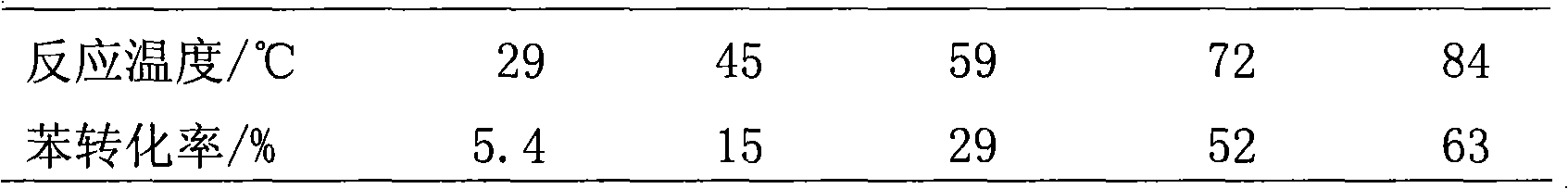
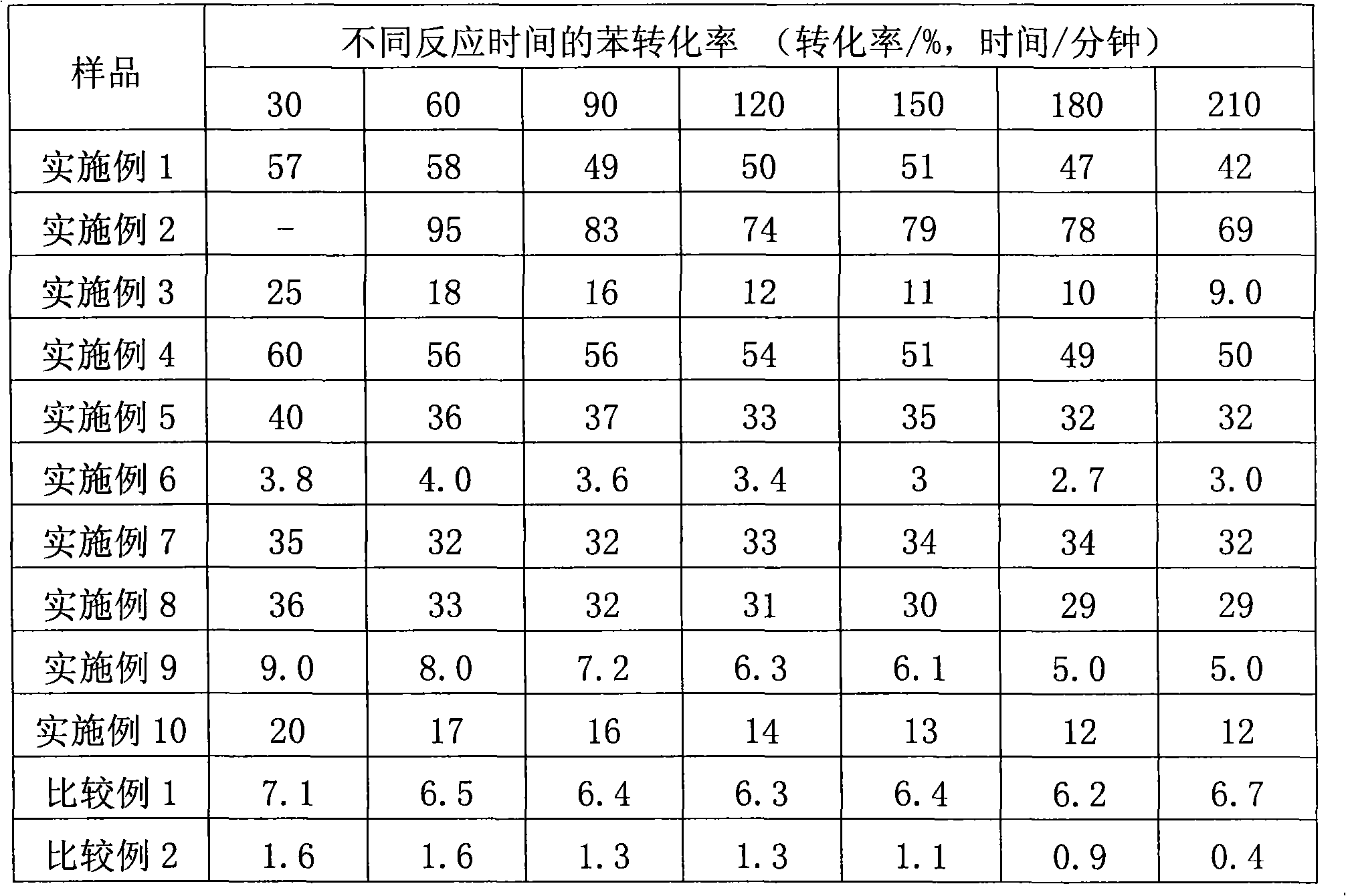
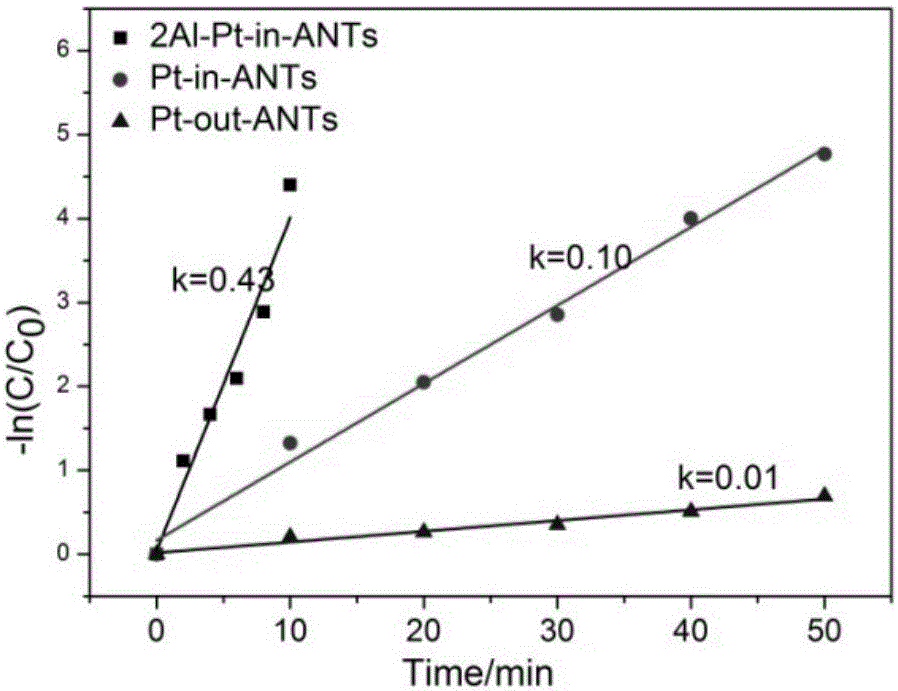
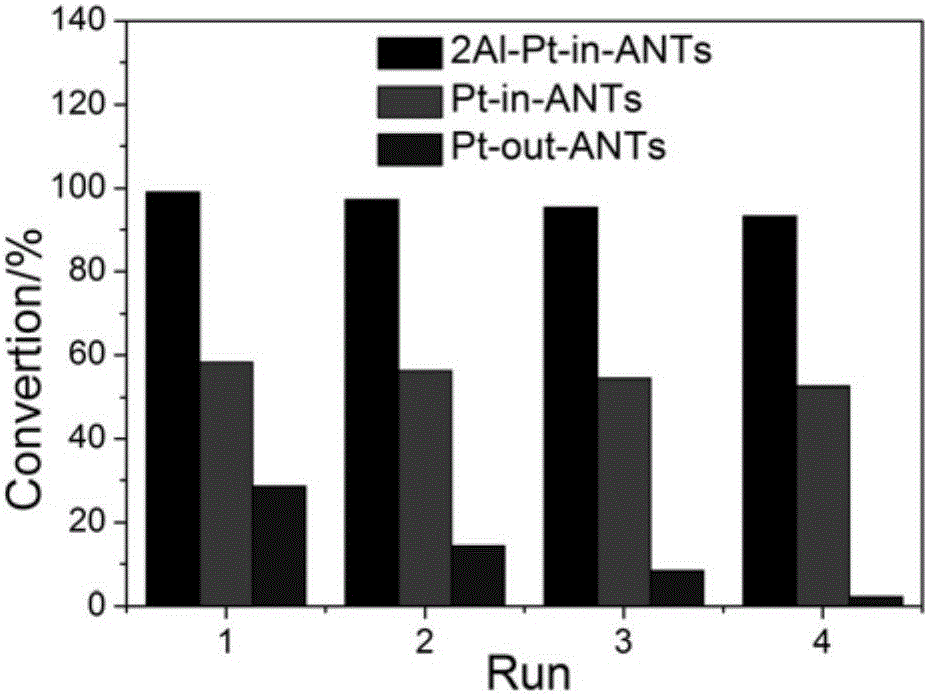
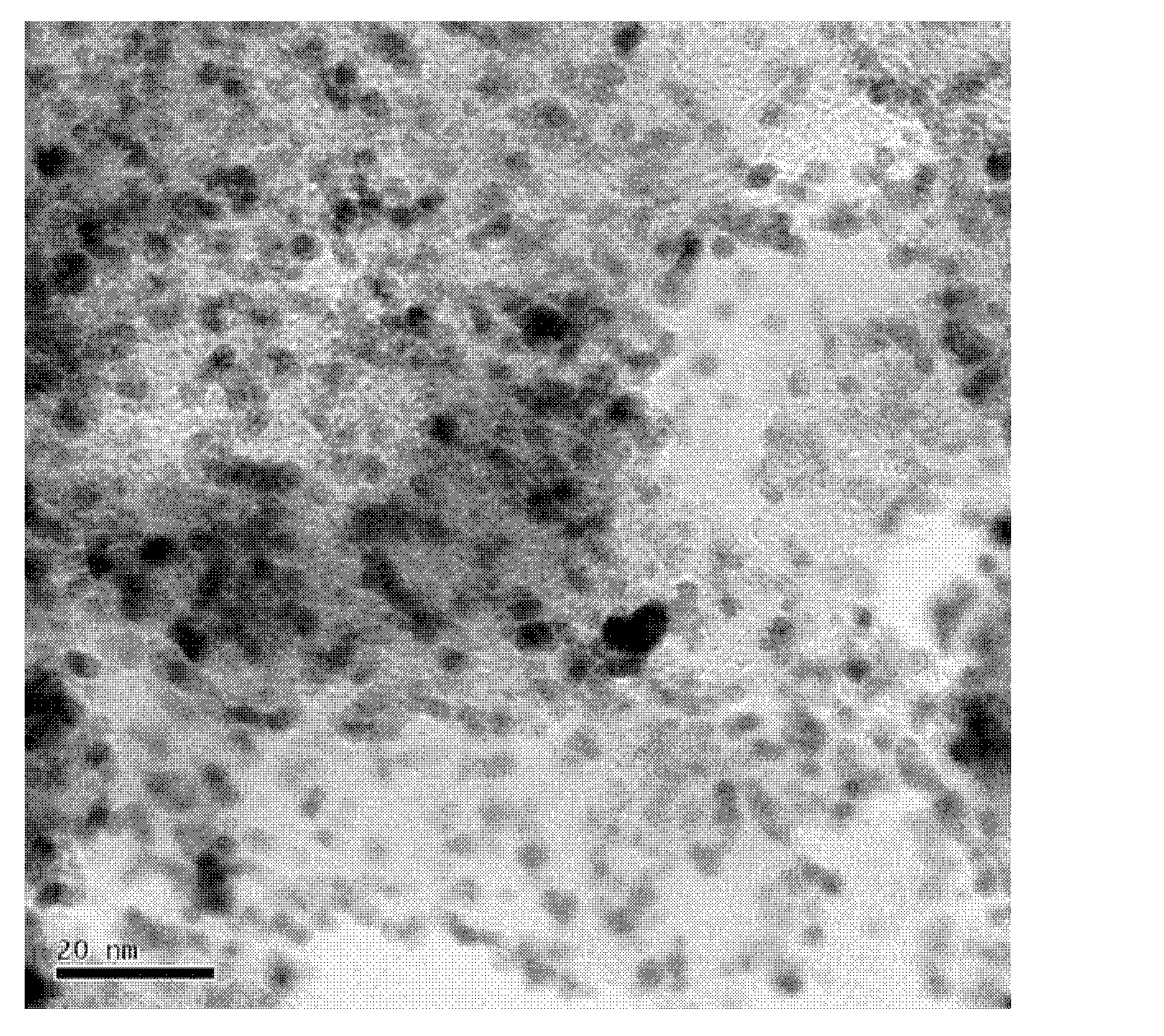
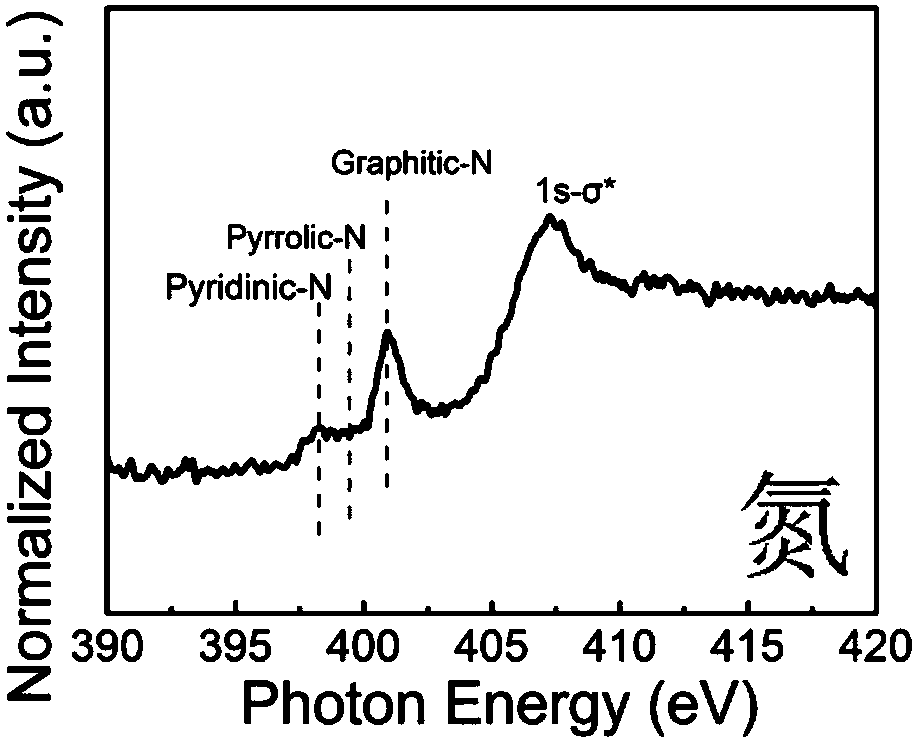
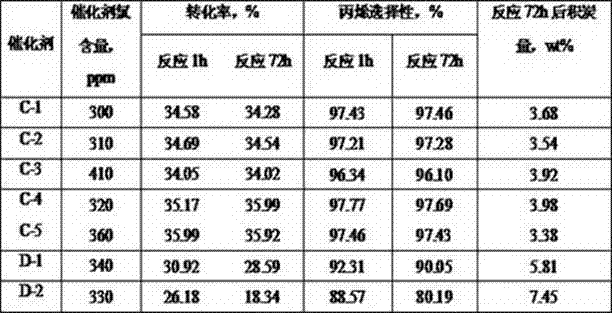
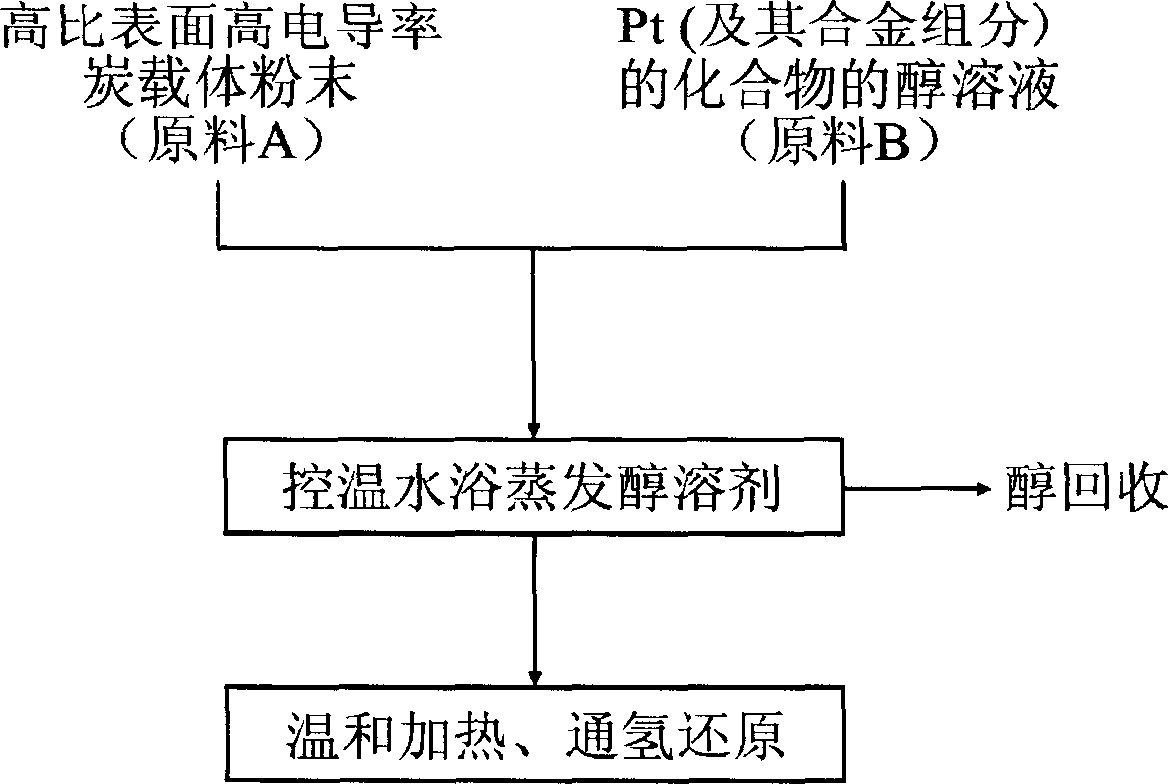
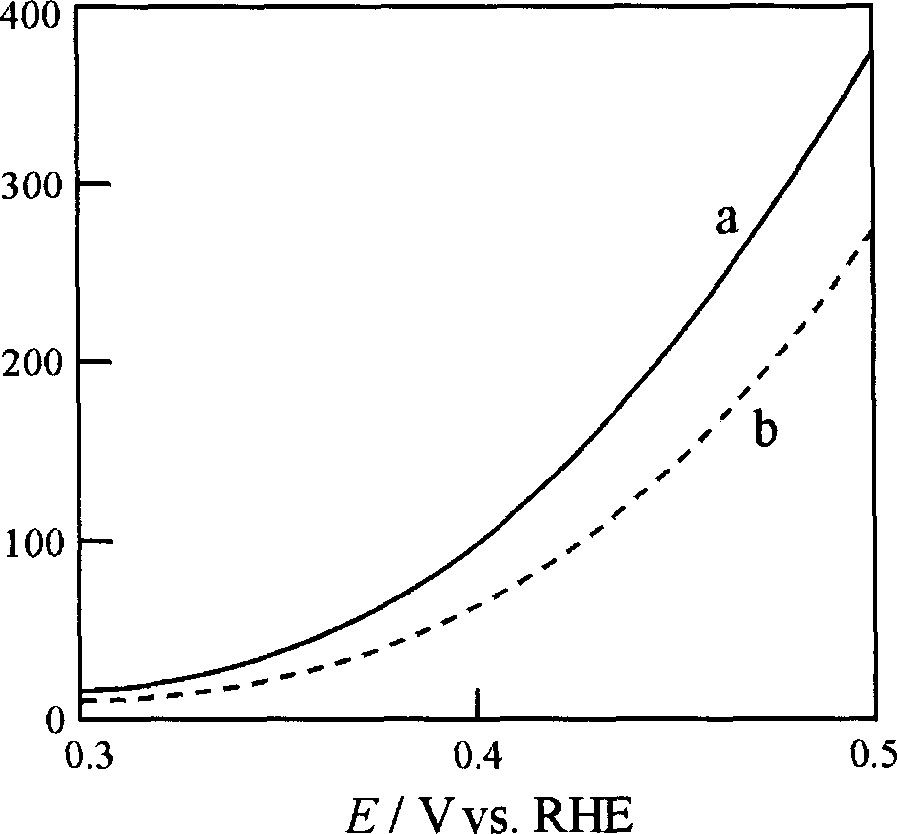
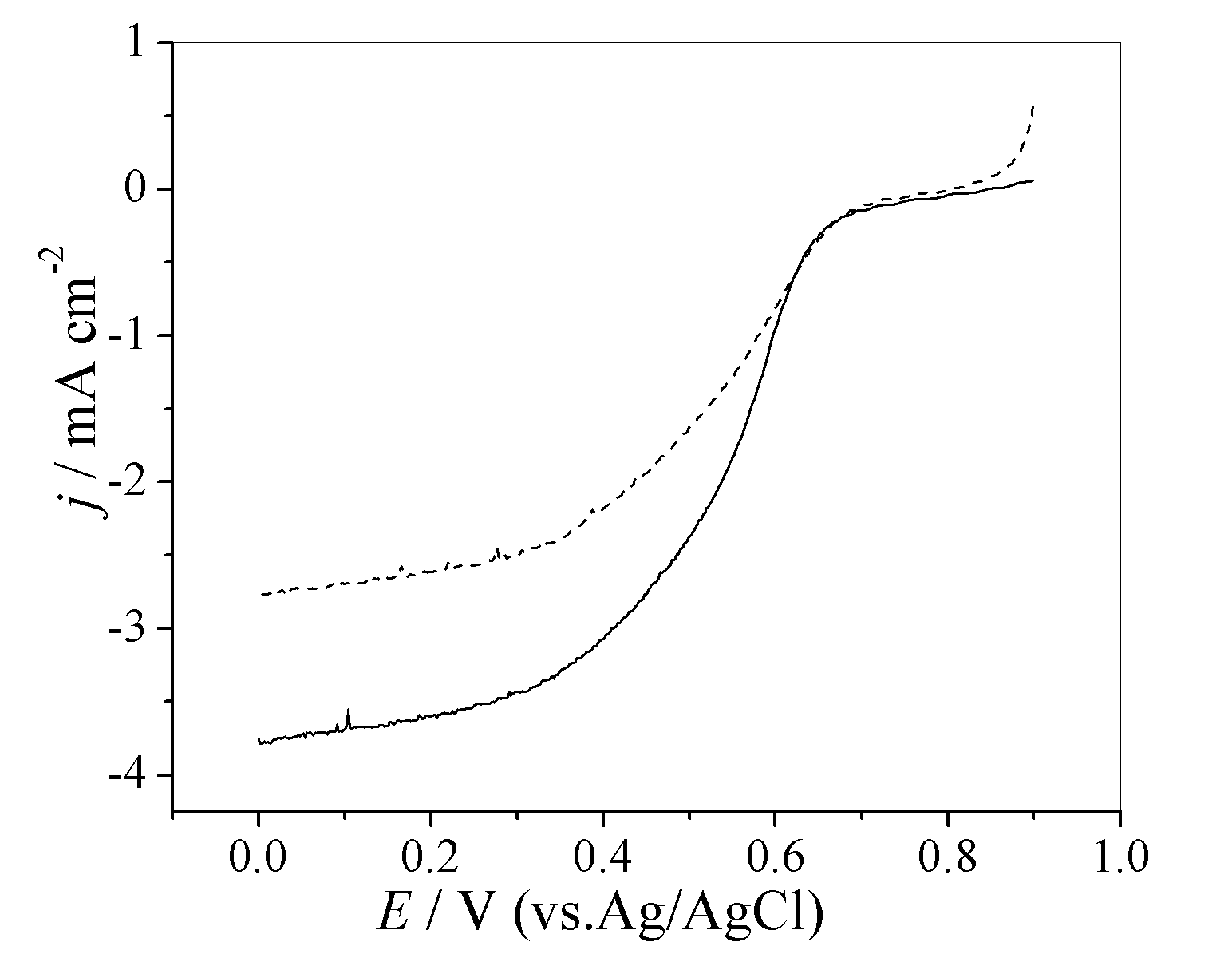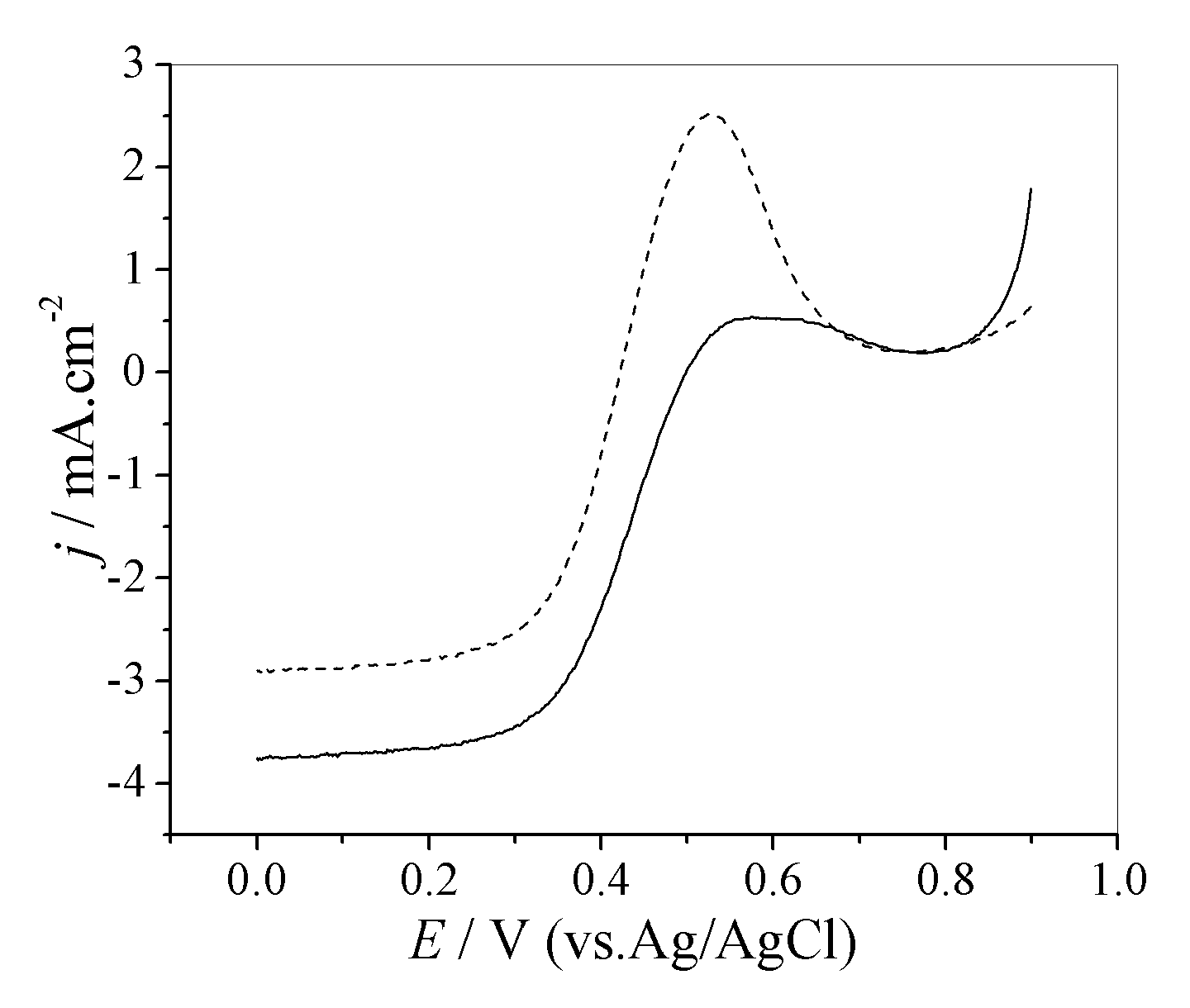Patents
Literature
62 results about "Pt based catalysts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for preparing three-dimensional carbon framework embedded nano platinum-based alloy catalyst
InactiveCN107331877AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesIonPt based catalysts
The invention discloses a method for preparing a three-dimensional carbon framework embedded nano platinum-based alloy catalyst, and aims to solve the problems that a conventional Pt-based catalyst is low in activity, poor in stability and Pt utilization rate. According to the method, in the growth process of a zeolite imidazolate framework structural material (ZIF), Pt nanoparticles modified by a surfactant are uniformly wrapped in a ZIF structure, the high-temperature reduction process is precisely regulated, the ZIF carbonization, metal reduction and alloying process is controlled, and thus a catalyst structure of a three-dimensional carbon framework embedded nano platinum alloy is constructed. According to the method, the structural shrinkage effect of the carbonization process is smartly utilized, the ZIF structure is converted into a three-dimensional through carbon framework pore structure, the range limiting function of a ZIF framework at high temperature is smartly utilized, platinum particles and metal ions in the ZIF structure are subjected to in-situ alloying and embedded into the framework structure, then the three-dimensional catalyst of a pore-communicated framework and a nano-grade platinum alloy particle embedded structure is formed, the activity and the stability of the catalyst are greatly improved, and the utilization rate of Pt is greatly increased.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
N-doped porous carbon coated Fe and Co bi-metal nanoparticle catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108493461AIncrease varietyInhibit aggregationMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufacturePorous carbonMetal alloy
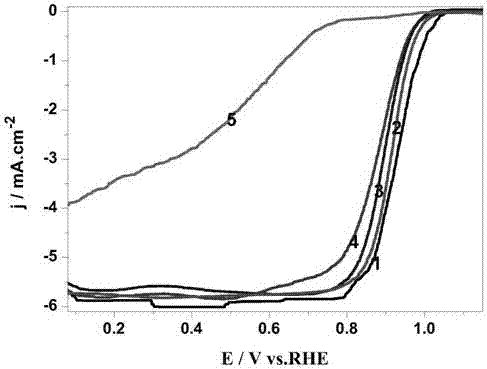
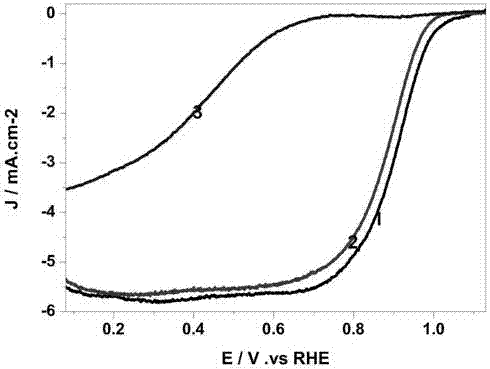
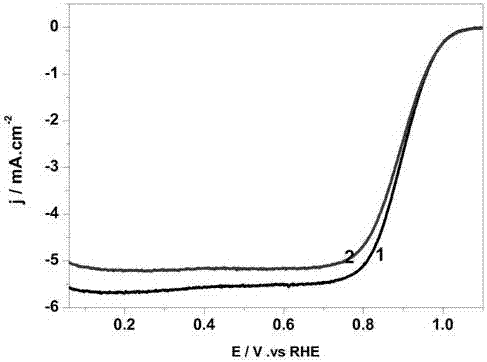
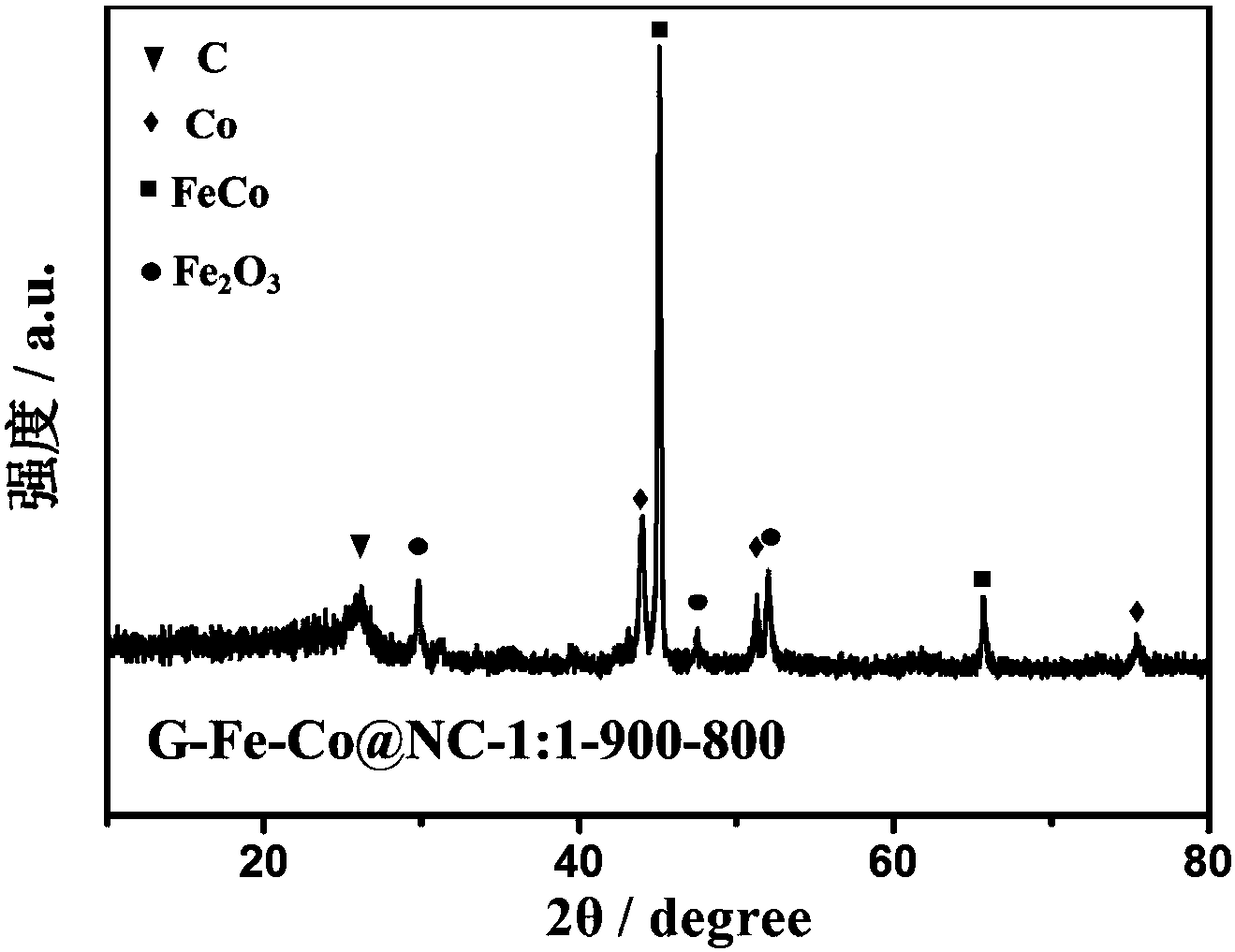
The invention discloses a N-doped porous carbon coated Fe and Co bi-metal nanoparticle catalyst and a preparation method of the N-doped porous carbon coated Fe an Co bi-metal nanoparticle catalyst, and belongs to the field of energy materials and electrochemistry. The catalyst takes glucose as the C source, g-C3N4 as the N source, the C source and the template, F3Cl3.6H2O and Co(NO3)2.6H2O are metal sources, a high-temperature stepwise calcining method is used to prepare the N-doped porous carbon coated Fe and Co Fe-Co@NC catalyst, and the catalyst is in a three-dimensional porous unordered stacking structure. Fe and Co exists in the forms of Fe0.3Co0.7, Fe2O3, and Co, and is evenly coated in the N-doped porous carbon. Compared with the commonly used Pt-based catalyst, the ORR (Overall Response Rate) performance in an alkaline medium is not much different from that of the commercial Pt / C catalysis, the OER (Oxygen Enhancement Ratio) performance is far better than that of the Pt / C catalyst, and the stability and the methanol tolerant property are better. Compared with the commonly seen bi-metal alloy catalyst, the catalyst has more active species, and the specific surface area is larger. In addition, the cost of the raw materials of the catalyst is low, the source of the raw materials is wide, the preparation process is simple and is favorable for large-scale production, and thecatalyst has a higher practical value.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing proton-exchange membrane fuel cell oxygen reduction catalyst based on PtNi (111) octahedral single crystal nanoparticles
InactiveCN104998658AHigh catalytic activity for oxygen reductionPt content decreasedCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsN dimethylformamideSingle crystal
Owner:昆明贵研催化剂有限责任公司
Low-hardness glue-dispensing shaping shielding conductive adhesive as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102516929ALower impedanceReduce connectivityElectrically-conducting adhesivesAdhesiveChemistry
The invention relates to a low-hardness glue-dispensing shaping shielding conductive adhesive as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The conductive adhesive comprises the following components in parts by weight: (A) 100 parts of organic polysiloxane of which each molecule comprises at least two alkenyl; (B) 2-10 parts of the organic polysiloxane of which each molecule comprises at least two silicon-hydrogen bonds and a hydrolysable group; (C) 100-350 parts of metal base conductive fillers; (D) 0.001-0.005 parts of Pt-based catalyst; and (E) 0.1-2.0 parts of aluminum compounds or zirconium compounds or titanium compounds. Compared with the prior art, the conductive adhesive provided by the invention has the advantages of low hardness, high conductivity, high shielding performance, strong shaping ability, excellent adhesiveness and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI RELAND PHOTOVOLTAIC MATERIAL
Method for preparing levulinic acid and co-producing gamma-valerolactone from biomass
InactiveCN103435577AAvoid emissionsAvoid separationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationSolid acidGamma-Valerolactone
The present invention provides a method for preparing levulinic acid and co-producing gamma-valerolactone from biomass. The method comprises: mixing biomass and a gamma-valerolactone aqueous solution according to a weight ratio of the biomass to the gamma-valerolactone of 1:5-1:200, and dissolving the biomass under a heating condition; adding a solid acid catalyst to the filtrate to prepare levulinic acid; and adding a Ru, Ni or Pt base catalyst to prepare gamma-valerolactone. According to the present invention, after cellulose and hemicellulose in the biomass are dissolved in the gamma-valerolactone, the contact area with the solid acid is substantially increased so as to improve reaction efficiency and a product yield; the solid acid can be reused after recycling, such that waste acid emission can be avoided, cost can be reduced, and pollution on the environment can not be caused; the final product is the gamma-valerolactone so as to avoid separation of the product and the solvent; and difficult problems of low product yield, easy catalyst deactivation and low product separation cost due to existing of a large amounts of water during a levulinic acid and gamma-valerolactone preparation process using biomass in the prior art are solved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Low-temperature catalytic benzene hydrogenation method and special catalyst thereof
InactiveCN101289365AEasy to understandHydrocarbon by hydrogenationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsBenzeneMetal catalyst
The invention discloses a catalyzing method of benzene hydrogenation at low temperature and a special catalyst thereof. The catalyzing method of the benzene hydrogenation at the low temperature provided by the invention uses a co-based catalyst to catalyze the benzene hydrogenation to react; wherein, the co-based catalyst is a cobalt single metal catalyst / or a noble metal-cobalt bimetal catalyst. Compared with a Ni-based catalyst or a Pt-based catalyst which is used for catalyzing the benzene hydrogenation to react at present, the invention can realize the benzene hydrogenation reaction at low temperature or even under condition of room temperature by using the co-based catalyst to catalyze the benzene hydrogenation to react and is provided with high hydrogenation activity. The invention provides a novel co-based catalyst, namely the noble metal-cobalt bimetal catalyst which is used in the benzene hydrogenation reaction. The noble metal-cobalt bimetal catalyst is provided with higher hydrogenation activity than the cobalt single metal catalyst. Besides being used in the preparation of cyclohexane, the co-based catalyst can be used in the intensive removal of aromatics, in particular the benzene in the fuel oil and the elimination of trace benzene in the environment.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Preparing method of limited-range catalyst modified through atomic layer deposition and application thereof
ActiveCN105771972AAddresses the drawback of limited carrier interface sitesImprove hydrogenation activityOrganic compound preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsFiberCarbon nanofiber
The invention provides a preparing method of a limited-range catalyst modified through atomic layer deposition and application.The atomic layer deposition technology is utilized, an ultra-thin oxide layer, Pt nanometer particles and a thick oxide layer are deposited on a carbon nanometer fiber template successively, then calcination is carried out in air to remove the carbon nanometer fiber template, and a Pt-based catalyst with oxide ultra-thin modification and the limited range within an oxide nanometer tube is obtained.The prepared catalyst greatly overcomes the defect that the site of a traditional catalyst metal-oxide interface is limited; compared with a limited-range Pt catalyst without ultra-thin modification and a Pt catalyst with the unlimited range, the limited-range Pt catalyst with ultra-thin modification has the best reduction hydrogenation activity to tetranitro-phenol, and the method can be popularized in preparation of other multi-phase catalysts.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of metal organic framework loaded Pt-base catalyst
InactiveCN103191778ADistribute quicklySmall particlesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsNano catalystAlcohol
The invention discloses a preparation method of a metal organic framework loaded Pt-base catalyst. The method comprises putting the metal organic framework into an alcoholic solution, vibrating with ultrasonic, adding drop by drop a mixed solution of chloroplatinic acid and cobalt oxide, adding NaOH, stirring, putting into a microwave oven for intermittent heating, cooling, filtering by pumping, and drying under vacuum to obtain the metal organic framework loaded Pt-base catalyst. The catalyst is small in particle, not easy to agglomerate, good in dispersibility and high in electrochemical catalytic activity.
Owner:HANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MATERIAL BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Preparation method of carbon-supported Pt-based nanometer catalyst
InactiveCN102218331ANot easy to reuniteRestore evenlyCell electrodesCatalyst activation/preparationNano catalystFiltration
The invention provides a preparation method of a carbon-supported Pt-based nanometer catalyst, relating to a preparation method for the carbon-supported Pt-based catalyst. The invention aims at solving the defects that by adopting the existing preparation method of the carbon-supported Pt-based catalyst, the operation is inconvenient, the grain size can not be controlled easily, and grains are easy to agglomerate and the like. The preparation method comprises the following steps of step 1: placing active carbons in a mixed acid solution containing concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid, and subsequently adding distilled water for three times in the mixed acid solution; stirring the solution under room temperature; subsequently cooling the solution to the room temperature; carrying out extraction filtration to obtain neutral filtrate; carrying out vacuum drying on the neutral filtrate; step 2: adding the active carbons processed in the step 1 into glycol; subsequently carrying out ultrasonic oscillation; subsequently dripping the mixed solution containing chloroplatinic acid and cobalt chloride; adding formic acid in the solution and stirring the solution for 30 minutes under the temperature of 25 DEG C; placing the solution in a microwave oven and intermittently heating the solution; and then carrying out cooling, extraction filtration and vacuum drying on the solution, thus obtaining the carbon-supported Pt-based nanometer catalyst. The preparation method has simple preparation steps, short required time and loss product loss. The catalyst has small grains, is not easy to agglomerate, is distributed uniformly and has high electrochemical catalytic activity.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
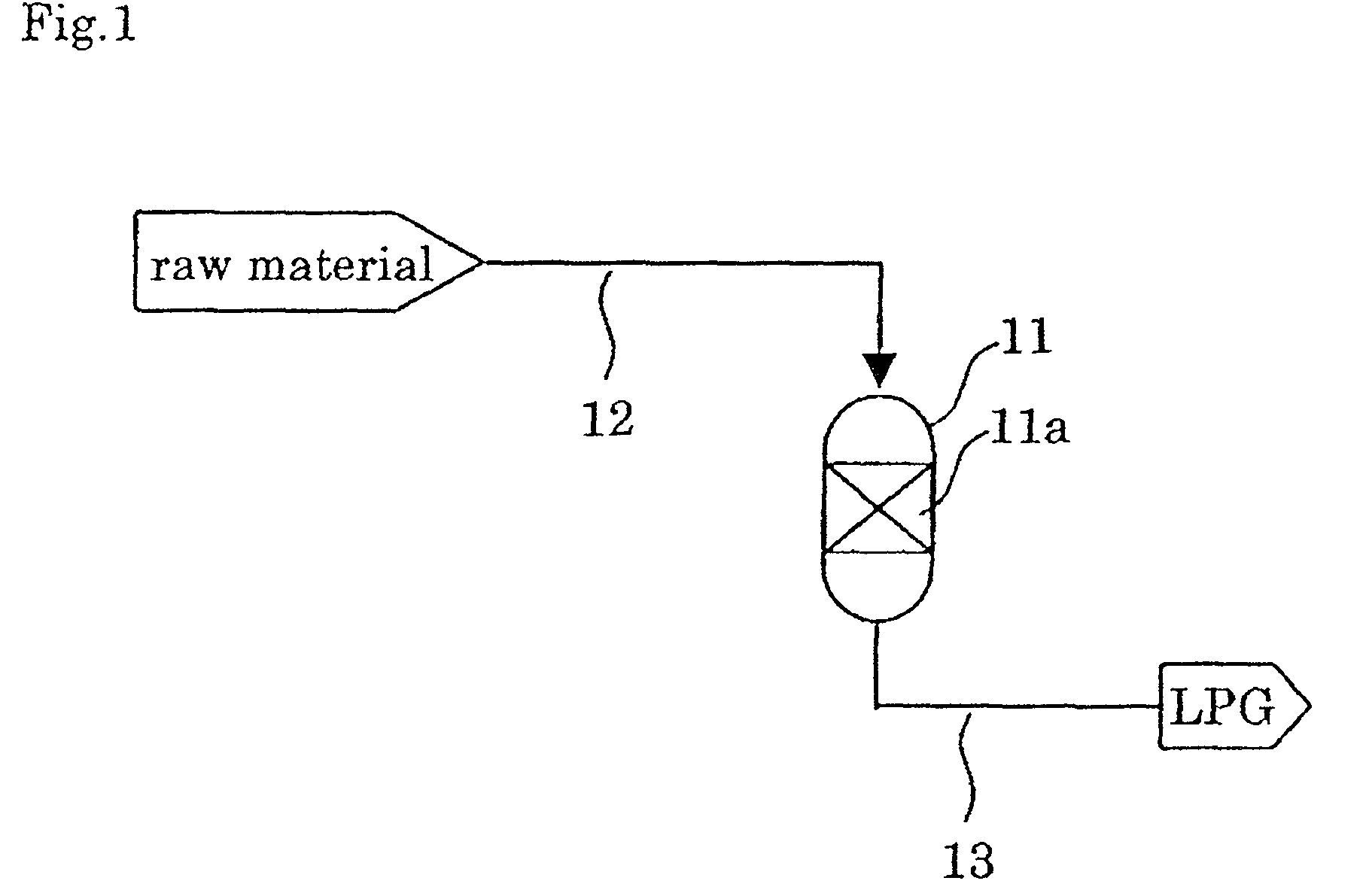
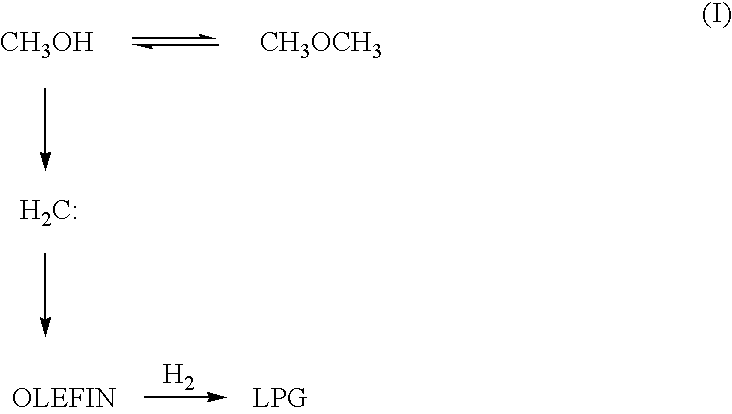
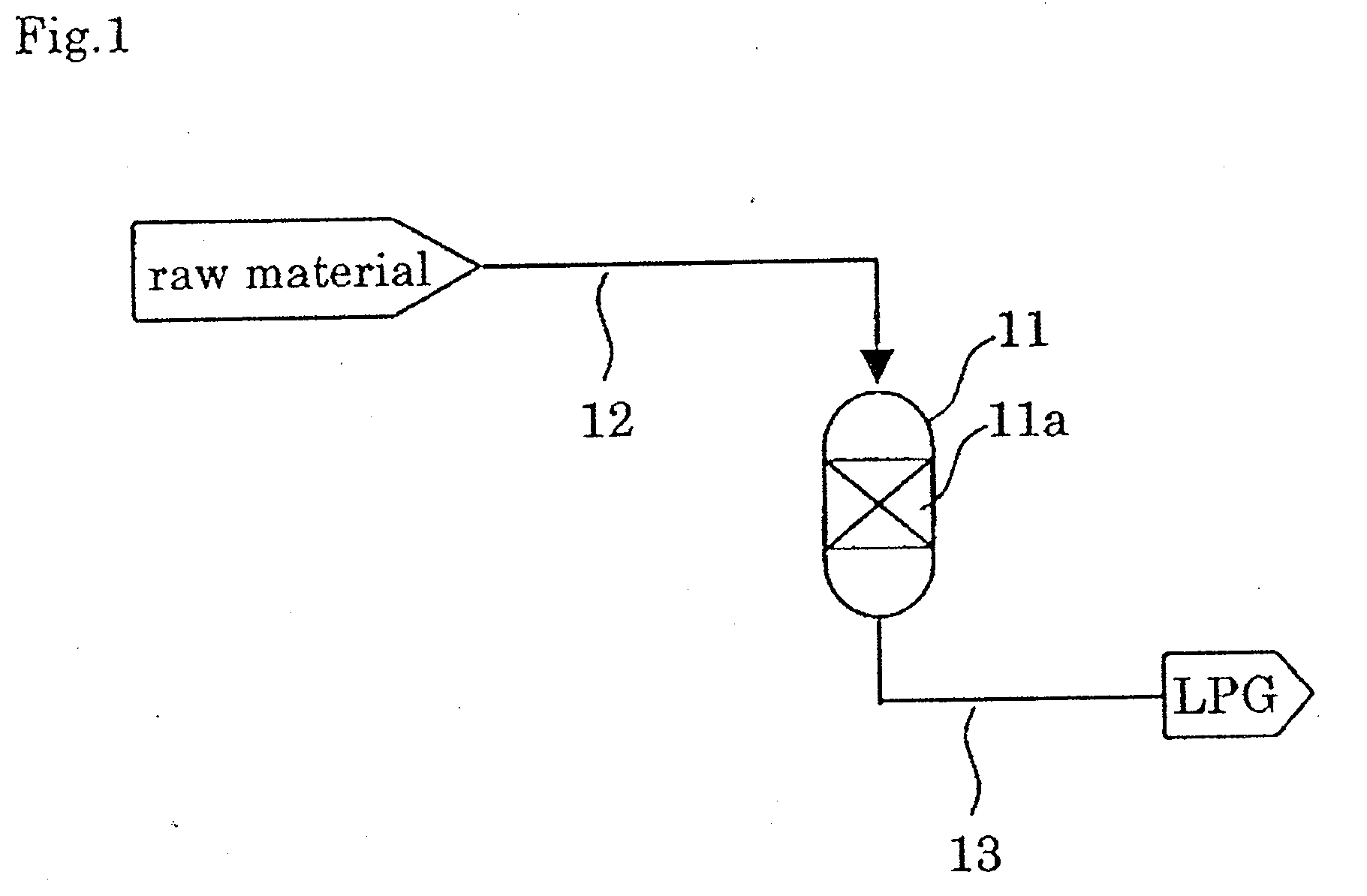
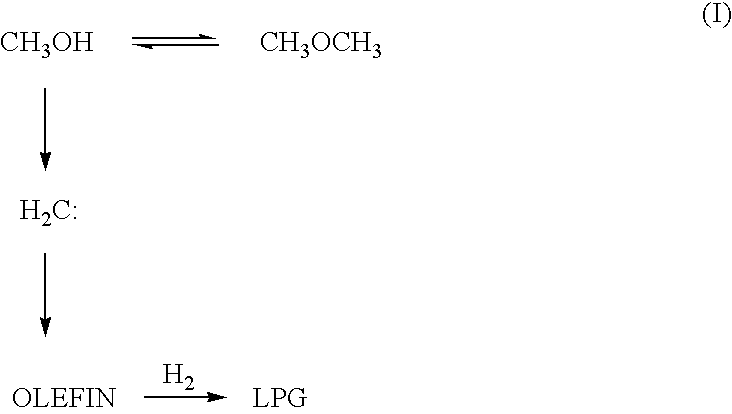
Catalyst and process for producing liquefied petroleum gas
InactiveUS7834230B2High activityHigh selectivityHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMolecular sieve catalystsPt based catalystsHigh activity
A catalyst for producing a liquefied petroleum gas according to the present invention comprises a Pd- and / or Pt-based catalyst component and a USY-type zeolite. By using the catalyst, a hydrocarbon containing propane or butane as a main component, i.e. a liquefied petroleum gas, can be produced with high activity, high selectivity and high yield from at least one of methanol and dimethyl ether.
Owner:JAPAN GAS SYNTHESIZE
Method for preparing direct methanol fuel cell carbon-carried Pt-based catalyst
InactiveCN101406833ASimple and safe operationSuitable for industrial scale productionCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSolventUltrasonic dispersion
The invention discloses a method for preparing a carbon-supported Pt-based catalyst of direct methanol fuel cells. The method comprises the following steps: carbon carriers are dispersed in secondary distilled water; Pt or an aqueous solution of the Pt and other metallic compounds is added to the secondary distilled water and then is subjected to ultrasonic dispersion; solvent water is volatilized through magnetic stirring at a temperature between 60 and 90 DEG C, so as to obtain a dry powder body; and the dry powder body is dispersed by use of glycol, added with a reducing agent at a temperature between 30 and 60 DEG C and reduced, so as to obtain the carbon-supported Pt or Pt-based catalyst. The method has the advantages of simple operation; as the glycol can be used as a solvent as well as a protective agent, the preparation process of the catalyst needs no surfactant, stabilizer, functional molecule and the like; and the method is suitable for industrial scale production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method of synthesizing Pt-Ni catalyst material by hydrothermal method
InactiveCN103157494ALow priceReduce manufacturing costMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNano catalystX-ray
The invention discloses a method of synthesizing a Pt-Ni catalyst material by a hydrothermal method. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a Pt source and a Ni source into a solution by secondary water and mixing, adding a carbon source in the mixing solution, and carrying out ultrasonic dispersion on the mixing solution; transferring the mixing solution in a high pressure kettle, and carrying out constant temperature heating; and filtering a liquid, and naturally drying under the room temperature after filtering and depositing, thus obtaining a Pt-Ni nano-catalyst material taking the carbon source as a carrier. The method is simple, a toxic substance is not participated in and released, and the Pt-based nano-particles generation is proved through an X-ray diffraction test; an electrochemical method of a cyclic voltammetry (CV) is utilized to test the catalysis action of the ethanol electrooxidation by the Pt-Ni nanometer catalyst, and the result displays that the synthesizing Pt-Ni catalyst has high catalytic activity on ethanol electrooxidation; and the Ni addition is contributed to the catalytic action, meanwhile, the preparation cost of a Pt-based catalyst is reduced, and the method has high business application value.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of high-stability and high-activity carbon-supported Pt-based catalyst for fuel cell
ActiveCN103191727AGood dispersionNarrow particle size distributionCell electrodesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsFuel cellsHigh energy
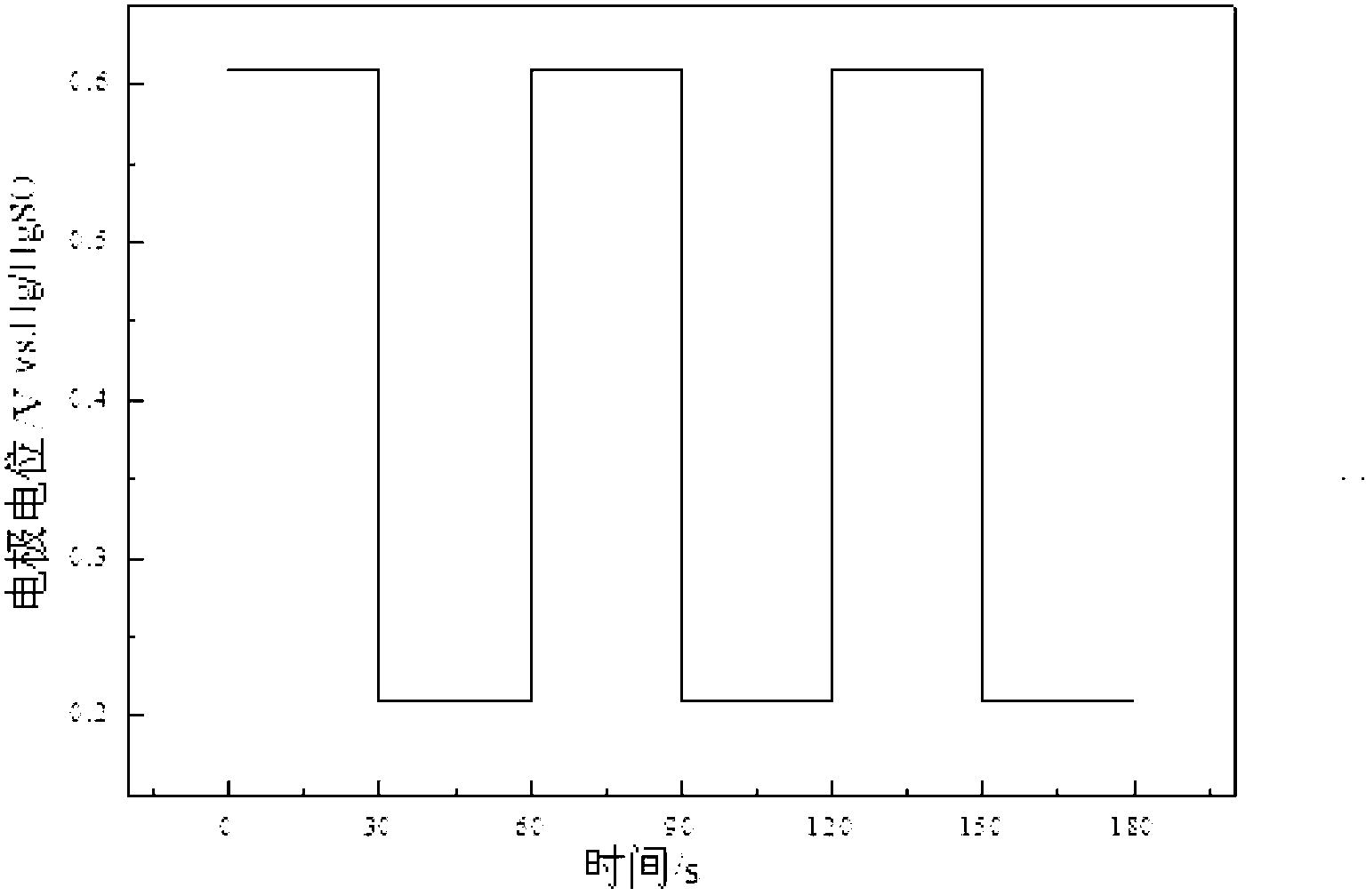
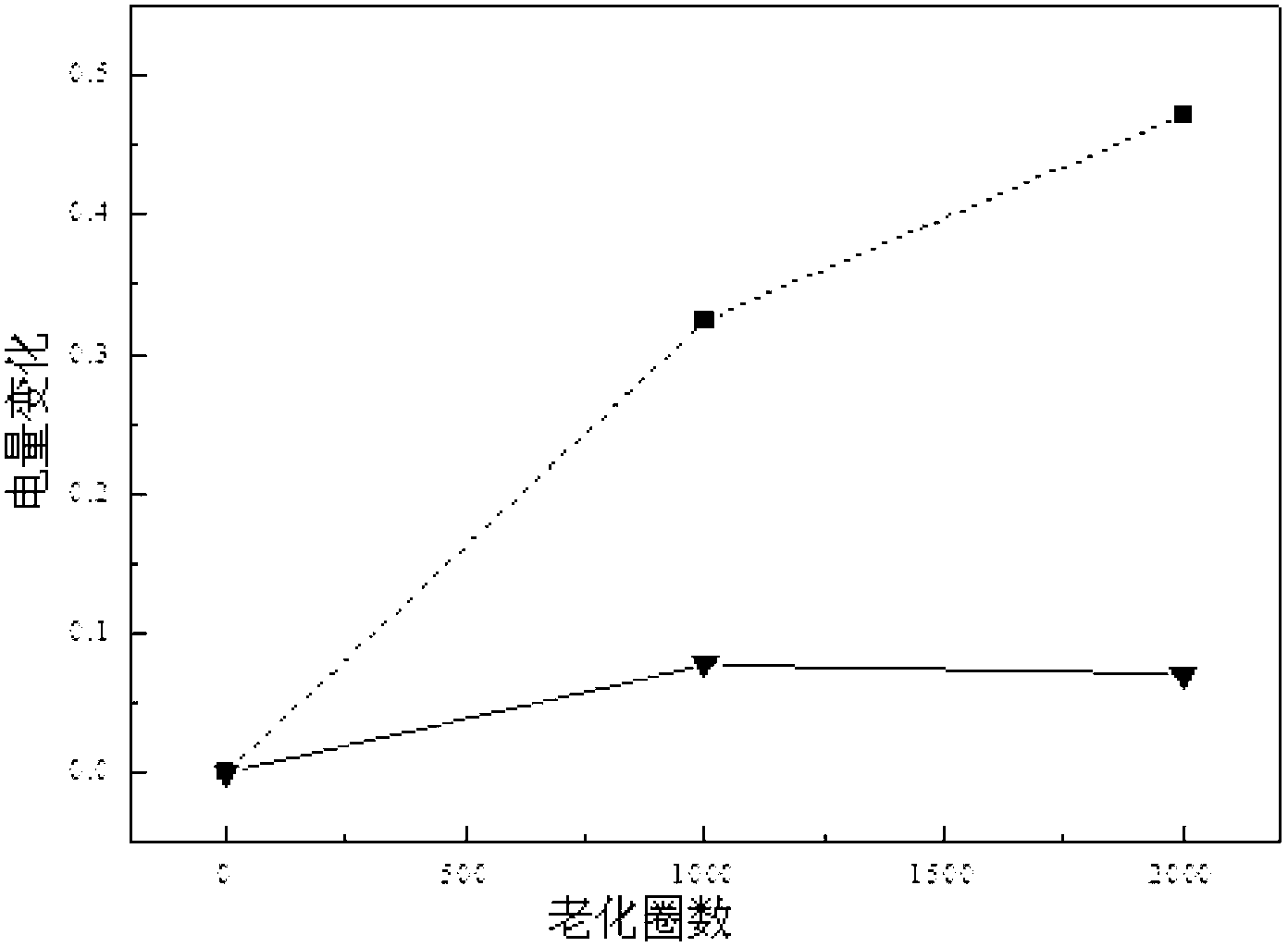
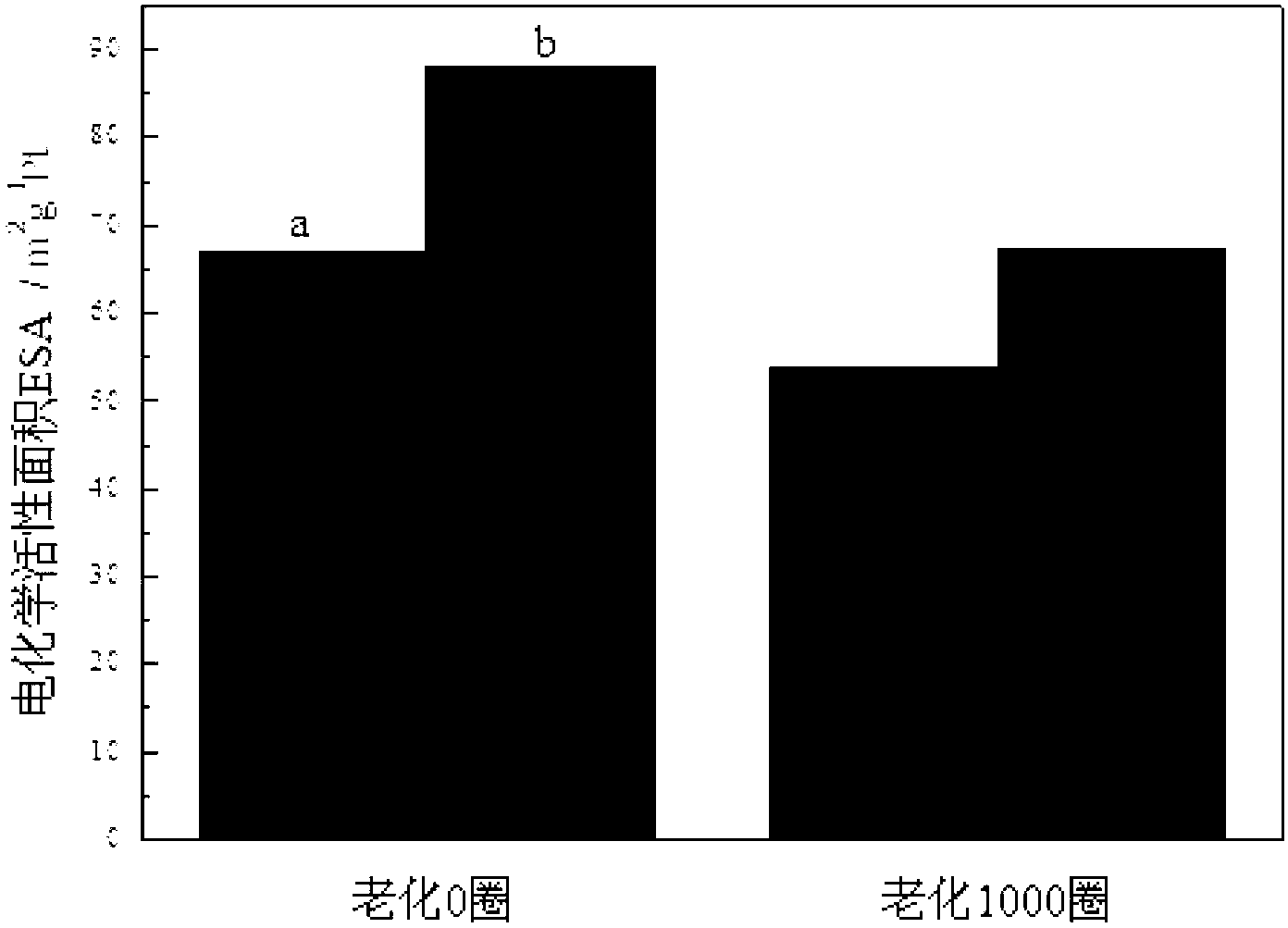
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-stability and high-activity carbon-supported Pt-based catalyst for a fuel cell, relates to the technical field of electrochemistry and aims to solve the problems of low stability and catalytic activity, poor circulating stability, difficult preparation process, high energy consumption and environment pollution of a catalyst used in the traditional fuel cell. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, pretreating a carbon support; secondly, introducing a carbon and nitrogen heterocyclic structure on the carbon support; and thirdly, preparing the carbon-supported Pt-based catalyst. The catalyst provided by the invention is small in particle size up to 1-2nm, good in dispersibility and stability and high in activity and has the electrochemical active area of 88m<2> / gPt and the change rate of 12% after being aged for 1000 circles; and when the voltage is 0.8V (vs.RHE), the catalyst has the oxidation reduction reaction activity ik of 356A / gPt and the change rate of 4% after being aged for 1000 circles, is high in cycling stability and can be applied to the field of electrochemistry.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
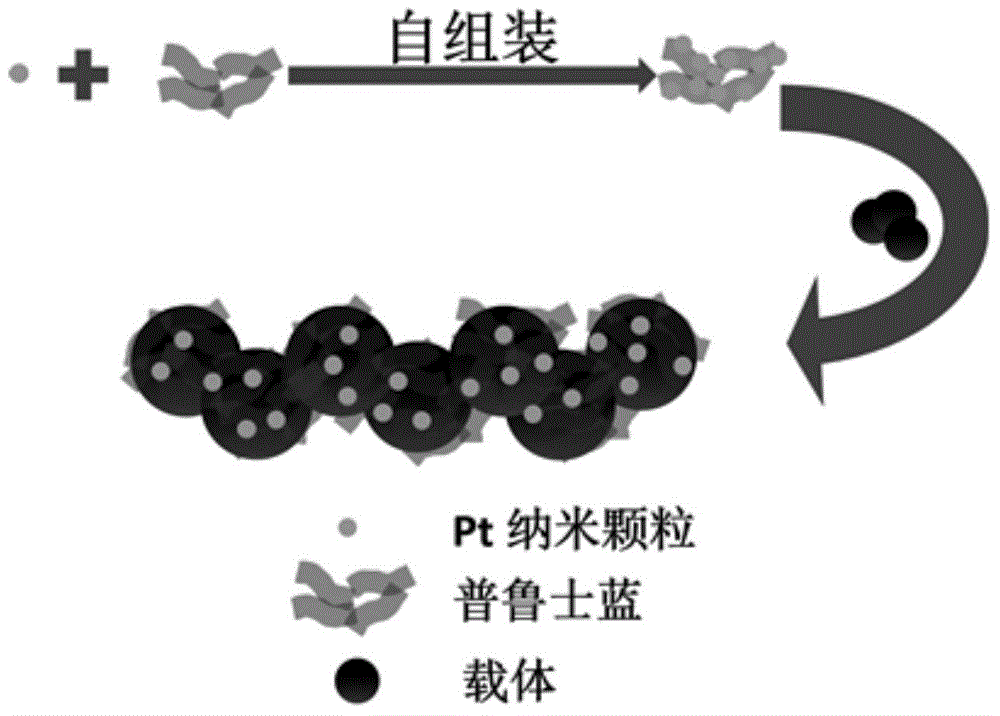
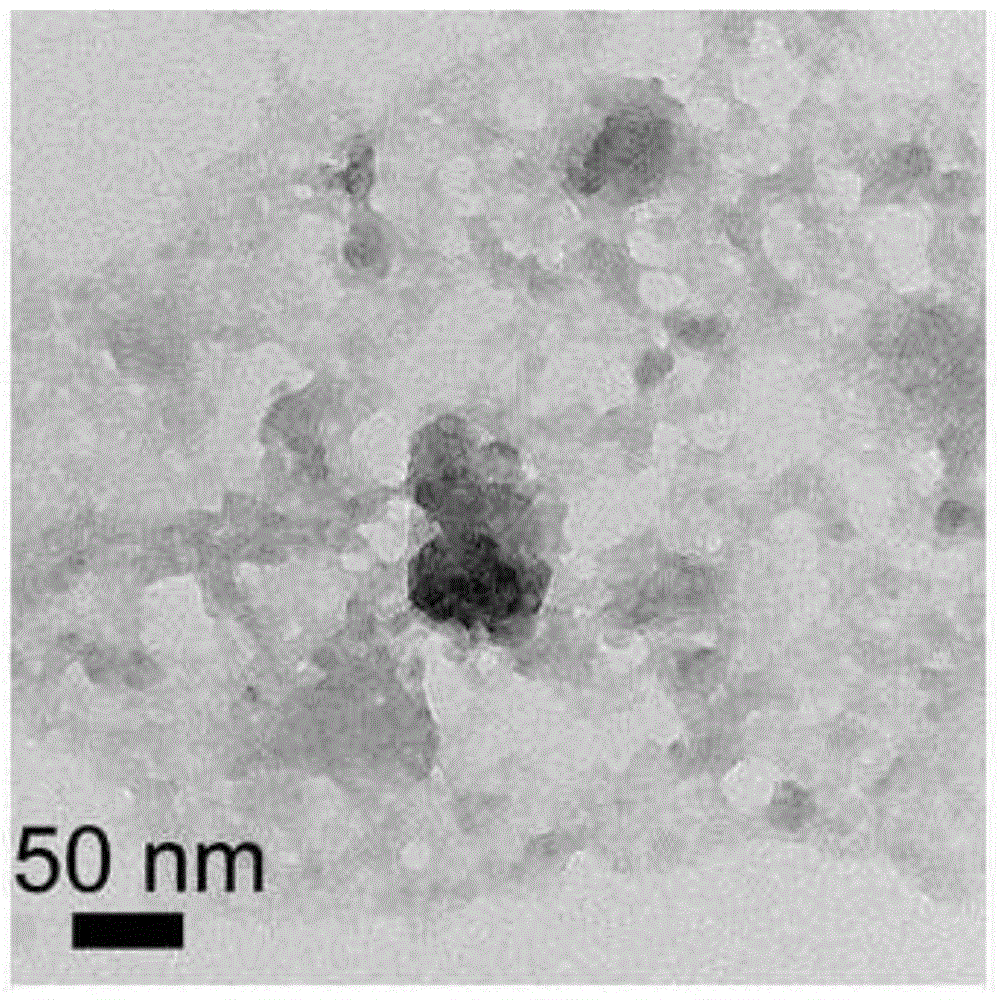
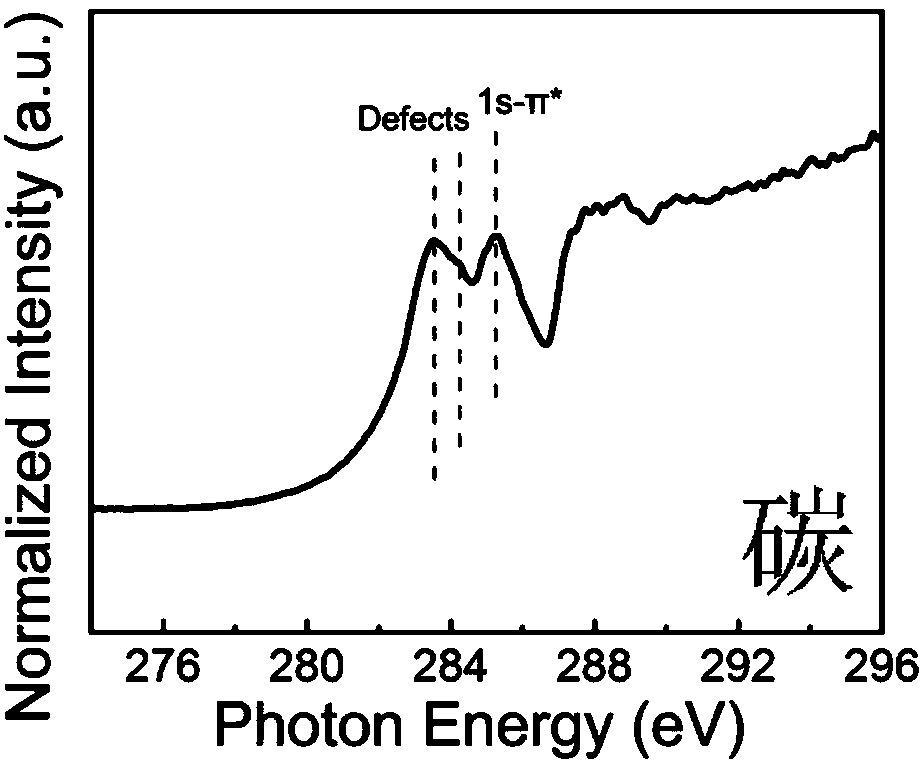
Prussian blue-based high-stability high-activity Pt-based catalyst for fuel cell and preparation method thereof
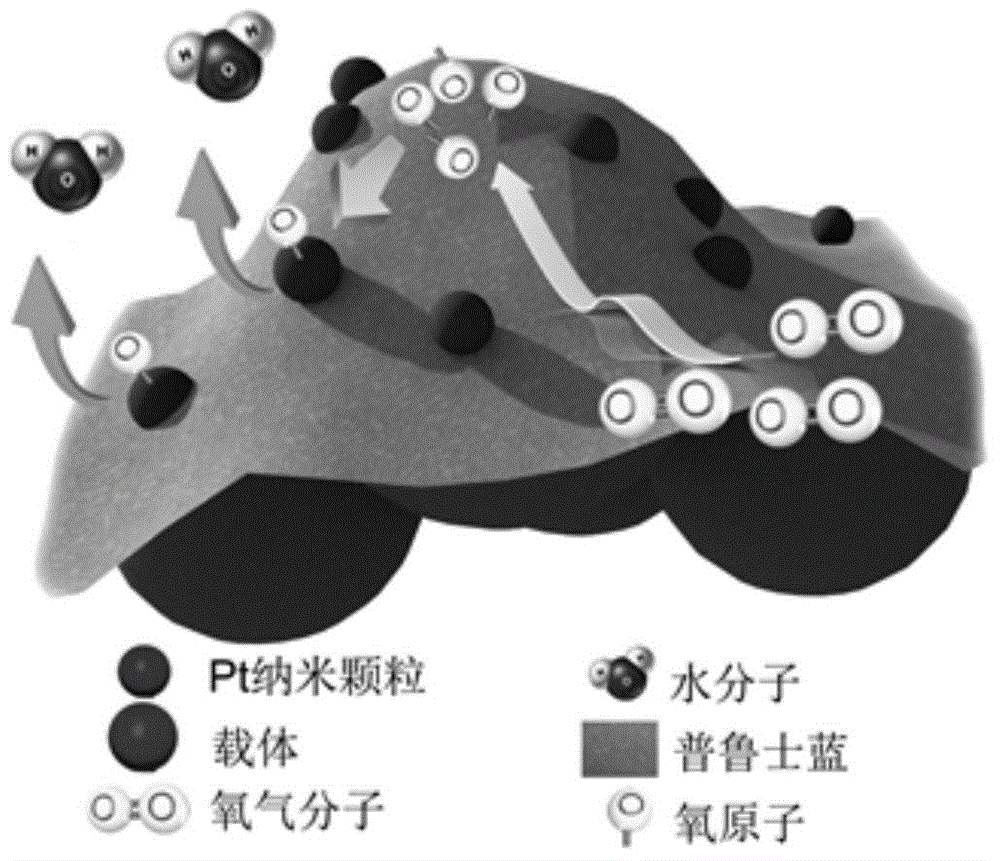
ActiveCN104485464ASmall particle sizeEvenly distributedPhysical/chemical process catalystsCell electrodesFuel cellsPrussian blue
The invention relates to a prussian blue-based high-stability high-activity Pt-based catalyst for a fuel cell and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the Pt-based catalyst for the fuel cell and the preparation method thereof, aiming at achieving the purposes of stability and activity of a cathode catalyst of the fuel cell. The catalyst is a composite catalyst which comprises Pt, the prussian blue and a carrier, wherein the weight ratio of the Pt to the prussian blue is (1-20) to 1, and the weight ratio of the Pt to total amount of the composite catalyst is (2.5-60) to 100. Compared with commercial Pt / C, the Pt-based composite catalyst disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the stability and the activity are greatly promoted, and a related Pt-prussian blue synergetic mechanism is provided for the first time to explain the promotion of the stability and the activity.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for preparing Pt-based catalyst by pulse electrodeposition under ultrasonic conditions
InactiveCN109331820AEvenly dispersedUniform and firm loadCell electrodesCatalyst activation/preparationPulse power supplyControllability
The invention discloses a method for preparing a Pt-based catalyst by pulse electrodeposition under ultrasonic conditions, and belongs to the technical field of electrodeposition. The method combinesadvantages of both pulse electrodeposition and ultrasonic conditions, and electrodeposits to prepare the Pt-based catalyst by separately preparing a desired salt solution as an electroplating solutionin an aqueous solution, an organic solvent or an ionic liquid, and using a carbon material as a carrier, and using a pulse power supply to set different pulse electrodeposition current densities, current on-off time ratios (ton / toff), temperatures and other process parameters. According to the invention, the method for preparing the Pt-based catalyst by combining the pulse electrodeposition withthe ultrasonic conditions is simple in process operation, environmentally-friendly and strong in condition controllability; and the prepared Pt-based catalyst is small in average particle size, largein specific surface area and firm to bond with the carrier.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of proton exchange membrane fuel cell negative electrode catalyst with defect-structure nitrogen/sulfur co-doped porous carbon aerogel
ActiveCN108448116AWide variety of sourcesImprove securityCell electrodesFuel cellsPorous carbonHierarchical porous
The invention discloses a preparation method of proton exchange membrane fuel cell negative electrode catalyst with defect-structure nitrogen / sulfur co-doped porous carbon aerogel, and belongs to thefield of a fuel cell. In the carbon aerogel, the PEMFCs negative electrode catalyst is successfully prepared by taking carrageenan and urea as raw materials. The carbon aerogel is provided with a richdefect structure and a nitrogen and sulfur heteroatom co-doped and hierarchical porous structure, and excellent oxidization-reduction reaction (ORR) catalytic activity is shown (a half-wave potentialunder 0.5M of H2SO4 electrolyte is 0.76V); and the ORR activity of a traditional heteroatom-doped carbon material under an acid electrolyte is not ideal compared with commercial Pt / C, thus, the ORR catalytic performance of the negative electrode catalyst under the acid condition is improved, and the negative electrode catalyst has important significance when applied to the PEMFCs instead of a previous metal Pt-based catalyst. In the negative electrode catalyst, the carrageenan is rich in source, and the nitrogen / sulfur co-doped porous carbon aerogel having the defect structure is excellent inORR catalytic performance and is a potential energy conversion material.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNRISE NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Preparation method for low carbon alkane dehydrogenation catalyst
InactiveCN104289219AAvoid churnAvoid gatheringHydrocarbonsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAlkaneDispersity
The invention discloses a preparation method for a propane dehydrogenation catalyst. Without hydrogen reduction, a reaction feed gas is directly introduced and the Pt reduction degree is controlled to improve the stability and sulfur tolerance of the catalyst. The method omits of the drying roasting process, can effectively remove chlorine from the catalyst without hydrothermal treatment, and can significantly improve the activity, selectivity, stability and sulfur tolerance of the catalyst without hydrogen reduction. The preparation method is simple. The catalyst prepared by the method can avoid excessive alkali loss, improve the dispersity of Pt based catalyst active metals, form more secondary active phases, and ultimately improve the selectivity of the target product propylene and the catalyst activity, stability and sulfur tolerance.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Process for preparing fuel cell carbon-carried Pt-based catalyst
InactiveCN1402367AEvenly distributedEasy to operateCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsWater bathsPolymer dielectrics
The invented preparing method includes only two steps. First, mixing the alcoholic solution of the compound of platinum (and alloy constituent) with the carbon carrier fully, making the admixture evenly. The alcohol solvent is vaporized by use of the water bath at the controlled temperature. Then, the dry powder obtained is deoxidized in hydrogen at the condition of mild heating. The granularity of the platinum (alloy) obtained by the method is 1-2 nm with evenly distributed on the carbon carrier. The catalyst possesses the better performances of the electrocatalysis reaction relevant to the polymer dielectric film fuel cell such as oxidation of hydrogen and deoxidization of oxygen, oxidation of carbon monoxide, oxidation of methanol. The invention provides the features of easy of operation, without need of filtering and washing only need of a little cheap chemicals.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Low-temperature catalytic benzene hydrogenation method and special catalyst thereof
InactiveCN101289365BEasy to understandHydrocarbon by hydrogenationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsBenzeneMetal catalyst
The invention discloses a catalyzing method of benzene hydrogenation at low temperature and a special catalyst thereof. The catalyzing method of the benzene hydrogenation at the low temperature provided by the invention uses a co-based catalyst to catalyze the benzene hydrogenation to react; wherein, the co-based catalyst is a cobalt single metal catalyst / or a noble metal-cobalt bimetal catalyst. Compared with a Ni-based catalyst or a Pt-based catalyst which is used for catalyzing the benzene hydrogenation to react at present, the invention can realize the benzene hydrogenation reaction at low temperature or even under condition of room temperature by using the co-based catalyst to catalyze the benzene hydrogenation to react and is provided with high hydrogenation activity. The invention provides a novel co-based catalyst, namely the noble metal-cobalt bimetal catalyst which is used in the benzene hydrogenation reaction. The noble metal-cobalt bimetal catalyst is provided with higher hydrogenation activity than the cobalt single metal catalyst. Besides being used in the preparation of cyclohexane, the co-based catalyst can be used in the intensive removal of aromatics, in particular the benzene in the fuel oil and the elimination of trace benzene in the environment.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
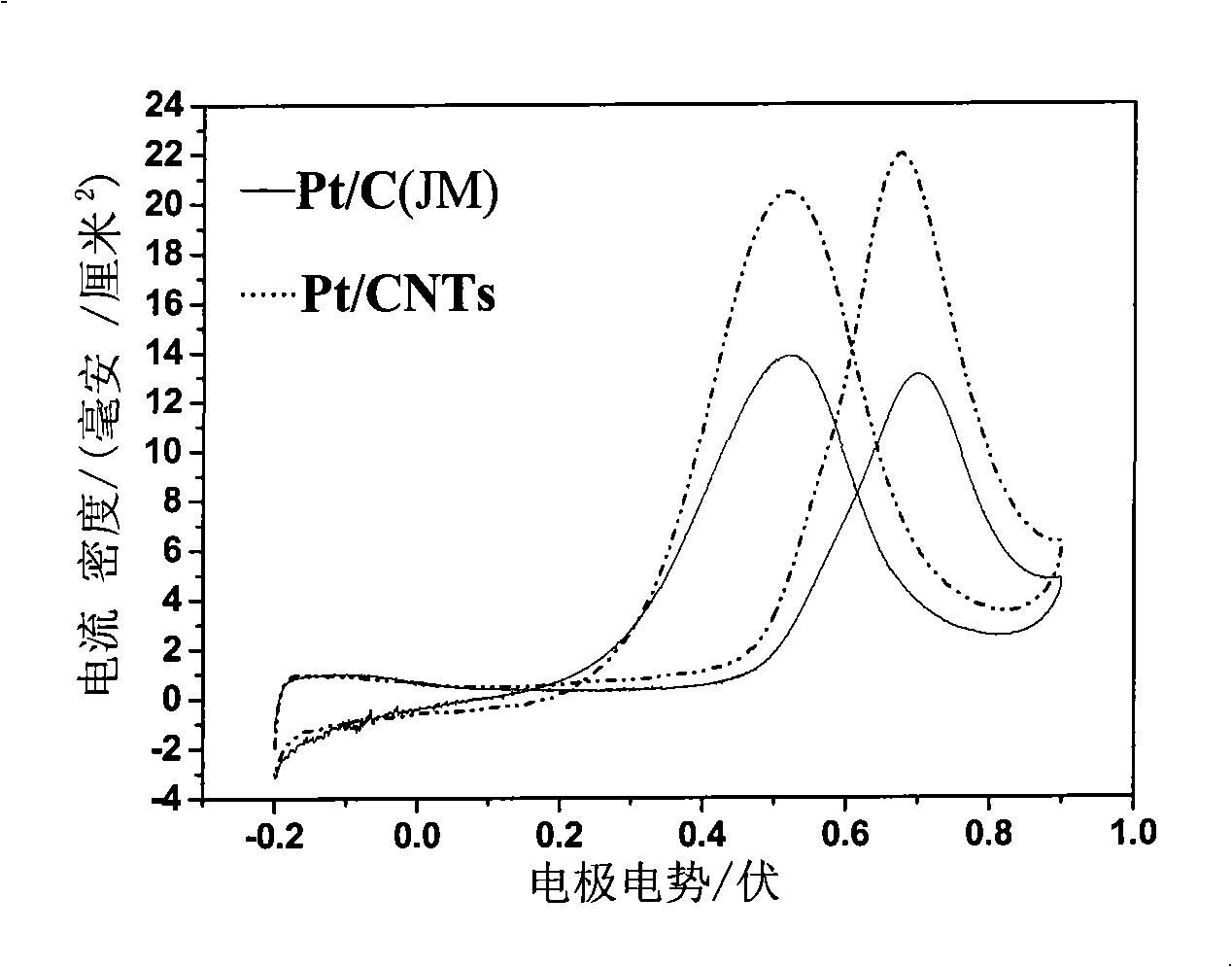
Preparation method of Pt-based catalyst for fuel cell
The invention relates to a preparation method of a Pt-based catalyst for a fuel cell. According to the invention, a carbon black-graphene compound functionally modified by PDDA is synthesized based ona solution self-assembly method, and further a three-dimensional porous Pt / functionalized carbon black-graphene composite catalyst is obtained through solvothermal reduction. The study found that thethree-dimensional composite catalyst has a high specific surface area, an abundant pore channel structure, good conductivity, an excellent ion transport ability, small particle size and uniform particle size distribution. The electrochemical test result shows that the three-dimensional porous Pt / functionalized carbon black-graphene composite catalyst has excellent catalytic activity and cycle stability in oxygen reduction, and can be used as a high-efficiency cathode catalyst for proton exchange membrane fuel cells.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Modified Pt-based fuel-cell catalyst and preparation methods thereof
InactiveCN102593475AEasy to operateCell electrodesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEnvironmental resistancePt based catalysts
The invention provides a modified Pt-based fuel-cell catalyst which is characterized by comprising a Pt-based catalyst and a heteropoly-acid modifier, wherein the heteropoly-acid modifier is adsorbed to the surface of the Pt-based catalyst by using an electrochemical method or a physical adsorption method. The catalyst provided by the invention has a good performance of resisting the poisoning of reactive intermediates such as CO and the like, and a good performance of carrying out catalytic oxidation on methanol. The invention also provides two methods for preparing the modified Pt-based fuel-cell catalyst, by which good-performance modified Pt-based fuel-cell catalysts can be prepared; the preparation methods are simple and easy to operate and short in preparation time; meanwhile, no organic solvent is used, therefore, the methods are environment-friendly and safe.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Platinum based catalyst highly dispersed in carrier silicon dioxide as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108067249ANot easy to aggregate and sinterImprove stabilityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalystsDehydrogenationSilicon dioxide
The invention discloses a Pt based catalyst highly dispersed in a carrier SiO2 as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The catalyst takes SiO2 as the carrier, takes metal Pt as an active component, and takes NiO, La2O3 and LaFeO3 as auxiliaries; based on the total mass of the catalyst, the Pt based catalyst is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 0.1-0.3%of metal Pt, 0.05-4% of NiO, 0.25-9.0% OF La2O3, 17.0-30.0% of LaFeO3 and 55.0-85.0% of SiO2, and the catalyst can be applied to isobutylene dehydrogenation. The selected SiO2 has a big specific surface area, so that each component can be highly dispersed, and therefore, the catalyst is not liable to gather and sinter; meanwhile, Pt is doped into a perovskite structure, so that the reduced Pt particles are small, and perovskite particles, lanthanum oxide particles and nickel oxide particles among the Pt particles achieve the dispersion effect as a result of the special structure of perovskite,and therefore, more active sites are exposed; and Pt is not liable to reunite at a high temperature, so that stability and reaction activity of the catalyst are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
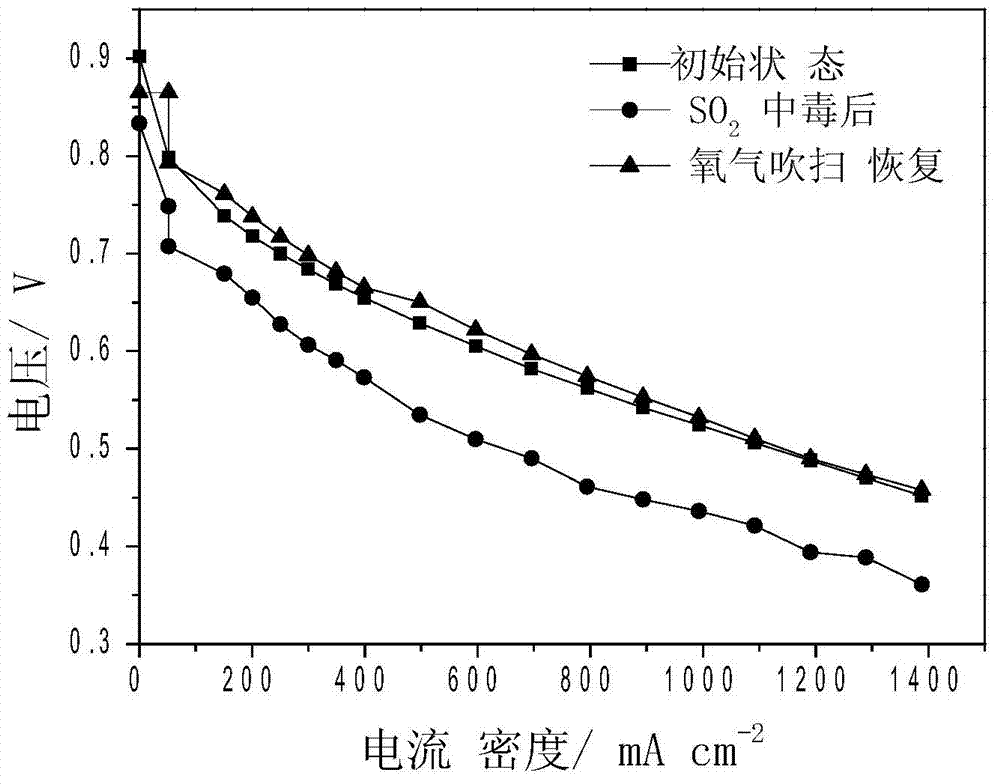
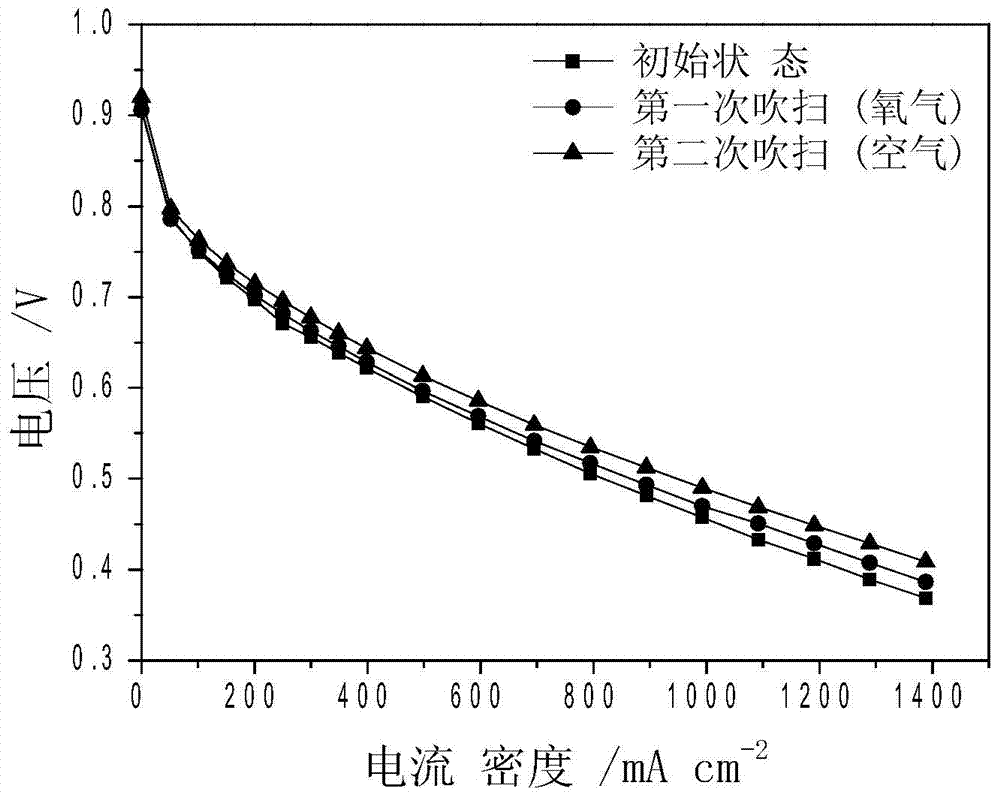
Application of catalyst in fuel cell SO2 poisoning resistance, and poisoning recovery method
ActiveCN104716344ARestore performanceWorks well when humidifiedCell electrodesRecovery methodFuel cells
The invention provides a cathode SO2 poisoning resistance catalyst suitable for a fuel cell, and a poisoning recovery method against the characteristics of easy SO2 adsorption and great reduction of performances of present fuel cell cathode Pt-based catalysts. A Pt-Ru alloy electro-catalyst with the Pt / Ru atom ratio of 1-5:0.5-5 has surface adsorbed SO2 self-catalysis oxidation performance and strong SO2 poisoning resistance as the cathode catalyst of the fuel cell. When Pt-Ru is adopted as the fuel cell cathode catalyst, air or nitrogen is introduced through anode after the SO2 poisoning of the fuel cell, and air or oxygen is introduced to the cathode to purge for 0.01-10h, so the performances of the catalyst can be completely recovered.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Anti-poisoning Pt-based nano-catalyst, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107732262AInhibition of CO poisoning effectExhibits anti-methanol poisoning performanceMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesNano catalystAlloy
The invention discloses an anti-poisoning Pt-based nano-catalyst, and a preparation method and application thereof. An ultrathin h-BN shell structure is formed on the surface of a carbon-supported Ptand Pt-based alloy nano-catalyst by utilizing a surface coating method to obtain a core-shell nano-structure of Pt@h-BN / C and PtTM@h-BN / C(TM is a transition metal, such as Ru, Sn, Au and Fe). The catalyst serves as an H2-O2 proton exchange membrane fuel cell anode catalyst which can remarkably inhibit the CO poisoning effect on a Pt-based catalyst; the catalyst can also be used in a direct methanol fuel cell and can show resistance to methanol poisoning.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
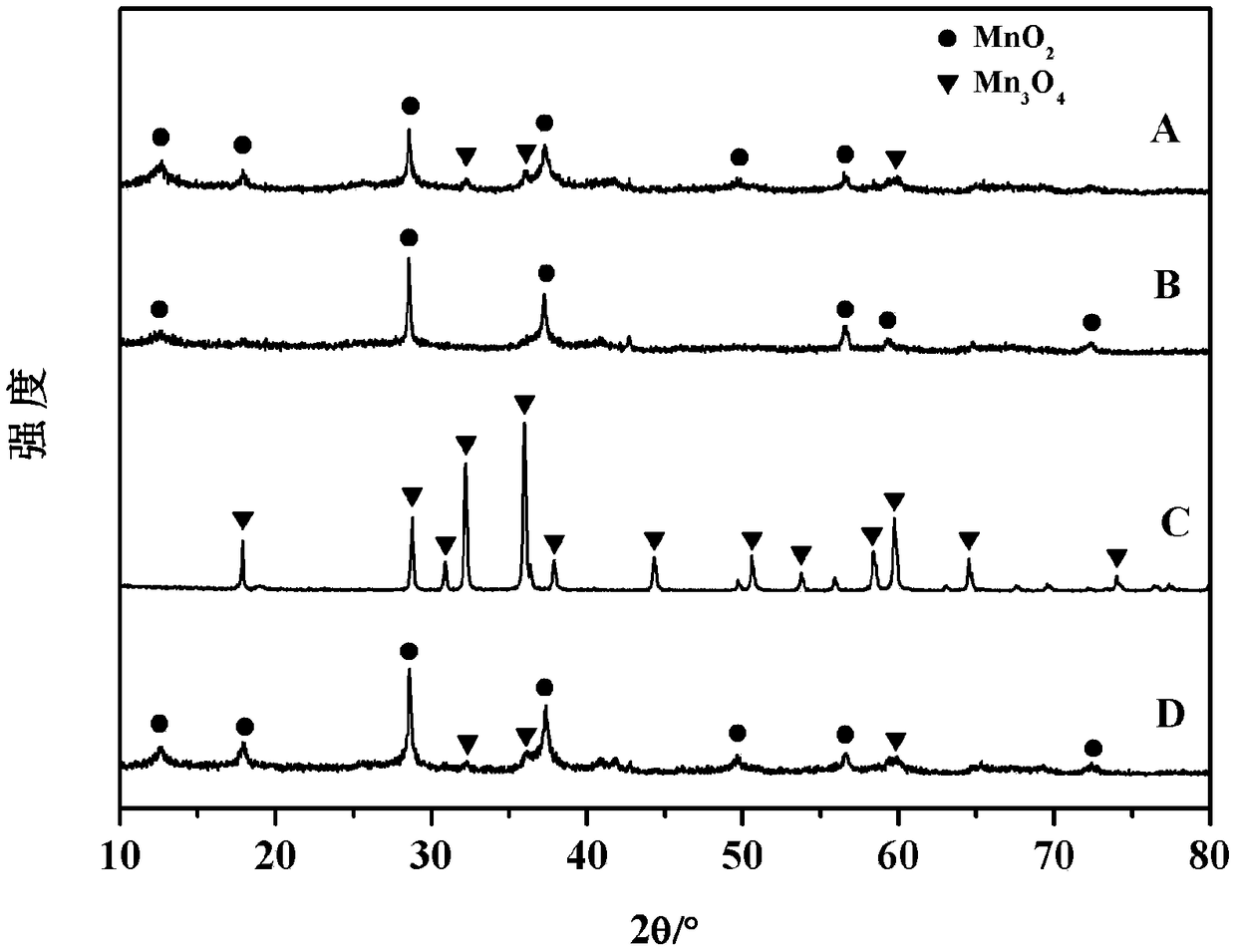
In-situ synthesized Pt/MnO2@Mn3O4 catalyst for catalytic combustion of VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) as well as preparation method and application of in-situ synthesized Pt/MnO2@Mn3O4 catalyst
ActiveCN108816225AAchieve complete catalytic combustionImprove stabilityCatalyst activation/preparationIncinerator apparatusPotassium permanganateReducing agent
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment catalytic purification and provides an in-situ synthesized Pt / MnO2@Mn3O4 catalyst for catalytic combustion of VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) as well as a preparation method and application of the in-situ synthesized Pt / MnO2@Mn3O4 catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking potassium permanganate and oxalic acid as raw materials and preparing MnO2 by utilizing a hydrothermal method; then taking MnO2 as an initial carrier and utilizing sodium borohydride as a reducing agent; carrying out liquid-phase reduction on H2PtC16 under a room-temperature condition, and carrying out structure regulation and control on the MnO2 carrier; carrying out one-step reduction to obtain an in-situ synthesized mixed-phase MnO2@Mn3O4 catalyst carrier loading type Pt-based catalyst, wherein the content of Pt is 0.2 to 0.5 weight percent. The preparation method provided by the invention has a simple preparation process; the dispersed loading of active components and the optimization of a carrier structure can be realized in one step. The catalyst provided by the invention is applied to the catalytic combustion of the VOCs including toluene, xylol and the like and has relatively good low-temperature activity and stability; no other waste gas is generated.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Pt-based catalyst for dehydrogenation of isobutane by using carrier Sn-containing mesoporous carbon, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106311201AHigh selectivityReduce manufacturing costHydrocarbonsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActive componentDehydrogenation
The invention discloses a Pt-based catalyst for dehydrogenation of isobutane by using a carrier Sn-containing mesoporous carbon. The weight of an active component Pt which is metered based on a simple substance is 0.5-4% of the weight of the carrier, and the weight of Sn which is metered based on a simple substance is 0.5-6% of the weight of the carrier. After 20 hours of reactions of the Pt-based catalyst for dehydrogenation of isobutane by using the carrier Sn-containing mesoporous carbon, conversion rate of the catalyst isobutane reaches 38.6%, corresponding selectivity of isobutene reaches 94.3%, activity is decreased by 3.2%, and the catalyst has low preparation cost and good industrial application prospects.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Platinum based catalyst highly dispersed in carrier aluminum oxide as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108067227AImprove easy sinteringHigh activityCatalystsHydrocarbon preparation catalystsIndiumDehydrogenation
The invention discloses a Pt based catalyst highly dispersed in a carrier Al2O3 as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The Pt based catalyst highly dispersed in the carrier Al2O3 takes Al2O3 as the carrier, takes In2O3 and La2O3 as auxiliaries and takes metal Pt as an active ingredient; based on the total mass of the catalyst, the catalyst is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 0.2-2% of Pt, 7-9% of In2O3, 10-12% of La2O3, 75-85% of Al2O3, and the catalyst can be applied in propane dehydrogenation. The Pt based catalyst has the advantages that the Ptand In are doped into perovskite B, so that Pt and In are uniformly dispersed into a perovskite structure in aspect of atomic level, and the reduced PT particles and indium oxide are highly dispersedand distributed onto the carrier aluminum oxide; the Pt particle diameter is small, and indium oxide particles and lanthanum oxide particles are distributed among the particles to achieve the blocking effect, so that Pt is not liable to reunite at a high temperature, and more active sites are exposed, and therefore, activity and stability of reaction are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
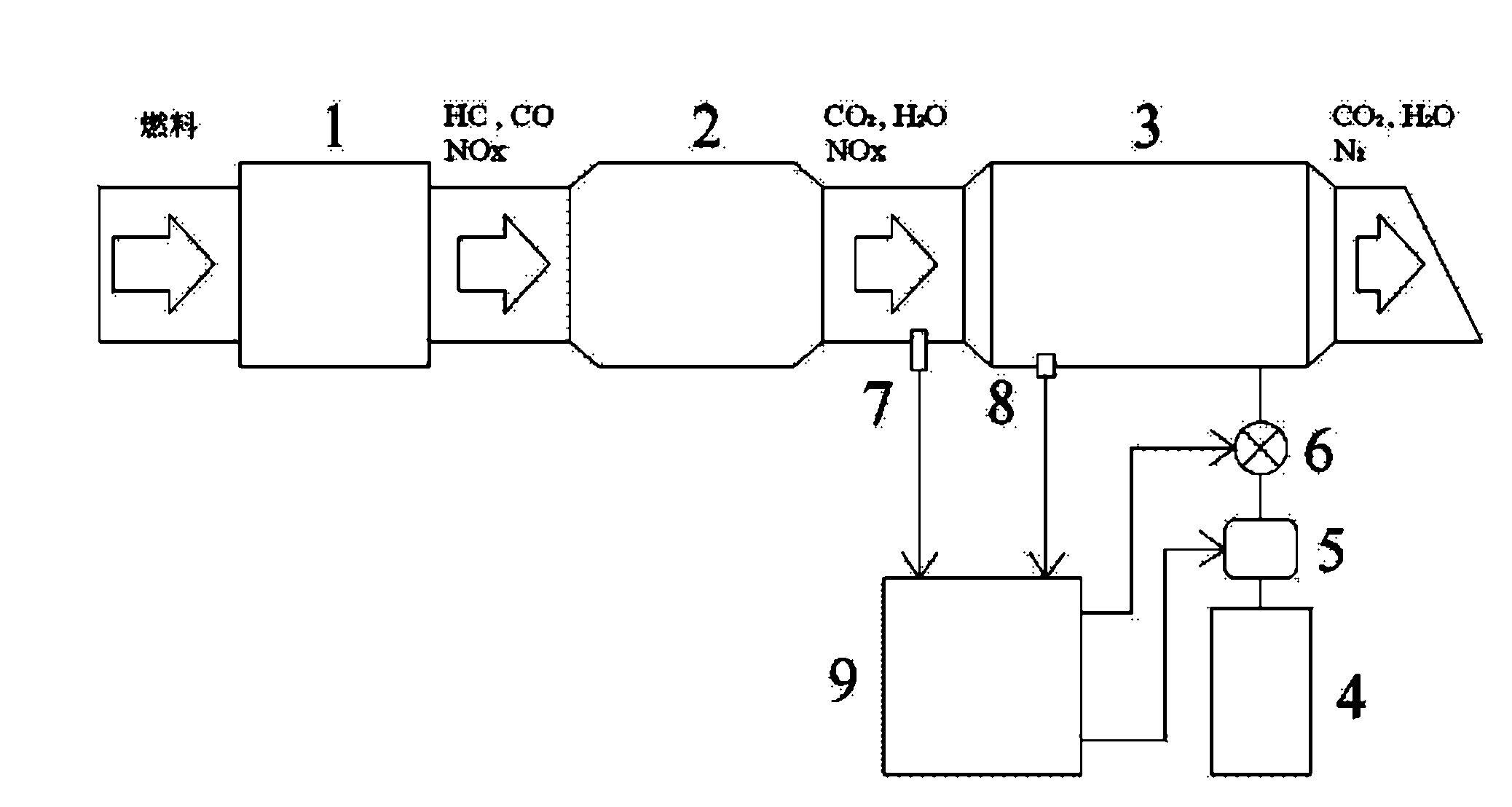
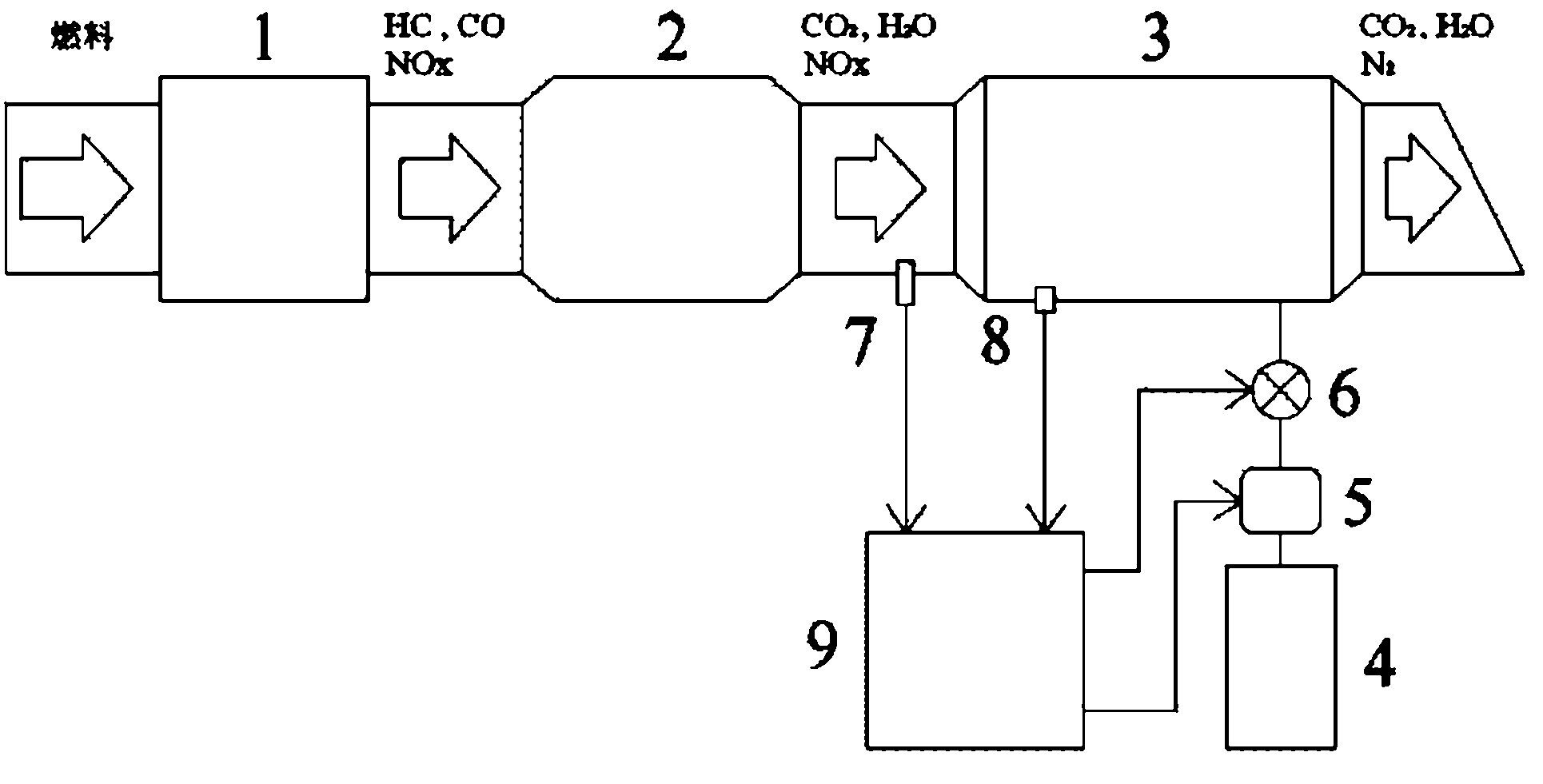
Reformed-gas-based device and method for purifying engine tail gas
InactiveCN102162389AInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusSteam reformingSolenoid valve
The invention relates to a reformed-gas-based device and a reformed-gas-based method for purifying engine tail gas. The device comprises three parts, namely a tail gas circulation unit, a reformed fuel supply unit and an electronic control unit, wherein the tail gas circulation unit comprises an engine, a platinum (Pt)-base catalytic reformer and a Cu-base catalytic reformer; the reformed fuel supply unit comprises a reformed fuel tank, a reformed fuel pump and a reformed fuel flow control solenoid valve; and the electronic control unit comprises a flow sensor, a temperature sensor and an electronic control unit. The device and the method apply a lean-burn control strategy. Under the lean-burn condition, O2 in the engine tail gas is sufficient, a product formed by burning fuel passes through the Pt-base catalytic reformer originally, and HC and CO in the tail gas react with the O2 in the presence of a Pt-base catalyst; then the product passes through the Cu-base catalytic reformer, and the fuel performs a steam reforming reaction in the presence of a Cu-base catalyst to generate hydrogen-enriched reformed gas containing the H2 and CO; and the H2 and the CO react with NOx in the tail gas to fulfill the aims of energy conservation and emission reduction.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Catalyst and process for producing liquefied petroleum gas
InactiveUS20070106106A1Long catalyst lifeStable productionMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystPt based catalystsComponents of crude oil
Owner:JAPAN GAS SYNTHESIZE
Method for preparing modified Pt-based catalysts with La loaded by metal organic framework materials used as carriers and application of modified Pt-based catalysts
ActiveCN107715873ALarge specific surface areaStrong ability to absorb hydrogenOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsN dimethylformamideMetal-organic framework
The invention discloses a method for preparing modified Pt-based catalysts with La loaded by metal organic framework materials used as carriers and application of the modified Pt-based catalysts. Themethod includes adding deionized water into terephthalic acid, chromic nitrate nonahydrate and hydrofluoric acid mixtures to obtain first mixtures; crystallizing the first mixtures for a period of time and then filtering and drying the first mixtures; adding N, N-dimethylformamide into the first mixtures and carrying out stirring reaction; filtering, washing and drying reaction products to obtainthe metal organic framework materials which are used as the carriers; adding chloroplatinic acid aqueous solution and precursor salt into the metal organic framework materials; carrying out reaction,then drying and calcining reaction products and carrying out reduction on the reaction products to obtain the ultimate required modified Pt-based catalysts La-Pt / MIL-101. The method and the application have the advantages that the modified Pt-based catalysts are low in cost, high in universality, free of equipment corrosion and good in cycle performance and are economical, effective and environmentally friendly; the modified Pt-based catalysts are high in activity and para amino phenol selectivity under relatively mild reaction conditions when applied to processes for preparing para amino phenol by means of nitrobenzene one-step hydrogenation rearrangement, production conditions can be improved, the production cost can be reduced, and the quality of products can be enhanced.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com