Solar collector
a solar collector and collector body technology, applied in the field of solar collectors, can solve the problems of premature stress cracking, water leakage at the weld, inadequate retention and sealing of the manifold,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
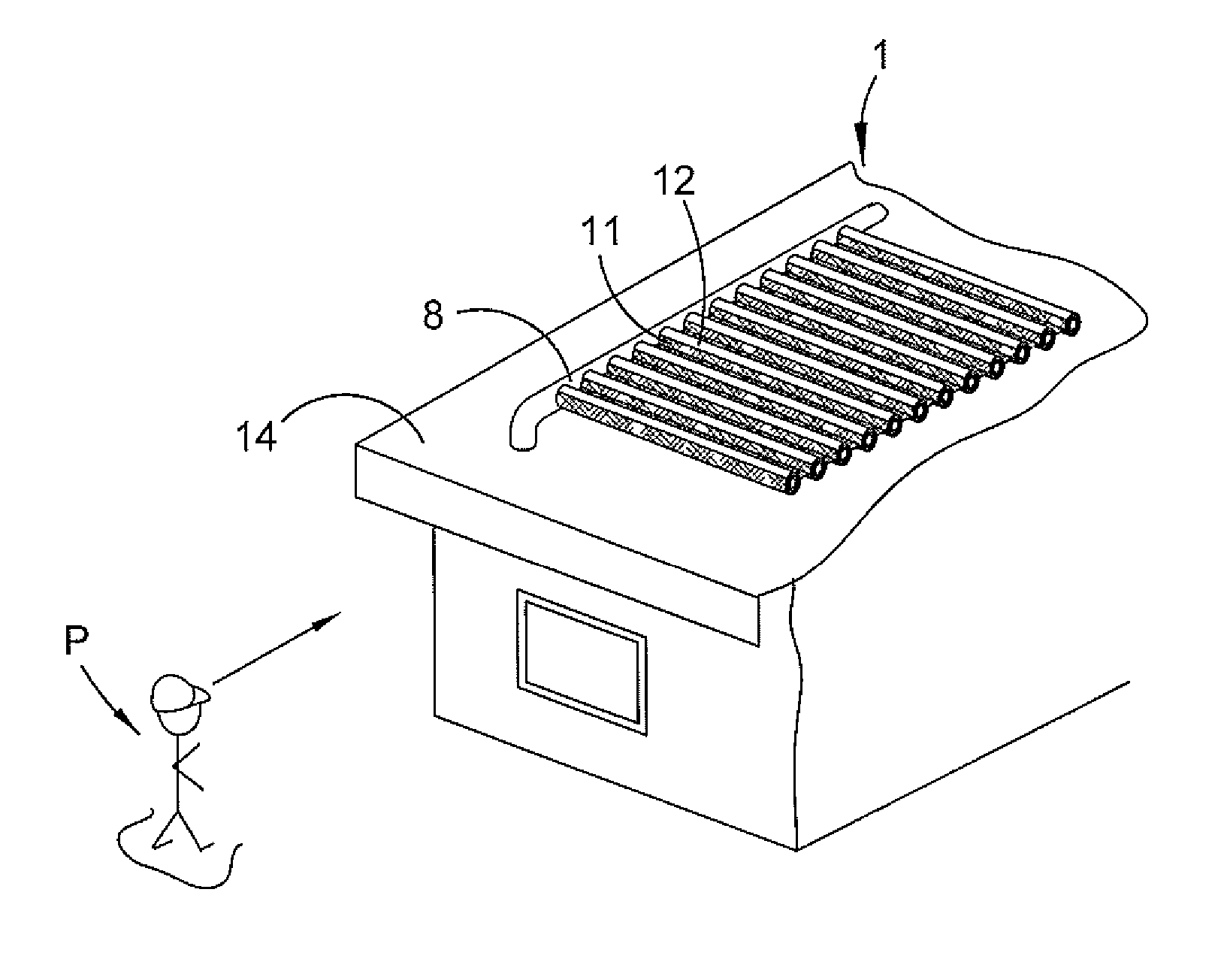
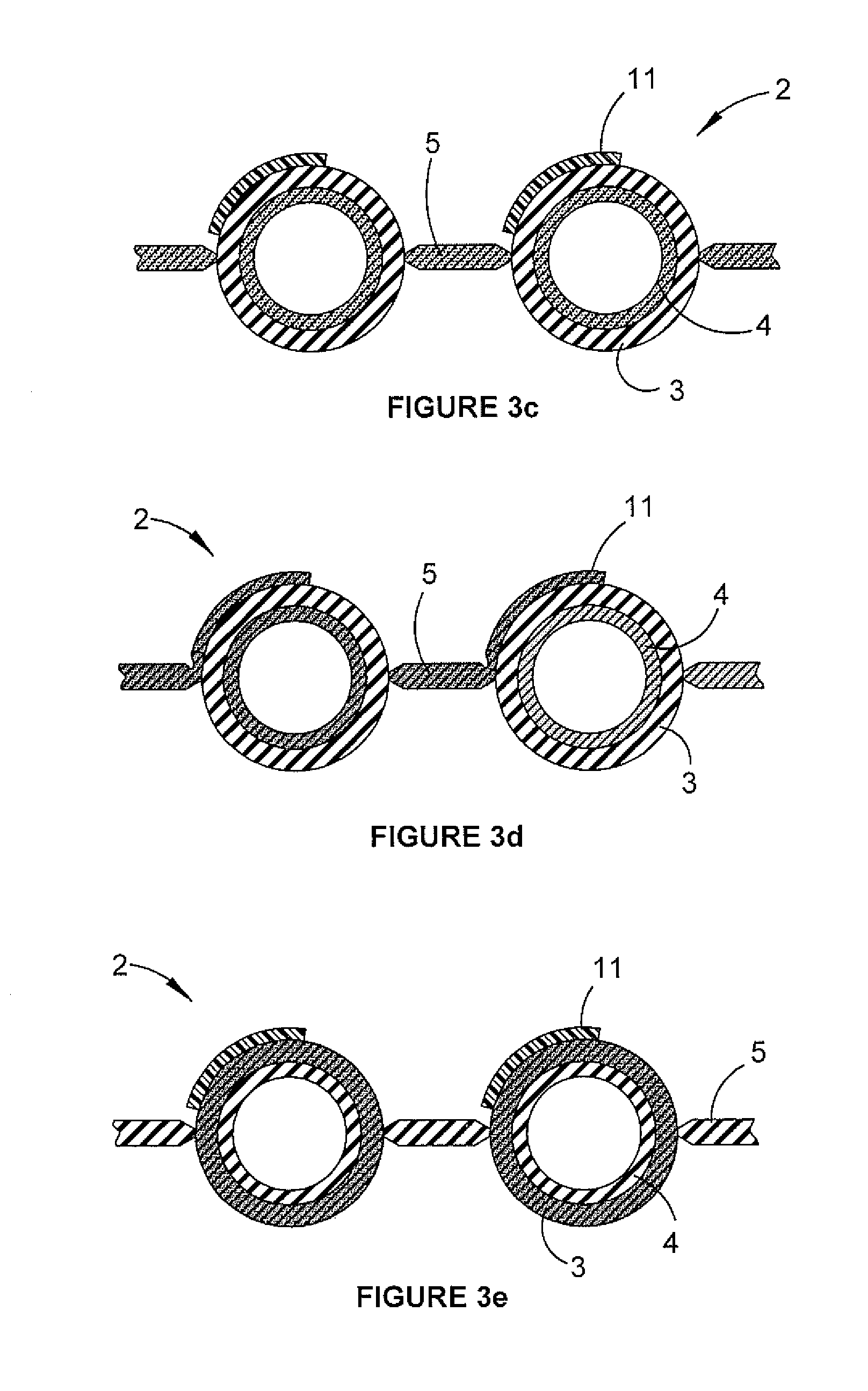
[0049]In a solar collector tube described herein the outer tube layer 3 is made of a harder polymer than the inner layer 4. This combination allows the solar collector polymer tube to absorb and transfer solar radiation to fluid inside the tubes with superior performance to that of known solar collectors while also ensuring product longevity.
[0050]The hardness of the outer layer 3 means it is able to withstand damage to the tube's integrity as a result of weight or sharp impact by various means such as humans, animals, or weather conditions, like storms, hail or projectiles.
[0051]With the material of the inner tube layer 4 being softer than the outer tube layer, it is more easily deformable and offers more friction so to be able to grip onto a manifold barb (not shown) used in connecting the polymer tubes to the inlet and outlet manifolds. The material of the inner tube layer 4 allows the polymer tube 2 to deform and securely grip the barbs of a manifold while still providing good s...
second embodiment
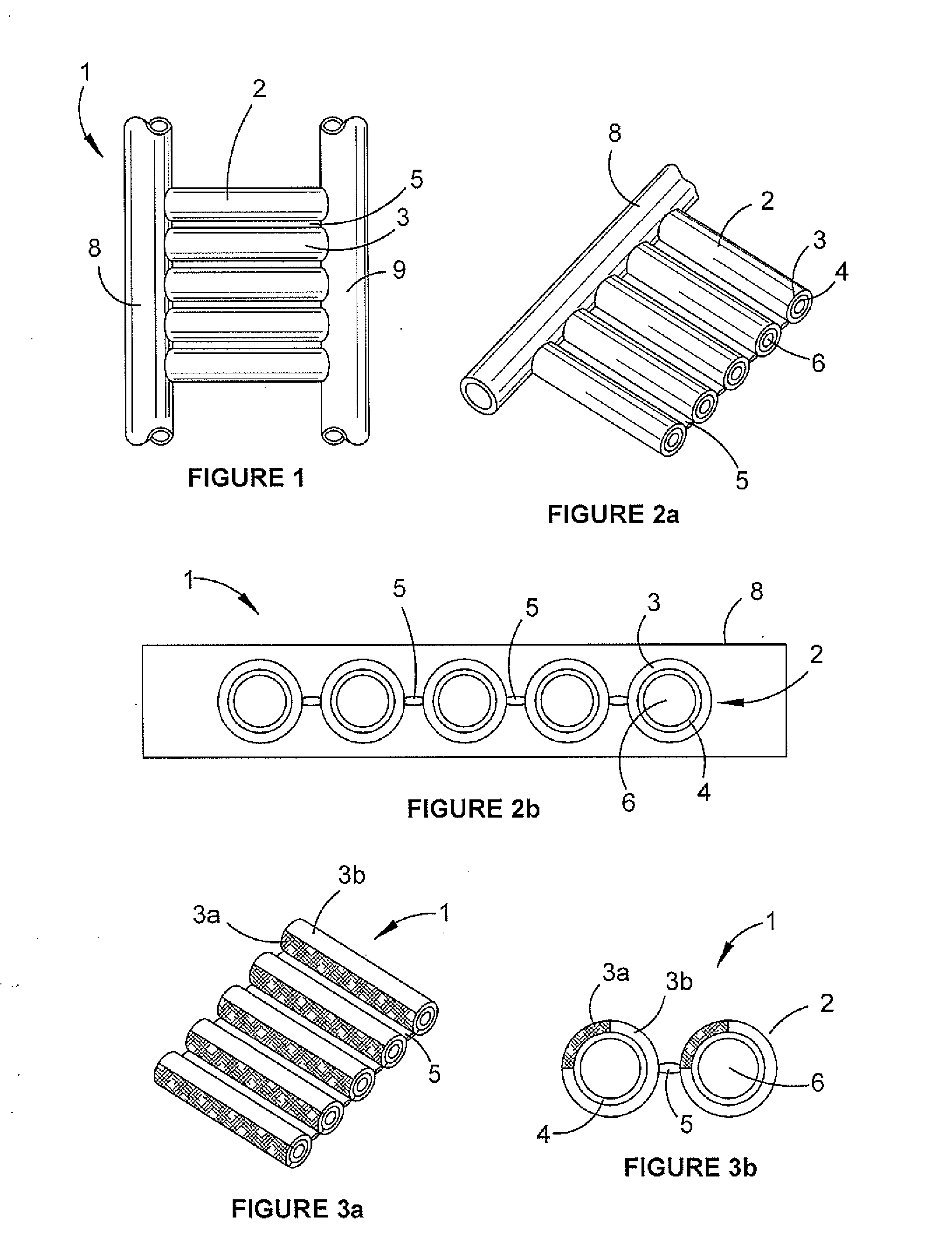
[0052]In a solar collector polymer tube described herein, the tube comprises at least two concentric and co-extruded tube layers where the inner tube is made of a cross-linked polymer and the outer layer is weldable. This version allows for each tube to be connected to a manifold by welding (typically in the factory) rather than by assembly onto a barb. The outer tube layer is fusable so that it can be welded to the manifold material by way of heat or sonic welding, over-moulding or other known polymer fusion techniques.
[0053]In the embodiment shown in FIG. 2b, the polymer tubes 2 are connected laterally via a web 5. Fluid, typically water, flows through a central bore 6 (see FIGS. 2a and 2b) in each co-extruded tube 2 and circulates within a closed or open solar collecting system to distribute heated fluid. In this embodiment, the web 5 connecting the tubes is a continuous hard, rigid web the same length as the tubes. The width of the web can be smaller, equal to or greater than th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com