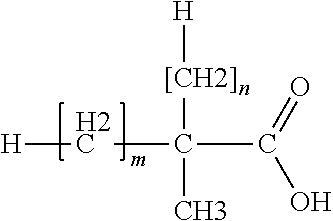
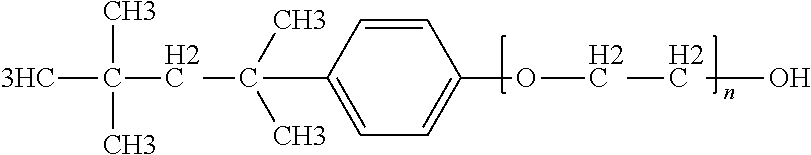
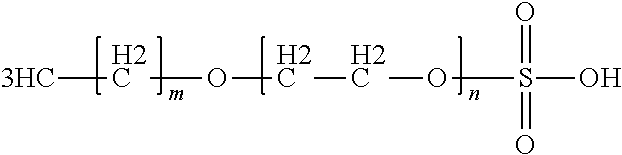Fluorination of Fluoropolymer Resin to Reduce Discoloration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Exposing Fluoropolymer Resin to Fluorine
[0093]Aqueous FEP dispersion polymerized as described above is coagulated in a heated glass reactor. 1250 ml of dispersion is heated to 85° C. in a water bath and then transferred to a 2,000 ml jacketed glass reactor with four internal baffles produced by Lab Glass or Vineland, N.J. where the temperature is maintained at by circulating 85° C. water through the jacket. Two high-shear impellers are turned at 2,470 rpm for 3600 seconds to cause the dispersion to separate into a polymer phase and a water phase. The water is separated from the solids by filtering through a 150 micron mesh filter bag model NMO150P1SHS manufactured by The Strainrite Companies of Auburn, Me. The polymer phase is dried for 40 hours in a circulating air oven set at 150° C. to produce a dry powder.
[0094]A sample of dried powder is molded to produce color films as described in the Test Methods section above as Measurement of Thermally Induced Discoloration for melt-proces...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com