Dilatation Catheter with Enhanced Distal End for Crossing Occluded Lesions
a technology of dilatation catheter and enhanced distal end, which is applied in the field of transluminal dilatation catheter, can solve the problems of lack of stiffness in catheters designed with flexible distal portions for trackability, and treatment of totally occluded arteries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
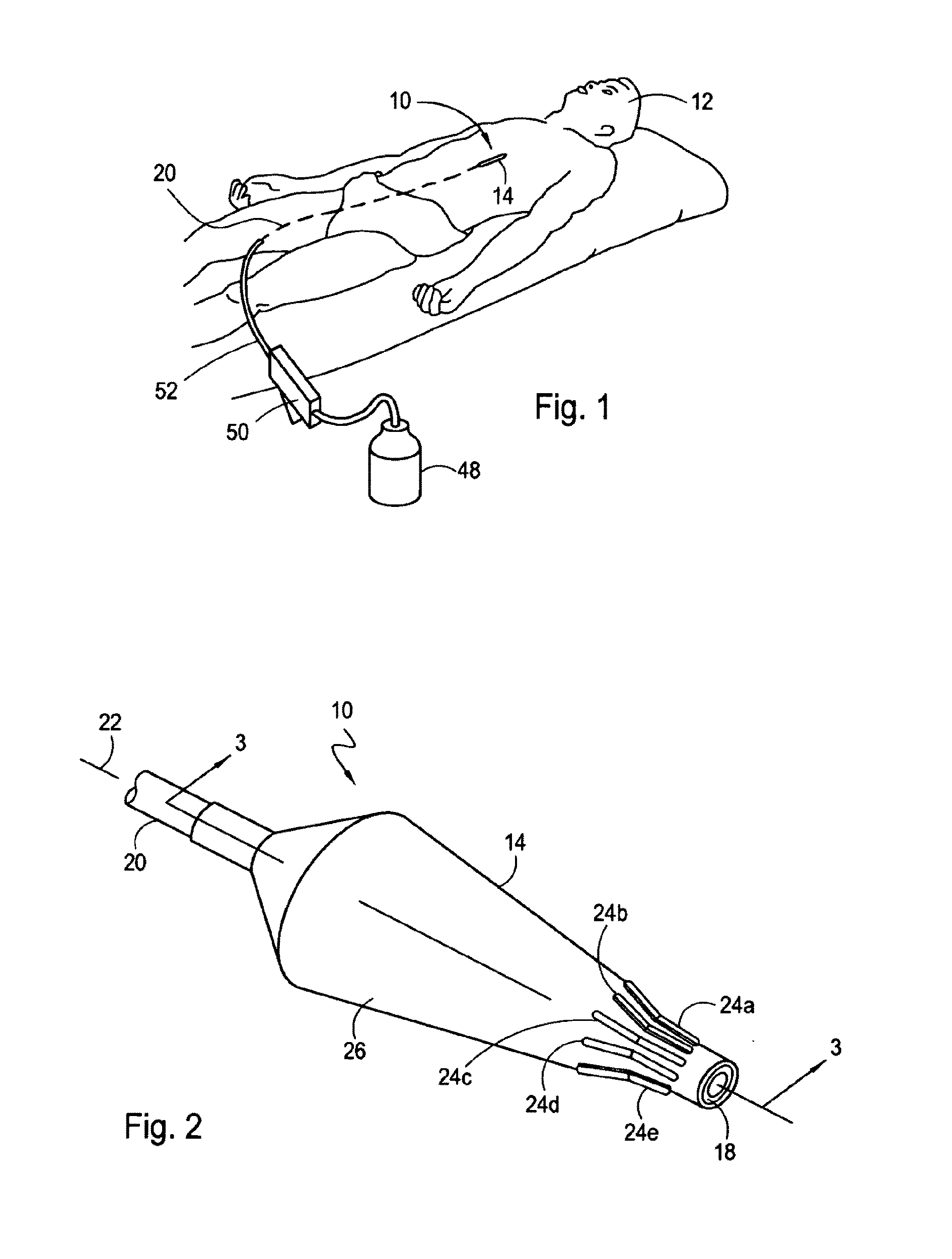
[0021]Referring initially to FIG. 1, a catheter for crossing an occluding lesion and dilating the lesion within a vascular conduit is shown and generally designated 10. More specifically, the catheter 10 is shown positioned for treatment of an upper body artery in a patient 12. Although the catheter 10 is capable of treating a lesion in an upper body artery such as a coronary artery, those skilled in the pertinent art will recognize that the use of the catheter 10 is not limited to upper body arteries, but, instead can be used in vascular conduits and other ductal systems throughout the human body.
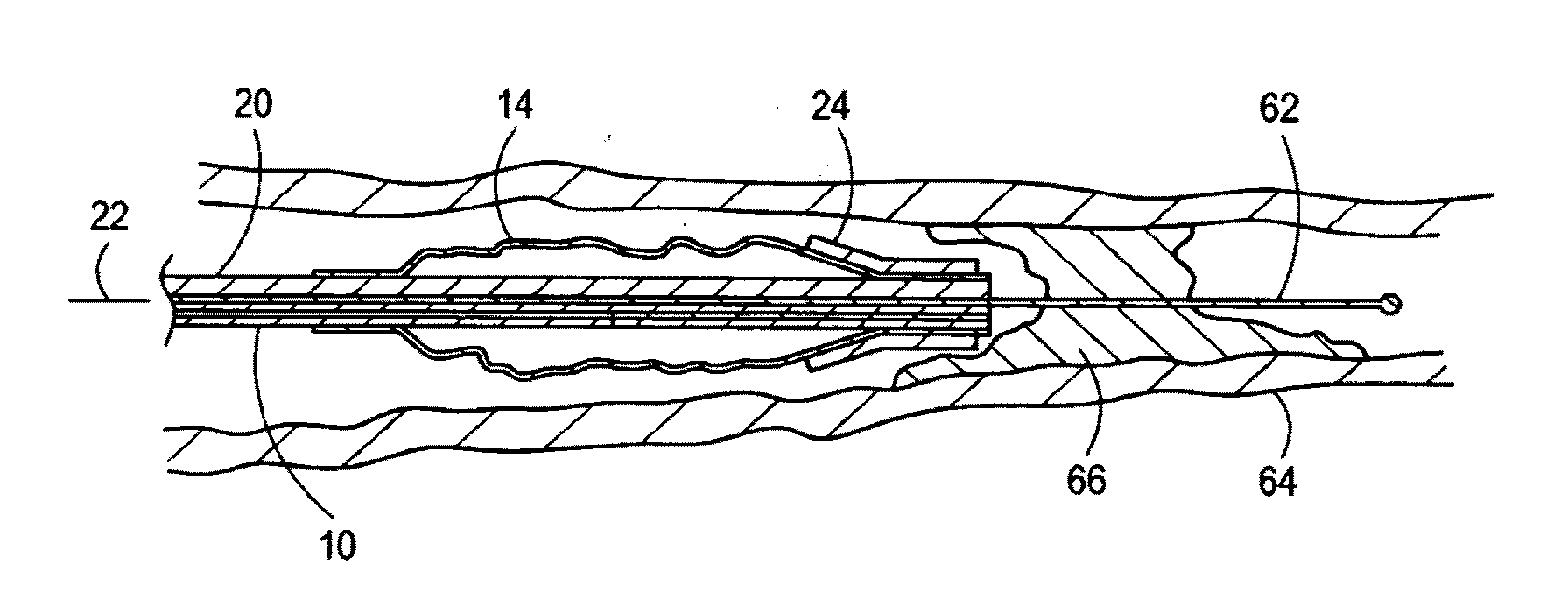
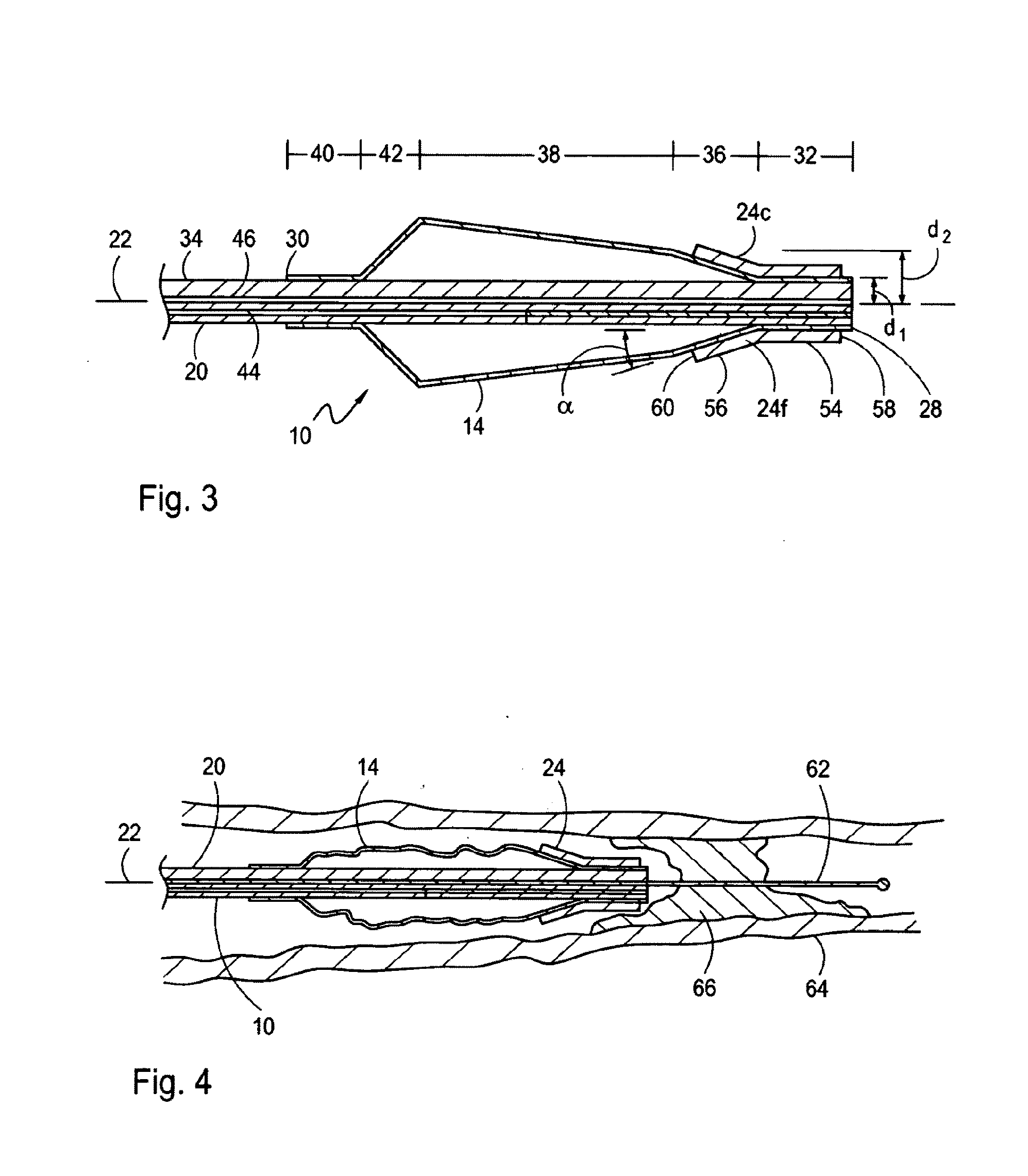
[0022]Referring now to FIG. 2, the distal portion of the catheter 10 is shown to include an inflatable dilatation balloon 14 that is attached to the distal end 18 of an inner tube 20. Cross-referencing FIGS. 1 and 2, it can be seen that the inner tube 20 is elongated and defines a longitudinal axis 22 in the direction of elongation. It can be further seen that the length of the inner tube ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com