Compositions, uses and methods for treatment of metabolic disorders and diseases
a metabolic disorder and metabolic technology, applied in the field of metabolic disorders and diseases, can solve the problems of hypoglycemic shock, adverse side effects, patients rarely attaining ideal glucose levels by insulin injection, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing glucose levels, increasing insulin sensitivity, and reducing insulin resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0213]The following is a description of various methods and materials used in the studies herein.
[0214]Animals.
[0215]db / db mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, Me.), Mice were kept in accordance with welfare guidelines under controlled light (12 hr light and 12 hr dark cycle, dark 6:30 pm-6:30 am), temperature (22±4° C.) and humidity (50%±20%) conditions. They had free access to water (autoclaved distilled water) and were fed ad libitum on a commercial diet (Harlan Laboratories, Indianapolis, Ind., Irradiated 2018 Teklad Global 18% Protein Rodent Diet) containing 17 kcal % fat, 23 kcal % protein and 60 kcal % carbohydrate. For diet-induced obesity, C57BL6 / J mice (Jackson Laboratory) were maintained on a high-fat diet (D12492, Research Diet, New Brunswick, N.J. USA) containing 60 kcal % fat, 20 kcal % protein and 20 kcal % carbohydrate for 16-20 weeks. All animal studies were approved by the NGM Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
[0216]DNA and Amino A...
example 2
[0237]The following is a description of studies showing the glucose lowering activity of various sequence variants of FGF19 and FGF21, and FGF19 / FGF21 fusion constructs.
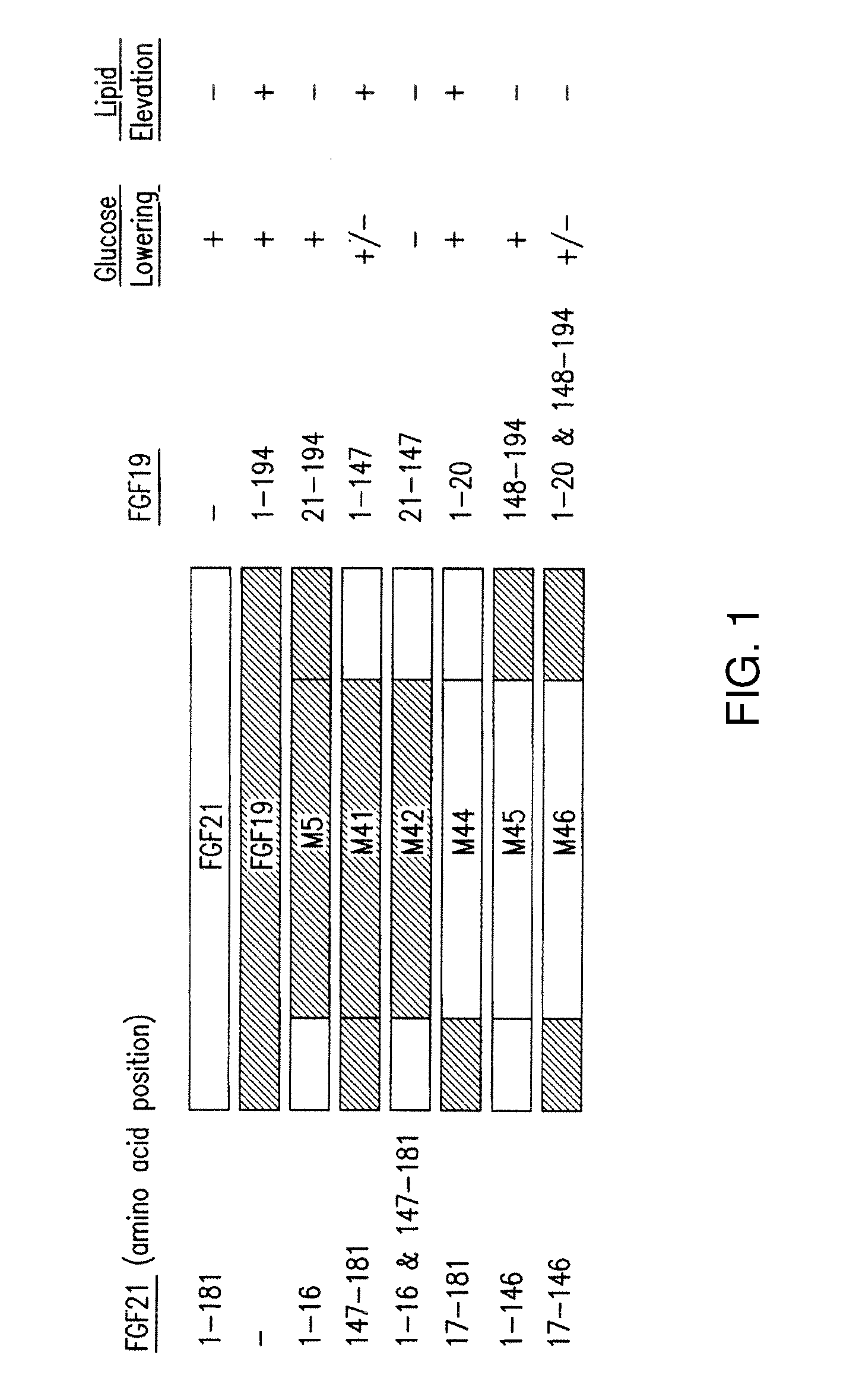
[0238]FIG. 1 illustrates exemplary FGF19 / FGF21 fusion constructs, and the segments from each of FGF19 and FGF21 present in the fusion peptides. These peptides were analyzed for glucose lowering activity and statistically significant lipid elevating or increasing activity (Tables 1-8 and SEQ ID NOs: 1, 2, 3, 5, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 69, 70, 71, 72 and 73 (M1, M2, M3, M5, M48, M49, M50, M51, M52, M53, M69, M70, M71, M72 and M73, respectively)).
[0239]Mice (db / db) were injected with viral vector expressing FGF19, FGF21 or variants, and analyzed after injection. Glucose-lowering activity of each sequence is represented by a “+” symbol (a “−” symbol means no glucose lowering activity, a “+ / −” symbol means variants retain minimal glucose-lowering activity); lipid elevating activity is represented by a “+” symbol (a “−” sy...
example 3
[0241]The following is a description of studies showing that variants M5, M1, M2 and M69 are not tumorigenic, as determined by hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) formation, and that variants M5, M2 and M69 also do not reduce lean muscle and fat mass.
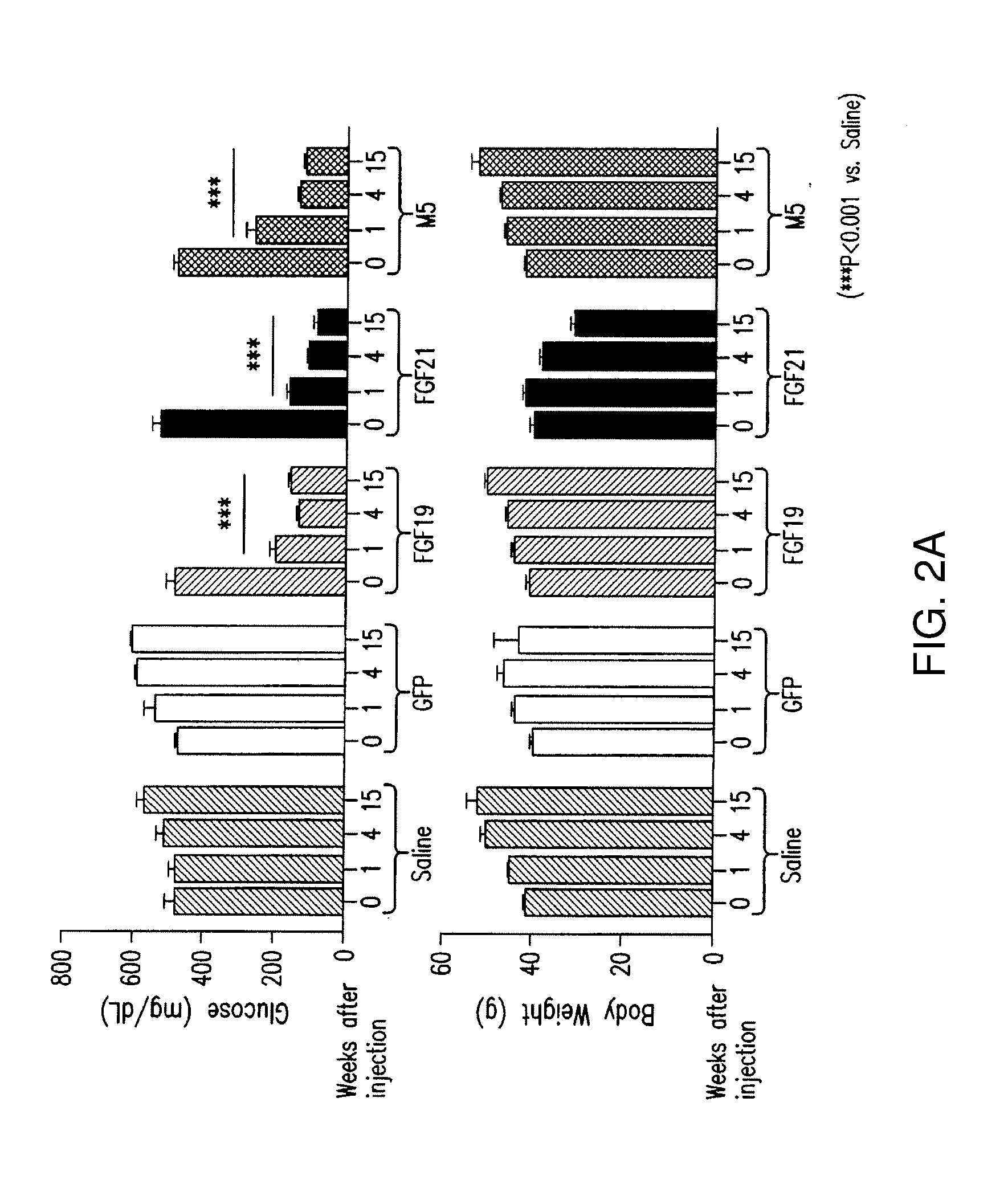
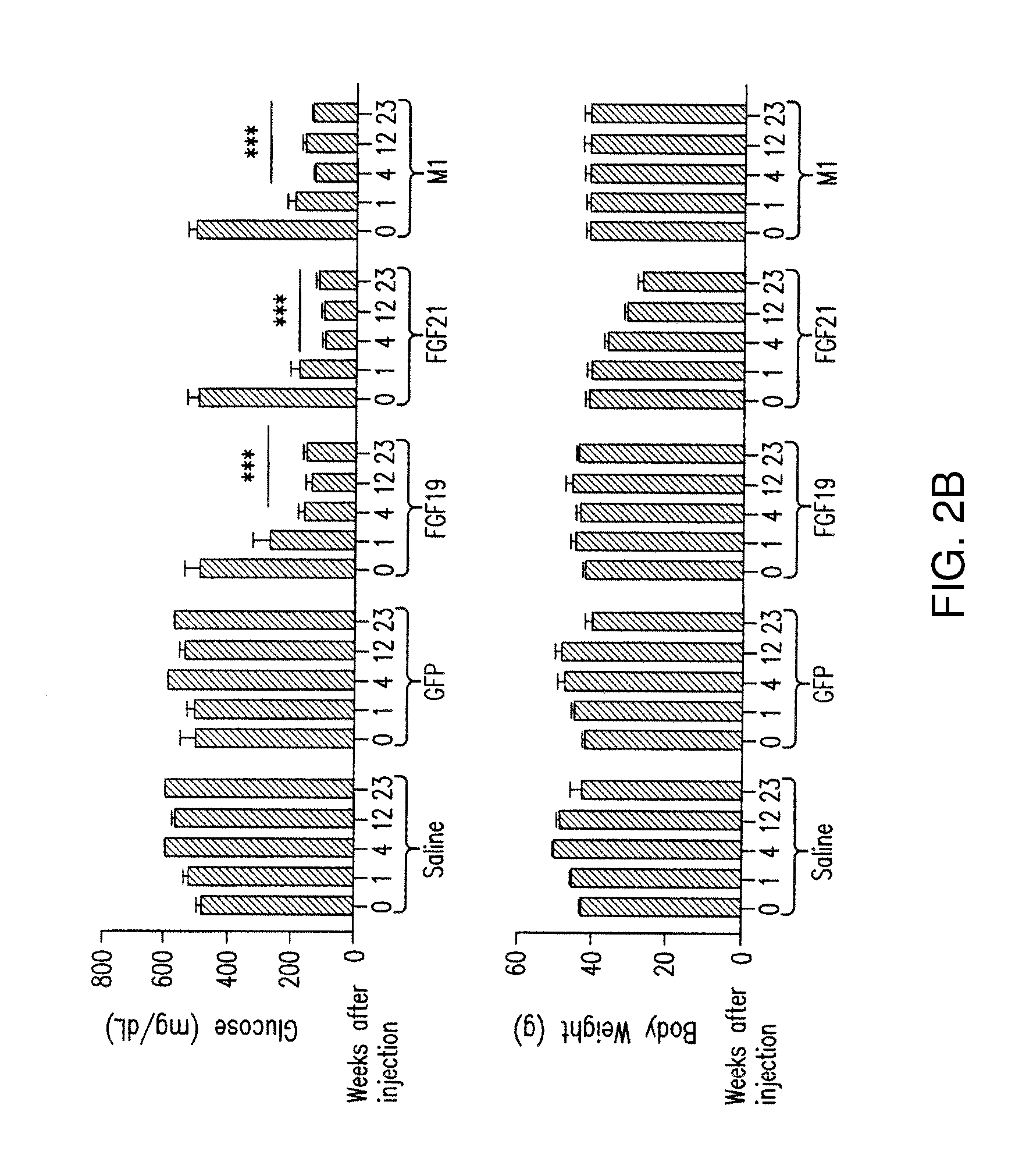
[0242]Animals (db / db) were injected with AAV vectors expressing FGF19, FGF21, M5, M1, M2, or M69, or injected with saline, and analyzed 6 months after injection. The data indicate that variants M5, M1, M2, and M69 did not induce (HCC) formation significantly (FIGS. 4A-4C).
[0243]Animals (db / db mice) were also injected with viral vector expressing FGF19, FGF21, M5, M1, M2 or M69, or injected with saline, and analyzed 6 months after injection for the effect of on lean mass and fat mass. The data indicate that M5, M2 and M69 peptides did not cause a statistically significant reduction in lean mass or fat mass, in contrast to FGF21, and that M1 peptide reduces lean mass (FIGS. 5A-5C).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com