Valve control apparatus and electric driving apparatus
a technology of electric driving apparatus and valve control, which is applied in the direction of mechanical equipment, operating means/releasing devices of valves, machines/engines, etc., can solve the problems of increasing manufacturing costs, unable to detect malfunctions in driving force-transmitting paths,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
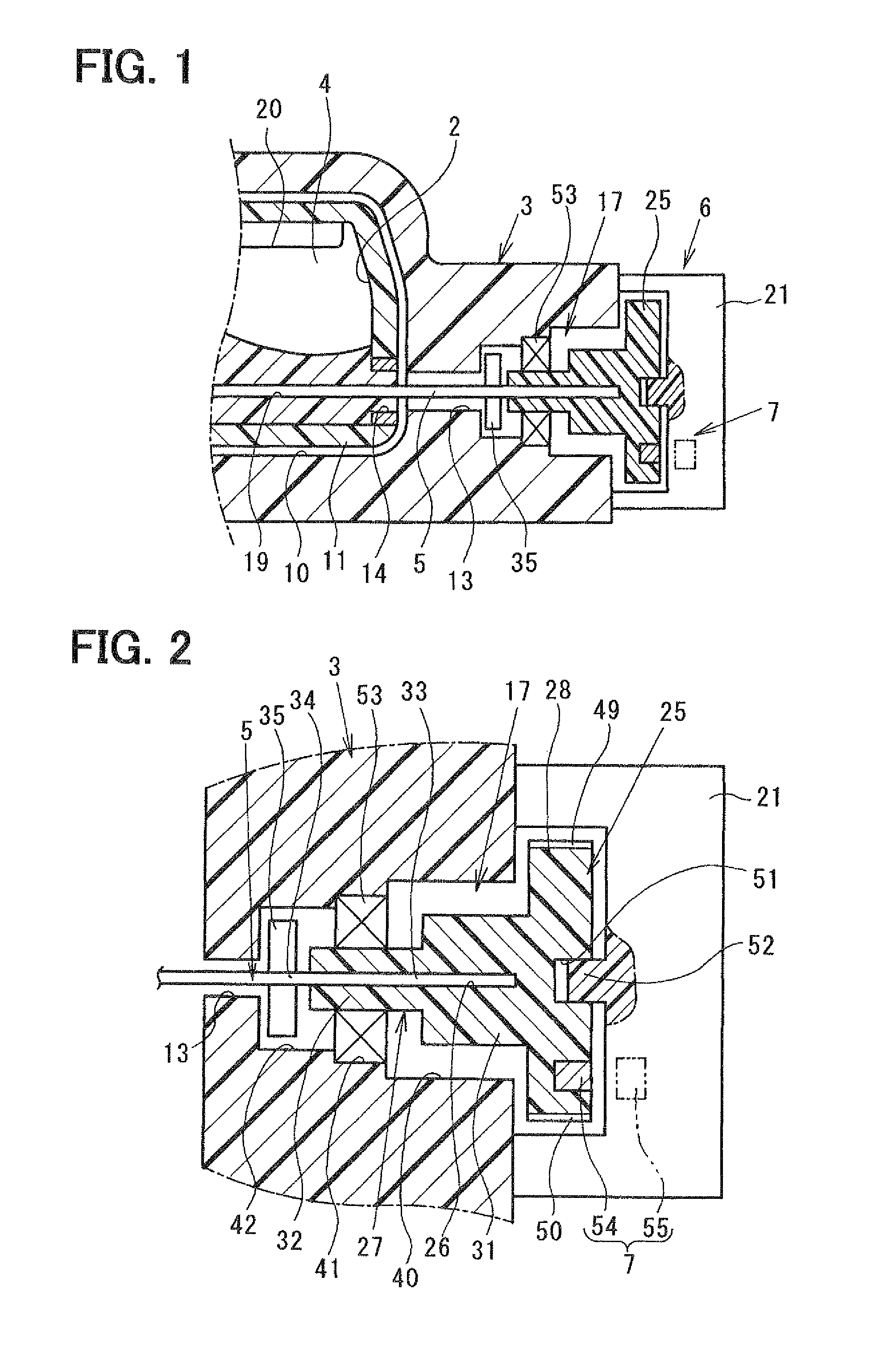
first embodiment
[Operation of First Embodiment]
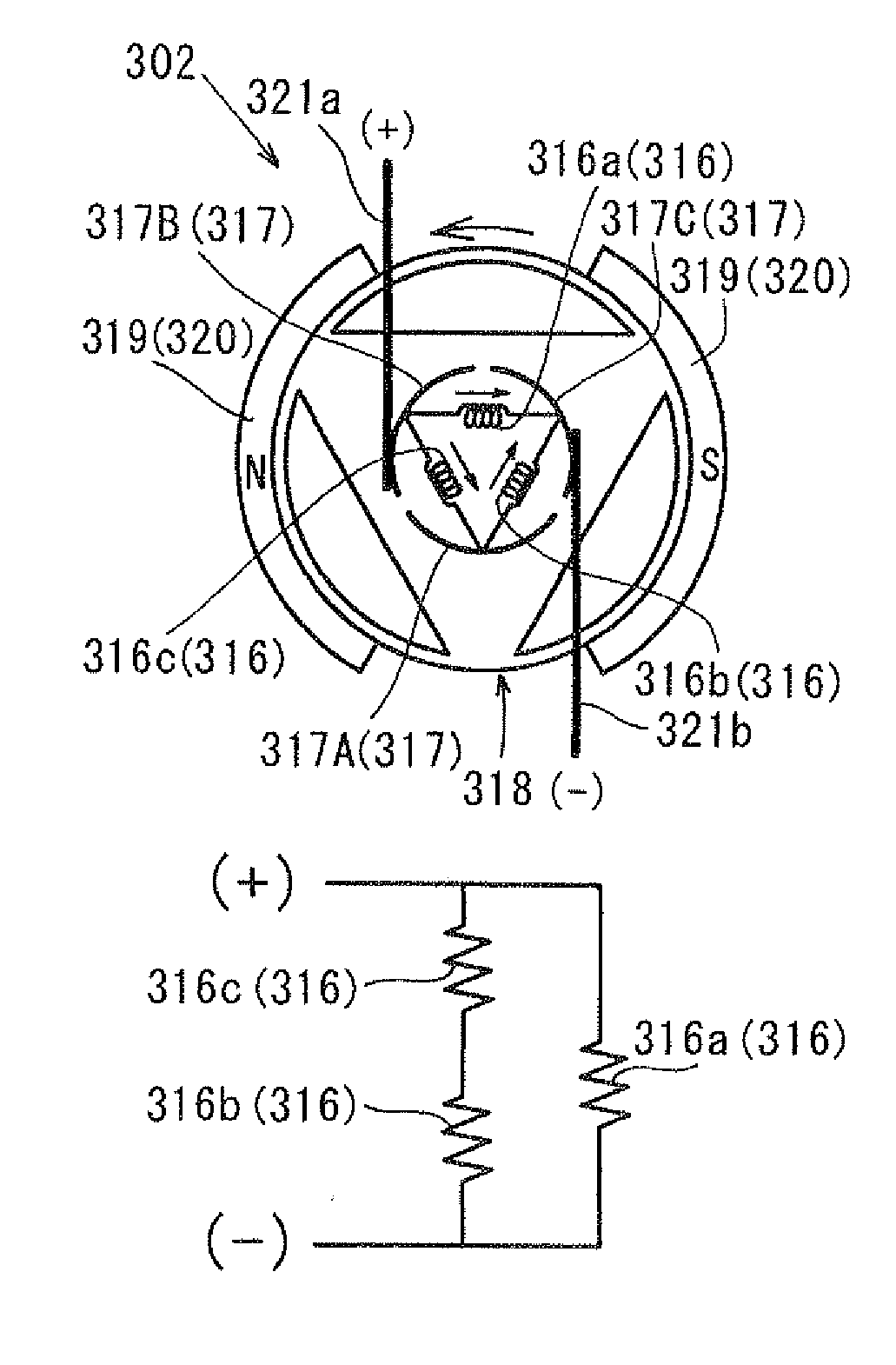
[0094](i) Normal condition
[0095]In a case that the end-gear 25 and the shaft 5 are normally connected to each other, the end-gear 25 rotates from the full-open gear position to the full-close gear position. Also, the valve 4 rotates from full-open position to the full-close position. When the stopper-contacting portion 38 is brought into contact with the full-close stopper wall 44, the valve 4 stops rotating at the full-close position. The end-gear 25 also stops at the full-close gear position.
[0096]The rotation angle sensor 7 outputs detection signals which indicate the rotation angle of the end-gear 25 is within the gear-operation-angle range. Thus, the malfunction detecting means determines that no malfunction occurs.
(ii) Abnormal condition
[0097]If the connecting portion between the end-gear 25 and the shaft 5 is broken, the end-gear 25 rotates over the full-close gear position. The end-gear 25 rotates free without respect to the full-close stopper ...
second embodiment
[0103]Referring to FIGS. 4A and 4B, a second embodiment will be described. In the second and the successive embodiments, the same parts and components as those in the first embodiment are indicated with the same reference numerals and the same descriptions will not be reiterated.
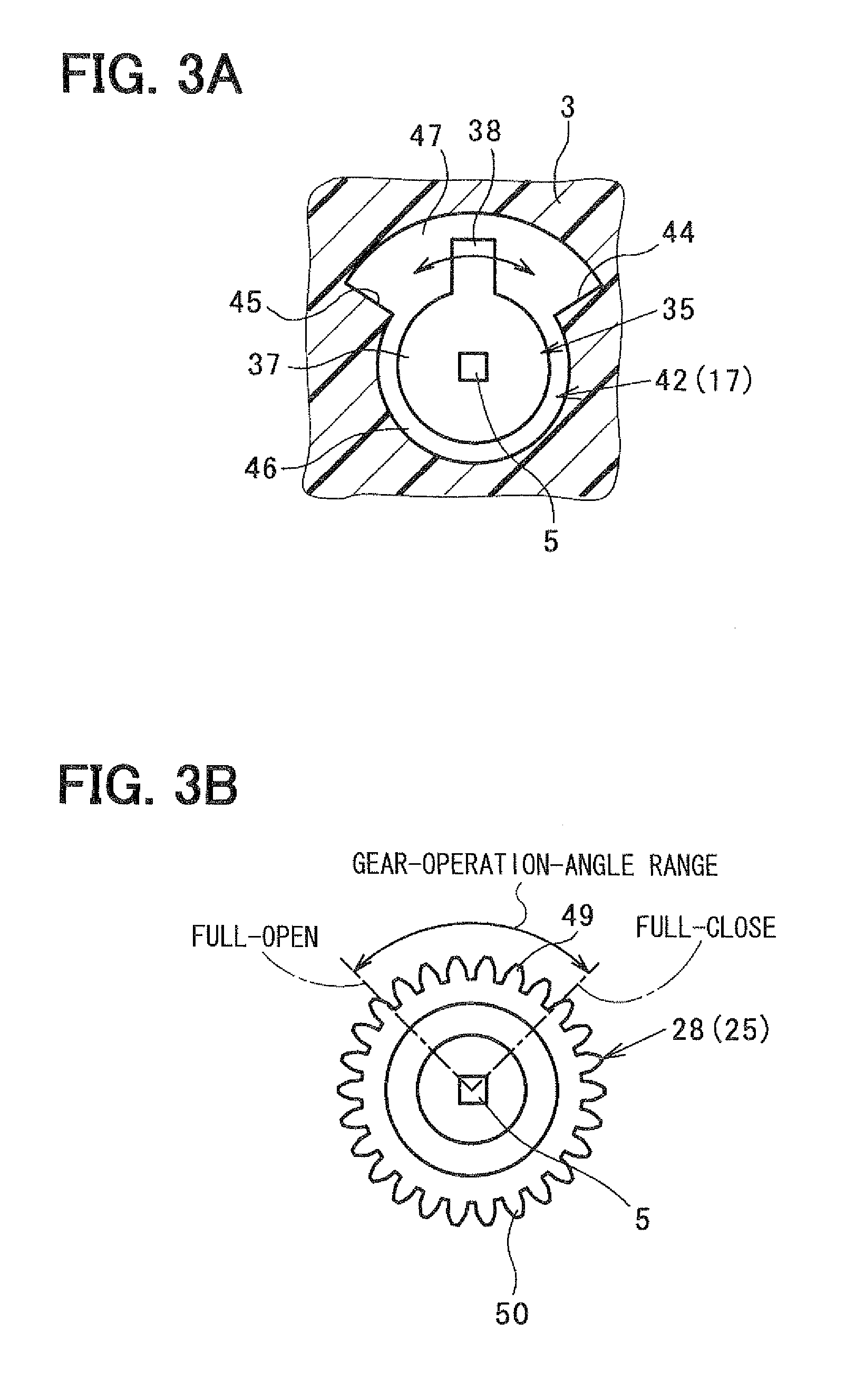
[0104]The second embodiment is different from the first embodiment in the configuration of the stopper. That is, stop-screws 58 are provided on step-surfaces 57 between the first small chamber 46 and the second small chamber 47. A tip end of the stop-screw 58 functions as a full-close position stopper 44, and a tip end of the other stop-screw 58 functions as a full-open position stopper 45.
[0105]In the second embodiment, the gear portion 28 has gear teeth partially along its circumferential periphery, as shown in FIG. 4B. That is, the inside gear teeth 49 are provided in the gear-operation-angle range, and the outside gear teeth 50 are provided at both sides of the inside gear teeth 49. The second embodiment...
third embodiment
[0106]Referring to FIG. 5, a third embodiment will be described. The third embodiment is different from the first embodiment in the configuration of the stopper and the stopper portion 35. The stopper portion 35 is comprised of a disc portion 37 and a concave portion 59. At circumferential both ends of the concave portion 59, step portions 60 are formed.
[0107]The inner diameter of the small chamber 42 is slightly larger than the outer diameter of the disc portion 37. A projection 61 is formed on an inner wall surface of the small chamber 42 in such a manner as to project toward the concave portion 59. One side surface of the projection 61 functions as the full-open position stopper 45, and the other side surface of the projection 61 functions as the full-close position stopper 44. These step portions 60 and stoppers 44, 45 regulate the operation angle range of the shaft 5. The third embodiment has the same advantages as the first embodiment.
[Modification]
[0108]The rotation angle sen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com