Method for driving liquid crystal display device
a liquid crystal display device and display device technology, applied in semiconductor devices, instruments, computing, etc., can solve the problems of display deterioration, reduced detection accuracy in image capture, and difficult to improve the characteristics of elements, so as to achieve sufficient imaging period, improve image quality and detection accuracy in image capture, and increase the frequency of image signal input to each pixel of the liquid crystal display device.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0064]In this embodiment, a liquid crystal display device in one embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. 1, FIGS. 2A to 2C, FIGS. 3A and 3B, FIGS. 4A and 4B, FIG. 5, FIG. 6, FIG. 7, FIGS. 8A and 8B, FIGS. 9A and 9B, FIGS. 10A and 10B, and FIG. 11.
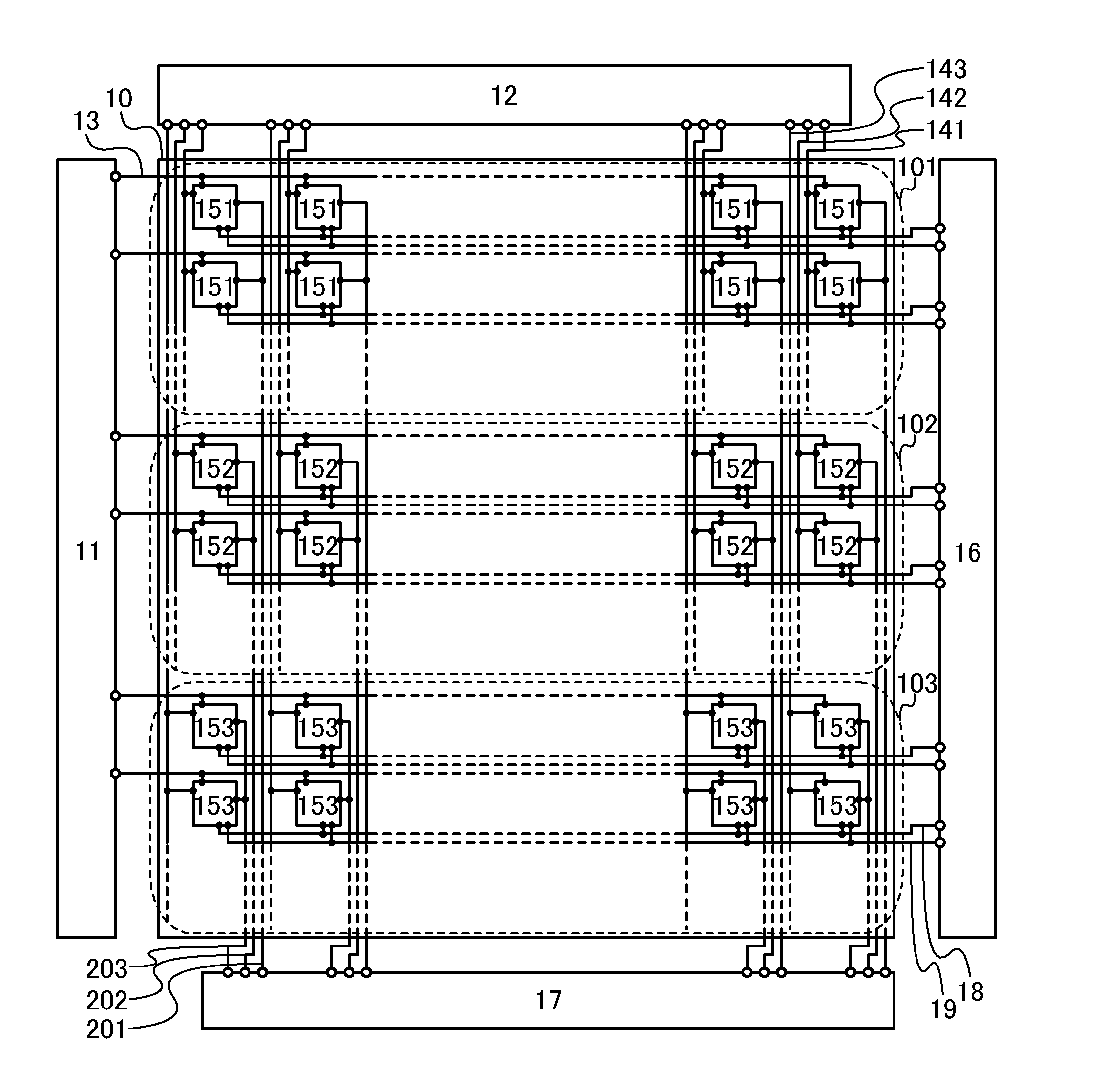
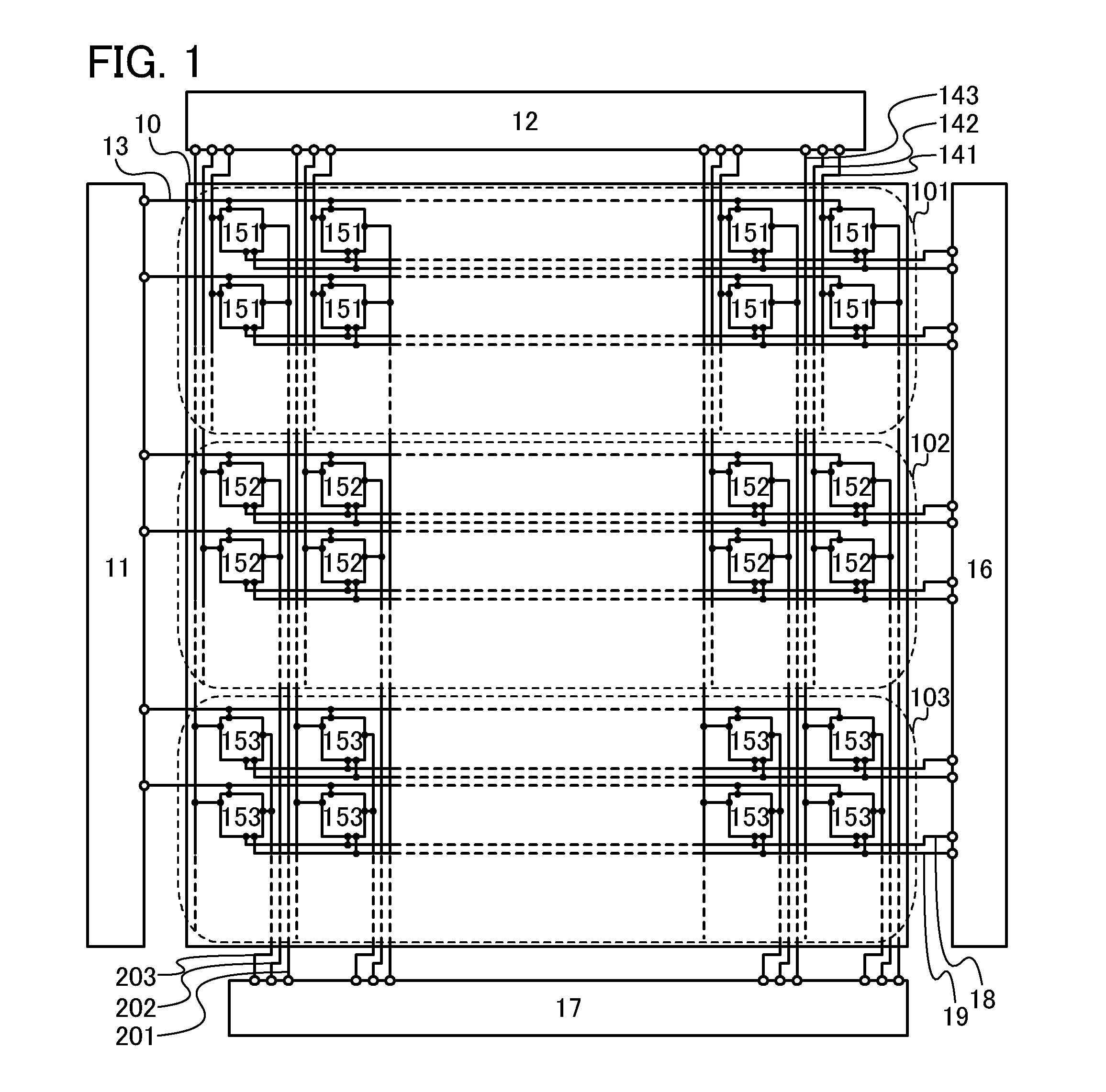
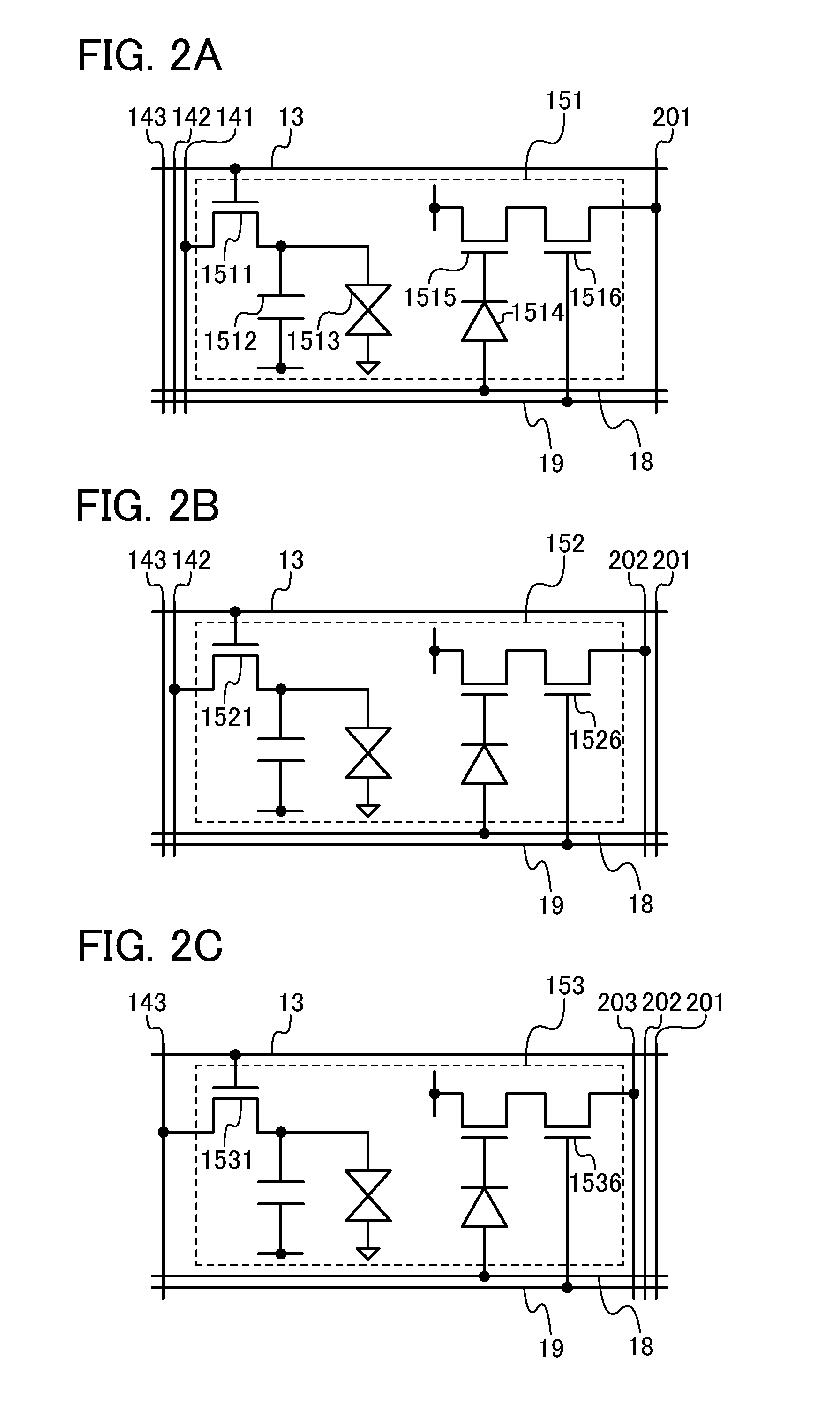
[0065]FIG. 1 illustrates a structure example of a liquid crystal display device. The liquid crystal display device illustrated in FIG. 1 includes a pixel portion 10; a scan line driver circuit 11; an image signal line driver circuit 12; an image sensor driver circuit 16; a detection circuit 17; m (m is a natural number of 3 or more) scan lines 13 which are arranged parallel or almost parallel to each other and whose potentials are controlled by the scan line driver circuit 11; n (n is a natural number of 2 or more) image signal lines 141, n image signal lines 142, and n image signal lines 143 which are arranged parallel or almost parallel to each other and whose potentials are controlled by the image sig...
embodiment 2
[0112]In this embodiment, operation of a liquid crystal display device of one embodiment of the present invention, which is different from the liquid crystal display device described in Embodiment 1 is described with reference to FIGS. 22A and 22B, FIG. 23, FIG. 24, FIG. 25, FIG. 26, FIG. 27, and FIG. 28.
[0113]As the liquid crystal display device in this embodiment, the liquid crystal display device (see FIG. 1 and FIGS. 2A to 2C) described in Embodiment 1 can be applied. Therefore, the description in Embodiment 1 is to be referred to.
[0114]As a scan line driver circuit included in the liquid crystal display device in this embodiment, the scan line driver circuit 11 (see FIG. 3A) included in the liquid crystal display device described in Embodiment 1 can be applied. Therefore, the description in Embodiment 1 is to be referred to for the structure of the scan line driver circuit.
[0115]An operation example of the scan line driver circuit 11 in this embodiment is described with referen...
embodiment 3
[0149]In this embodiment, operation of a liquid crystal display device of one embodiment of the present invention, which is different from the liquid crystal display device described in Embodiment 1 or 2 is described with reference to FIG. 29, FIG. 30, FIG. 31, FIG. 32, and FIG. 33.
[0150]As the liquid crystal display device in this embodiment, the liquid crystal display device (see FIG. 1 and FIGS. 2A to 2C) described in Embodiment 1 can be applied. Therefore, the description in Embodiment 1 is to be referred to.
[0151]As a scan line driver circuit included in the liquid crystal display device in this embodiment, the scan line driver circuit 11 (see FIG. 3A) included in the liquid crystal display device described in Embodiment 1 can be applied. Therefore, the description in Embodiment 1 is to be referred to for the structure of the scan line driver circuit. Further, the scan line driver circuit can be operated in the same manner as the scan line driver circuit described in Embodiment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com