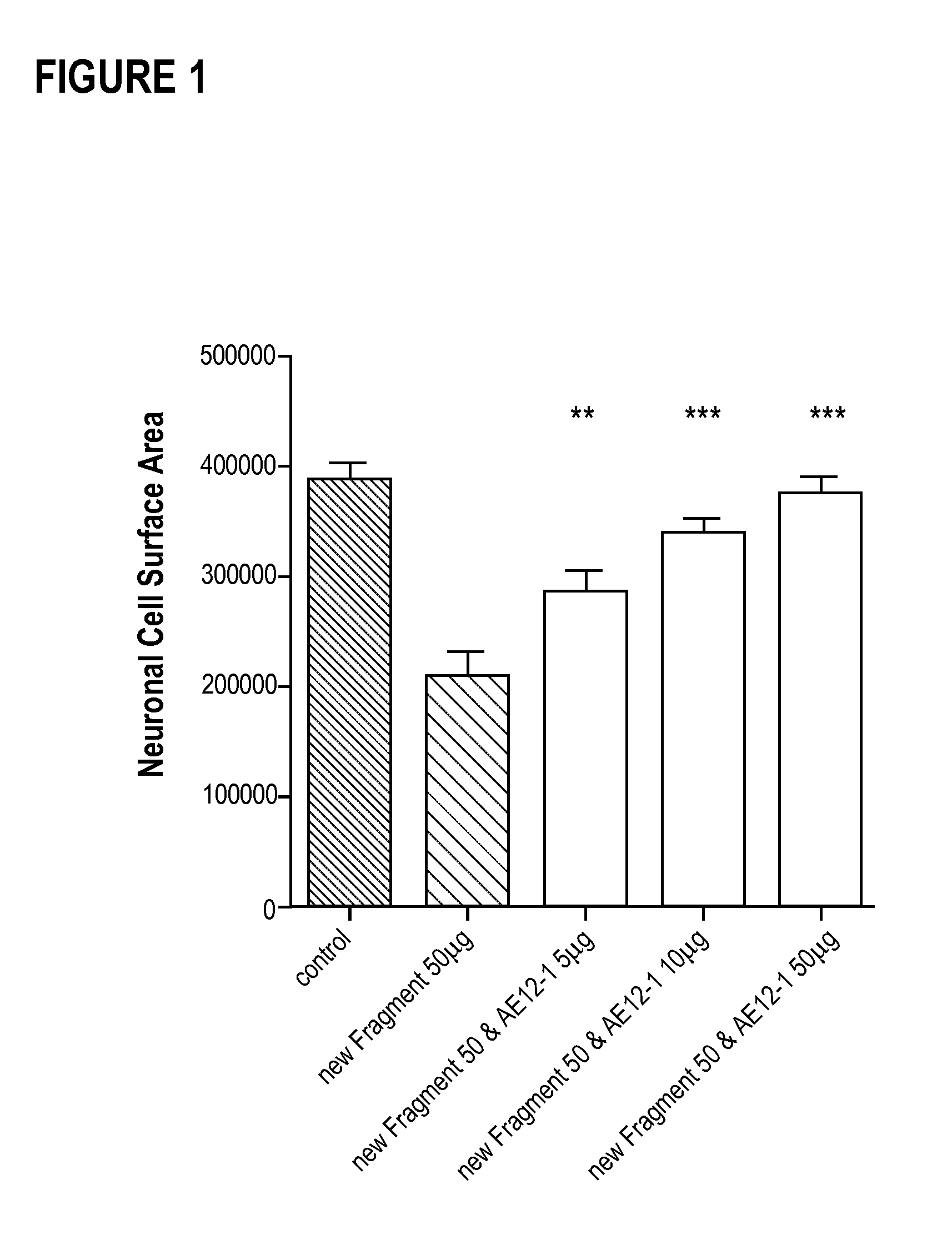
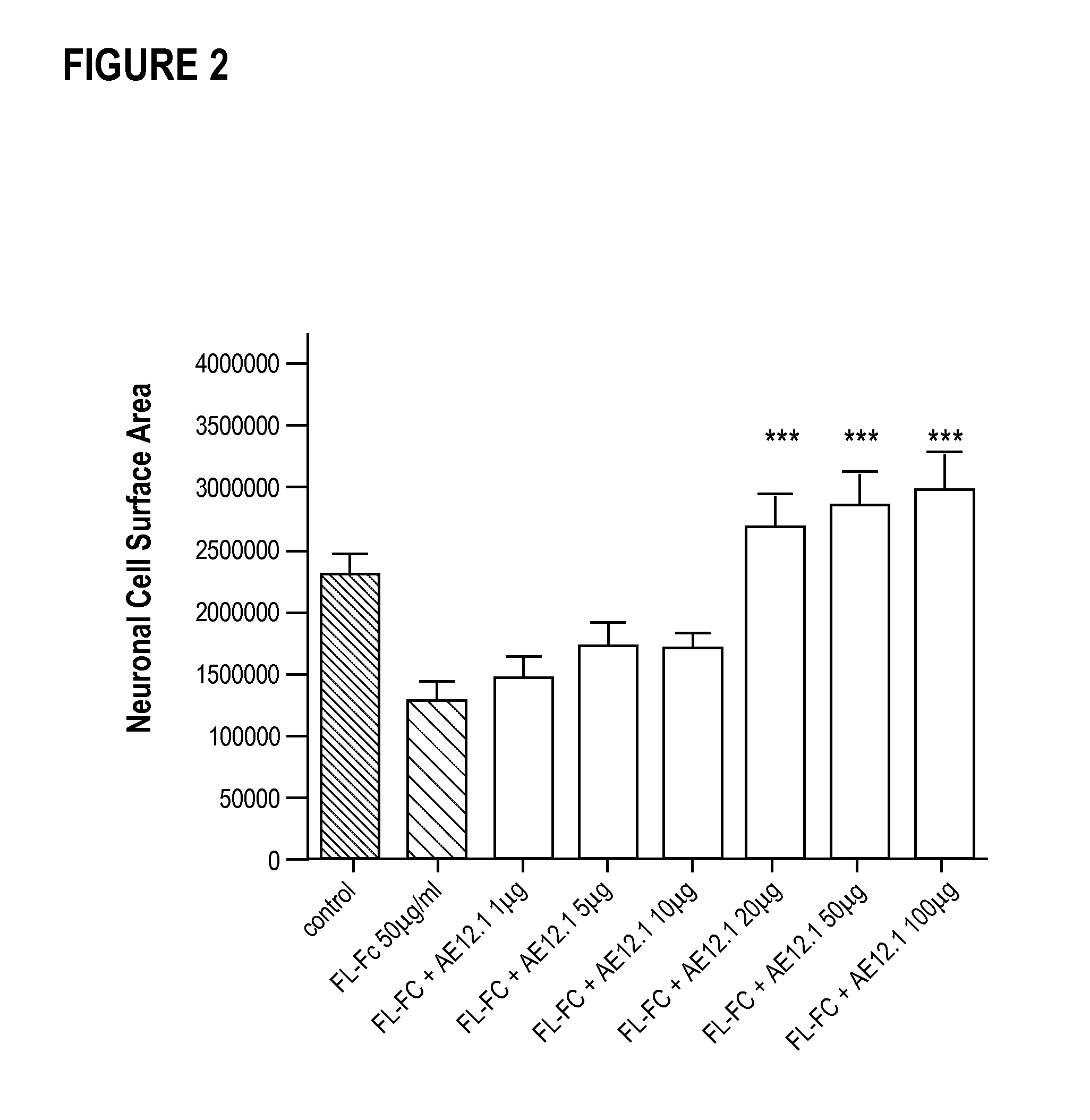
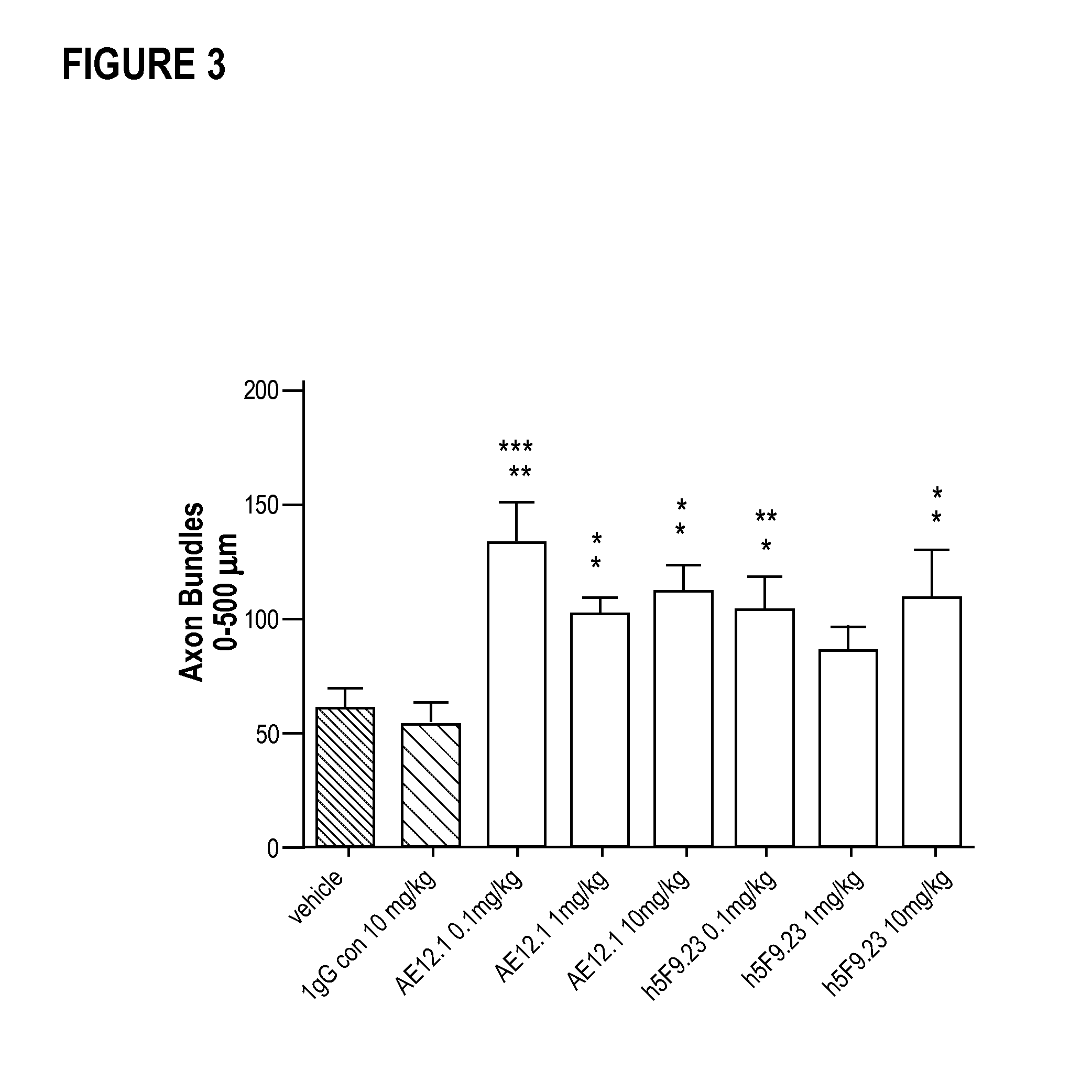
Composition and method for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases associated with neurite degeneration
a technology of neurite degeneration and composition, applied in the direction of drug composition, peptide, metabolic disorder, etc., can solve the problems of no cure, no cure, no cure, and no improvement in sensation, movement, cognition, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing the level of rgma
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Anti-RGMa Human Monoclonal Antibody Production and Isolation
[0352]Using PROfusion mRNA display technology, pooled human spleen, tonsil, PBMC and lymph node antibody libraries were selected through eight rounds against RGMa antigens: 100 nM biotin-labeled human or rat RGMa. PROfusion technology is described in U.S. Patent Application Publication Nos: 20100099103 and 20100105569, the contents each of which are herein incorporated by reference. Selected sc-Fv fragments were reformatted into fully human IgGs. Following screening of IgGs in RGMa-based ELISAs, AE12-1 through AE12-8 were identified as positive binders to human and rat RGMa.
[0353]Antibodies AE12-13, AE12-15, AE12-20, AE12-21, AE12-23, and AE12-24 are fully human anti-RGMa antibodies identified from large naïve human scFv yeast libraries selected against human RGMa using standard yeast display technologies. 2 rounds of Magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS) and 4 rounds of Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) were perf...
example 2
Antibody Characterization
[0354]The 8 PROfusion mAbs (AE12-1, AE12-2, AE12-3, AE12-4, AE12-5, AE12-6, AE12-7, and AE12-8), were tested by direct binding ELISAs to examine binding to human RGMa (hRGMa) and rat RGMa and cross-reactivity to hRGMc. hRGMa competition ELISA was employed to test if any of these mAbs would compete h5F9.23 for binding to hRGMa. h5F9.23 is a humanized anti-RGMa lead mAb derived from rat hybridoma and known to bind the N-terminal domain of RGMa. H5F9.23 has the following sequences:
VH h5F9.23151EVQLVESGGGLVQPGGSLRLSCAASGFTFSNYGMNWIRQAPGKGLEWIGMIYYDSSEKHYADSVKGRFTISRDNSKNTLYLQMNSLRAEDTAVYYCAKGTTPDYWGQGTMVTVSSVL h5F9.23152DVVLTQSPLSLPVTLGQPASISCRSSQSLEYSDGYTFLEWFQQRPGQSPRLLIYEVSNRFSGVPDRFSGSGSGTDFTLKISRVEAEDVGVYYCFQATHDPLTFGQGTKLEIKRVH h5F9.23 CDR-H1153NYGMNVH h5F9.23 CDR-H2154MIYYDSSEKHYADSVKGVH h5F9.23 CDR-H3155GTTPDYVL h5F9.23 CDR-L1156RSSQSLEYSDGYTFLEVL h5F9.23 CDR-L2157EVSNRFSVL h5F9.23 CDR-L3158FQATHDPLT
Neogenin or BMP-2 / BMP-4 competition ELISA was employed ...
example 3
Antibody Variants and Binding Data
[0367]Table 4 shows that by substituting for the Cys residue in AE12-1 VL CDR3 (SEQ ID NO:8), one can generate variants having improved affinity to hRGMa. See SEQ ID NOs:67-73. For example, see Table 4, wherein antibody clone AE12-1-Y showed at least a 10-fold increased affinity to hRGMa and AE12-1-F showed a 5-fold increased affinity to hRGMa. Others showed comparable affinity as the parental AE12-1. All variants blocked hRGMa binding to SH-SY5Y cells in MSD-based cell binding assay, neutralized RGMa but not RGMc activity in BMP reporter assays, and exhibited high thermal stability and good solubility in preformulation studies.
TABLE 4AbAE12-1AE12-1-FAE12-1-HAE12-1-LAE12-1-VAE12-1-IAE12-1-KAE12-1-YhRGMa binding (ELISA)+++++++++++++++++++Cyno RGMa binding (ELISA)+++++++++++++++++++++++hRGMa-Hiska (M-1s-1)3.1 × 104 2.7 × 104 3.2 × 104 3.8 × 104 2.5 × 104 3 × 1043.4 × 104 2.2 × 104kd (s-1)2.3 × 10−43.9 × 10−51.2 × 10−42.5 × 10−41.5 × 10−4 1.3 × 10−43...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pharmaceutical composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| neurite degenerative disorder | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| acid | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com