Controllable indium doping for high efficiency czts thin-film solar cells
a solar cell, high-efficiency technology, applied in the field of photovoltaic devices, can solve the problems of limited very large-scale deployment of this technology, several major limitations of cztsse solar cells, and low fill factor of cztsse, so as to increase junction potential and junction potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
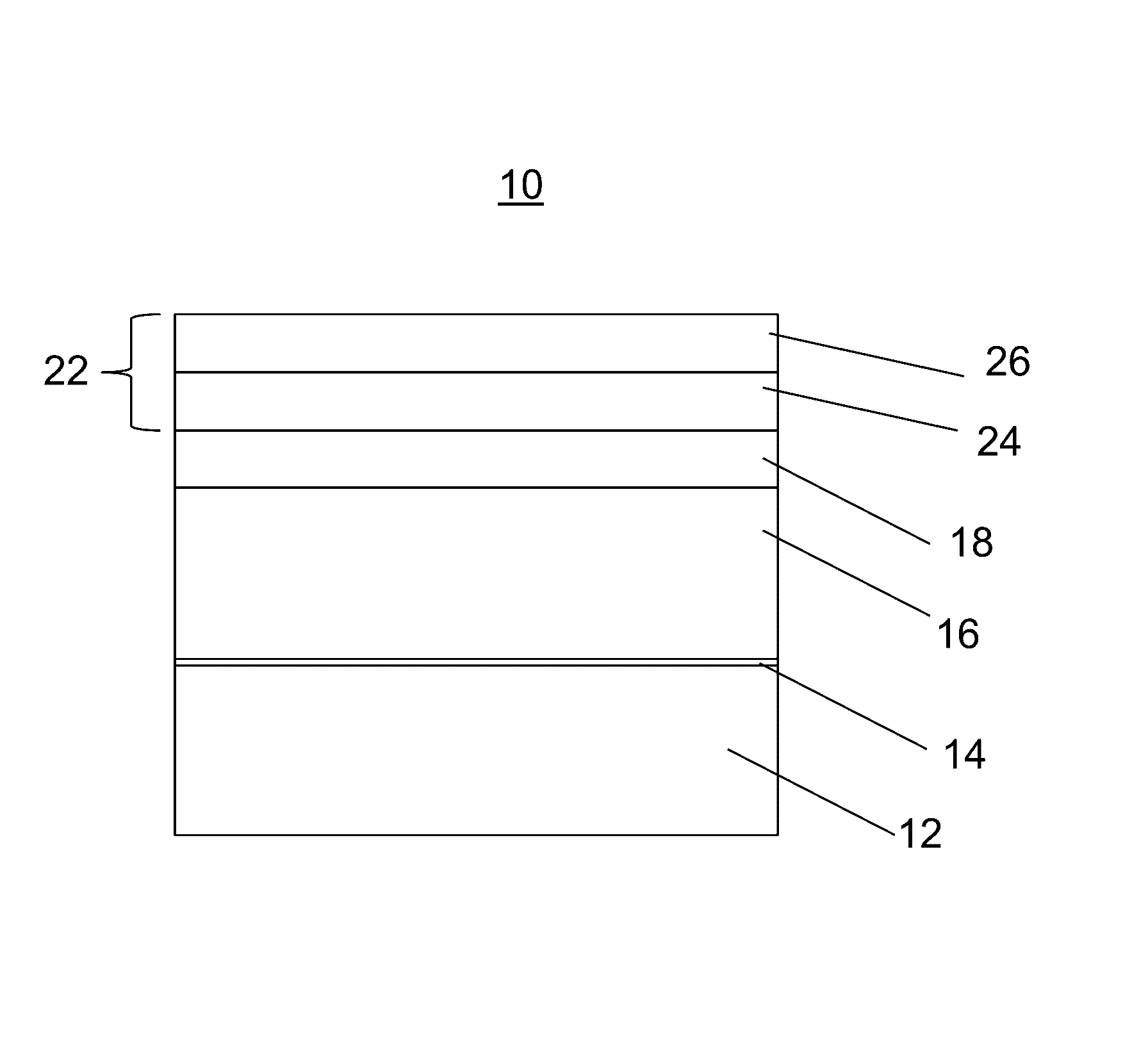
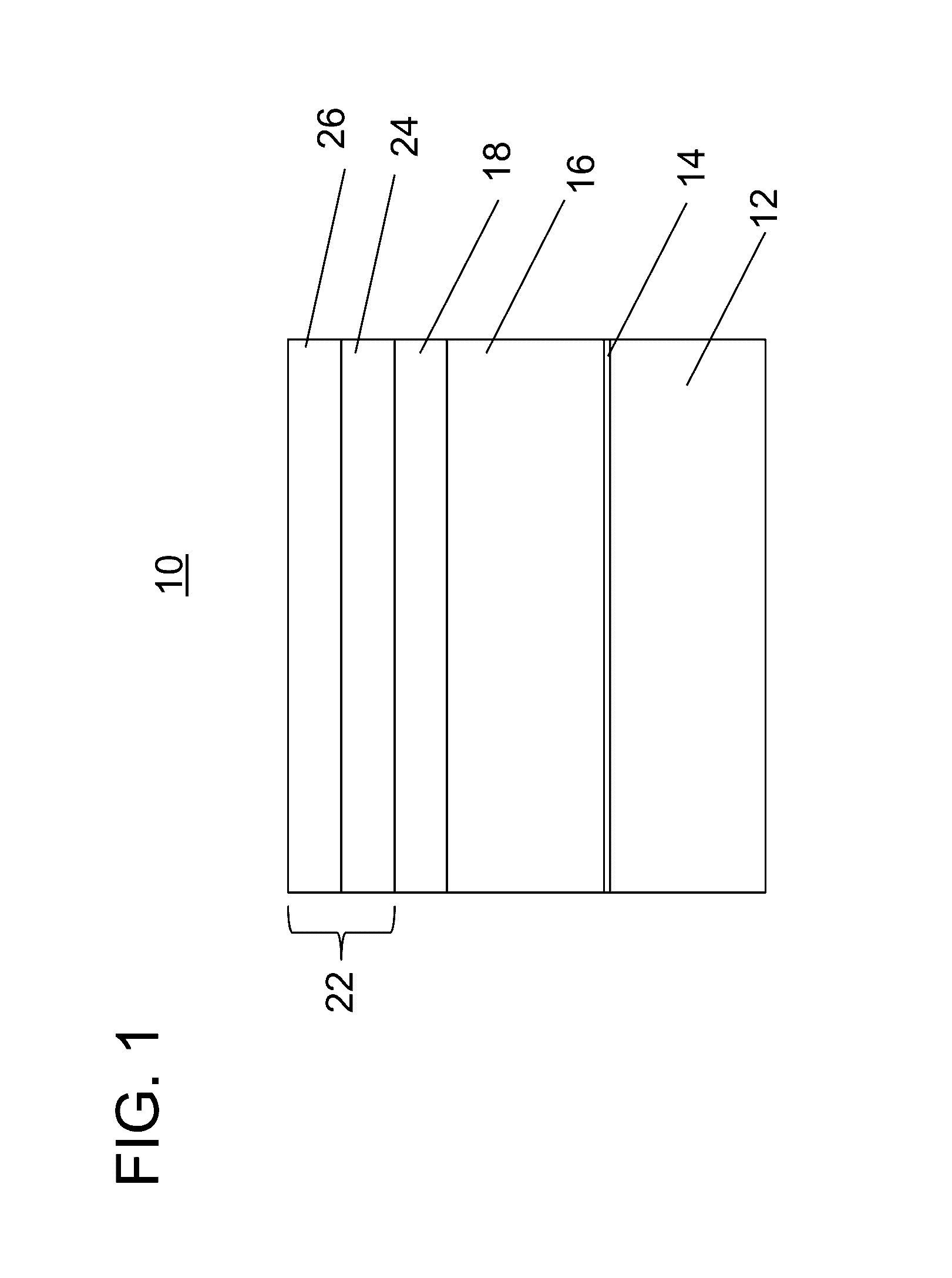
[0020]In accordance with the present principles, a Cu2(Zn,Sn)(S,Se)4 (CZTSSe) photovoltaic device is provided that includes benefits of earth-abundant constituent elements of the CZTSSe and may provide higher performance than conventional CZTSSe devices. The CZTSSe may be grown as a single crystal and transferred to a substrate where it can be employed as an absorber layer in a photovoltaic device, such as, e.g., a solar cell. In other embodiments, the CZTSSe (polycrystalline) may be formed on a Mo coated substrate. Single crystal CZTSSe devices may provide higher power conversion efficiency.
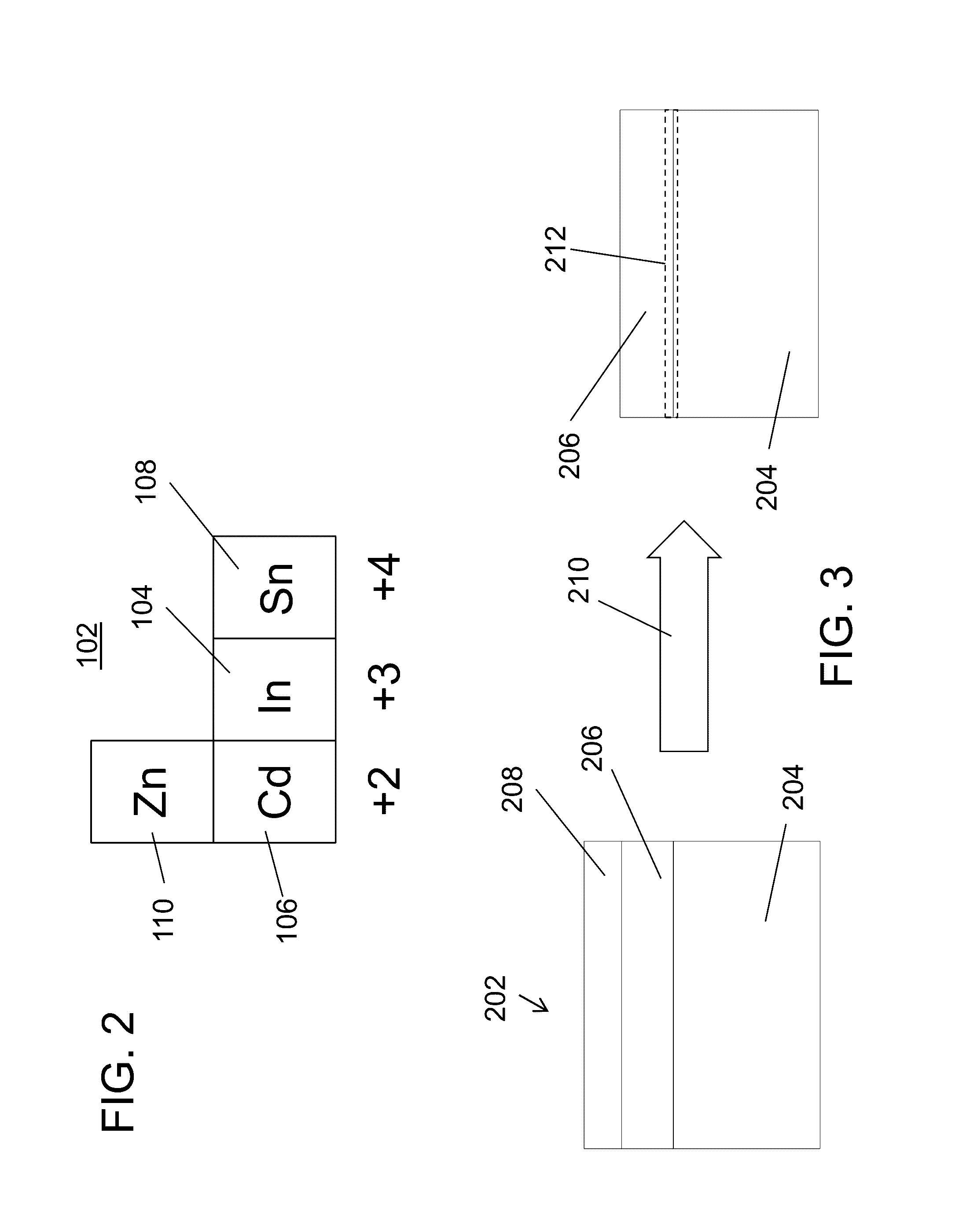
[0021]In one illustrative embodiment, a buffer layer may include CdS or other material formed on the CZTSSe layer. In accordance with the present principles, a thin indium metal layer is formed, e.g., by thermal evaporation, on the buffer layer and then diffused by an anneal process. The indium diffuses into the CdS / CZTSSe junction to enhance the operating parameters of the device.
[0022]It is to...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| band gap | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com