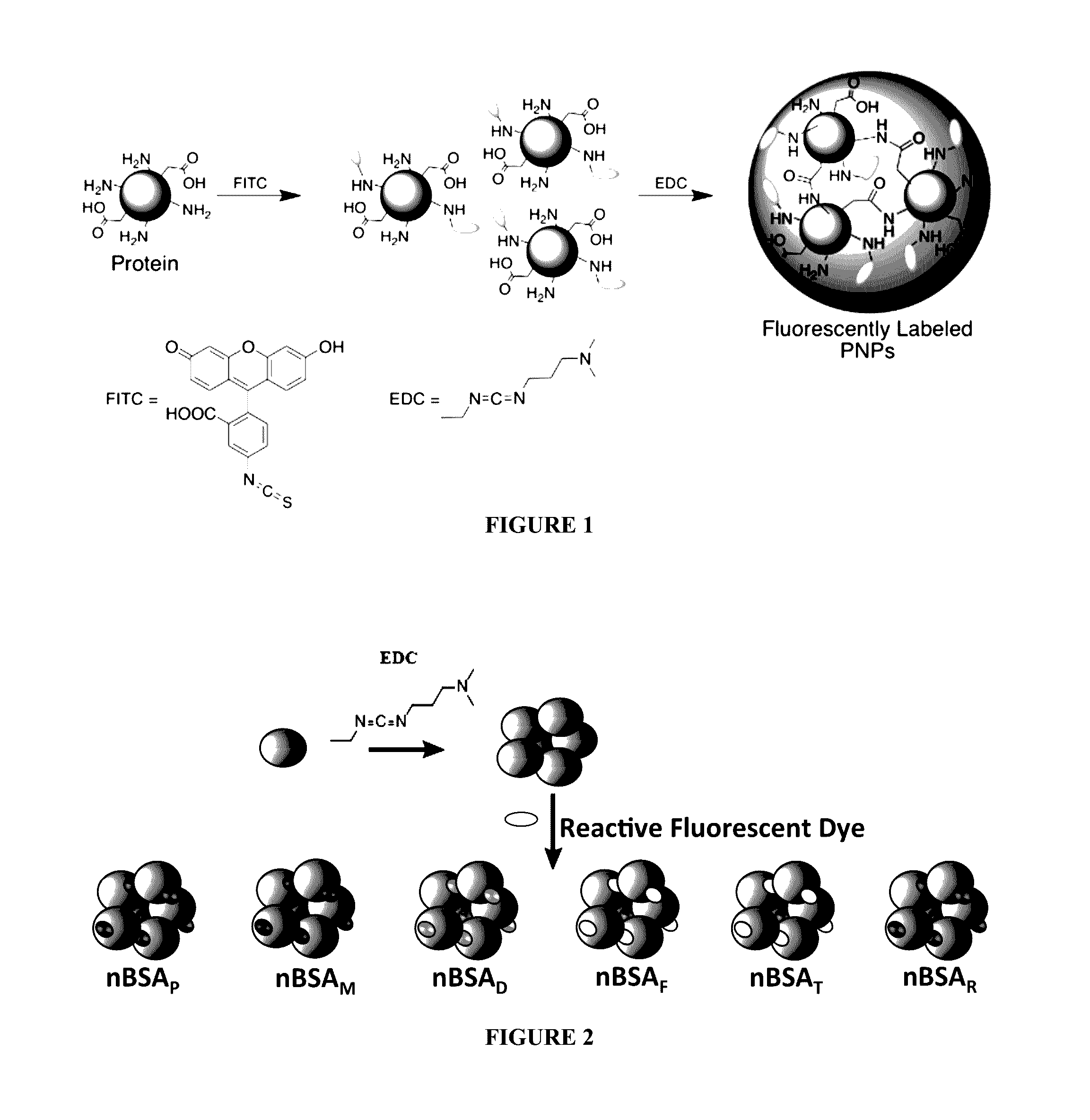
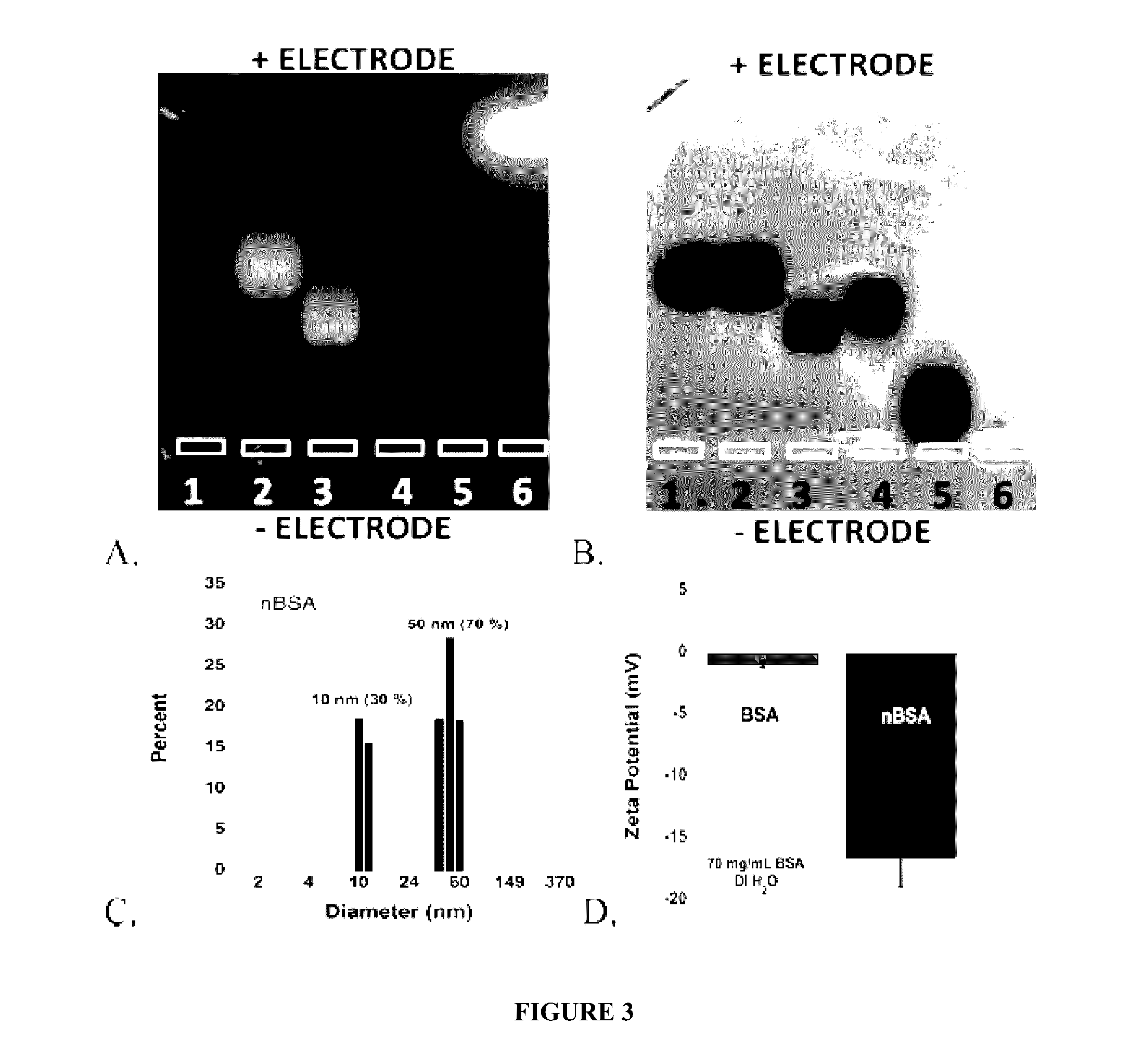
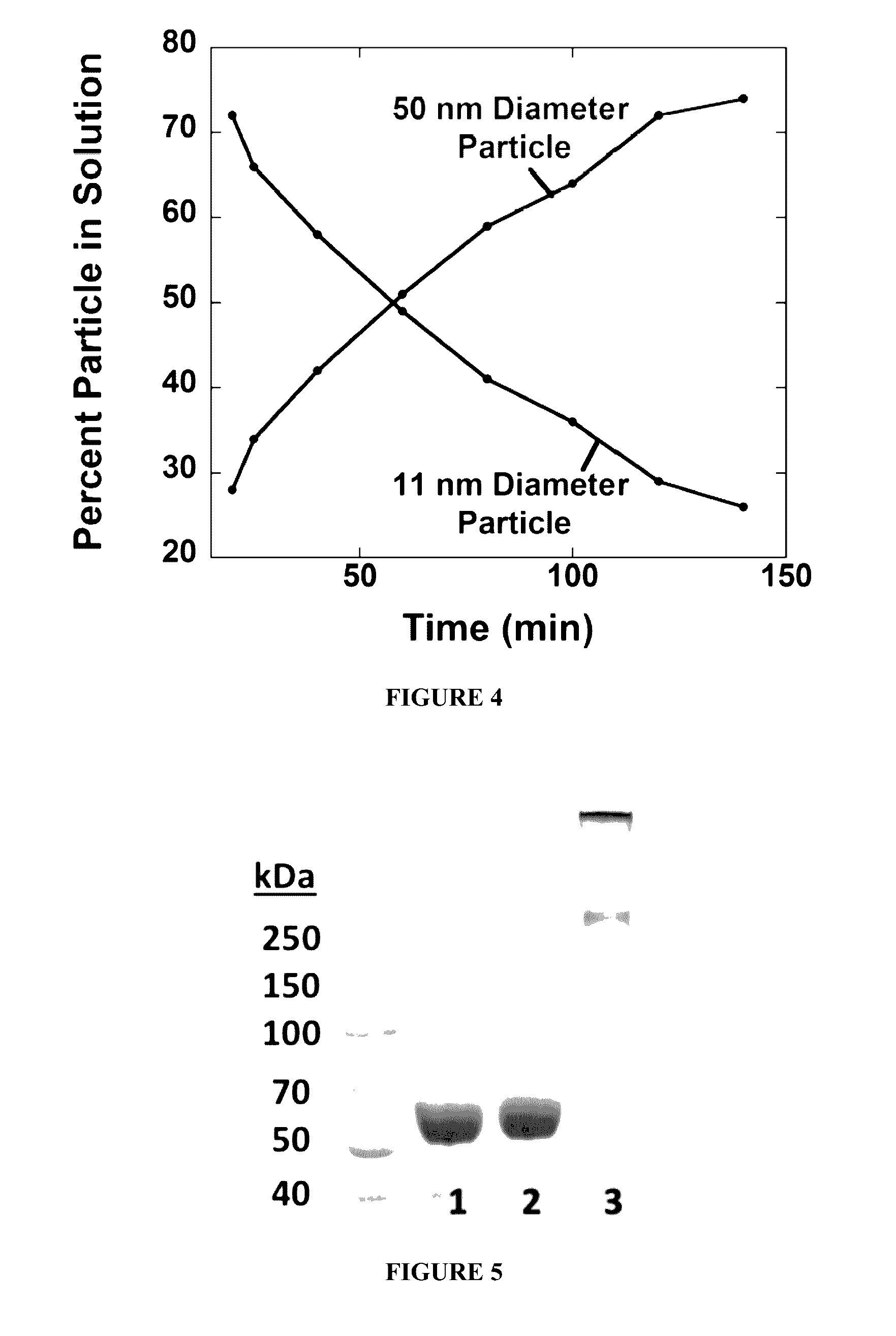
Protein fluorescent nanoparticles and methods of synthesis thereof
ActiveUS20170023580A1Less-expensive and flexibleSynthetic is simpleMaterial heat developmentBiological material analysisSynthesis methodsBiological imaging
Disclosed herein are stable and versatile protein nanoparticles having a range of tunable fluorescent properties. Such nanoparticles may find utility in biological imaging. Methods of synthesis of such nanoparticles are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
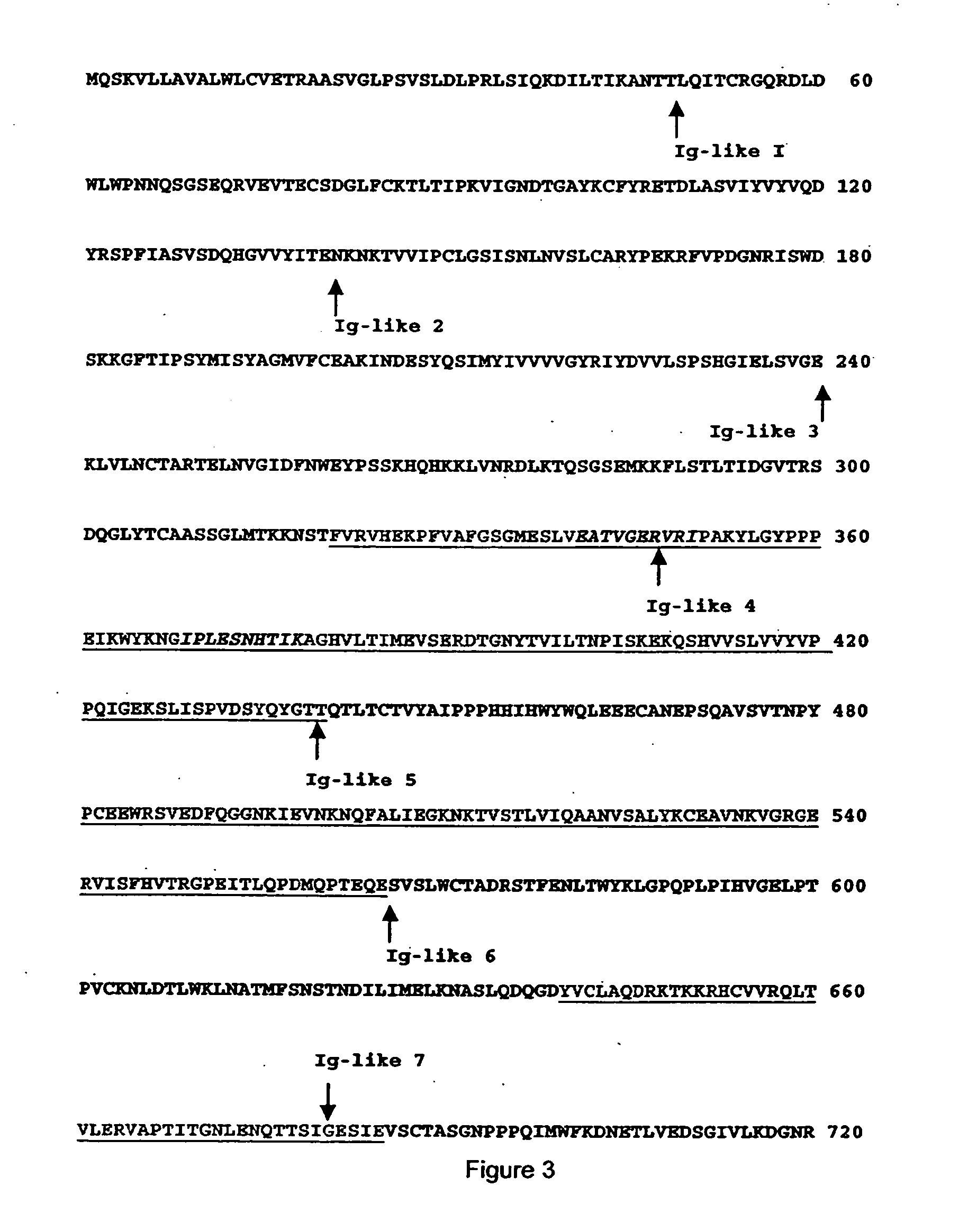
Cytokine receptor modulators, method of identifying same, and method of modulating cytokine receptors activity with same
InactiveUS20070037210A1Preventing oligomerizationInhibition of activationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBiological activationNon competitive
The present invention relates to a method for identifying a non-competitive peptide, which inhibits the activity of a cytokine receptor. This method includes the steps of selecting a candidate peptide containing from about 7 to about 20 amino acids derived from a flexible region of a cytokine receptor, and determining the ability of the peptide to inhibit or promote the oligomerization and / or activation of the receptor by measuring an activity of the receptor in the absence or the presence of the candidate peptide, wherein the non-competitive peptide is selected when the activity of the receptor is measurably lower in the presence of the peptide as compared to in the absence of the peptide so identified. This invention also provides agonists of cytokine receptor activity. Pharmaceutical compositions that comprise the identified peptides are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for treating patients with a disease or condition associated with abnormal cytokine receptor mediated function or activity such as inflammatory, autoimmune and vascular diseases.
Owner:VALO HSJ PARTNERSHIP
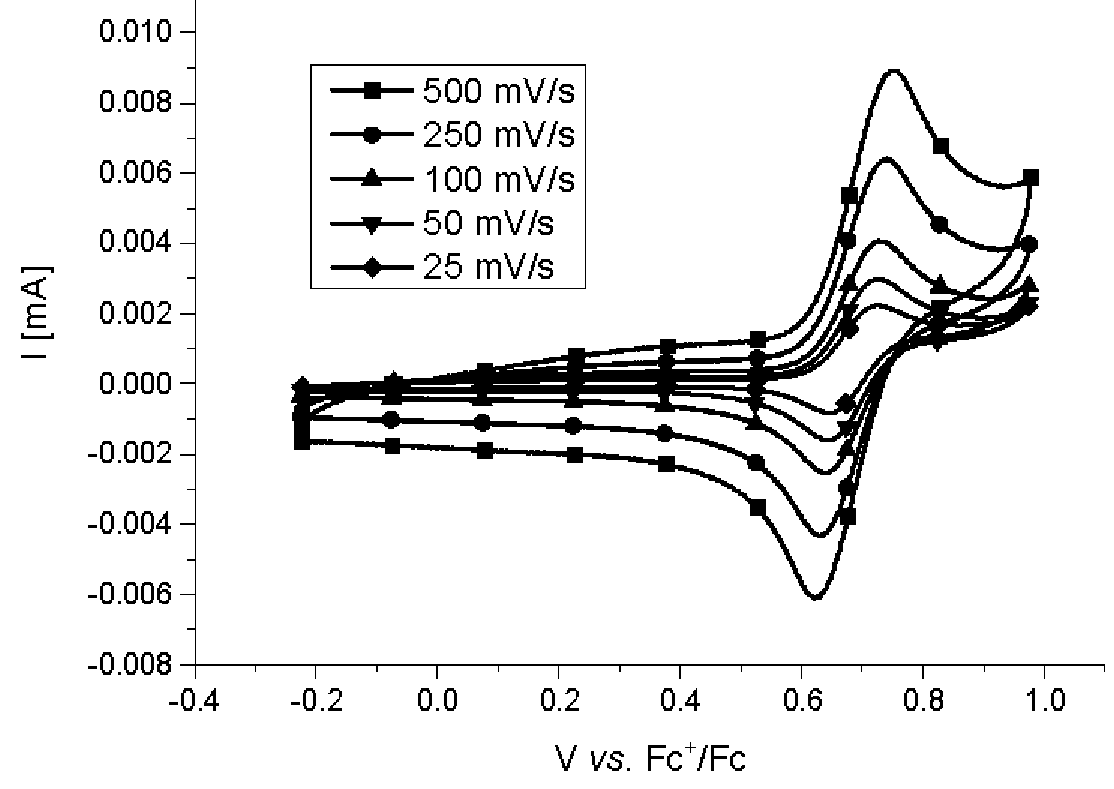
Use of certain polymers as a charge store
ActiveUS20180108911A1Easy to prepareHigh voltageElectrode manufacturing processesCoatingsScreen printingHigh cell
The present invention relates to polymers and to the use thereof in the form of active electrode material or in an electrode slurry as electrical charge storage means, the electrical charge storage means especially being secondary batteries. These secondary batteries are especially notable for high cell voltages, and simple and scalable processing and production methods (for example by means of screen printing).
Owner:INNOVATIONLAB
Molecular decomposition processes for the synthesis of nanosize metallic powders
InactiveUS7311754B2Improve solubilitySmall granularityMaterial nanotechnologyOxide/hydroxide preparationMetal alloySolvent
A method for synthesizing nanosize metallic powders can include providing a metallic precursor. The metallic precursor can include a metal alloy formed having a fugitive constituent and a target metal. The fugitive constituent and target metal are chosen such that the fugitive constituent can be selectively dissolved or removed by leaching with an appropriate solvent while leaving the target metal undissolved. The fugitive constituent can be leached from the metallic precursor to leave a metallic residue which is a mass of nanosize metallic particles made substantially of the target metal. The nanosize metallic particles can then be recovered from the metallic residue either merely by removing the solvent and / or breaking up the mass of nanosize metallic particles. The disclosed methods allow for a convenient avenue for production of nanosize particles from readily formed materials for use in a wide variety of potential industrial and commercial applications.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Topical treatment of cataracts in dogs
ActiveUS8158667B2Improved stereospecific synthesis of R-methylReduces number of stageBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiabetic retinopathyGlycerol
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Use of certain polymers as a charge store
ActiveUS20180102541A1Quality improvementMaximize capacityElectrode manufacturing processesHybrid capacitor electrodesHigh cellScreen printing
Owner:INNOVATIONLAB
Material used for rapid separation of oil and water and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveUS20180178144A1Easy to separateEasy to getFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater contaminantsMethacrylatePolymer modified
The present invention discloses a material used for rapid separation of oil and water and preparation method and application thereof, the mesh material is placed into monomer solution, reacting with the presence of initiator to prepare material used for rapid separation of oil and water. The monomer is divinylbenzene or 2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate, and the mesh material is stainless steel mesh. The present invention modifies the functional small molecules and polymers to the surface of the materials, thereby preparing multifunctional composite materials, effectively separating oil-water emulsion, so as to achieve the purpose of oil-water separation.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Specific detection of proteolytic enzymes
InactiveUS7329505B2Reduced measurement timeDefinite increasePeptide-nucleic acidsPeptide/protein ingredientsSpecific detectionExtinction
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Molecular decomposition process for the synthesis of nanosize ceramic and metallic powders
InactiveUS6803027B1Easy to implementImprove scalabilityMaterial nanotechnologyTantalum compoundsSolventMetal powder
A process is disclosed for forming a nanosize ceramic powder. A precursor ceramic material is formed of a fugitive constituent and a non-soluble constituent in a single phase. The precursor is contacted with a selective solvent (water, acid, etc.) to form a solution of the fugitive constituent in the solvent and a residue of the non-soluble constituent. The precursor is sufficiently reactive with the solvent to form the solution of the fugitive constituent in the solvent and form the nondissolved residue of the non-soluble constituent. The precursor material and the non-soluble residue are sufficiently insoluble in the solvent such that there is insufficient precursor material and non-soluble residue in solution to deposit and precipitate upon the residue of the non-soluble-constituent. The fugitive constituent is sufficiently soluble in the solvent such that the precursor reacts with the solvent to form the solution of the fugitive constituent without precipitation and deposition of fugitive constituent upon the residue of the non-soluble constituent in the form of nanosize particles. After the fugitive constituent is dissolved the selective solvent containing the fugitive constituent is removed from the residue. The residue remains in the form of a nanosize powder of the non-soluble constituent.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Novel Liquid Chromatographic Media and Methods of Synthesizing the Same
InactiveUS20140116932A1Good peak shapeHigh selectivityIon-exchange process apparatusSilicon organic compoundsStationary phaseHydrogen
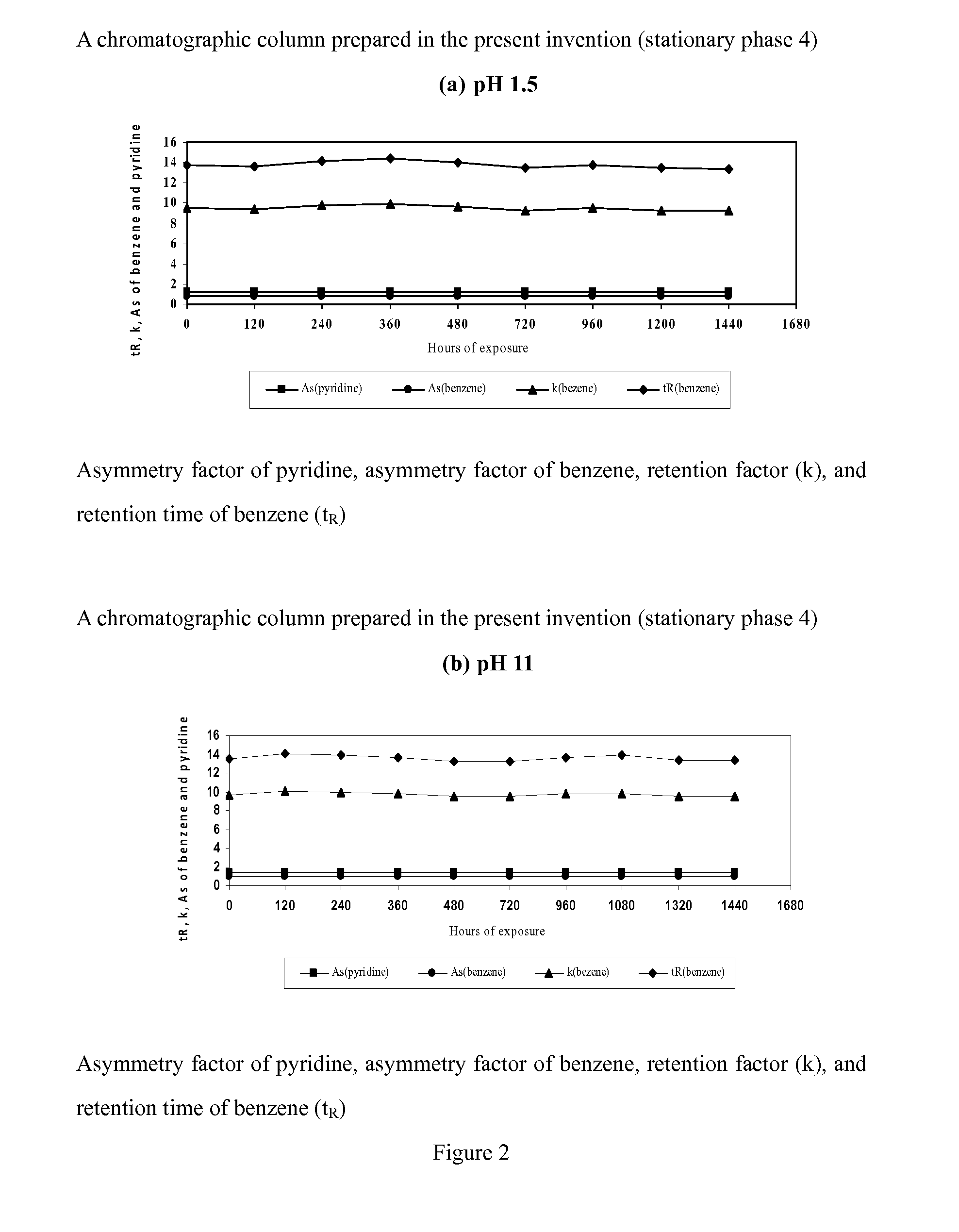
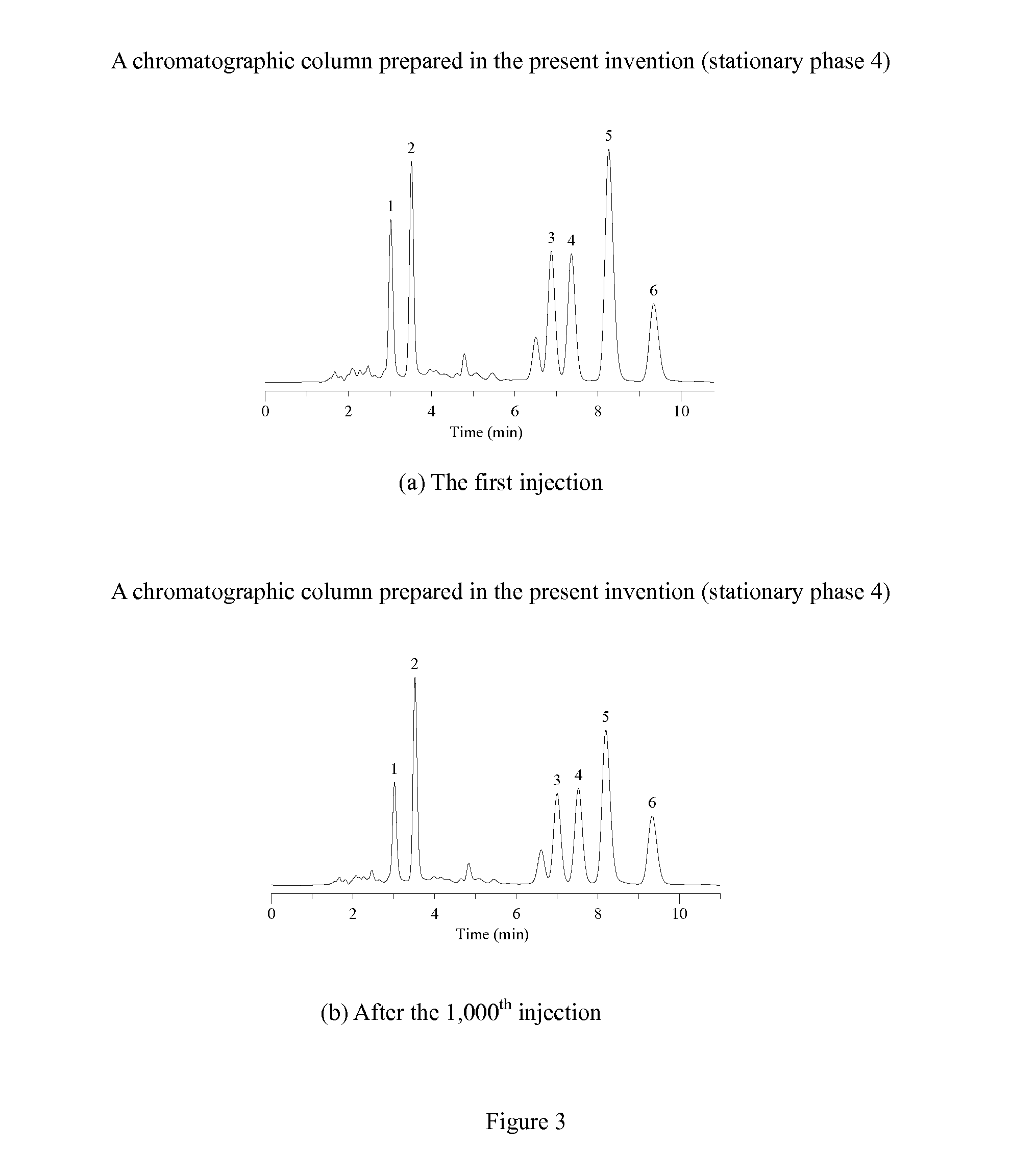
The present invention provides a bisamide-containing novel liquid chromatographic media and method of synthesizing the same. A novel polar bisamide functional group, which can form hydrogen bonds or ion pairs with residual silanols on the surface of silica gel, is used as the bonded phase on the surface of silica gel to better shield the activity of silanols and to eliminate the influence of residual silanol groups. Compared with conventional C18 columns, these novel bonded phases have different selectivity; they can work not only in 0 to 100% water but also in 0 to 100% organic mobile phase. In particular, they exhibit good peak shapes and resolutions for polar and basic compounds and have good stability within a very wide pH range. These properties make the new stationary phases a useful complement to conventional C18 columns for a variety of HPLC applications.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Bioluminescence imaging of myeloperoxidase activity in vivo, methods, compositions and apparatuses therefor
InactiveUS20110250145A1Improve stabilityLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic chemistryLuminolMyeloperoxidase activity
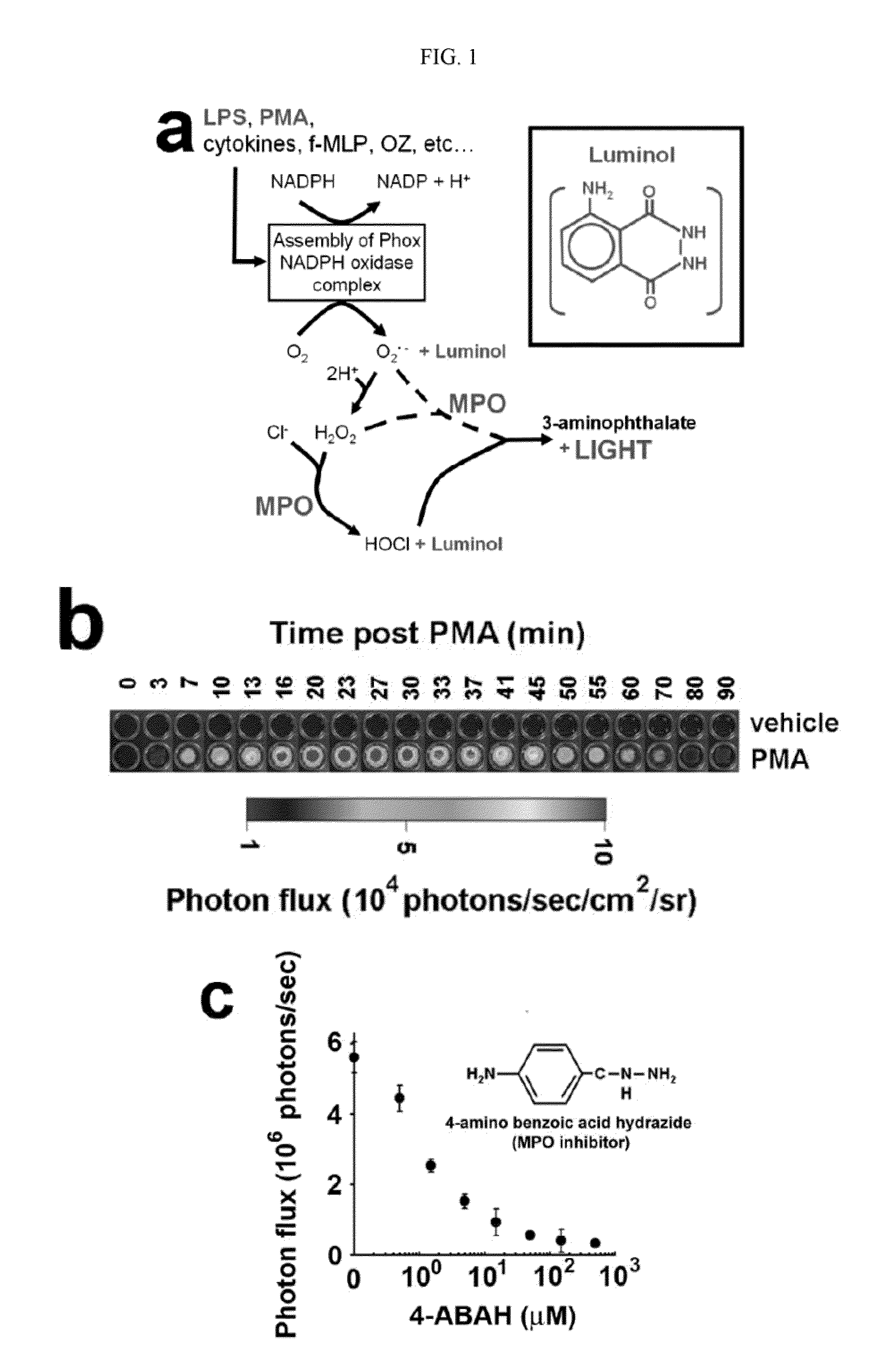
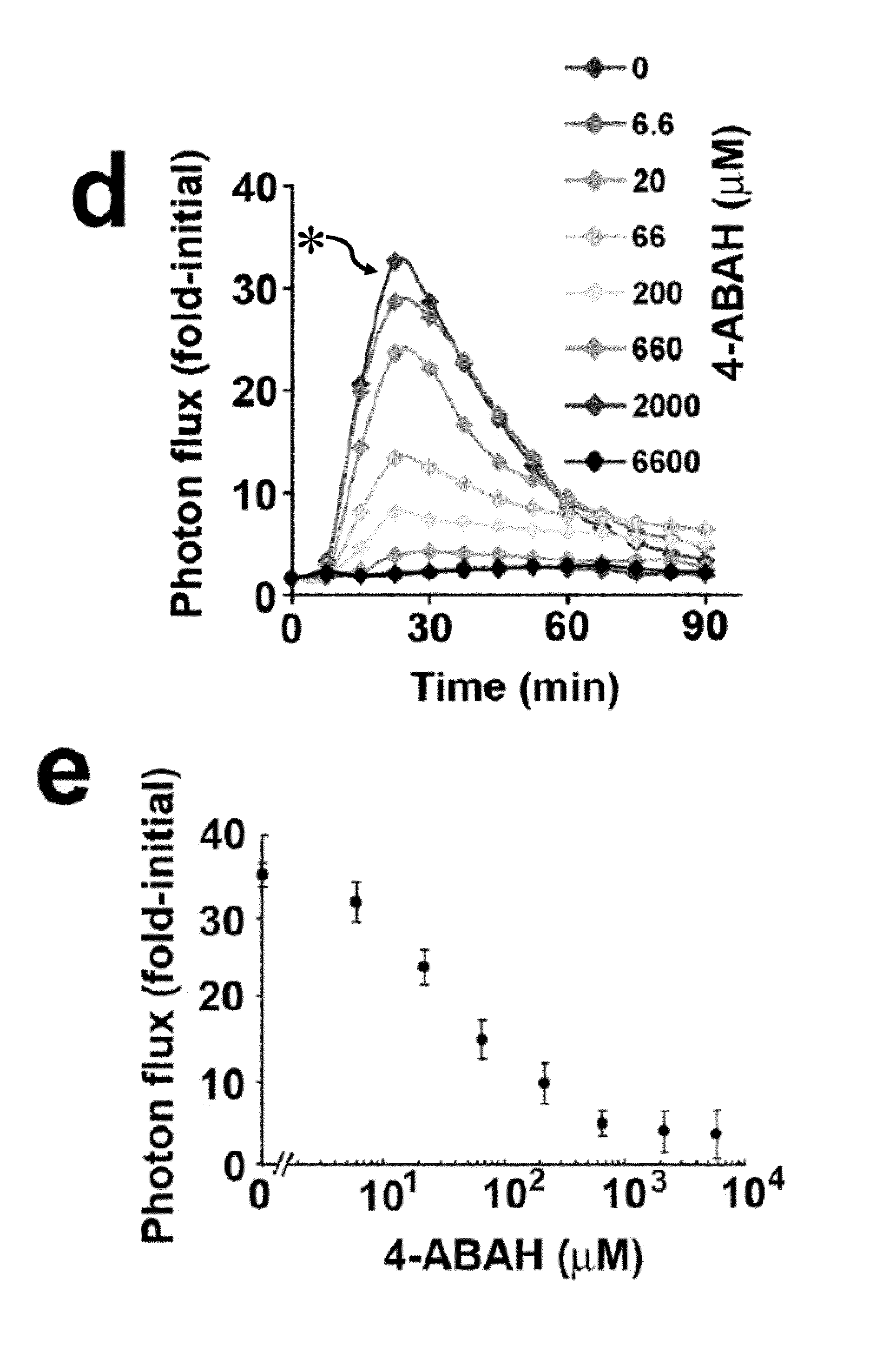
Methods of imaging distribution of myeloperoxidase activity in a subject are disclosed. These methods include the use of bioluminescent substrates, including luminol and wavelength-shifted analogues of luminol. Bioluminescent myeloperoxidase substrates that emit light at longer wavelengths compared to luminol are shown to be useful for imaging myeloperoxidase activity in vivo. The disclosed methods can be used for imaging sites of inflammation and other pathological conditions associated with abnormal levels of MPO activity in vivo. Methods of synthesis of luminol analogues are also disclosed.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com