Energy-Saving Mode of Freely Staying in Water
a technology of free and energy-saving, water-based activities, applied in the direction of sports equipment, etc., can solve the problems of unskilled swimmers, inability to overcome the main difficulty, fear of sinking into water, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding water admission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
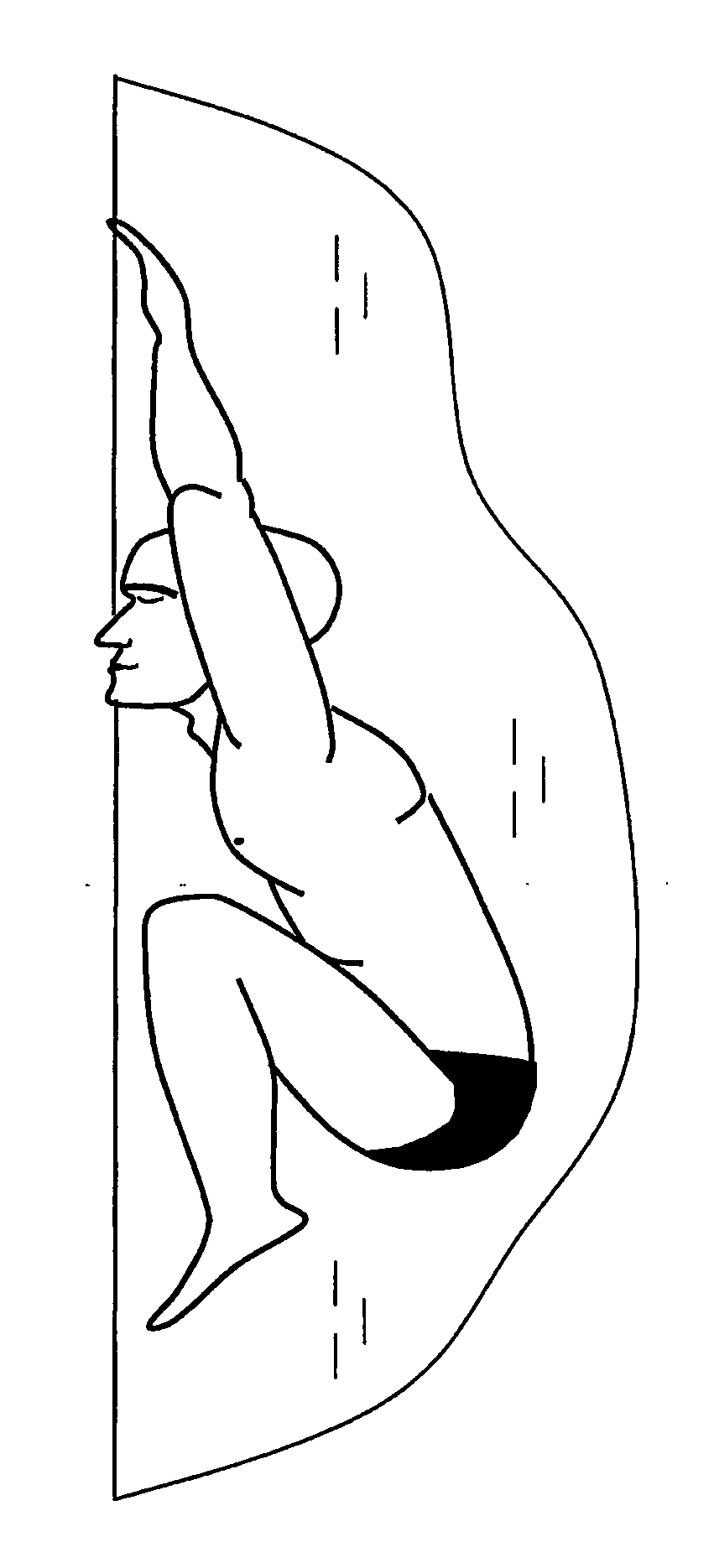
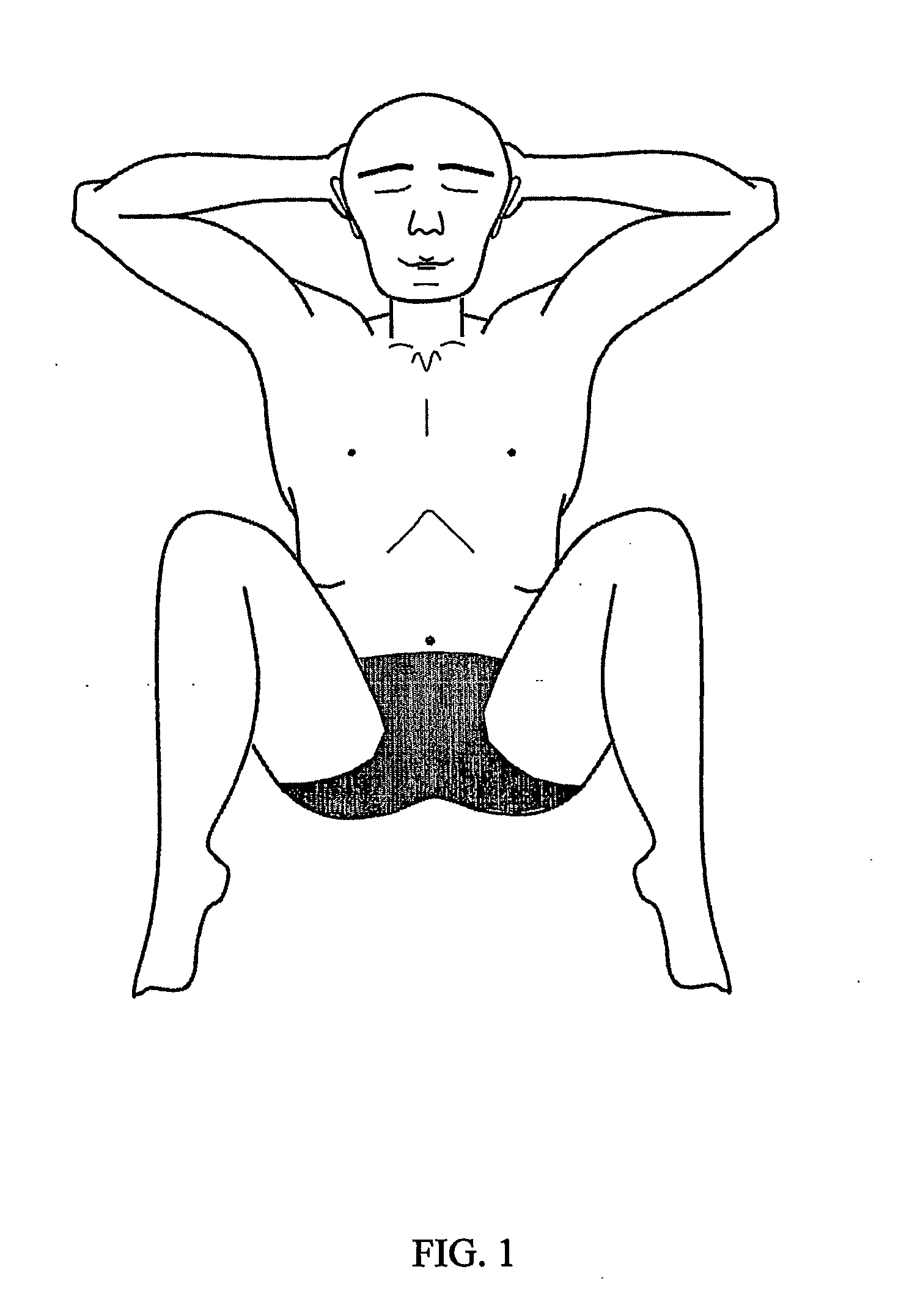
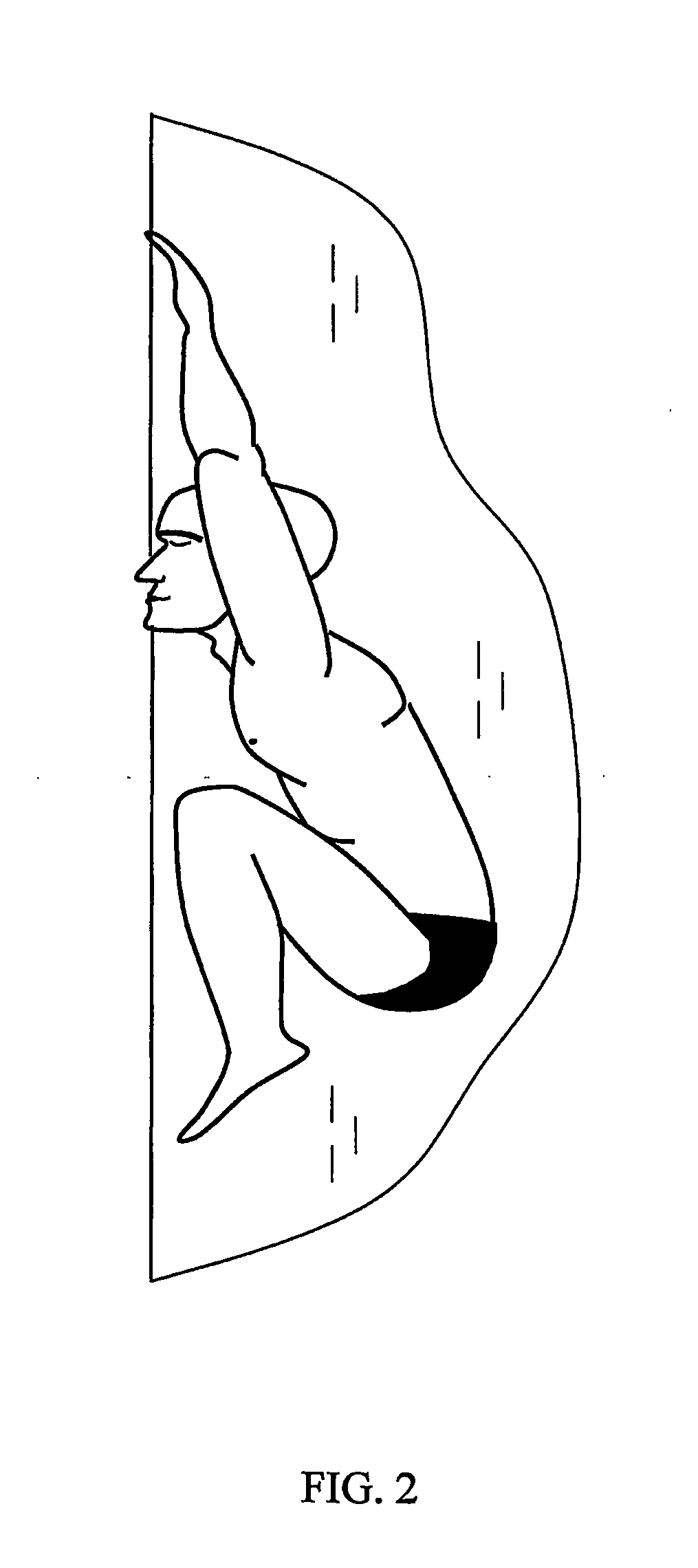
[0029]In FIGS. 1 and 3, gray contours show parts of the body, which are not protruding out of the water. FIGS. 1 to 5 fully reveal the main idea of the present invention and show possible variants of its realization in accordance with the main distinctive features.
[0030]Everywhere in this description, the word combination “relative to water” in most cases implies “relative to the water surface” (that is, relative to the median line of the air-water interface). This word combination can also be understood as “in stationary flows—relative to the center of gravity of the main volume of water, and in turbulent flows—relative to the center of gravity of the volume of surface layers of water commensurate with the body weight.”
[0031]By stationary staying in water is implied the occurrence in water with a depth above 0.25 m (far from any supports), whereby the body is at the surface (with some parts, primarily the face, occurring in air) and the body center of gravity is predominantly at re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com