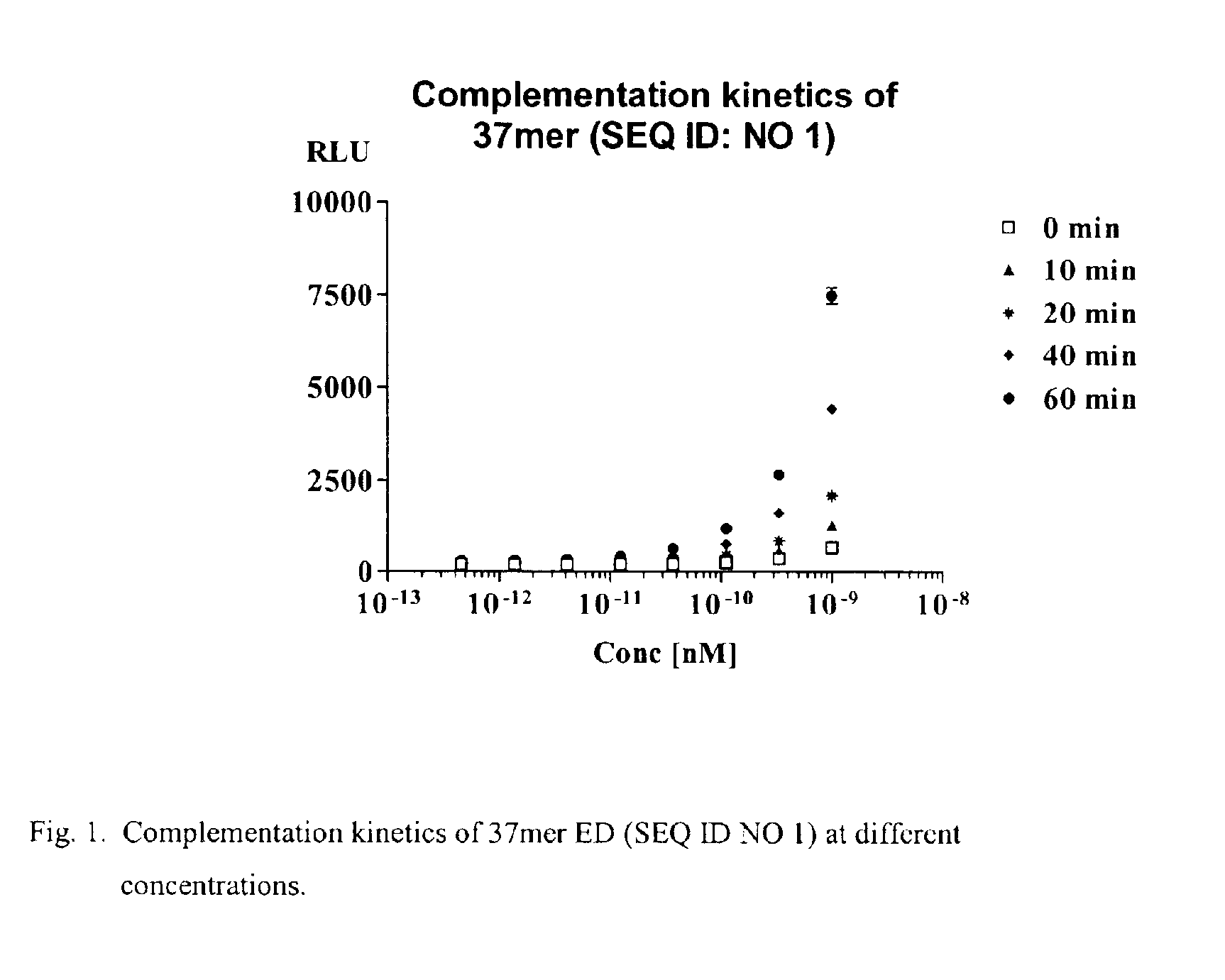
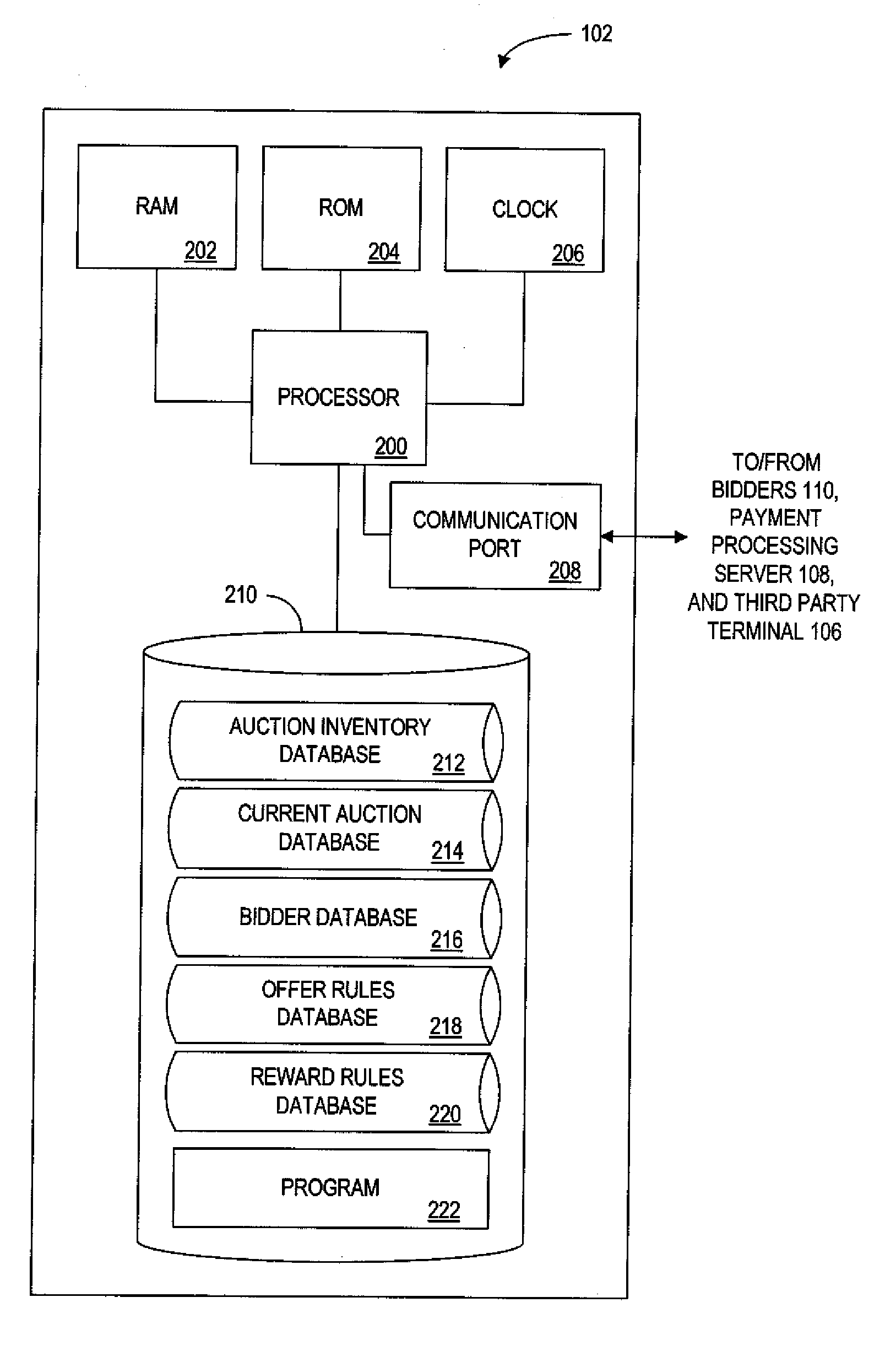
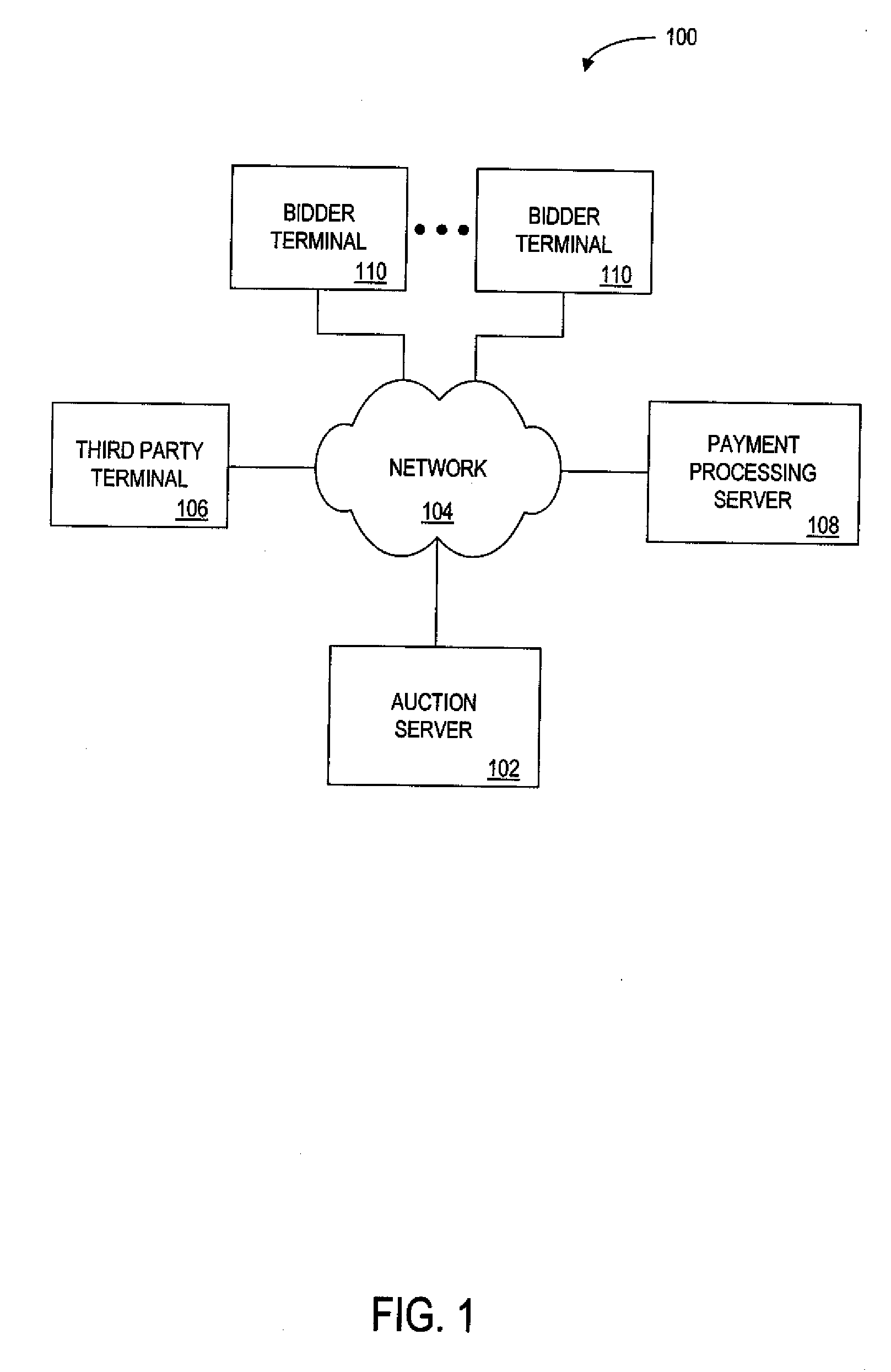
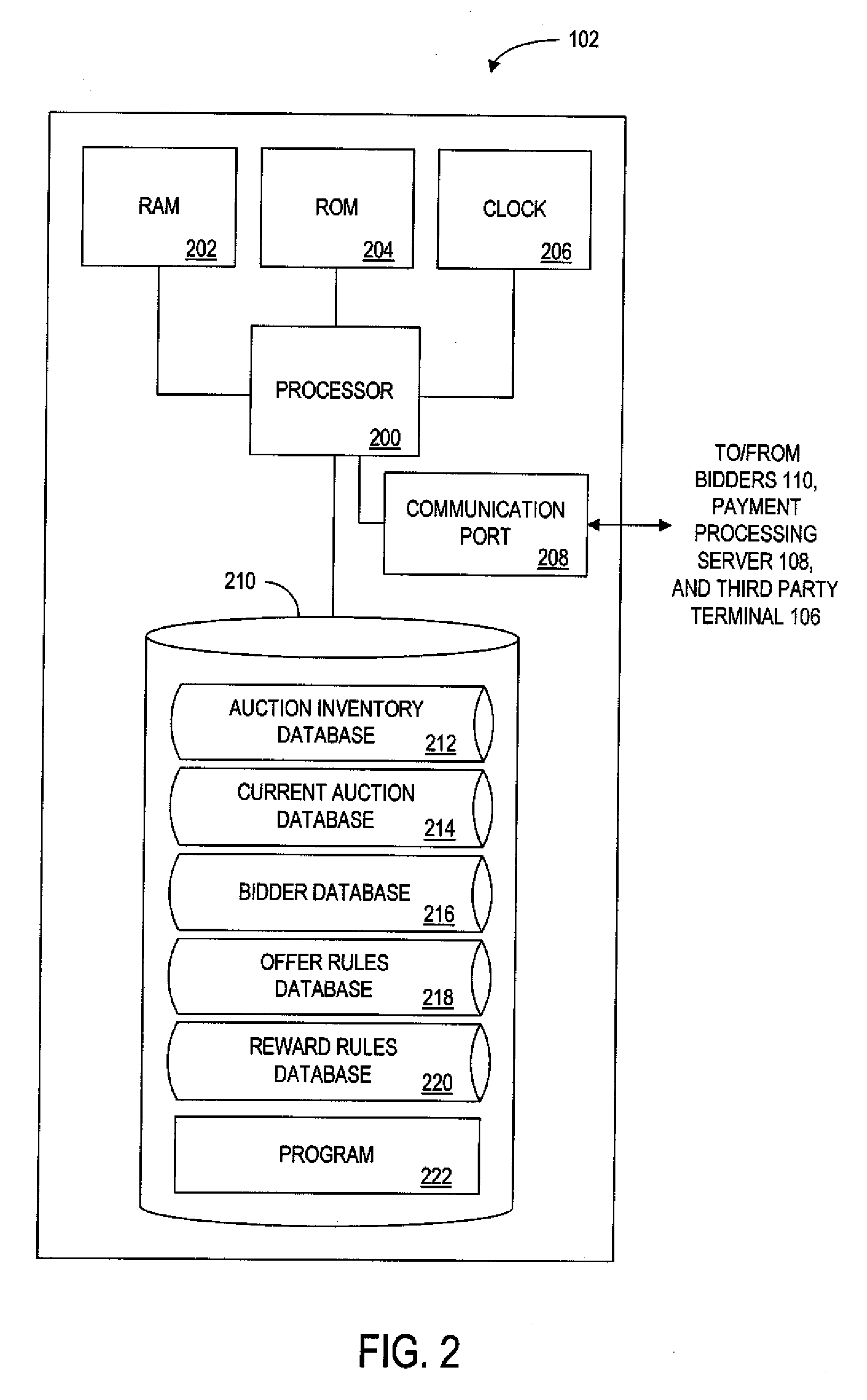
Patents
Literature
156 results about "Non competitive" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A non-competitive tender is a bid made by a small investor to purchase a debt issue which has its price based on the average price of all competitive tenders submitted.
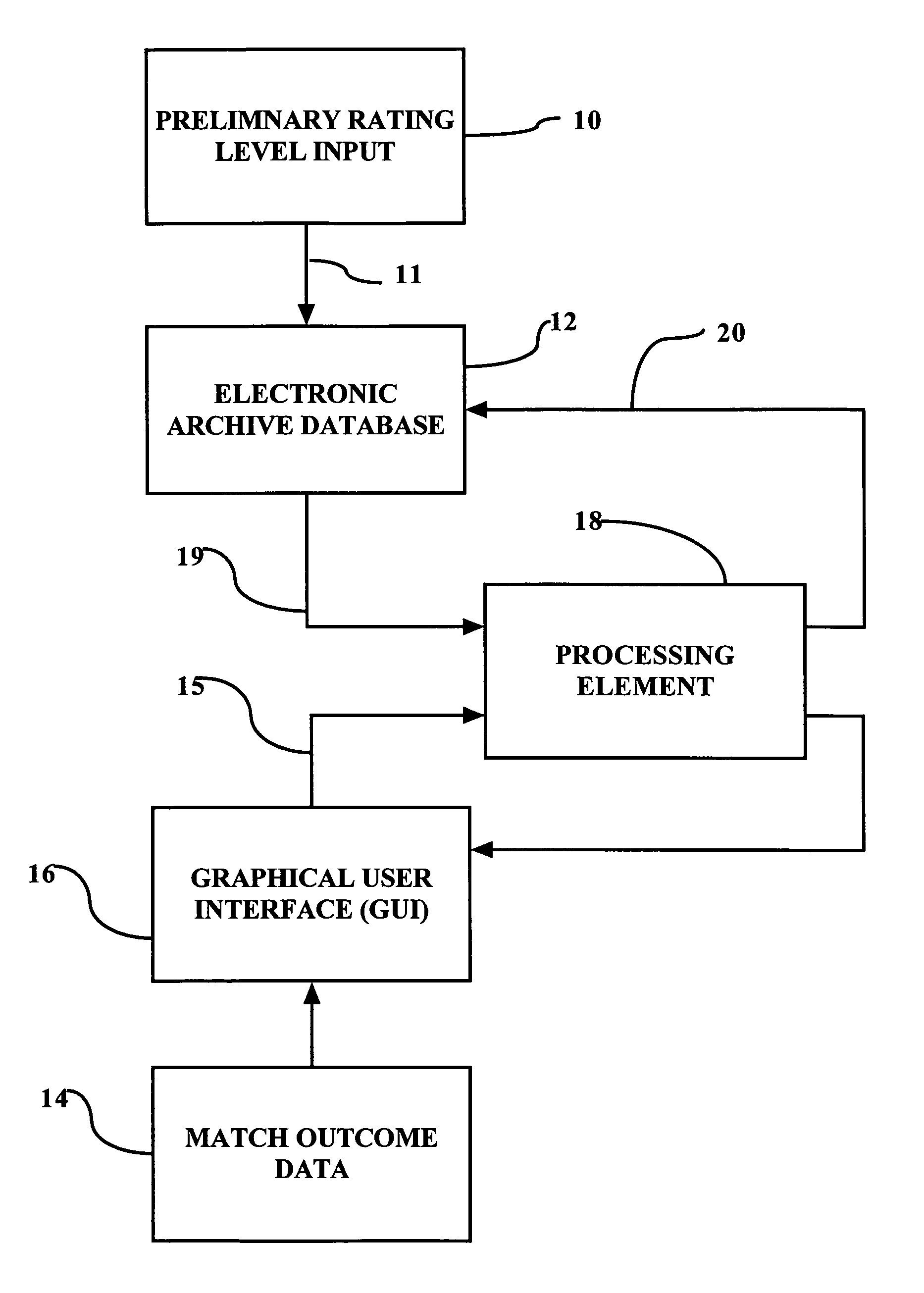
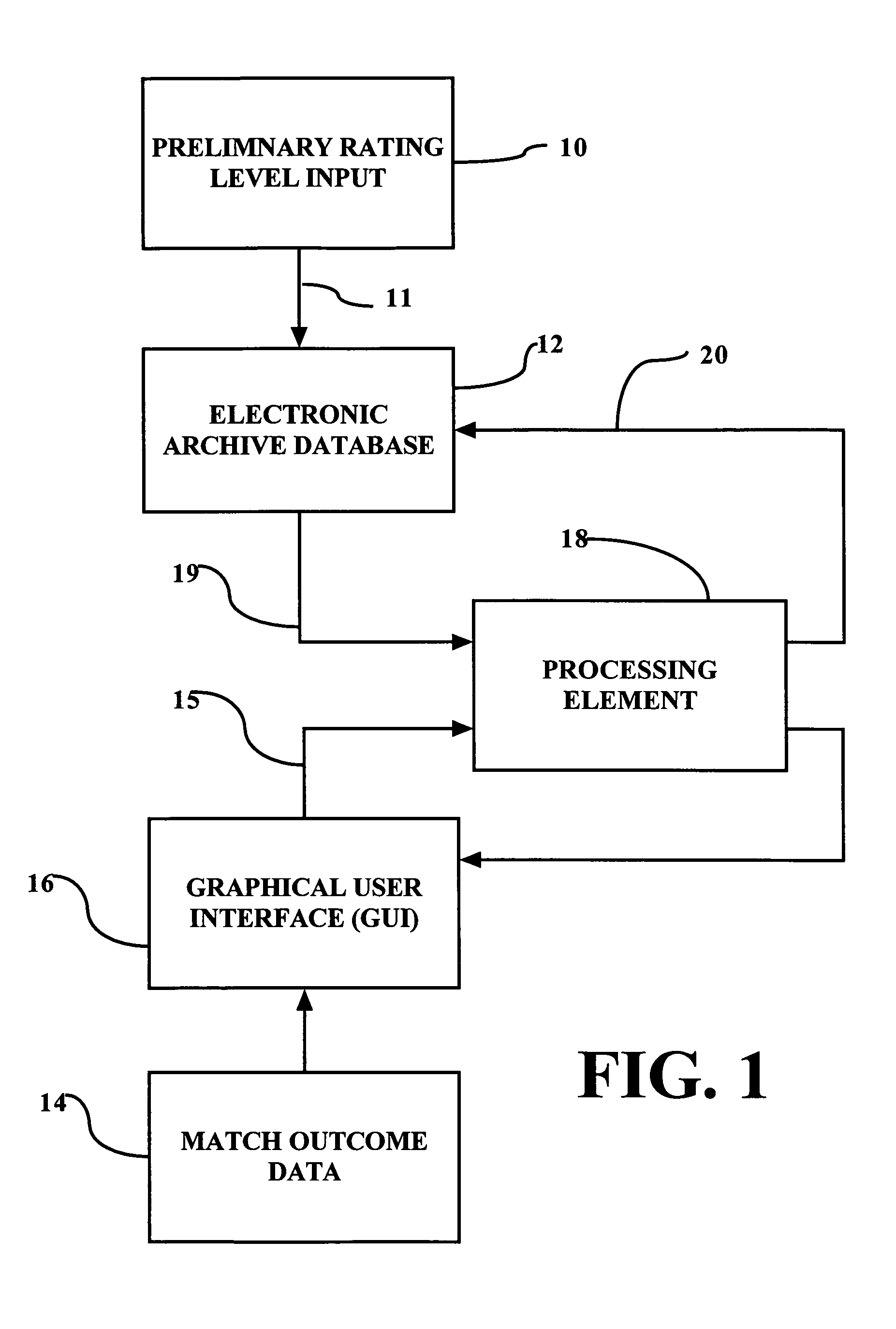
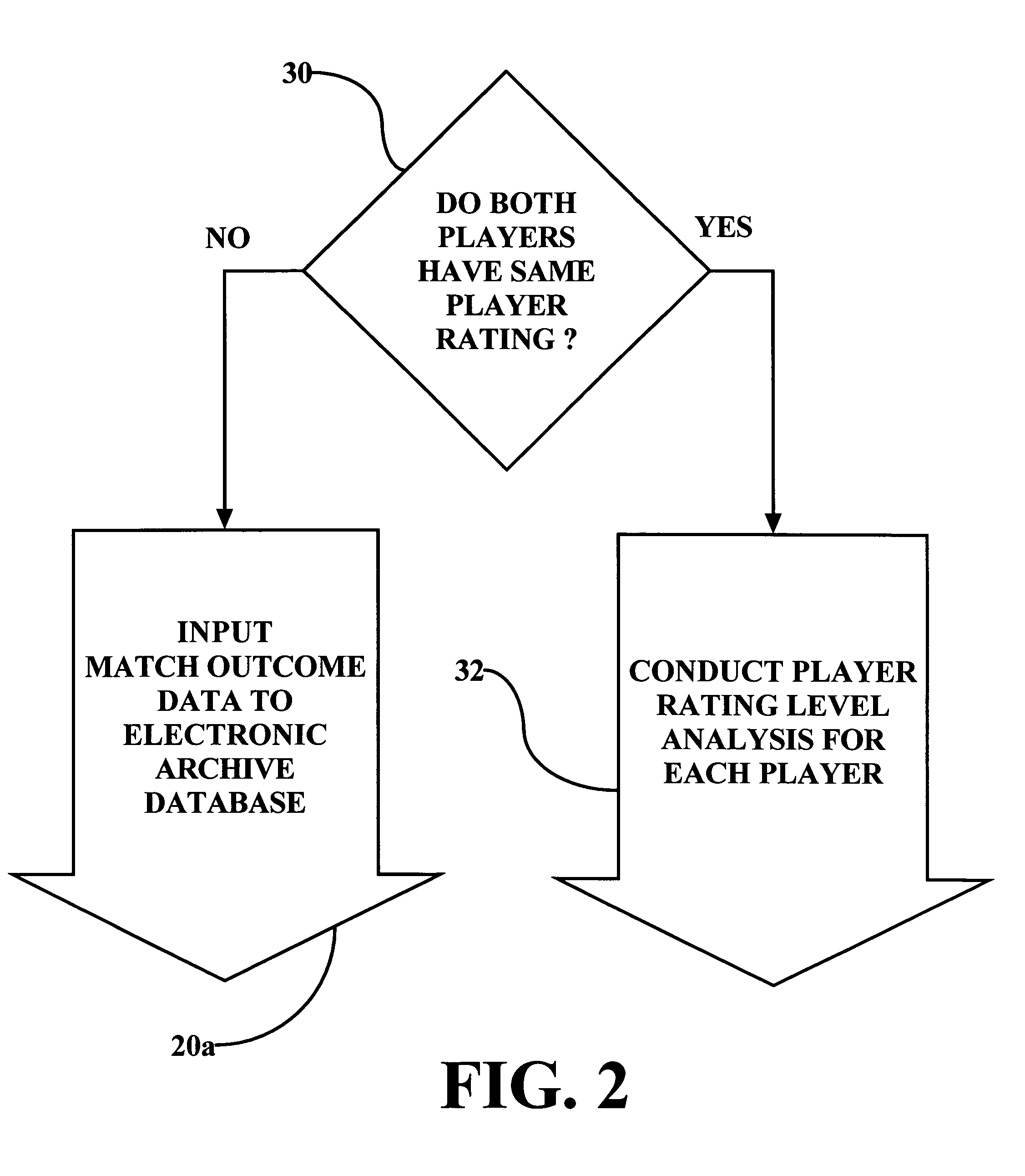
System, method and computer program product for determining a tennis player rating
InactiveUS7813821B1Improve playback experienceAccurately reflectVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsRating systemEngineering
Systems, methods and computer program products for determining a player rating for at least one tennis player enhances the tennis playing experience of by matching tennis players of comparable tennis skills. The methodology comprises assigning numerical player ratings generally corresponding to each player's individual tennis skill level. A competitive threshold is established, corresponding to a minimum number of games that a player must win in a match between players having the same player rating. A player is considered to be competitive within a rating level, regardless of whether the player wins or loses matches, provided the player wins at least the minimum number of games that corresponds to the established competitive threshold. Adjustments are made to a player's rating only if / when the player has a sustained record of “non-competitive” matches with similarly rated players.
Owner:HOWELL DAVID
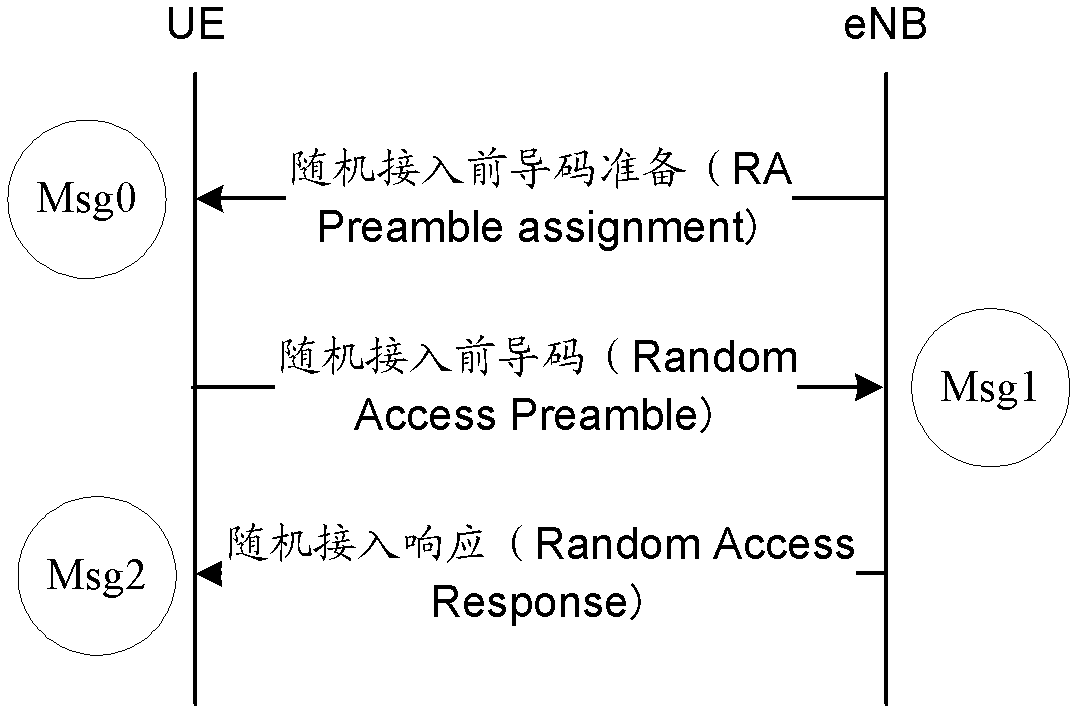
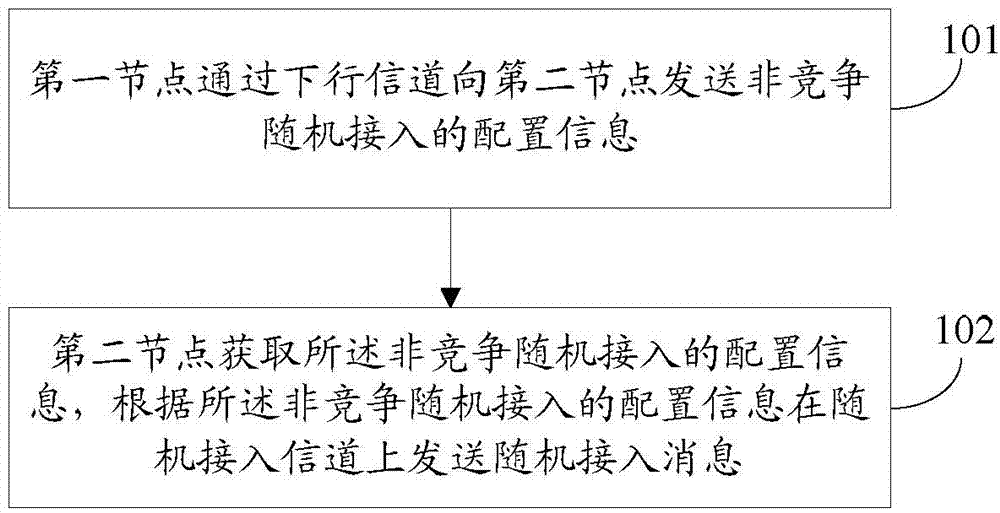
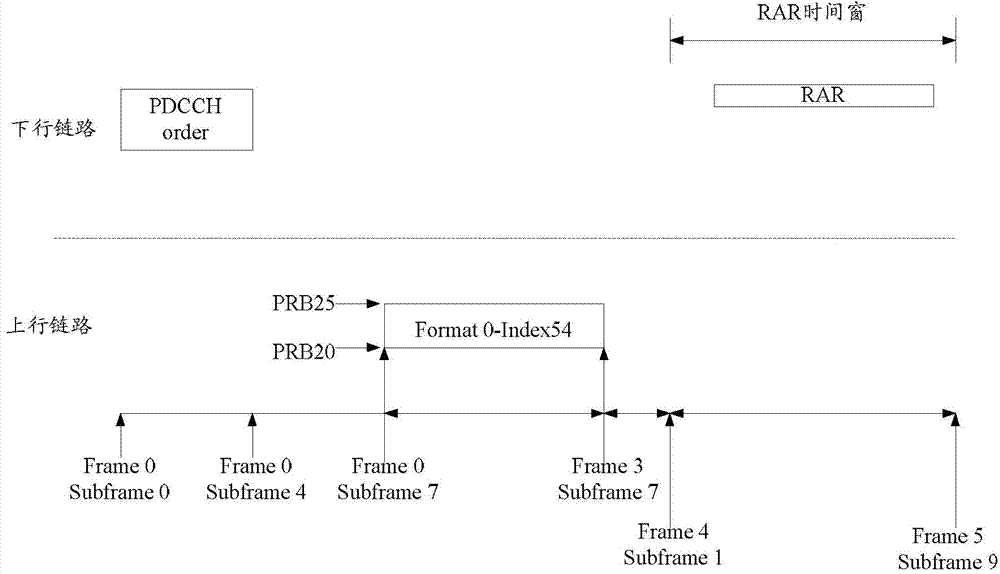
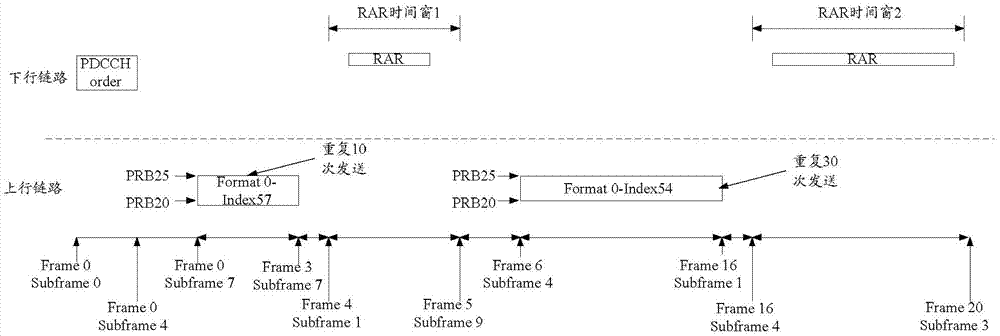
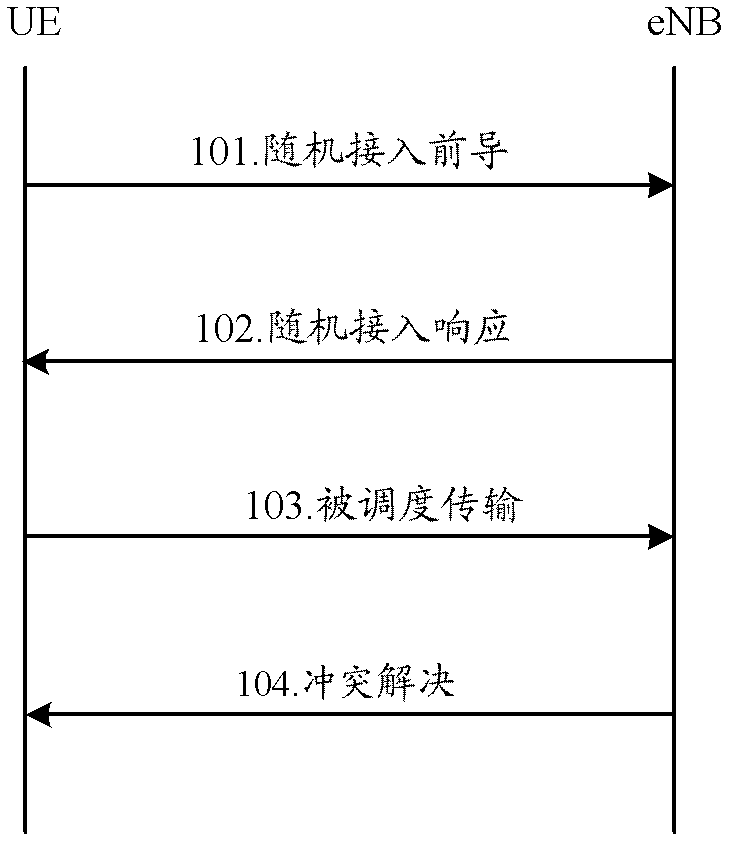
Random access and random access control methods and devices, and random access system
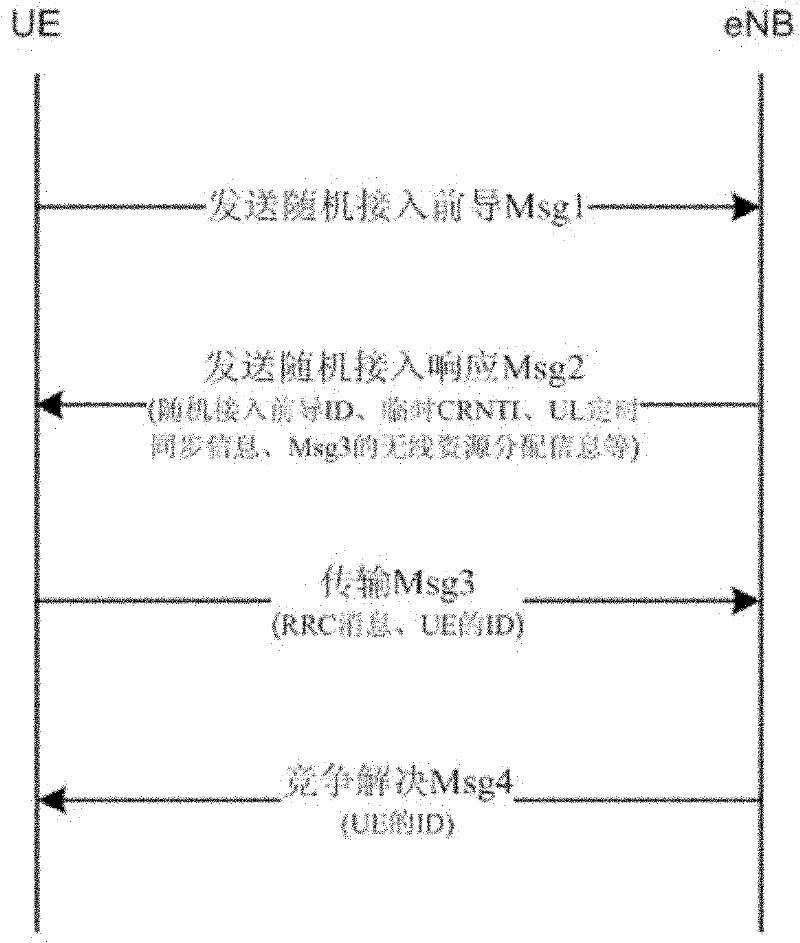
The invention discloses a random access method, a random access control method, a random access device, a random access control device and a random access system, and aims to realize random access through secondary cells. The random access method for a terminal side comprises the following steps of: receiving a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) instruction of initiating non-competitive random access on a specified secondary cell from a base station by using user equipment (UE), wherein the PDCCH instruction comprises a special preamble number and a physical random access channel (PRACH) resource indication; transmitting a special preamble corresponding to the special preamble number on the secondary cell by utilizing indicated PRACH resources; and performing cell radio network temporary identifier (C-RNTI)-scrambled PDCCH blind detection in a UE specific search space within a determined set time bucket, determining that the random access succeeds if an Msg2 scheduled by a PDCCH is obtained within the set time bucket, and determining that the random access fails if the Msg2 scheduled by the PDCCH is not obtained within the set time bucket.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TELECOMM TECH
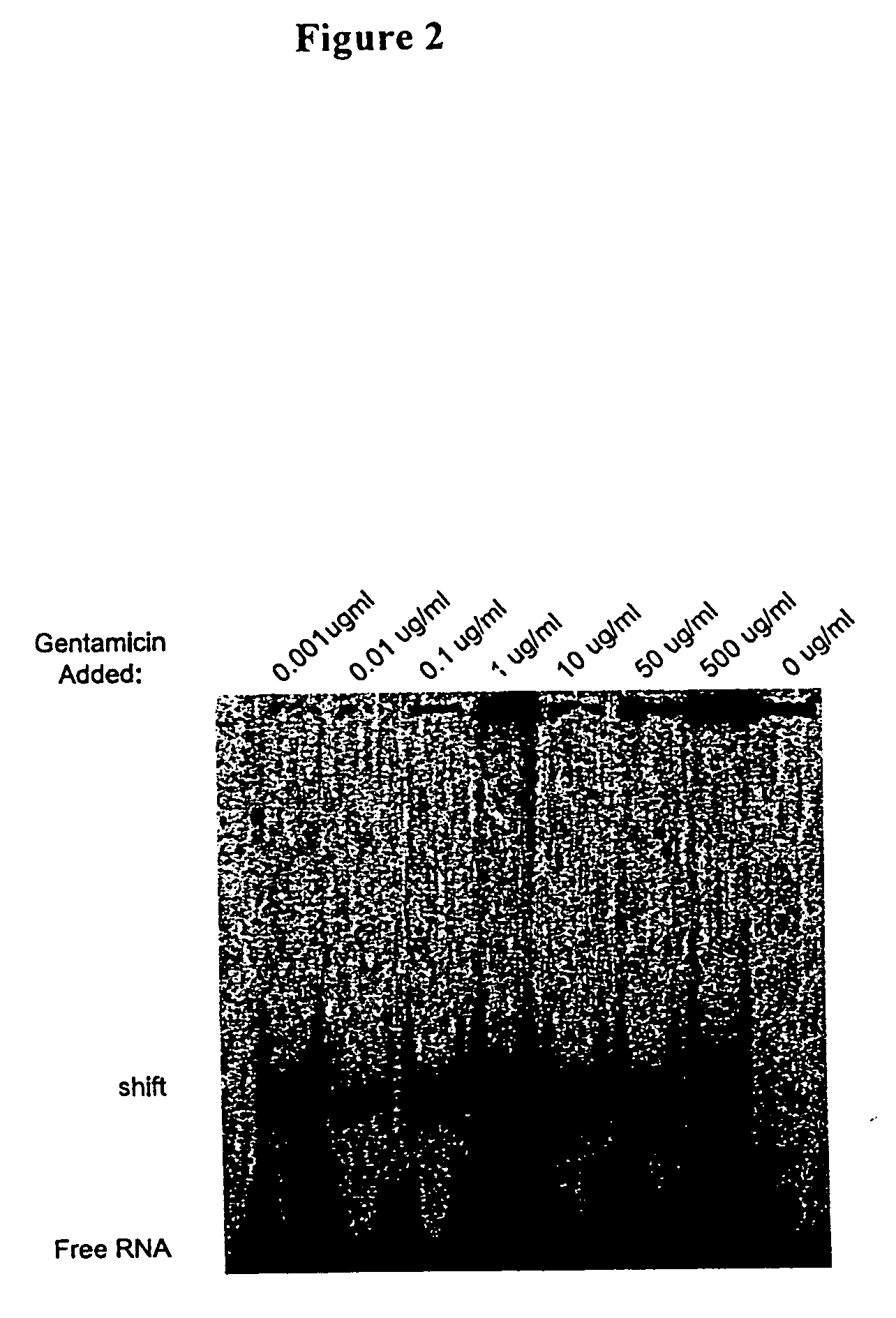
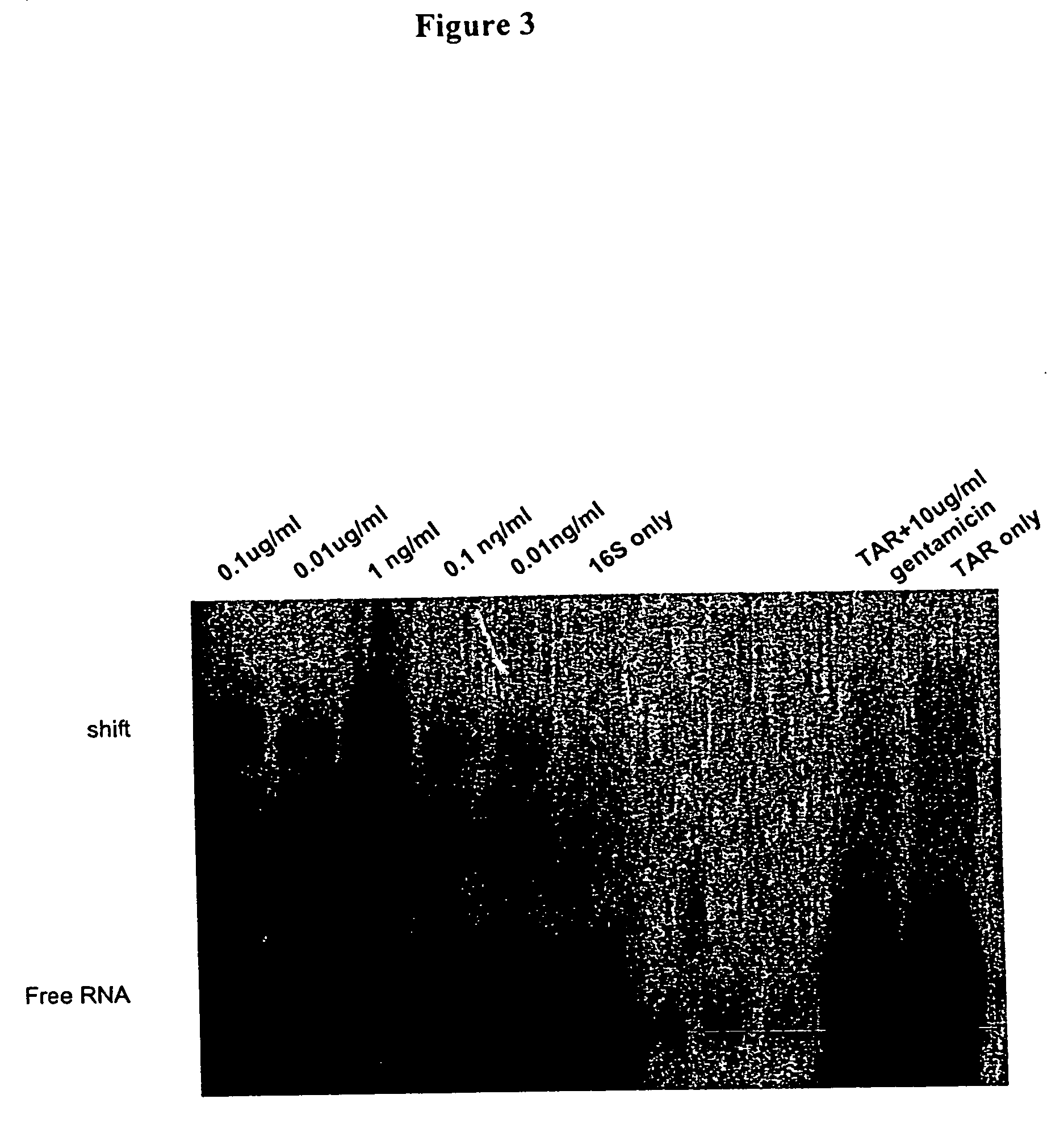
Reducing leukocyte interference in non-competitive immunoassays
ActiveUS20110117580A1Reducing and eliminating leukocyte interferenceReducing leukocyte interferenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteWhite blood cell
The invention is directed to methods and devices for reducing interference from leukocytes in an analyte immunoassay, and in particular in non-competitive immunoassays. In one embodiment, the invention is to a method comprising the steps of (a) amending a biological sample such as a whole blood sample with sacrificial beads; and (b) performing a non-competitive immunoassay on the amended sample to determine the concentration of said analyte in said sample. Preferably, the sample is amended with IgG-coated sacrificial beads.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Non-competitive random access method and equipment on secondary cell (SCell)
The invention discloses non-competitive random access method and equipment on a secondary cell (SCell). The method comprises the following steps: a network side notifies UE (user equipment) to initiate non-competitive random access on the SCell; the network side receives a special preamble from the UE; and the network side sends the scheduling information carrying TA (timing alignment) value information to the UE through the search space of a non-SCell public search space of the UE. In the embodiment of the invention, the UE can initiate a non-competitive random access process on the SCell; and moreover, the UE can finish the random access process on the premise of not monitoring the PDCCH (physical downlink control channel) of the SCell public search space, and can obtain the TA information on the SCell.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
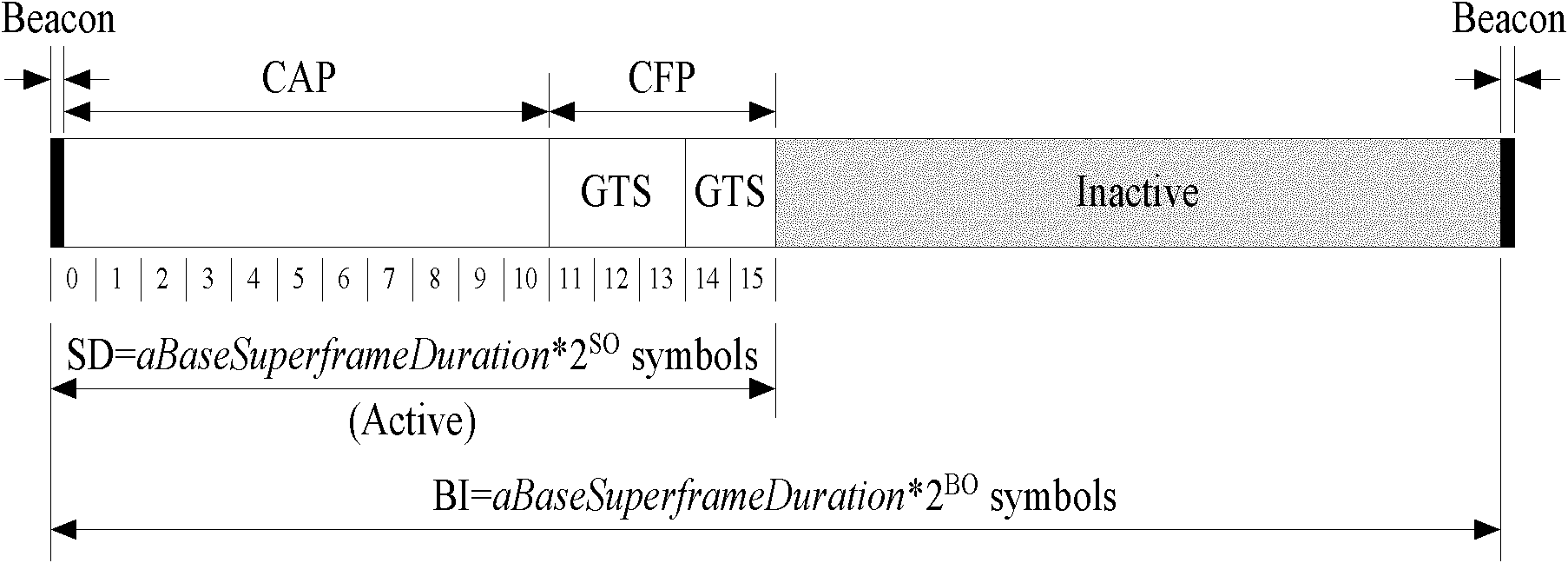
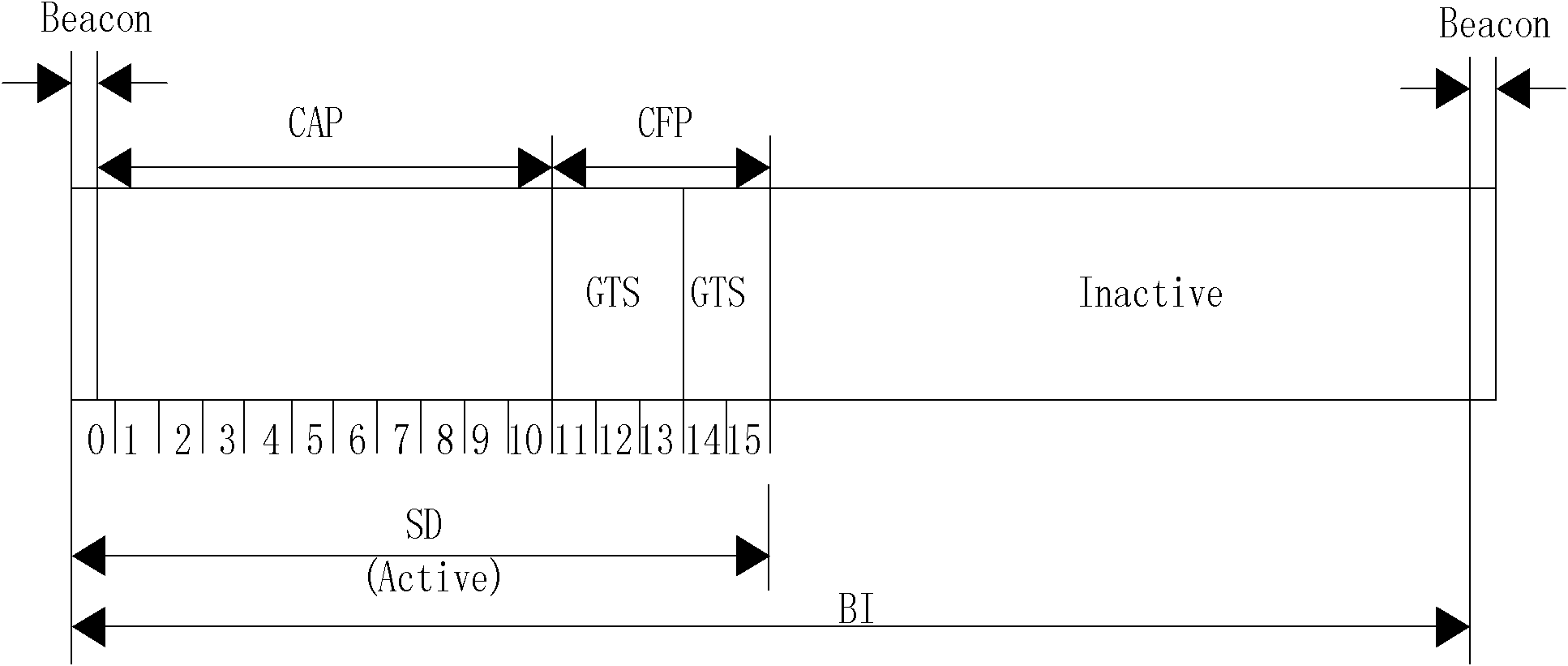
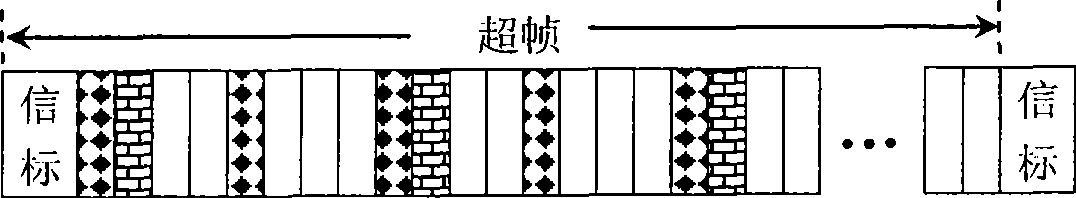
Superframe-based efficient media access control method in wireless body area network
ActiveCN102123515AIncrease success rateImprove performanceWireless communicationBody area networkAloha
The invention discloses a superframe-based efficient media access control method in a wireless body area network, mainly solving the problems that an IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers) 802.15.4 protocol is incapable of distinguishing service priorities and has time slot waste in a non-competitive period in a wireless body area network. The superframe-based efficient media access control method is realized by adopting the steps of: in a competitive period, setting the competitive period into a high priority service dedicated time slot H, a high priority service spare time slot h and a common time slot by adopting a time slot ALOHA competition mechanism based on the service priority, wherein a common node adopts the three different competition mechanisms according to the quantity of high priority services in the current superframe competitive period; and in a non-competitive period, ensuring that allocation and utilization of a GTS (Guarantee Time Slot) service are carried out by utilizing a micro time slot as a unit and adopting a micro time slot mechanism so as to realize the effective utilization of the time slot. Compared with the IEEE 802.15.4 protocol, thesuperframe-based efficient media access control method disclosed by the invention can not only ensure that the high priority service is transmitted with a higher success probability, but also effectively improve the time slot utilization ratio in the non-competitive period and is suitable for the wireless body area network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
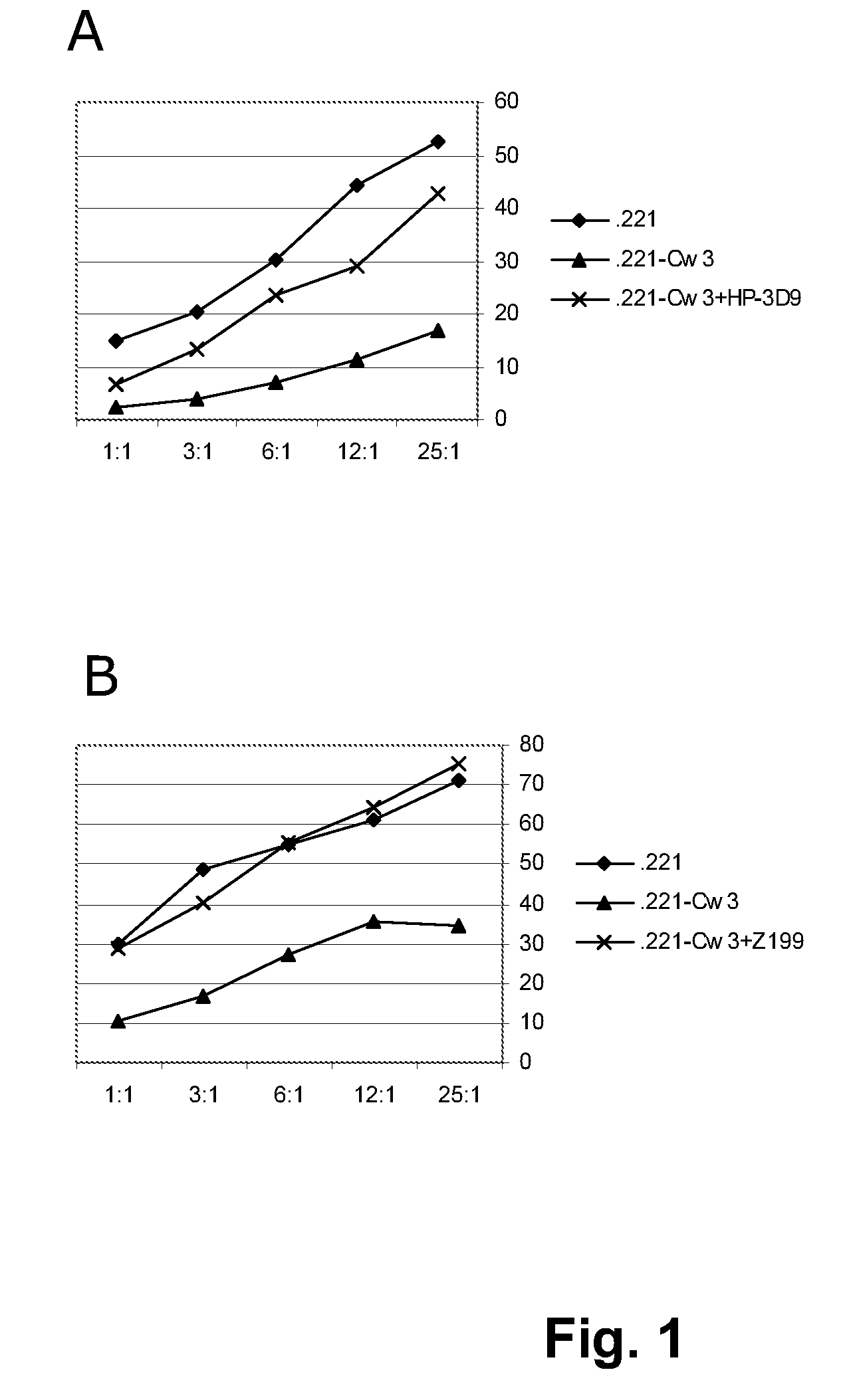
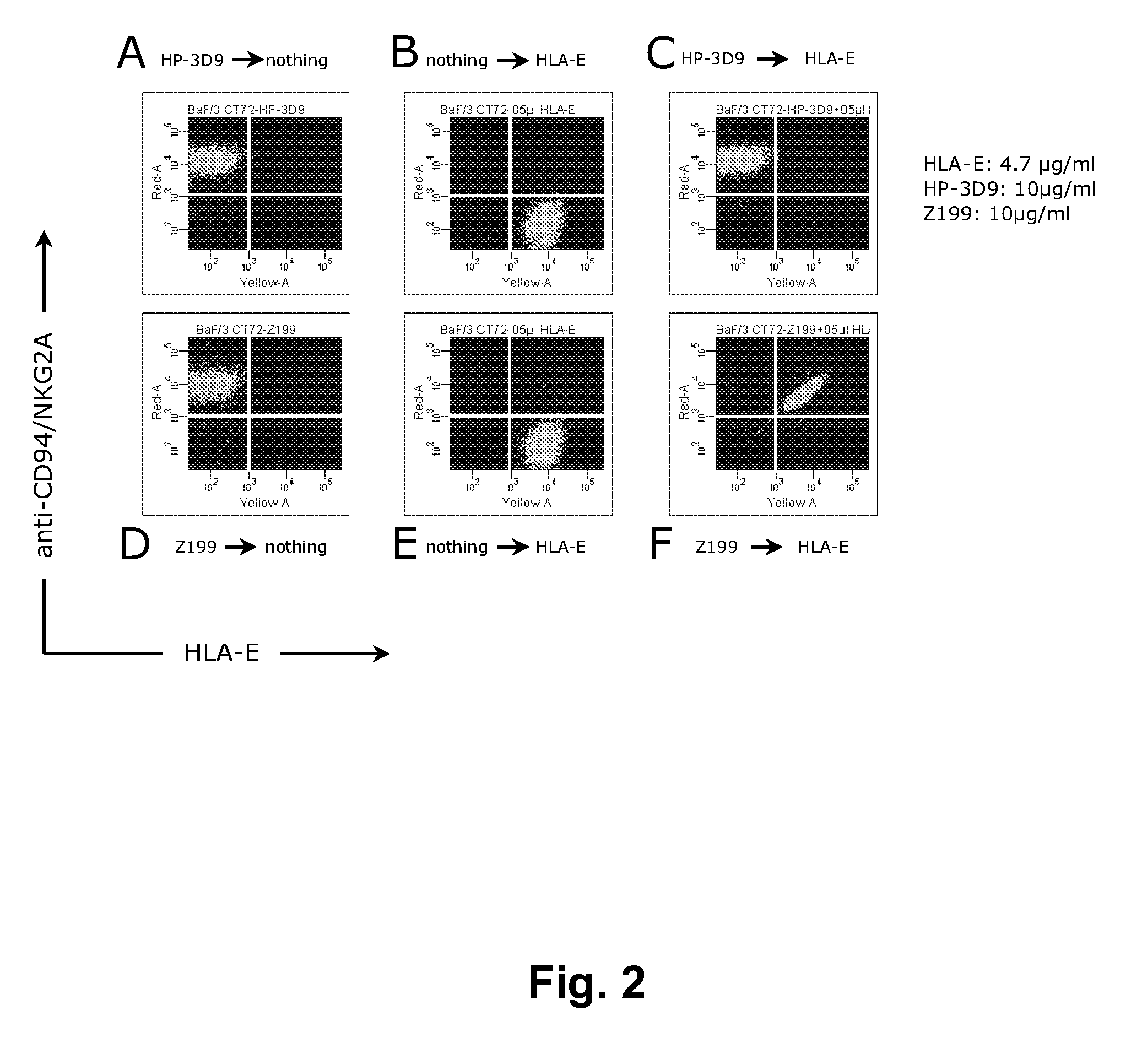
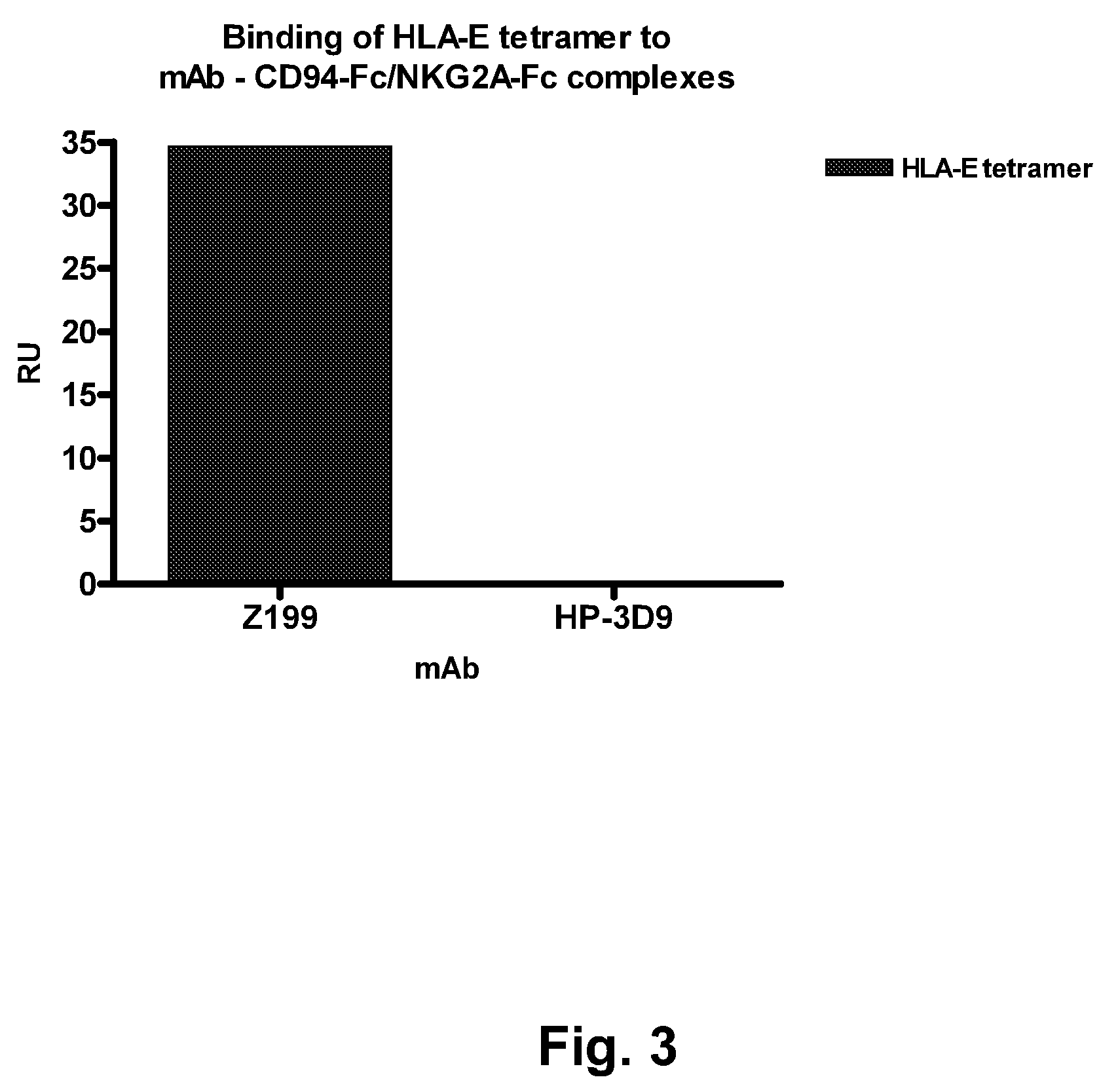
Humanized anti-human NKG2A monoclonal antibody
ActiveUS8796427B2Improved propertyLow immunogenicityAntipyreticAnalgesicsMonoclonal antibodyNon competitive
The present invention relates to agents that are non-competitive antagonists of the CD94 / NKG2A receptor such as certain anti-NKG2A antibodies, in particular humanized versions of murine anti-NKG2A antibody Z199, as well as methods of producing and using such agents and antibodies.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Non-competitive random access method, node device and system
ActiveCN104780617AImprove random access performanceReduce access delayNetwork traffic/resource managementRandom-access channelNon competitive
Disclosed are a non-contention random access method, a node, a system, and a computer storage medium. The non-contention random access method comprises: a first node sending configuration information of non-contention random access to a second node through a downlink channel; and the second node obtaining the configuration information of non-contention random access, and sending an random access message over a random access channel according to the configuration information.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Self-adaptive low-delay media access control method in WBAN (wireless body area network)
InactiveCN102026099AAdd supportImplement Adaptive SupportEnergy efficient ICTPower managementBody area networkTime delays
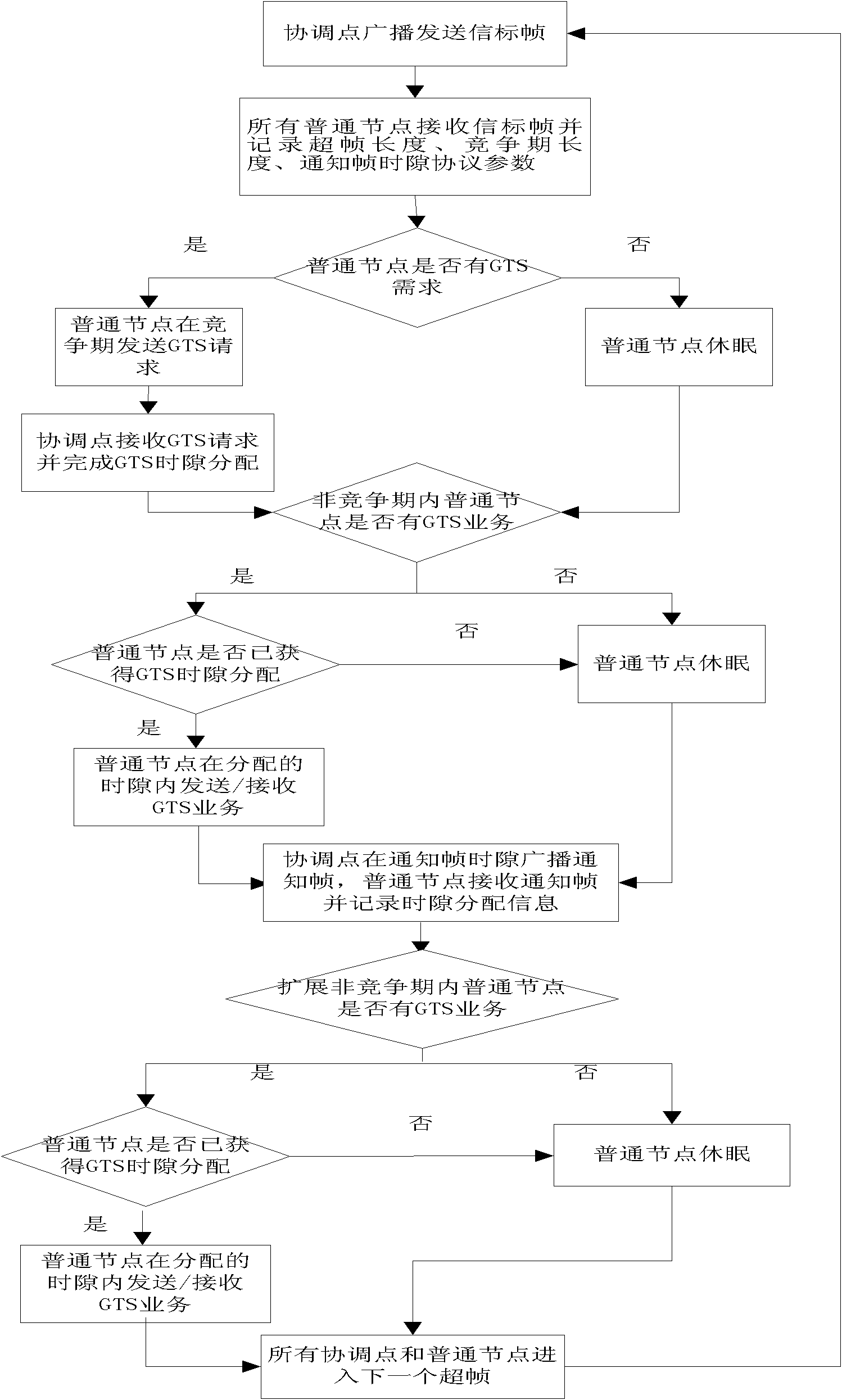
The invention discloses a self-adaptive low-delay media access control method in a WBAN (wireless body area network), mainly solving the problem that a GTS (guaranteed time slot) slot can not realize self-adaptive distribution and has long time delay for ensuring time slot service when IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers) 802.15.4 is applied to the WBAN. The self-adaptive low-delay media access control method comprises the following realization steps: a coordinating point receives the GTS request of a common node in a competitive period, an inactive period is compressed to expand a non-competitive period, and the GTS time slot is dynamically distributed according to amount requested by GTS; the common node of the obtained GTS time slot finishes GTS service transmission with the coordinating point in the non-competitive period; the coordinating point broadcasts and sends a notification frame in a notification frame time slot after the non-competitive period to notifythe common node to expand the time slot distribution of the non-competitive period; and the common node of the obtained GTS time slot finishes GTS service transmission with the coordinating point in the expanding non-competitive period. Compared with the IEEE 802.15.4, the self-adaptive low-delay media access control method can be used to realize the self-adaptive distribution of the GTS time slot, lower the delay of GTS service grouping, reduce the energy consumption of the coordinating point and is suitable for the WBAN.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Virtual lead code based random access method of wireless mobile broadband system
InactiveCN101990311AImprove random access success rateReduce random access delayWireless communicationTime delaysRandom access memory
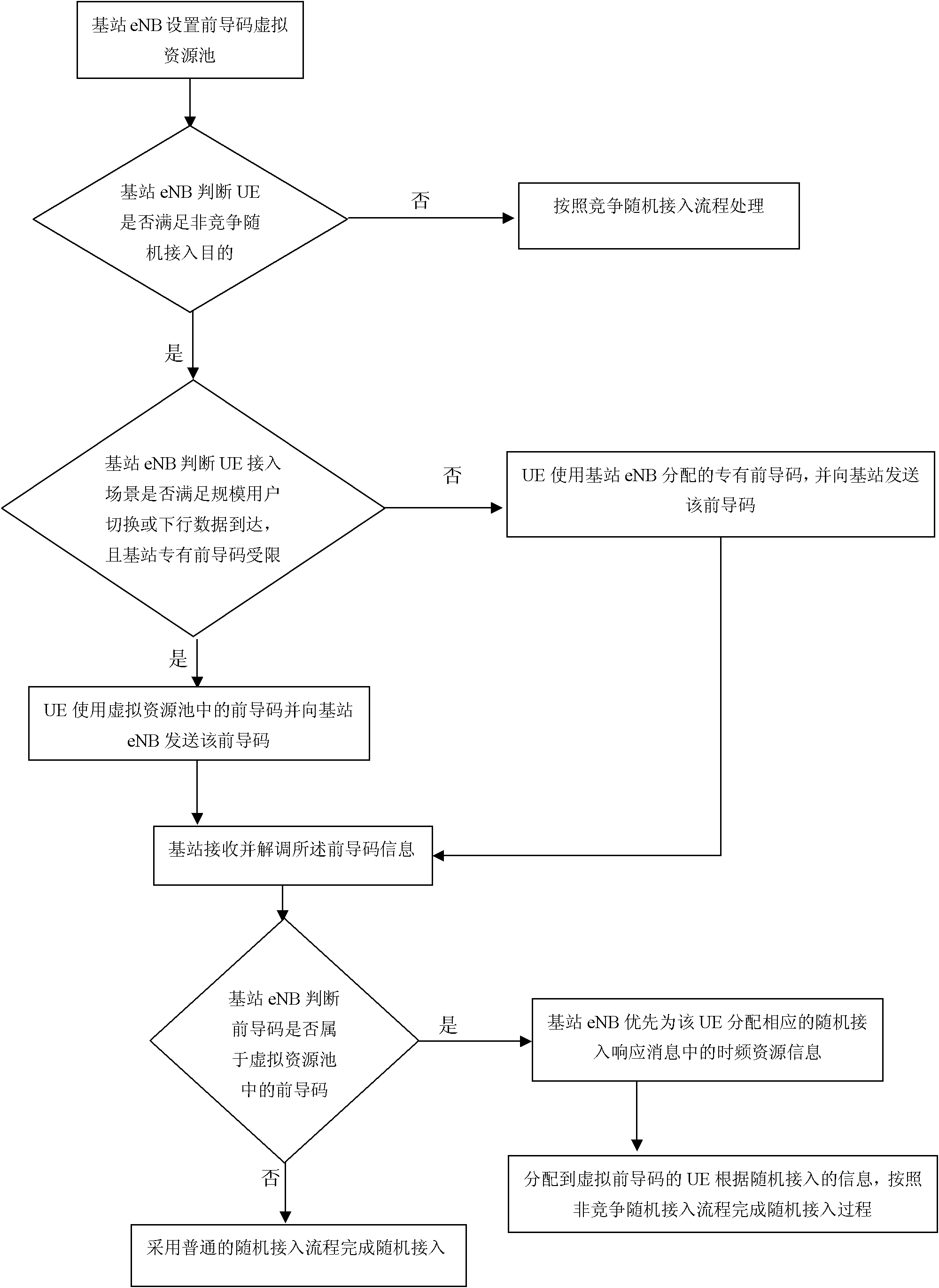
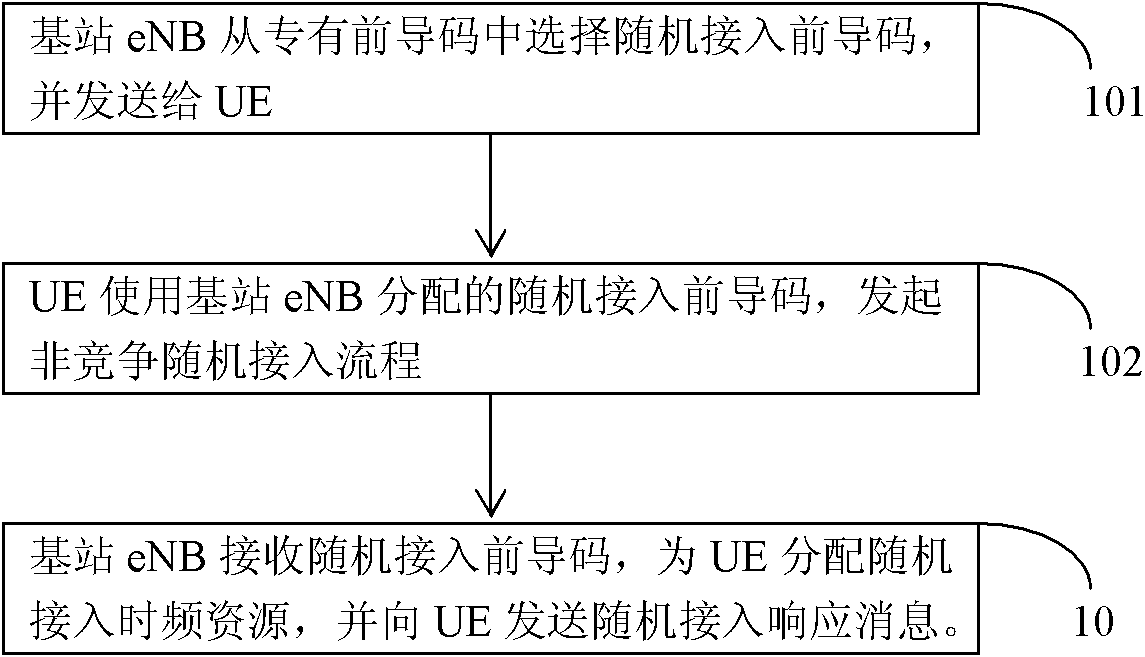
The invention relates to a virtual lead code based random access method of a wireless mobile broadband system. The method comprises the following steps: a base station sets a front lead code virtual resource tank and selects a lead code for a UE (User Equipment) meeting a non-competitive random access scene from a dedicated lead code package or a virtual resource tank; the UE transmits the distributed lead code to the base station in a corresponding random access channel; the base station judges whether the received lead code belongs to the virtual resource tank or not, if so, the corresponding time frequency resource information is distributed for the UE preferentially, and otherwise, ordinary random access flow is used for completing the random access; and the UE distributed with the virtual lead code finishes the random access process by the non-competitive random access flow according to the distributed time frequency resource information. The invention has simple and reliable method, does not need to physically change the base station or change the LTE (Long-Term Evolution) protocol, overcomes the shortage of the traditional non-competitive random access method, improves the random access success rate of the UE and reduces the random access time delay of the UE.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
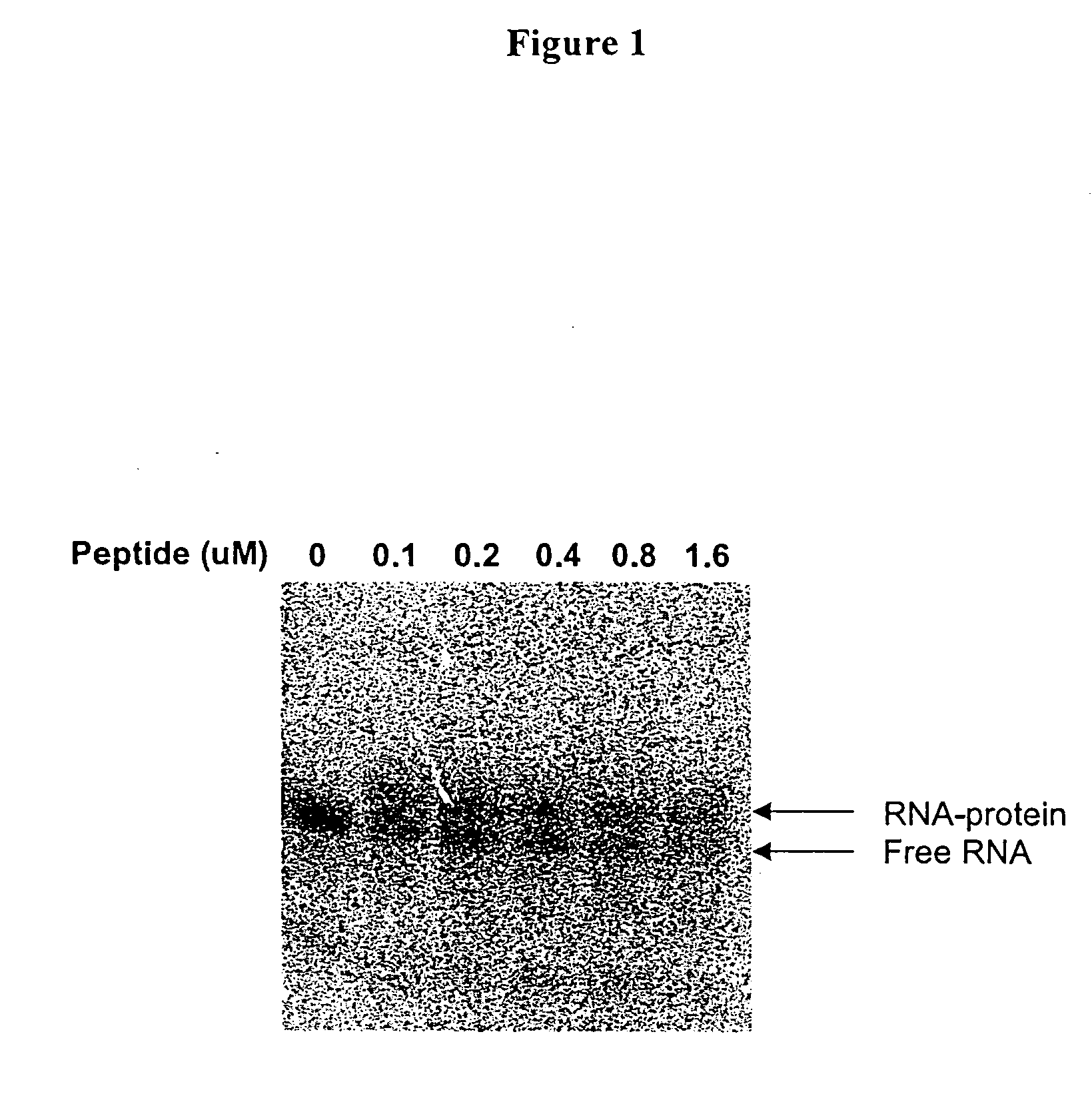
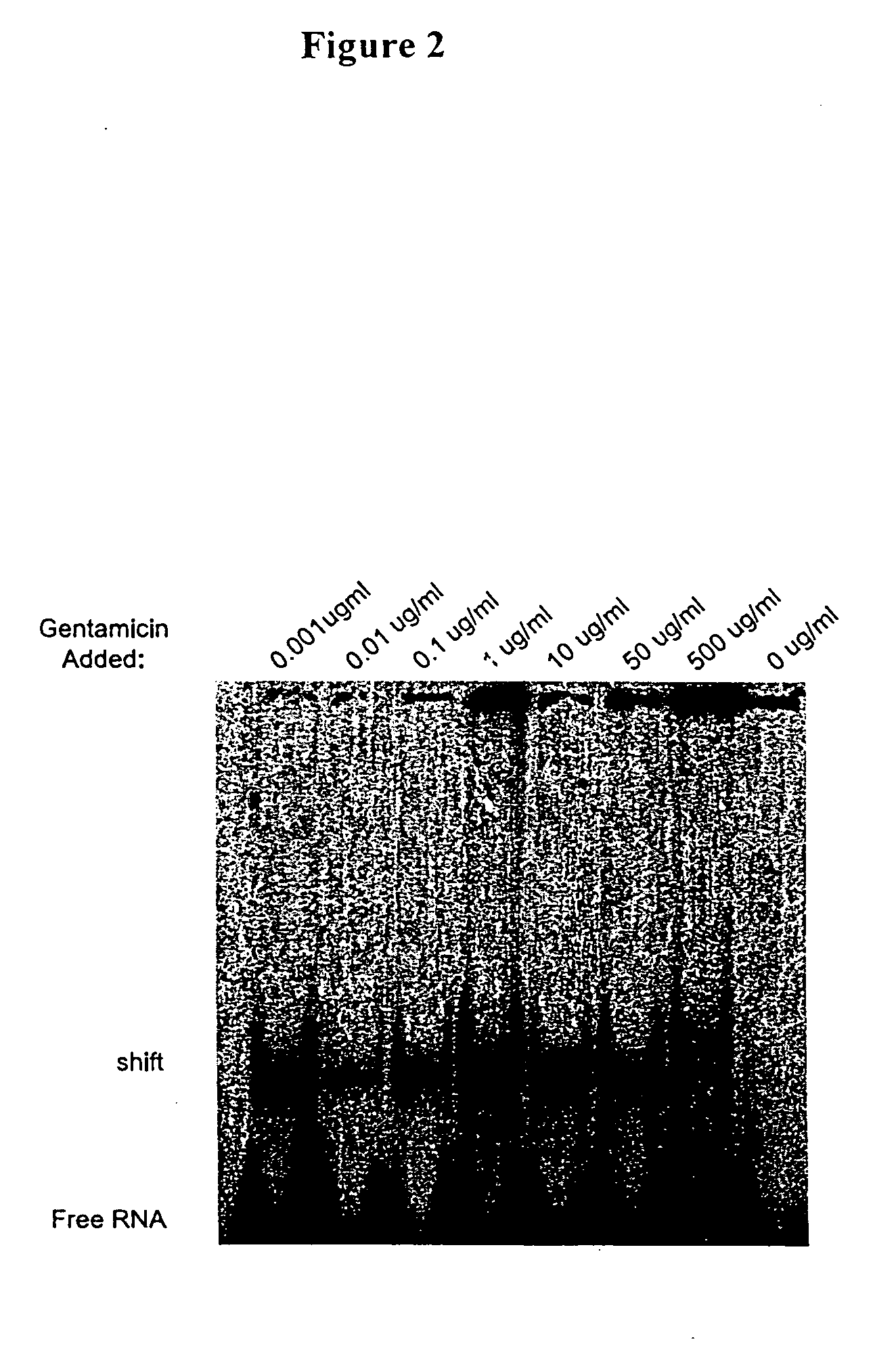
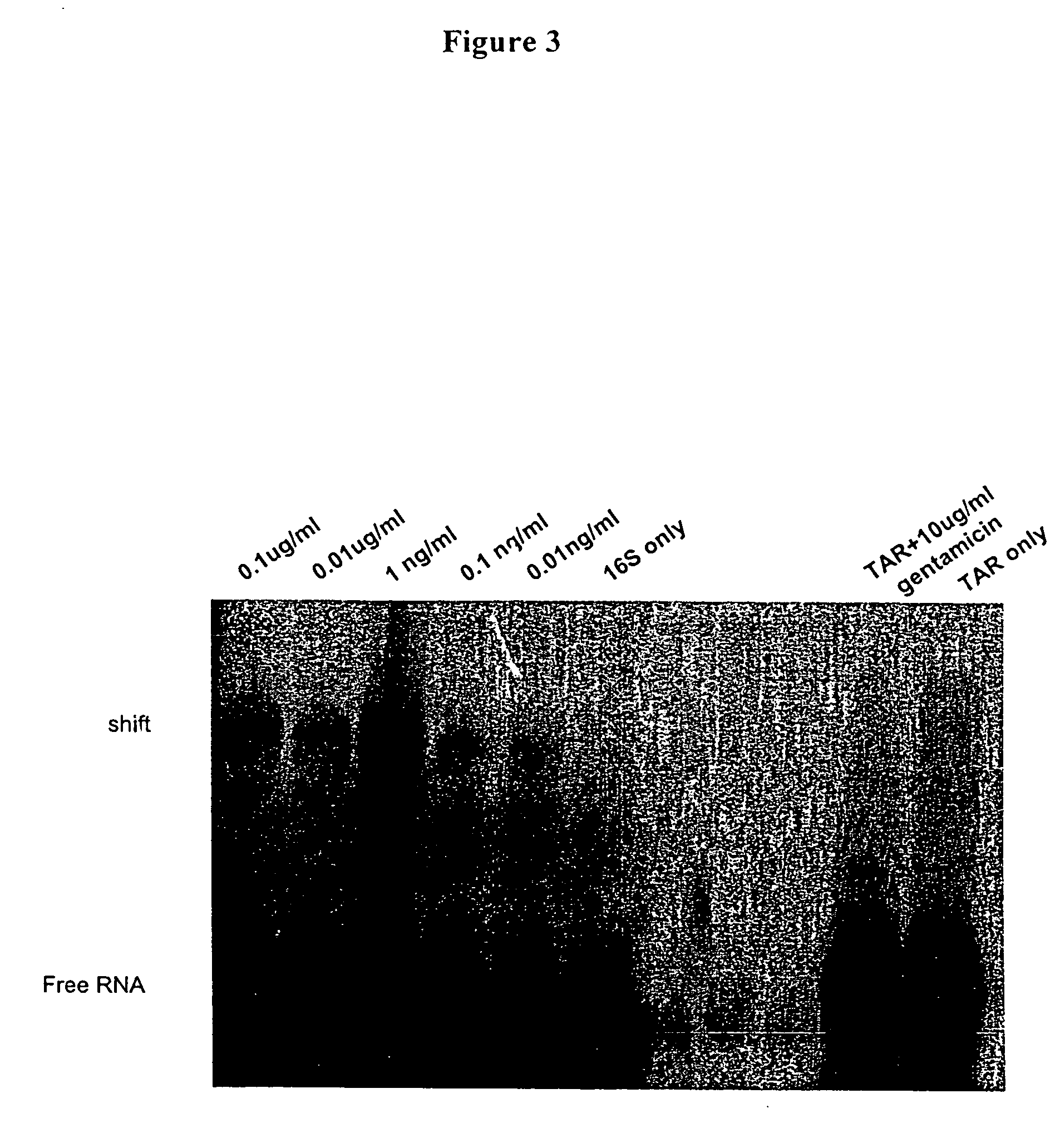
Methods for identifying small molecules that bind specific rna structural motifs
InactiveUS20040219545A1Easy to identifyEliminate biasMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsBiology
The present invention relates to a method for screening and identifying test compounds that bind to a preselected target ribonucleic acid ("RNA"). Direct, non-competitive binding assays are advantageously used to screen libraries of compounds for those that selectively bind to a preselected target RNA. Binding of target RNA molecules to a particular test compound is detected using any physical method that measures the altered physical property of the target RNA bound to a test compound. The structure of the test compound attached to the labeled RNA is also determined. The methods used will depend, in part, on the nature of the library screened. The methods of the present invention provide a simple, sensitive assay for high-throughput screening of libraries of compounds to identify pharmaceutical leads.
Owner:RANDO ROBERT F +1
Methods of treating tardive dyskinesia and other movement disorders
InactiveUS7498361B2Decreases postsynaptic responseSpread the wordBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorAcamprosate
The present invention describes a novel treatment for movement disorders, including tardive dyskinesia, tic disorders, Tourette's syndrome, and blepharospasm, and other focal dystonias. The treatment of the present invention utilizes agents that simultaneously act as NMDA-type glutamate receptor antagonists and GABA-A receptor agonists. Preferably these two activities are characteristic of a single agent, for example acamprosate. Alternatively, separate agents having these activities can be combined and administered together. The invention also provides a third agent that acts as a non-competitive NMDA-receptor blocking agent or ion channel blocker that augments the effect of the primary treatment. A particularly preferred ion channel blocking agent is magnesium. Alternatively, magnesium can be administered alone for prevention and treatment of movement disorders.
Owner:SYNCHRONEURON
Hybrid media access control method based on collaborative collision decomposition
InactiveCN101399833AIncrease delayGuaranteed service qualityData switching networksTime division multiple accessCode division multiple access
The invention discloses a mixed media access control method of a wireless network. System channels are of time slot, and time slots with fixed cycle are distributed to non-competitive business nodes, non-competitive business data frame is transmitted in the mode of time division multiple access. Competitive business nodes transmit competitive business data frame in the competitive time slots by using the method of random competitive access. After the competitive business data frames conflict, the competitive business nodes send the competitive business data frame again under the condition that the estimated gain value of the channels is more than or equal to a given threshold. Or else the competitive business data is forwarded by a relay node; an access point buffers the signals received before, and realizes the data frame separation by methods of serial interference cancellation and minimum mean-square error detection. At the same time, a superimposed pilot channel estimation method is used by the competitive business data, no additional time slot is needed in the method, thus being convenient for orthogonal design. The method is suitable for the unexpected properties of competitive businesses and the cyclical properties of non-competitive businesses, and the mixed transmission of the two businesses can be supported.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Short enzyme donor fragment
InactiveUS7135325B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFunctional activityOrganic compound
Short enzyme donor fragments of β-galactosidase are provided of not more than 40 amino acids, where the short fragments are used as a label and may be substituted with a wide variety of organic compounds, particularly polypeptides having independent functional activity. The enzyme donor finds use in competitive and non-competitive assays, monitoring intracellular events, or other processes where a sensitive non-interfering label is desired.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
System and method for encouraging competitive participation in an auction
Owner:INVENTOR HLDG
Methods for identifying small molecules that bind specific rna structural motifs
InactiveUS20050142545A1Easy to implementHigh throughput screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsAssay
The present invention relates to a method for screening and identifying test compounds that bind to a preselected target ribonucleic acid (“RNA”). Direct, non-competitive binding assays are advantageously used to screen bead-based libraries of compounds for those that selectively bind to a preselected target RNA. Binding of target RNA molecules to a particular test compound is detected using any physical method that measures the altered physical property of the target RNA bound to a test compound. The structure of the test compound attached to the labeled RNA is also determined. The methods used will depend, in part, on the nature of the library screened. The methods of the present invention provide a simple, sensitive assay for high-throughput screening of libraries of compounds to identify pharmaceutical leads.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
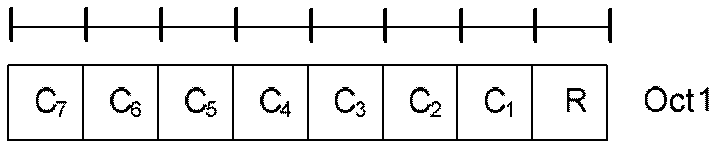
Configuration method and device for random access leading sequence
InactiveCN102685892AFully configuredIncrease profitWireless communicationAccess timeComputer science
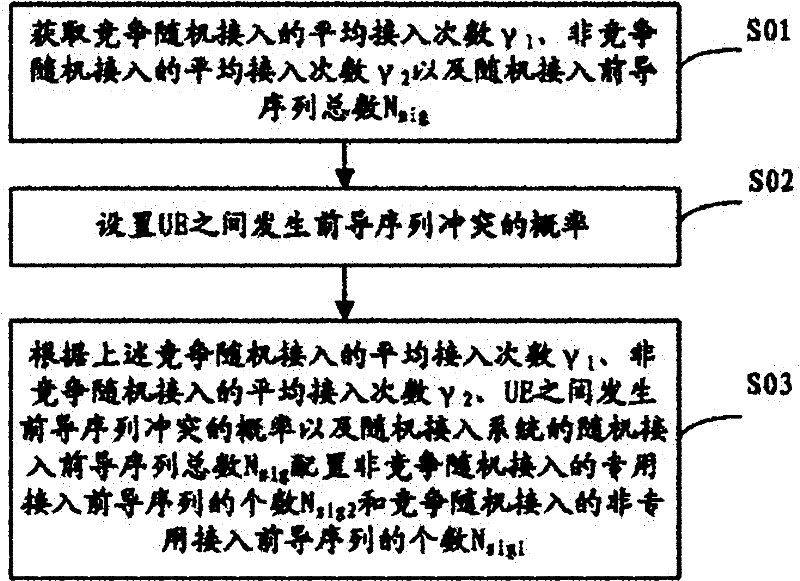
The invention discloses a configuration method and a configuration device for a random access leading sequence; the method comprises the following steps that: the average access times gamma 1 of competitive random access, the average access times gamma 2 of non-competitive random access and the total number Nsig of the random access leading sequence are acquired; the probability Prob_collision of leading sequence collision among user equipment (UE) is set; and the number Nsig2 of the special access leading sequence of the non-competitive random access and the number Nsig1 of the non-special access leading sequence of the competitive random access are configured according to the average access times gamma 1 of the competitive random access, the average access times gamma 2 of the non-competitive random access, the total number Nsig of the random access leading sequence and the probability Prob_collision of leading sequence collision among UE. Through the technical scheme of the invention, the leading sequence collision among the UE can be effectively reduced or prevented, so that the configuration of the random access leading sequence is more comprehensive.
Owner:深圳市恒程汇文化科技有限公司
Non-competitive immunoassay for small analytes
ActiveUS20060246506A1Rapid and reliable and simple immunoassayCost-effective and feasiblePeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningWAS PROTEINAnalyte
A non-competitive immunoassay for small analytes, wherein the analyte is reacted with two binding partners. The first binding partner binds to the analyte to form a complex between the first binding partner and the analyte, and the second binding partner binds to the complex formed by the first binding partner and the analyte. The resulting complex formed between the analyte and the binding partners is detected. The binding partners are proteins, such as antibodies including antibody fragments.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
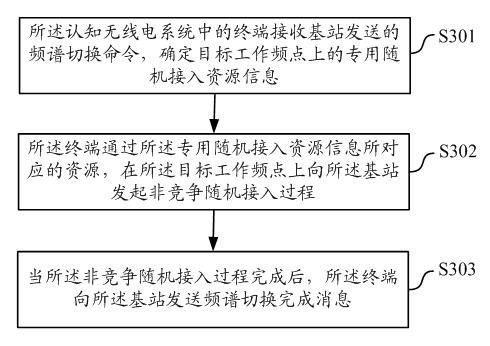
Spectrum switching method and equipment in cognitive radio (CR) system
InactiveCN102625387AReduce the probability of access failureLower latencyWireless communicationFrequency spectrumUser equipment
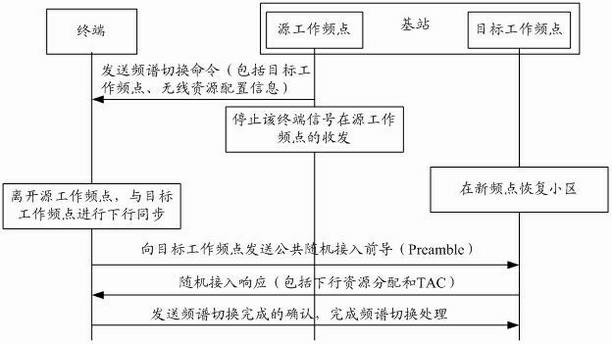
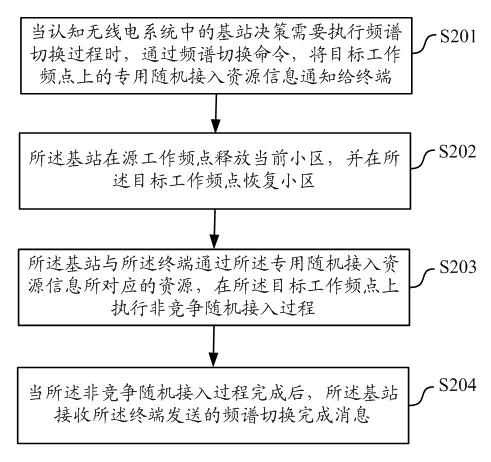
The invention discloses a spectrum switching method and equipment in a cognitive radio (CR) system. By adopting the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, in a CR system, a base station designates the dedicated random access resources on a target working frequency point required by a terminal in the spectrum switching process through a spectrum switching command; and the terminal executes a non-competitive random access process on the target working frequency point based on the dedicated random access resources, finishes uplink synchronization of the target working frequency point, and sends a spectrum switching completion message to the base station of the CR system. Since the dedicated random access resources among different terminals do not conflict, in the spectrum switching process, the terminal executes a non-competitive random access process on the target working frequency point by use of the dedicated random access resources after finding the target working frequency point, and the random access failure probability and delay on the target working frequency point can be reduced, thus the spectrum switching failure probability and the UE (user equipment) service interruption time are reduced, and the user experience of the CR system is improved.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TELECOMM TECH
Point-of-Care Immunoassay for Quantitative Small Analyte Detection
InactiveUS20130102003A1Fast and accurate determinationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementPoint of careAnalyte
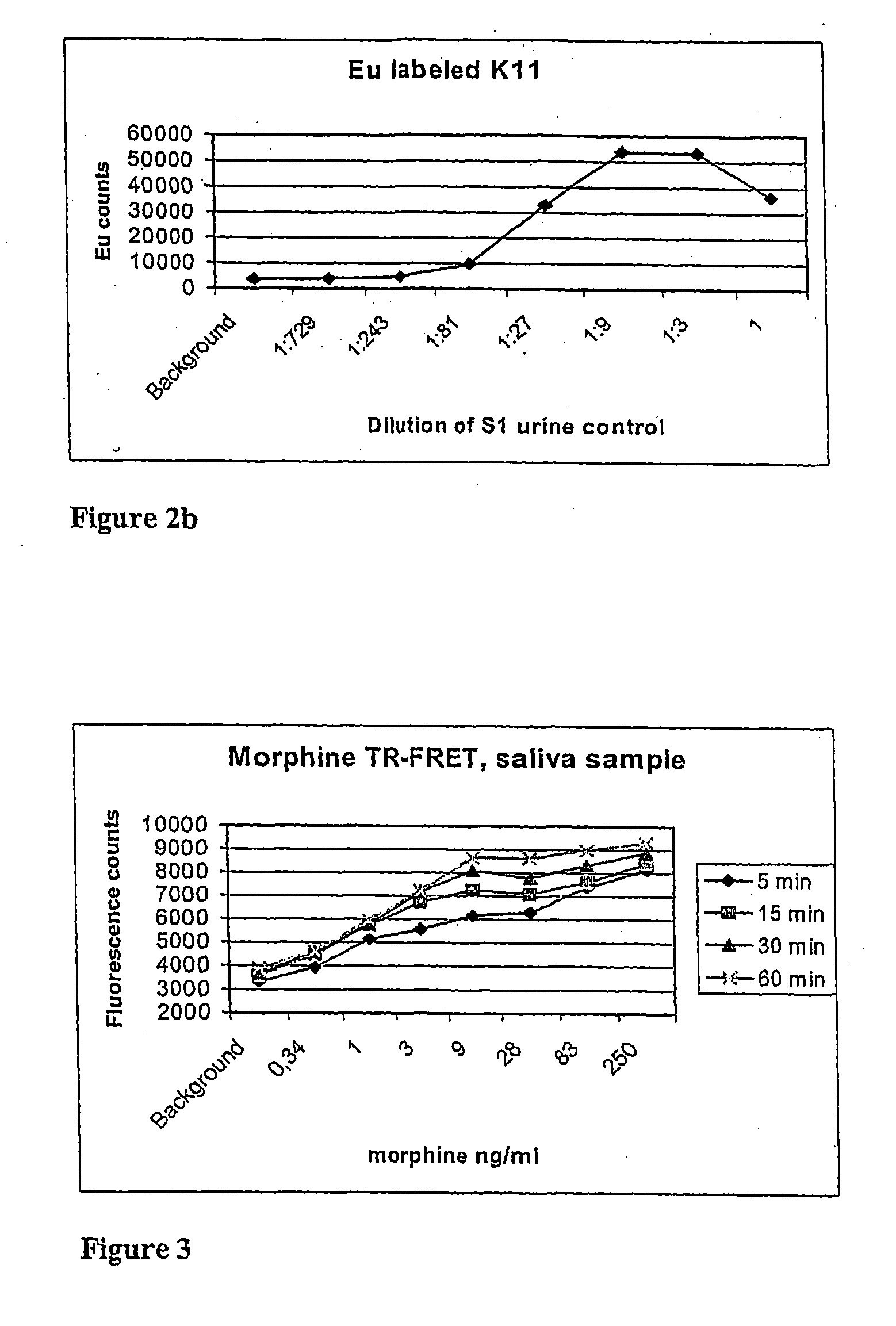
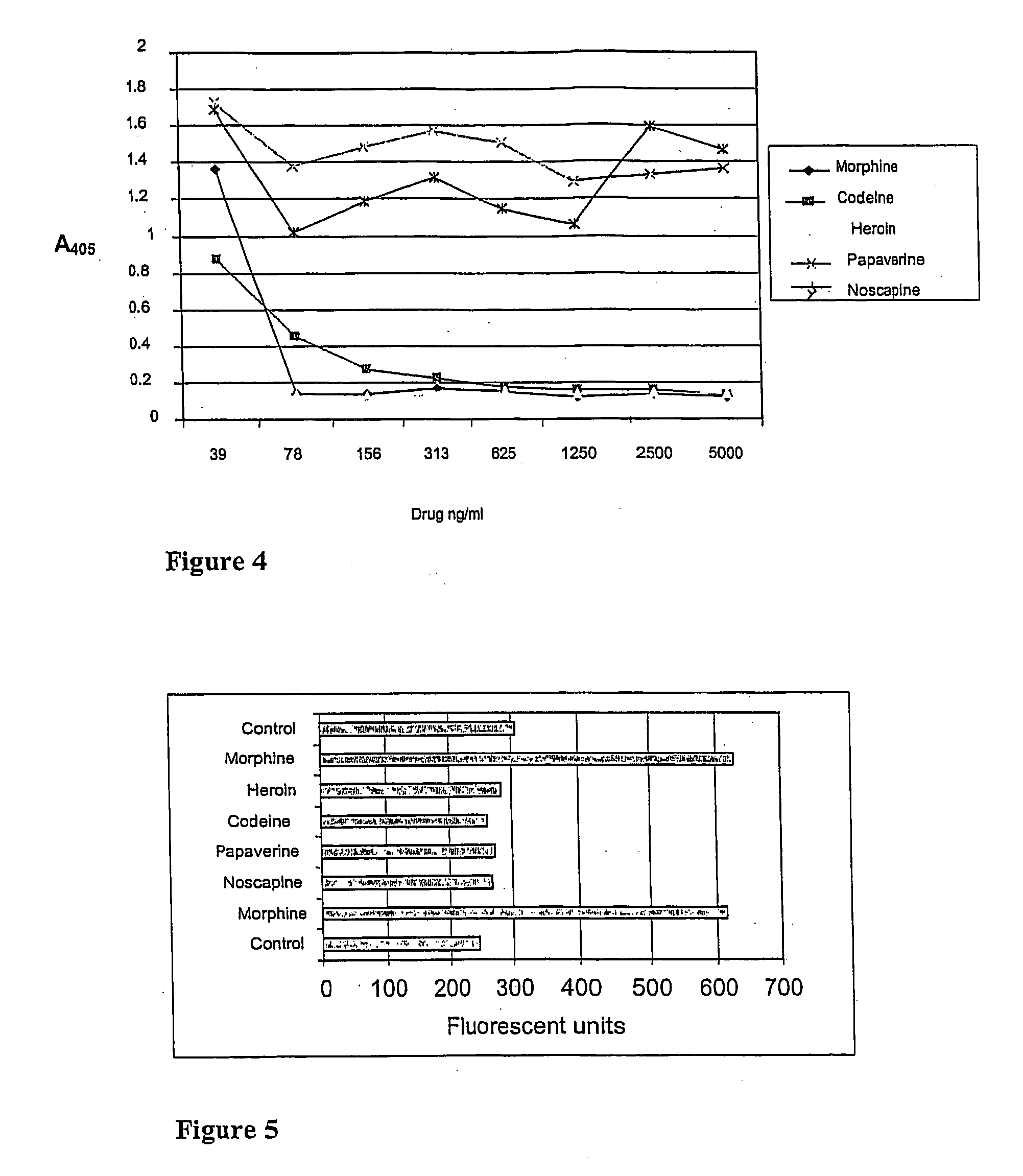
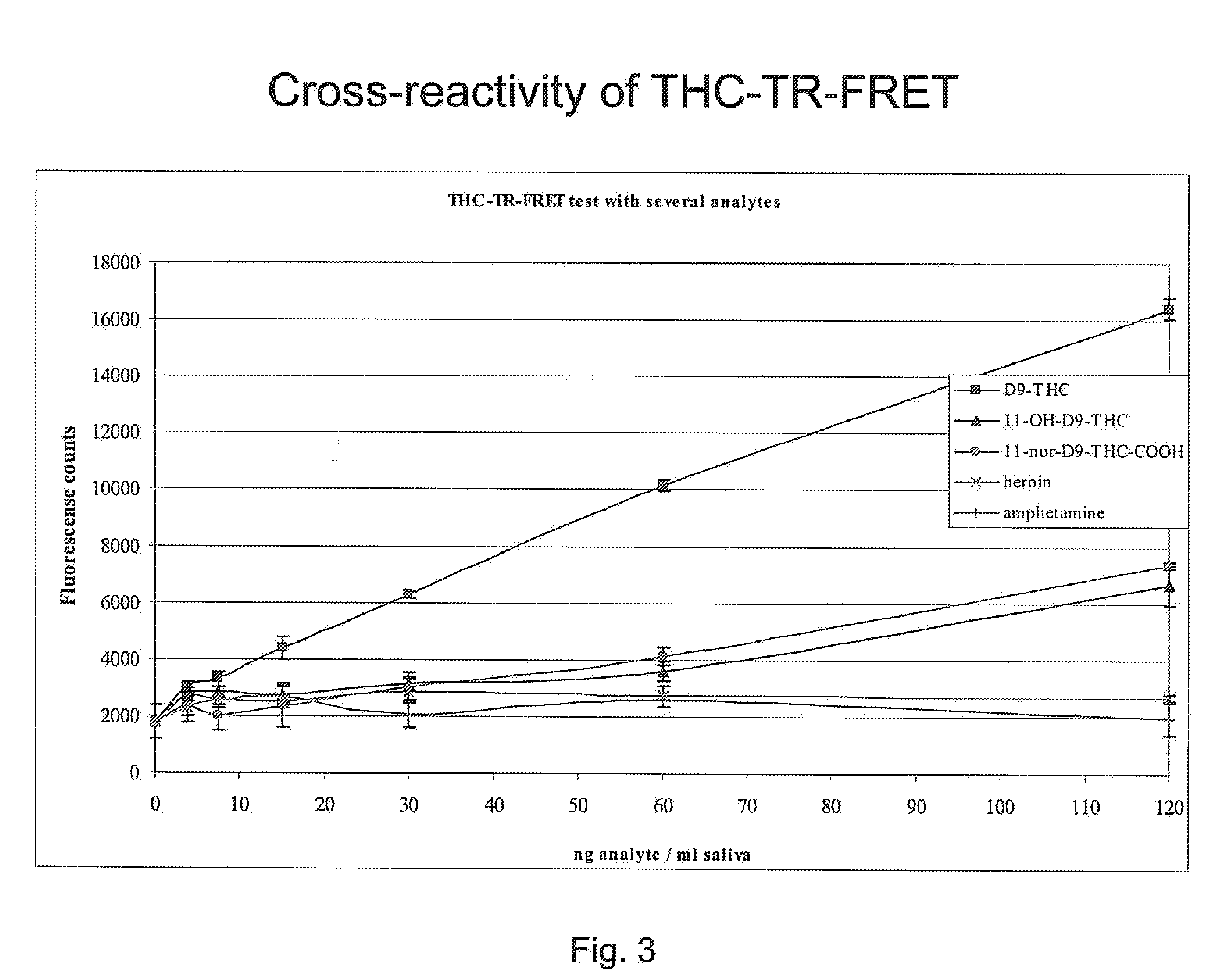
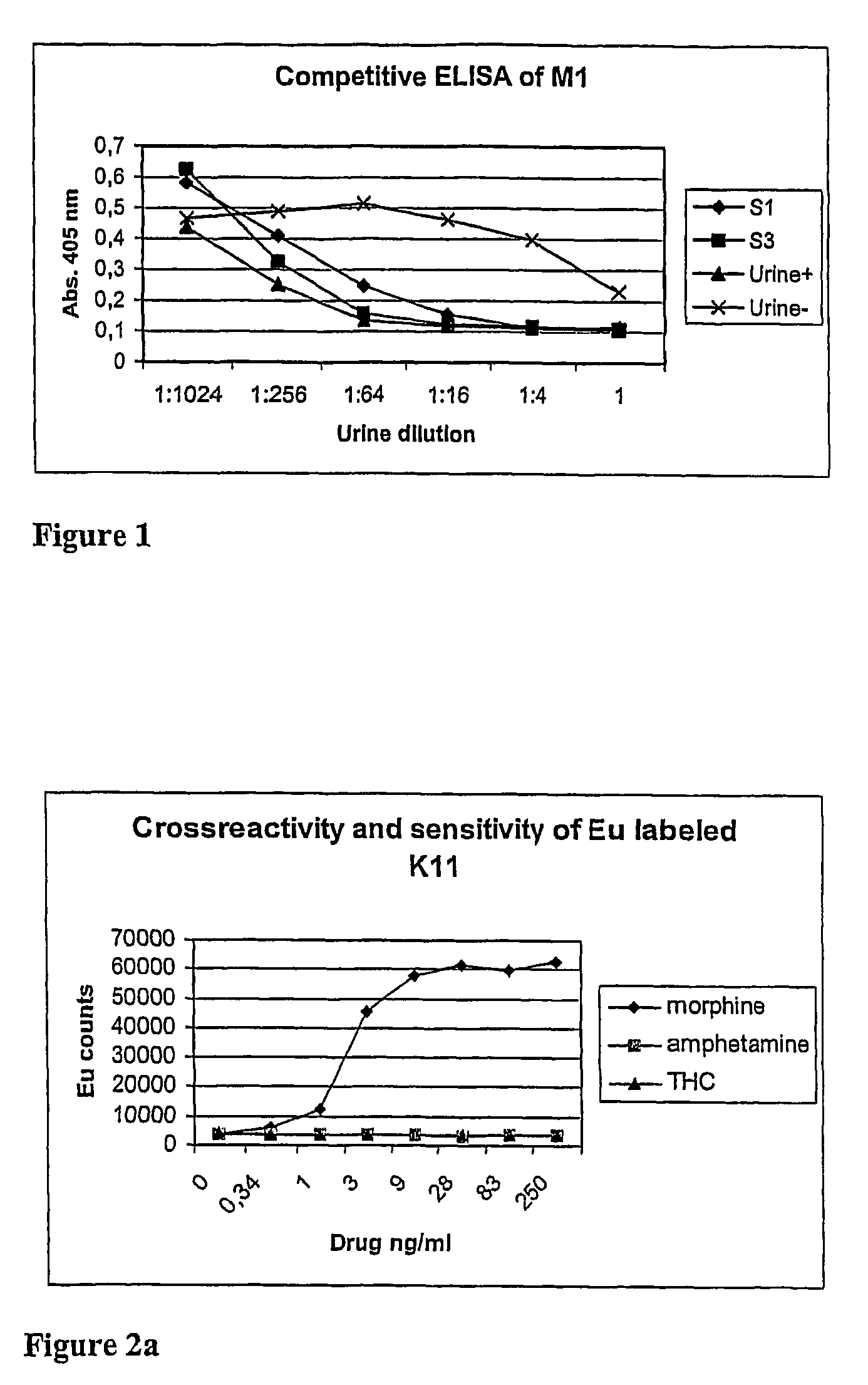
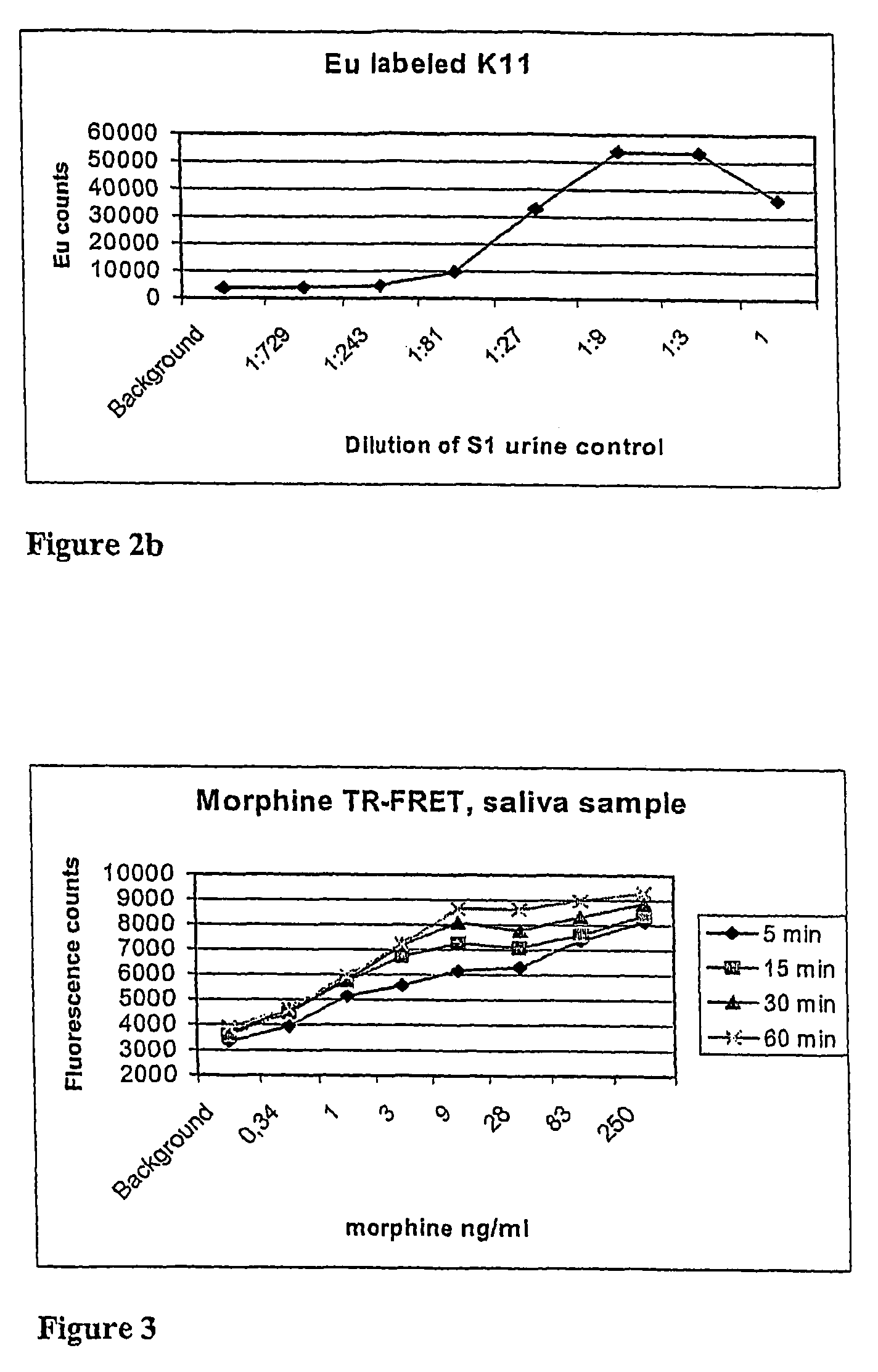
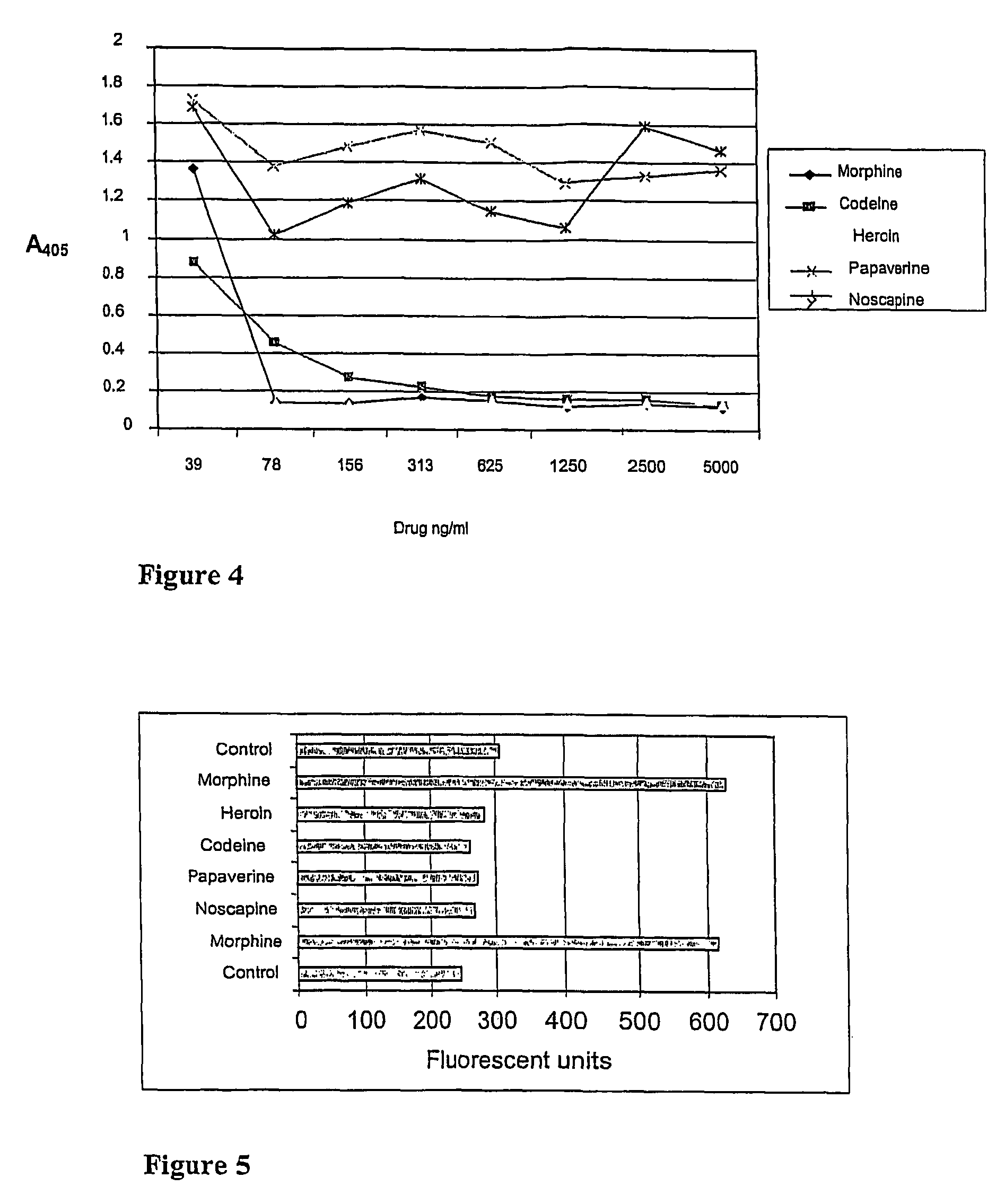
Point-of-care assays for quantitatively measuring the amount of small analytes, such as opioids, tetrahydrocannibinol (“THC”), or hormones, in a biological sample are disclosed. The assays are capable of non-competitive detection of a small analyte using binding agents that selectively bind the analyte and capture agents that selectively bind a complex of the binding agent and analyte but do not bind either free binding agent or free analyte. The assay is capable of simultaneous diction of multiple analytes for multiplex analysis and quantitative control. Quantitative measurements are obtained by plotting results against a response surface calculated from a plurality of analyte standards and adjusted using internal controls.
Owner:DECIMADX
Detection of cannabis use
ActiveUS20110086364A1Facilitates rapidFacilitates reliable detectionSugar derivativesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceImmune complex depositionAntibody fragments
A binding partner, especially an antibody fragment that specifically recognizes an antigen-antibody immune complex between anti-THC and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), is disclosed. The binding partner facilitates a non-competitive homogenous immunoassay for detection of cannabis use. A test kit comprising the binding partner is also described. Preferably the immunoassay is applied for roadside testing of saliva from suspected drivers.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
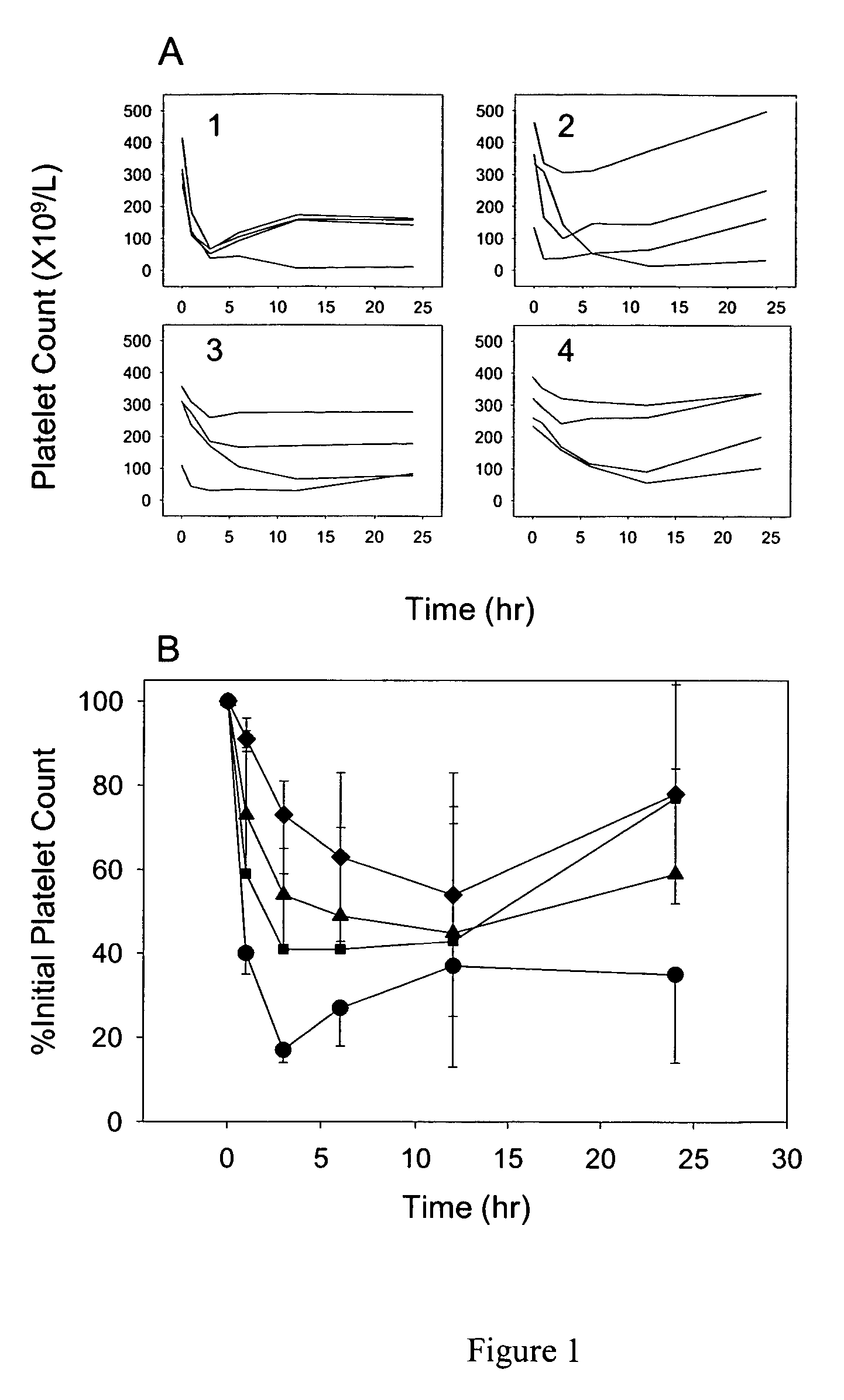
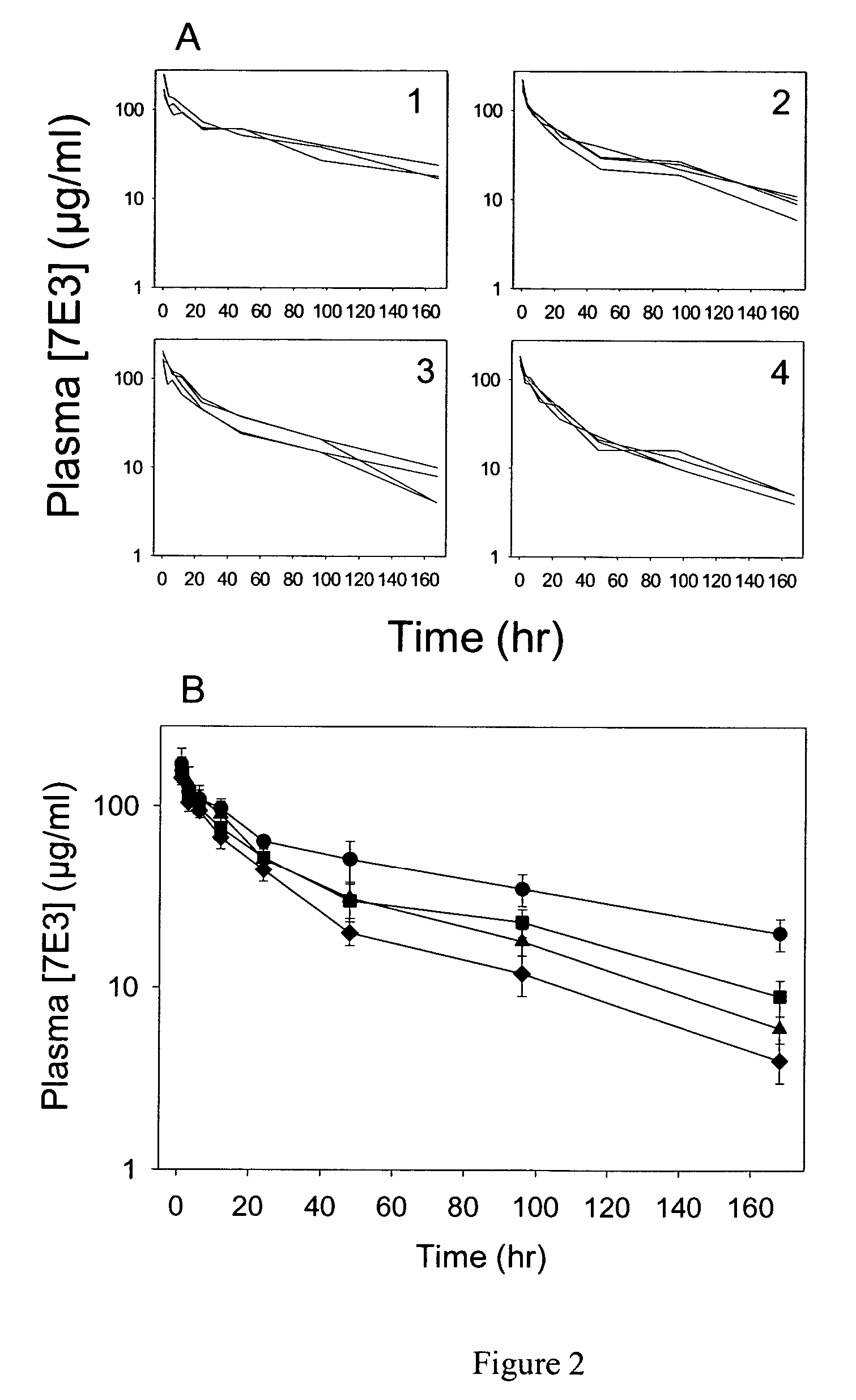
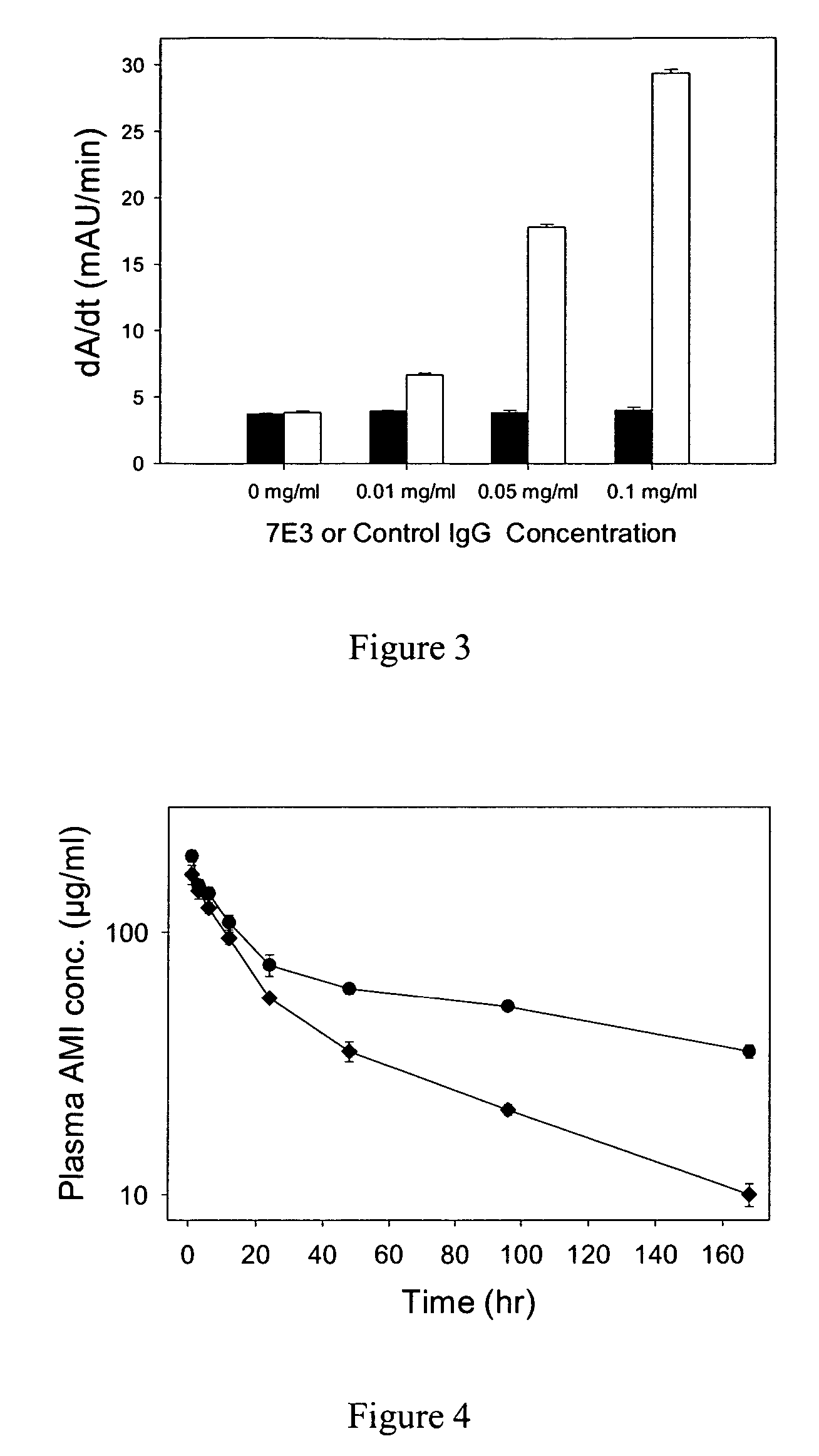
Anti-FcRn antibodies for treatment of auto/allo immune conditions
ActiveUS7662928B2Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeavy chainAntigen Binding Fragment
Antibodies to heavy chain of human FcRn are provided which function as non-competitive inhibitors of IgG binding to FcRn. The antibodies may be polyclonal, monoclonal, chimeric or humanized, or antigen binding fragments thereof. These antibodies are useful for reducing the concentration of pathogenic IgGs in individuals and therefore used as a therapeutic tool in autoimmune and alloimmune conditions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Homogeneous double receptor agglutination assay for immunosuppressant drugs
A homogeneous, non-competitive, double receptor agglutination assay for measuring immunosuppressant drugs is described. The assay employs at least two receptors wherein each receptor is specific for a separate binding site on the drug and wherein each receptor is bound to a detection particle. The immunosuppressant drug binds to the receptors and causes particle agglutination, which can be measured and correlated with the presence or amount of immunosuppressant drug in a sample.
Owner:SIGLER GERALD F +5
Methods for identifying small molecules that bind specific RNA structural motifs
InactiveUS20060228730A1Easy to implementHigh throughput screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPhysical approach
The present invention relates to a method for screening and identifying test compounds that bind to a preselected target ribonucleic acid (“RNA”). Direct, non-competitive binding assays are advantageously used to screen libraries of compounds for those that selectively bind to a preselected target RNA. Binding of target RNA molecules to a particular test compound is detected using any physical method that measures the altered physical property of the target RNA bound to a test compound. The structure of the test compound attached to the labeled RNA is also determined. The methods used will depend, in part, on the nature of the library screened. The methods of the present invention provide a simple, sensitive assay for high-throughput screening of libraries of compounds to identify pharmaceutical leads.
Owner:RANDO ROBERT +1
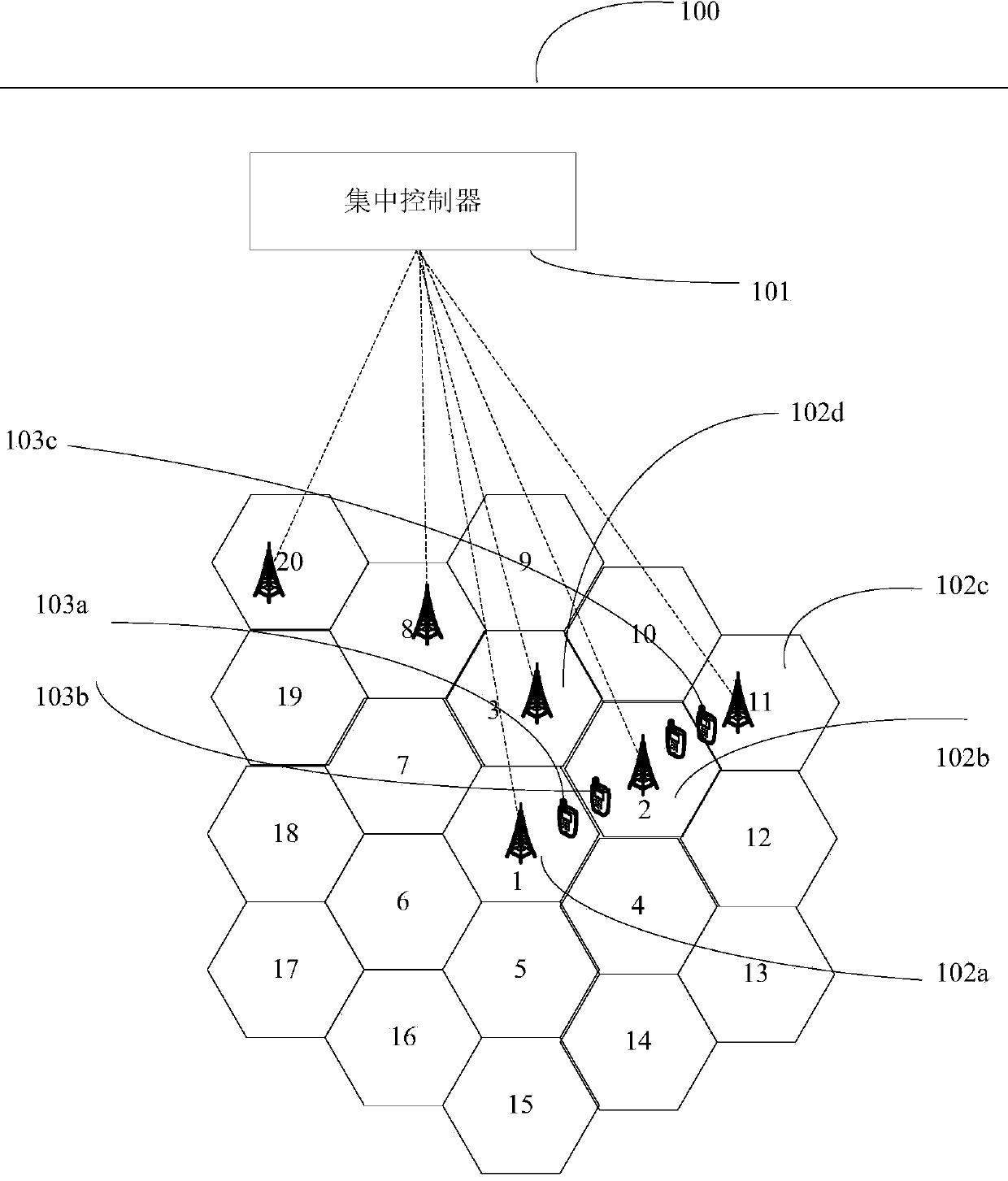
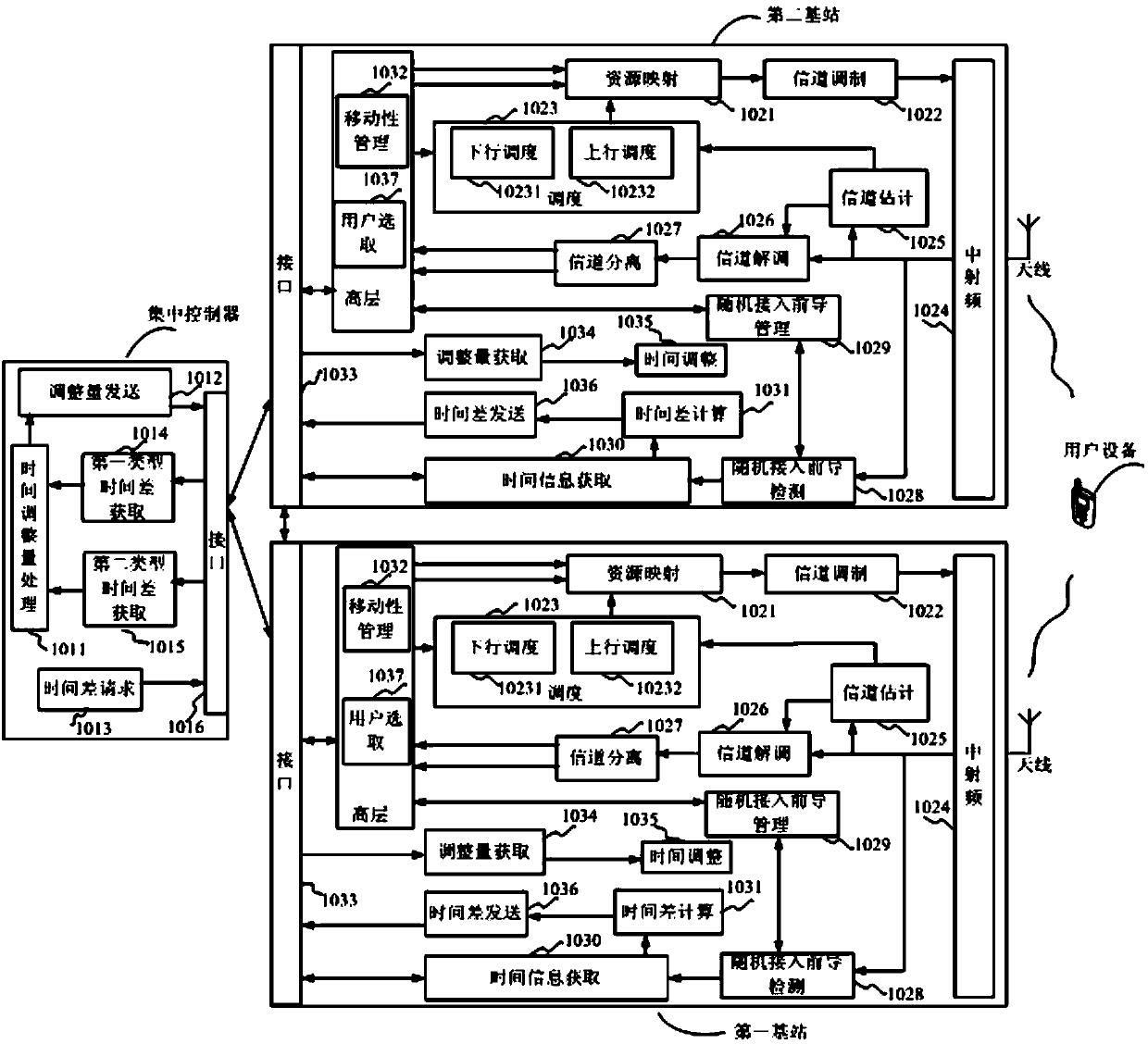
Air interface synchronizing method, base station and control device thereof, and wireless communication system
ActiveCN103797869ATime synchronizationReduce construction costsSynchronisation arrangementCommunications systemSystem requirements
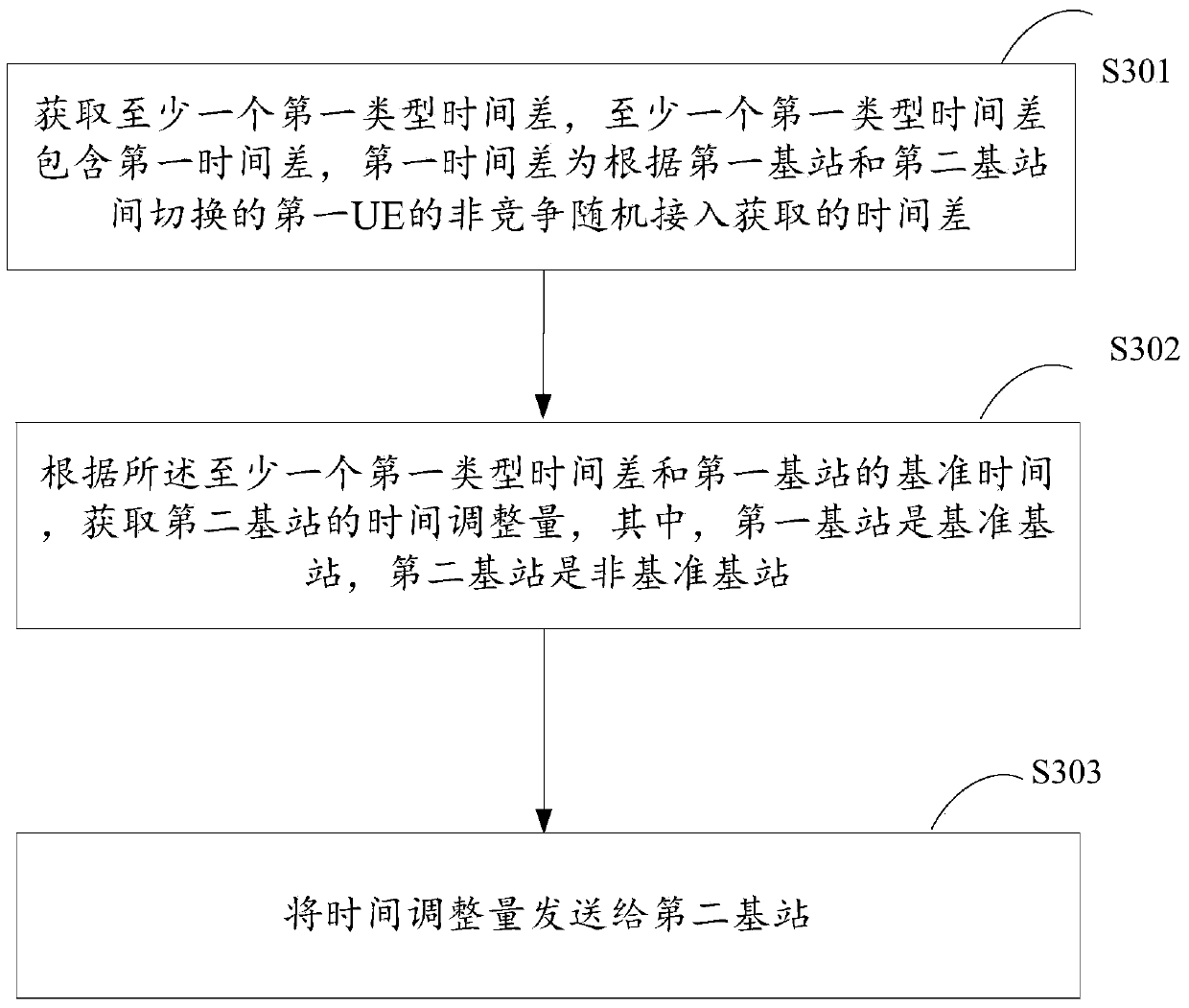
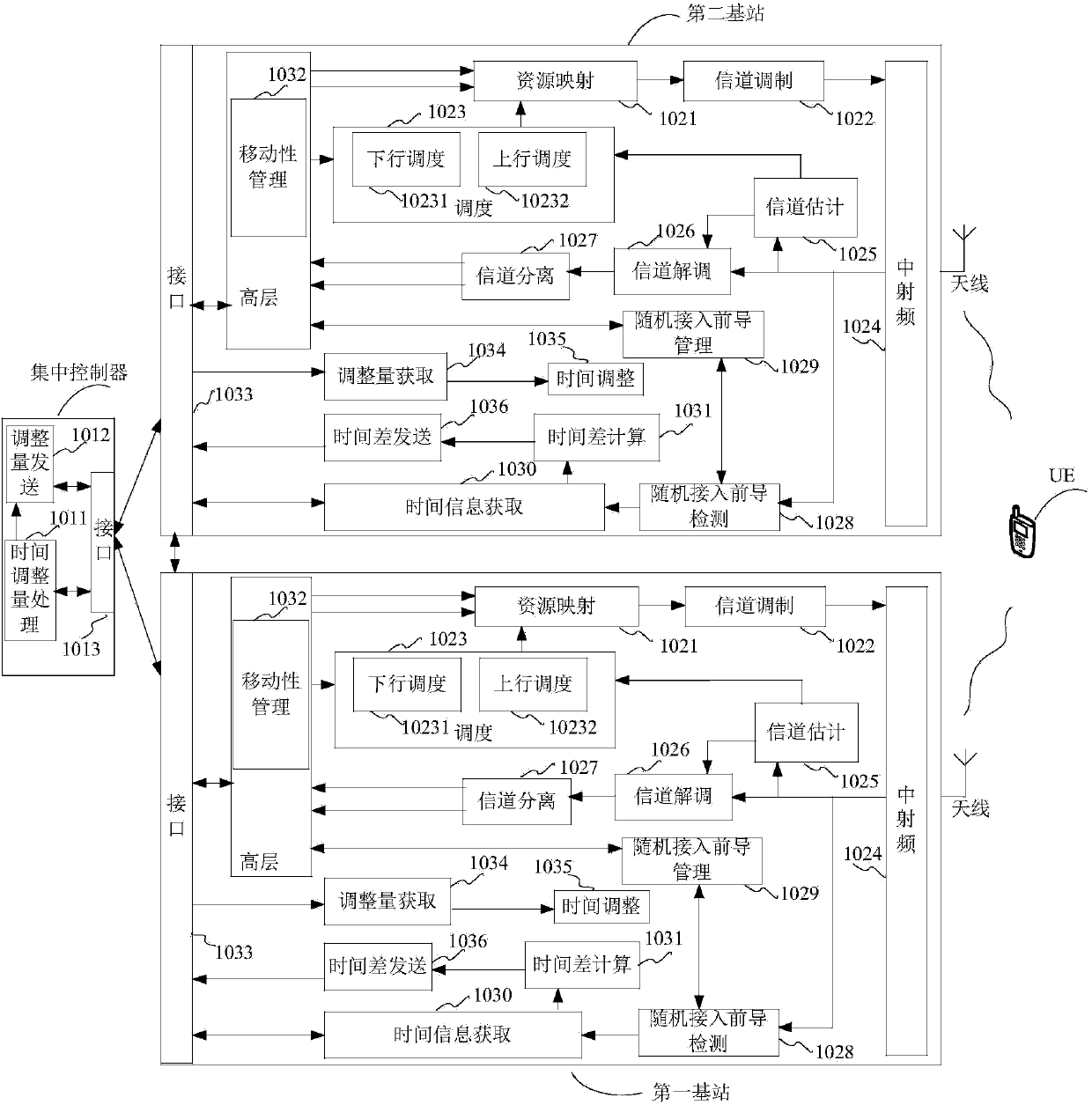
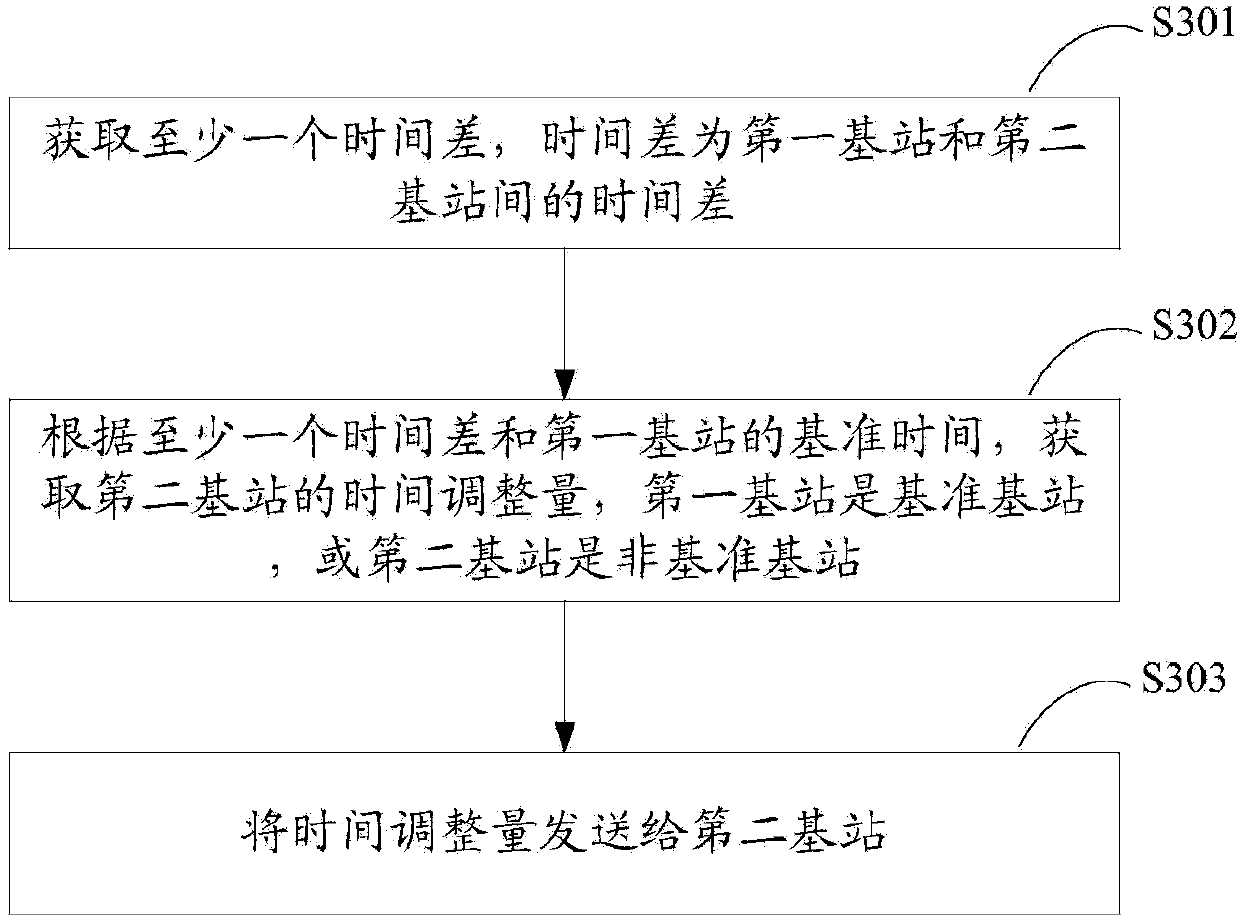
The invention discloses an air interface synchronizing method, a base station and a control device thereof, and a wireless communication system. A second-type time difference between base stations is further obtained by using active random access of user equipment if a system requirement cannot be satisfied by obtaining a first-type time difference with signalling interaction and using a non-competitive random access process of the user equipment switched between the base stations. According to the obtained time difference and reference time of a reference base station, the time adjustment amount of a non-reference base station is obtained in order that the non-reference base station performs time adjustment according to the time adjustment amount, and achieve time synchronization between the non-reference base station and the reference base station. The air interface synchronizing method does not need expensive synchronizing equipment, reduces construction and maintenace cost, and achieves economical and conventient technical effects.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Air interface synchronization method, base stations, control device and wireless communication system
InactiveCN103797870AAchieve synchronizationReduce maintenanceSynchronisation arrangementData synchronizationCommunications system
The invention discloses an air interface synchronization method, base stations, a control device thereof and a wireless communication system. By utilization of a non-competitive random access process of user equipment switched between the base stations, time difference between the base stations is obtained through signaling interaction, time adjustment amount of the non-reference base station is obtained according to a reference time of the reference base station, so that time adjustment is performed for the non-reference base station according to the time adjustment amount, and therefore time synchronization between the non-reference base station and the reference base station is achieved. According to the invention, air interface synchronization of the base stations is achieved simply and effectively by utilization of wireless network, expensive synchronization equipment is not required to be used, construction and maintenance costs are reduced, and economic and convenient technical effects are achieved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and system for randomly accessing relay station
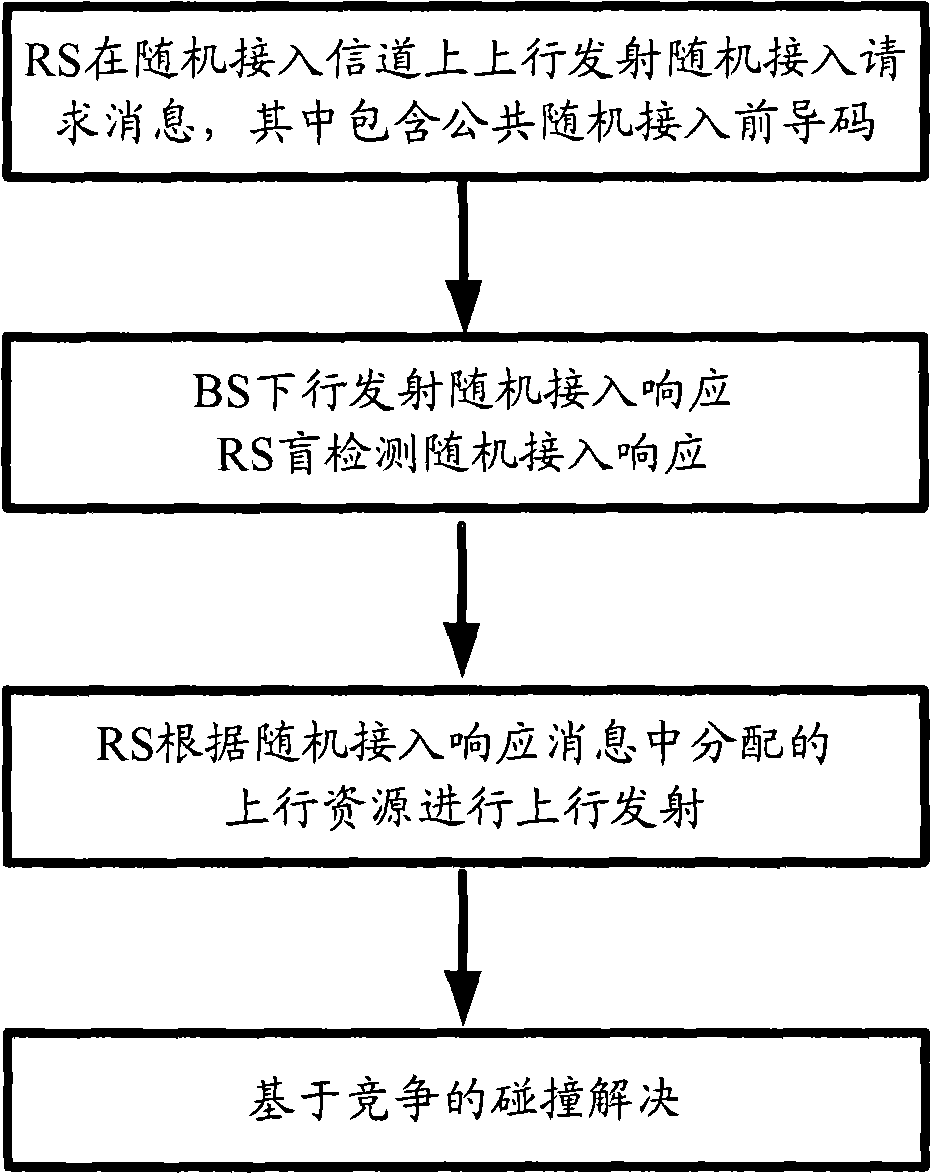
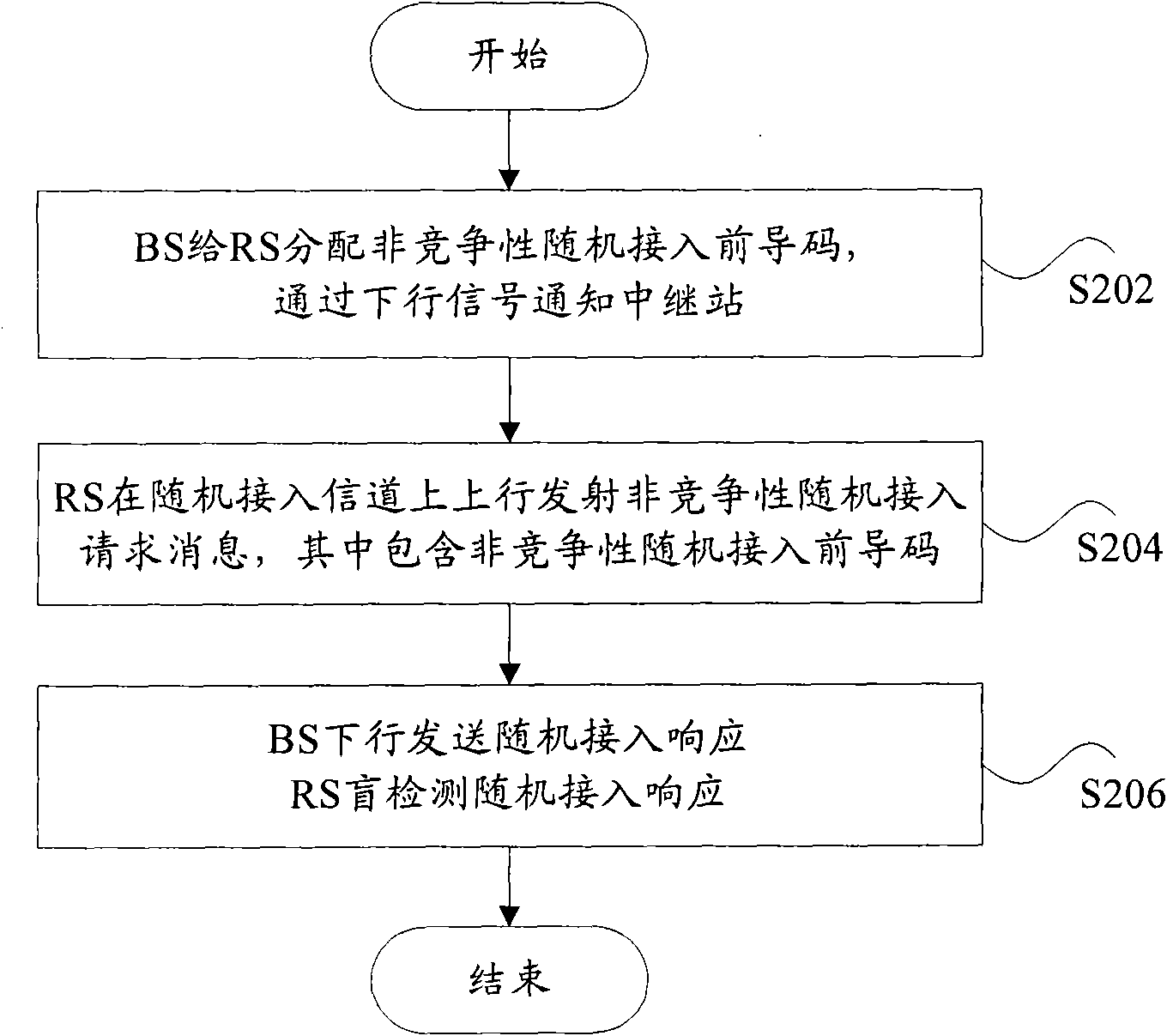
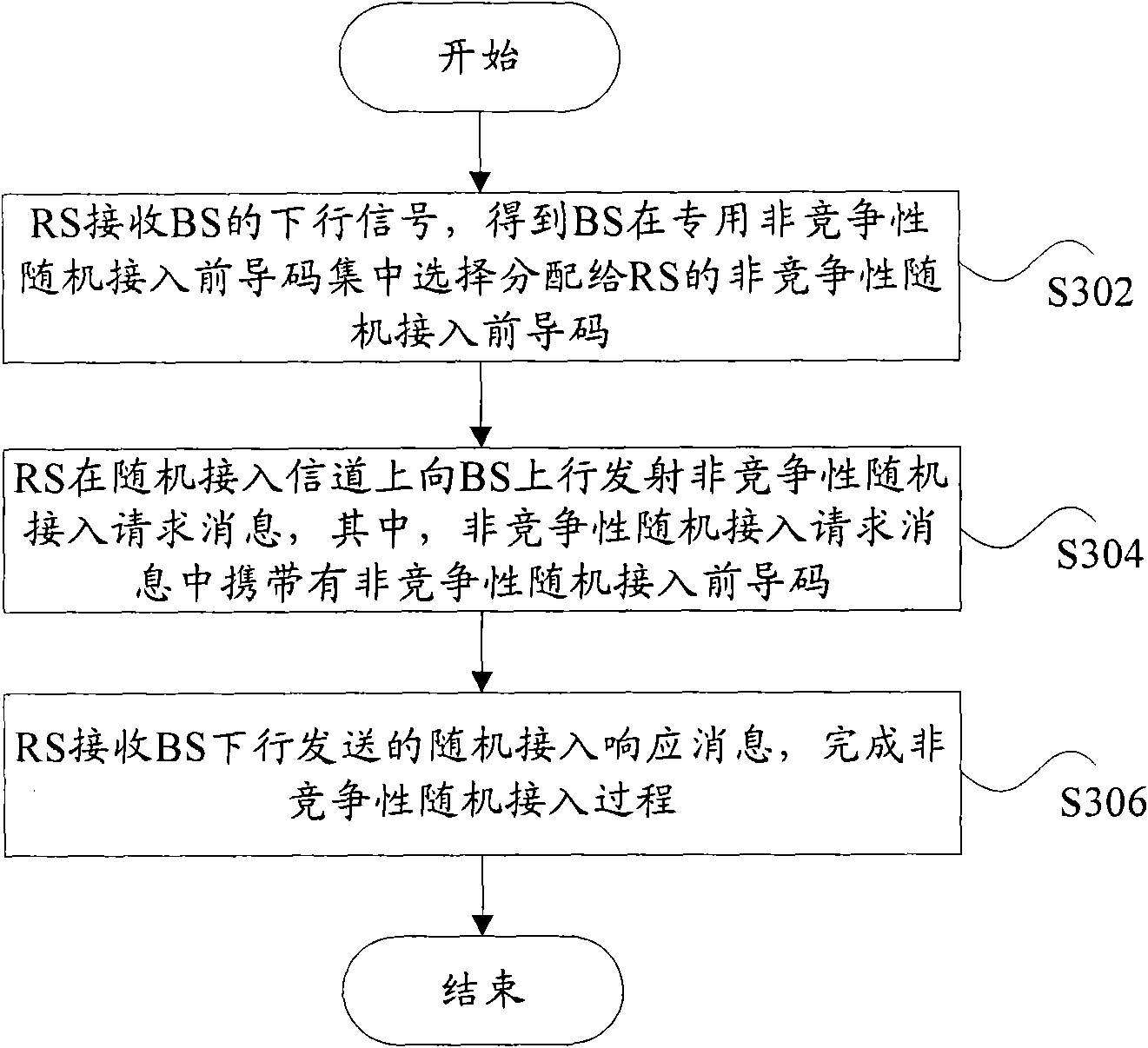
InactiveCN101686559AEasy to handleImprove access efficiencyNetwork topologiesUplink transmissionAccess time
The invention discloses a method and a system for randomly accessing a relay station (RS). The method comprises the following steps: a base station selects a non-competitive random access lead code indedicated non-competitive random access lead codes in a concentrating manner, distributes the non-competitive random access lead code to the relay station, sends a downlink signal to the relay station, notifies the distributed non-competitive random access lead code, and receives a non-competitive random access request message which is in uplink transmission by the relay station on an uplink of arandom access channel, wherein, the non-competitive random access request message comprises a non-competitive random access lead code, carries out the random access response on the relay station, andsends a downlink signal of the random access response to the relay station. By the above processing, the invention can avoid the condition that the RS occupies the resources of cell public random access, simplify the process of random access, and reduce access time delay, thus effectively improving the efficiency of the RS random access.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method for producing edible fungus mycorrhizal seedling of mycorhiza
InactiveCN101595803AEasy to operateImprove efficiencyHorticultureFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologyHigh pressure
The invention relates to a method for producing the edible fungus mycorrhizal seedling of a mycorhiza. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: the mycelium of a target mycorrhizal fungus and the mycorhiza of a non-competitive mixed fungus are synthesized into a culture medium, are uniformly mixed, are spread in a container and are cultured under a condition which is suitable for the growth of hypha, wherein the surface of the container is disinfected by a potassium permanganate solution or sterilized under high temperature and high pressure, and the lower part of the container is spread with a layer of non-competitive mixed fungi or media sterilized under high temperature and high pressure; and a sterile germinated host plant seed of which the surface is disinfected and the culture medium culturing the target hypha are mixed and cultured under a proper ecological condition until the mycorhiza of a tree seedling root is formed. The synthesis experiment of the edible fungus mycorrhizal seedlings of various mycorhiza shows that the method has simple and effective operation and high efficiency, is very suitable for popularization and application in mass production, can be used for producing mycorrhizal seedlings at any time in one year and has obvious economic benefits.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
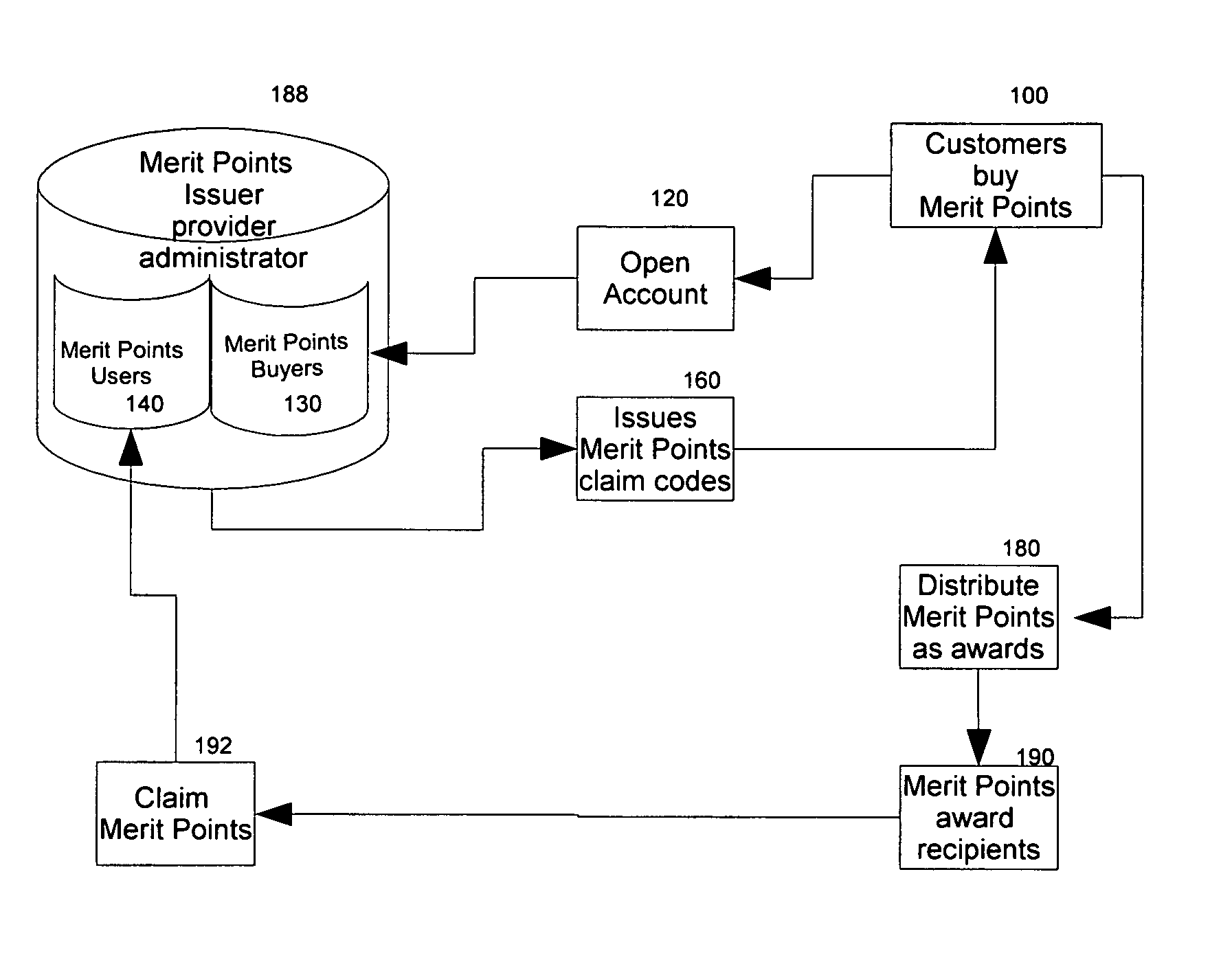
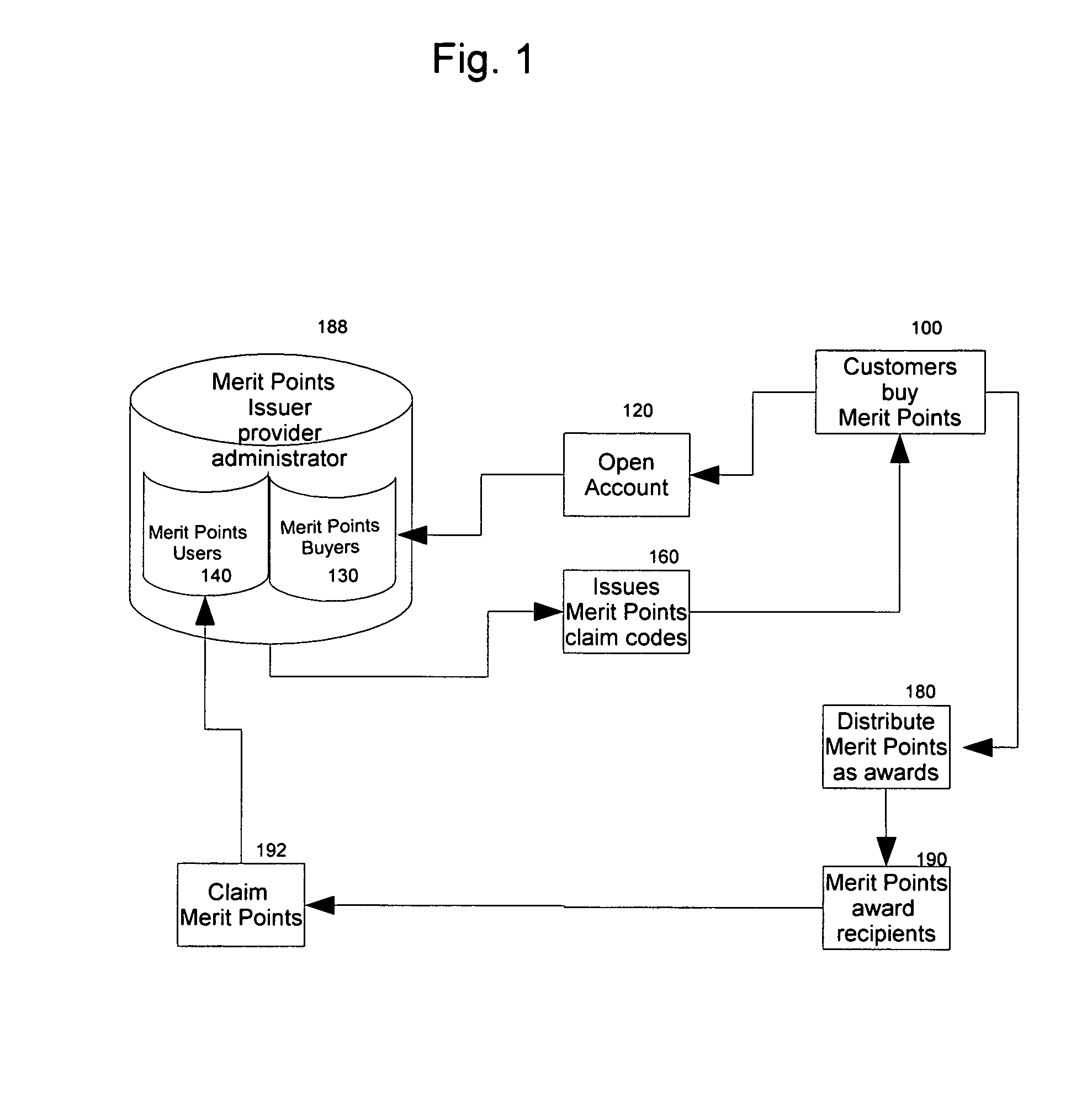
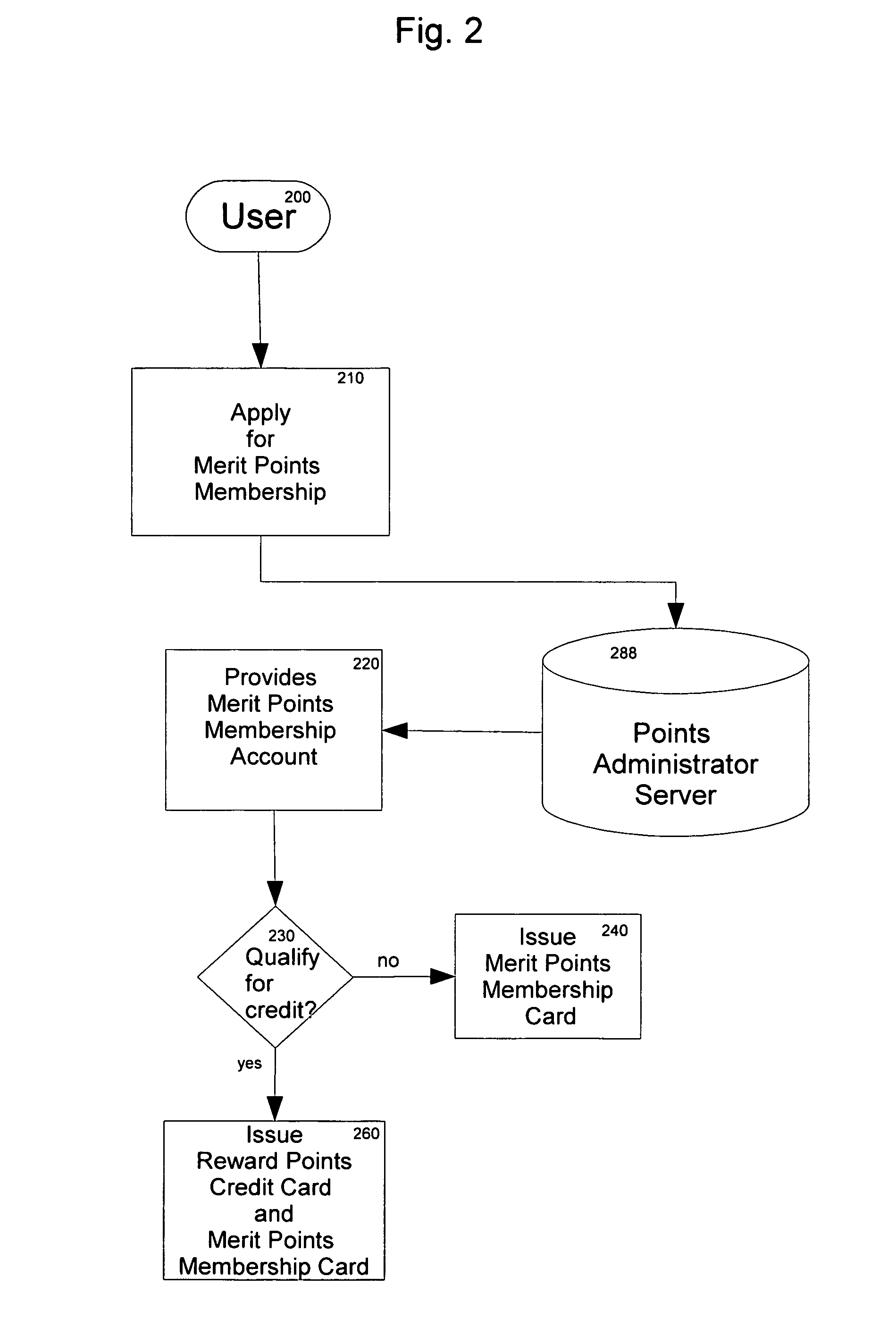
System and method for awarding and redeeming merit points for participation, competition, and performance in sports and in the arts and sciences
A method and process for providing a merit-based incentive points system for amateur sports and competitive and non-competitive events wherein merit points are purchased from points administrator and distributed by event organizers and sponsors as participation and performance awards to contestants and participants. Such merit points functioning as points currency of value, can be accrued, traded, exchanged, and redeemed for scholarships, goods and services. In order to maximize points accumulation and benefits, an auxiliary support system in a form of social network of parents, relatives, friends, and boosters and supporters, in conjunction with pre-existing reward points credit cards, are recruited to sign up for reward points credit cards, thereby having the earned reward points routed to any designated points recipient. To enhance the liquidity and convertibility of two distinct points systems, and to provide a platform where points can be traded, exchanged, an electronic market exchange provides the means and apparatus to achieve such objectives. Additionally, this invention further maximizes points return by providing the means, method, and platform for points' cash value to be invested in the financial and capital markets, thereby functioning as an alternative form of financial instrument.
Owner:LIANG GLADSTONE CHIKUANG +1
Method and system for non-contention random access, network side network element and user equipment
InactiveCN102917468AMeet the needs of fast sending and receiving large amounts of dataShorten the timeWireless communicationAccess timeMedia access control
The invention discloses method for non-contention random access. The method includes: a network side sends an MAC (medium access control) CE (control element) to UE (user equipment), wherein random access opportunity information of cells or UL (uplink) grant information is set in the MAC CE; the UE sends random access guide to the cells according to the random access opportunity or sends random access guide or uplink data at opportunity indicated by UL grant; and the network side calculates TA (time adjustment) according to the received random access guide or uplink data and feeds back to the UE, and the UE successfully accesses to the cells to transmit and receive data normally. The invention further discloses a system for non-contention random access, a network side network element and the user equipment. Access of auxiliary service cells can be realized in a non-competitive way, cell access time is greatly shortened, and the requirement of the UE on quickness in mass data transceiving is met.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Non-competitive immunoassay for small analytes
ActiveUS7749712B2Rapid and reliable and simple immunoassayCost-effective and feasiblePeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesWAS PROTEINAnalyte
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com