Process for the production of an abuse-proofed dosage form
a technology of dosage form and process, which is applied in the direction of presses, manufacturing tools, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of many pharmaceutical active ingredients, abuse potential, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing parenteral, nasal and/or oral abus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0155]
ComponentsPer tabletComplete batchTramadol HCl100.0 mg 60.0 gPolyethylene oxide, NF, MFI221.0 mg132.6 g(190° C. at 21.6 kg / 10 min)MW7,000,000 (Polyox WSR 303,Dow Chemicals)Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose 20.0 mg 12.0 g100,000 cP (Metholose 90 SH100,000)Magnesium stearate 9.0 mg 5.4 gTotal weight350.0 mg210.0 g
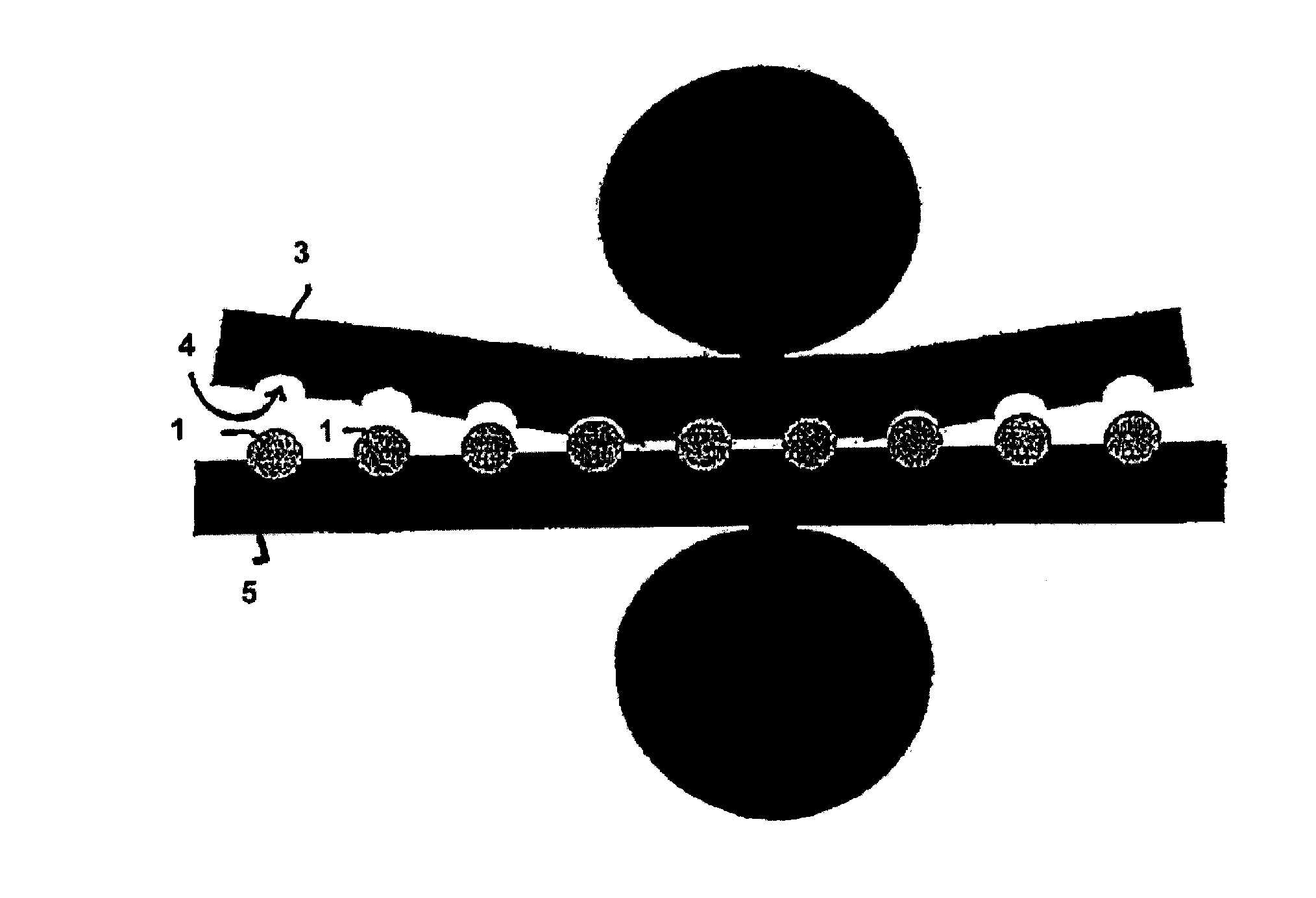
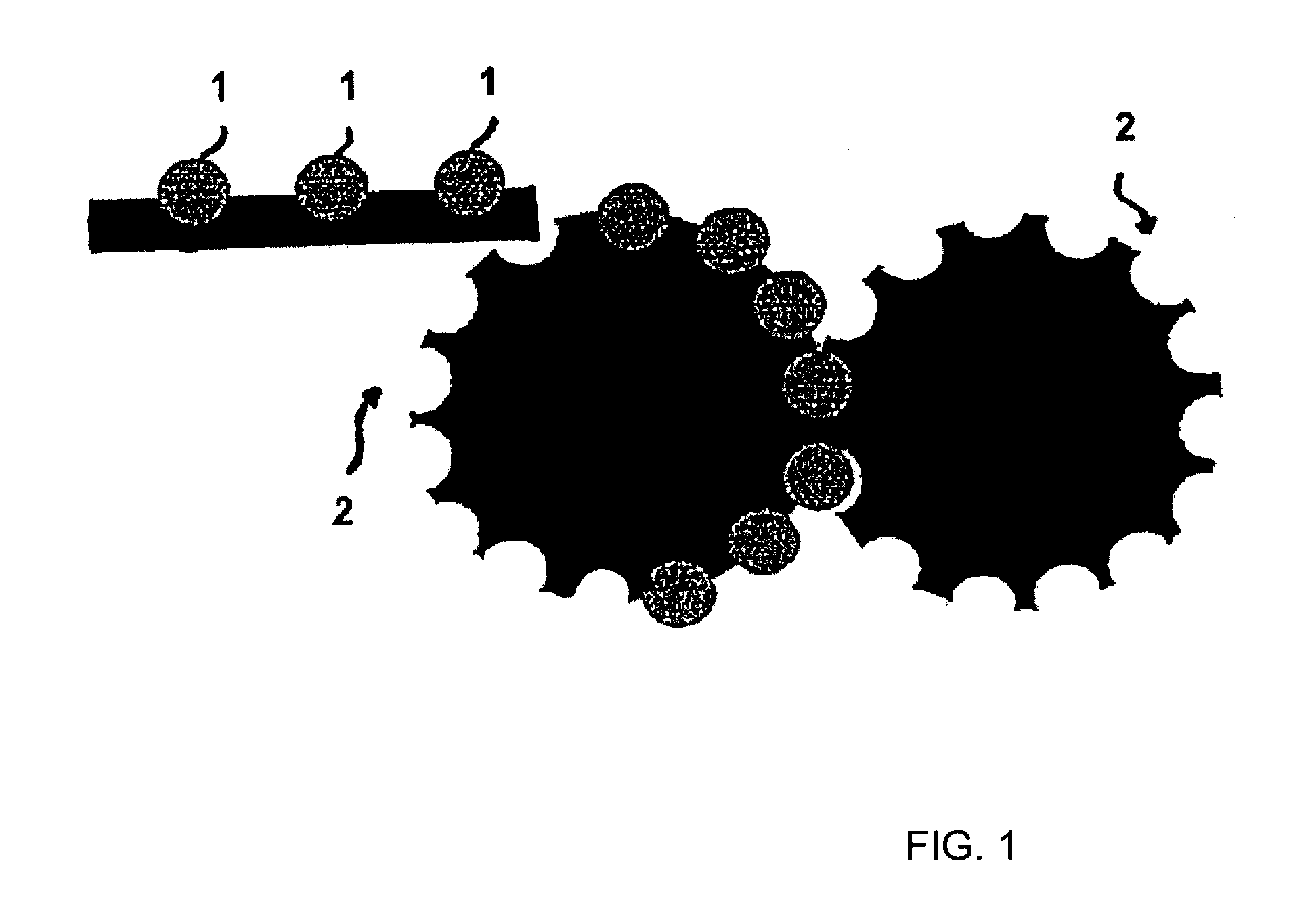
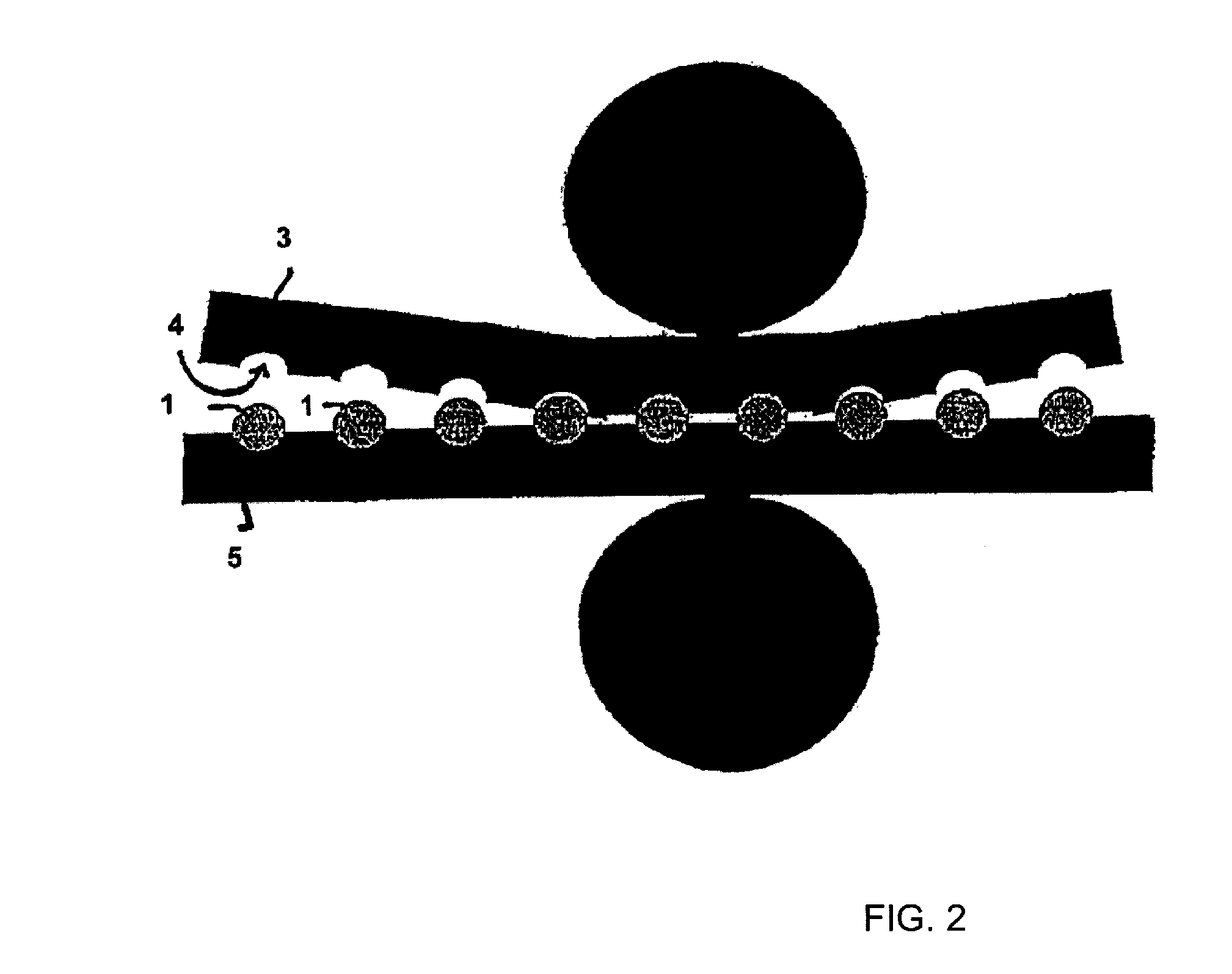
[0156]Tramadol hydrochloride and polyethylene oxide powder and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose were mixed in a free-fall mixer. The magnesium stearate powder was then mixed in. The powder mixture was pressed into tablets on a Korsch EK0 eccentric press. The tabletting tool has a diameter of 10 mm and a radius of curvature of 8 mm. These tablets were further processed with the assistance of a laboratory heat sealer (Kopp laboratory sealer SPGE 20, Hot & Cold tack heat-sealed seam strength tester from Kopp). The heat sealing bars were replaced with two metal rails, into each of which had been milled a concavity having a diameter of 10 mm and a radius of 8 mm. The surface of the ...
example 2
[0159]
ComponentsPer tabletComplete batchTramadol HCl100.0 mg60.0gPolyethylene oxide, NF, MFI221.0 mg132.6g(190° C. at 21.6 kg / 10 min)MW5,000,000 (Polyox WSRCoagulant, Dow Chemicals)Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose 20.0 mg12.0g100,000 cP (Metholose 90 SH100,000)Magnesium stearate 9.0 mg5.4opTotal weight350.0 mg210.0g
[0160]As stated in Example 1, tablets with a diameter of 10 mm and a radius of curvature of 8 mm were produced.
[0161]The tablets were also further processed as in Example 1, except that the sealing bars were heated to 100° C.
[0162]The breaking strength of the tablets is determined using the above-described method. No breakage occurred when a force of 500 N was applied. The tablets could not be comminuted using a hammer, nor with the assistance of a pestle and mortar.
[0163]In vitro release of the active ingredient from the preparation was determined in a paddle stirrer apparatus with sinker in accordance with Pharm. Eur. The temperature of the release medium was 37° C. and the...
example 3
[0164]
ComponentsPer tabletComplete batchTramadol HCl100.0 mg 60.0 gPolyethylene oxide, NF, MFI221.0 mg132.6 g(190° C. at 21.6 kg / 10 min)MW7,000,000, fine powder (PolyoxWSR 303 FP, Dow Chemicals)Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose 20.0 mg 12.0 g100,000 cP (Metholose 90 SH100,000)Magnesium stearate 9.0 mg 5.4 gTotal weight350.0 mg210.0 g
[0165]Tablets were produced as described in Example 1. The tablets were also further processed as explained in Example 1.
[0166]The breaking strength of the tablets was determined using the above-described method. No breakage occurred when a force of 500 N was applied. The tablets could not be comminuted using a hammer, nor with the assistance of a pestle and mortar.
[0167]In vitro release of the active ingredient from the preparation was determined in a paddle stirrer apparatus with sinker in accordance with Pharm. Eur. The temperature of the release medium was 37° C. and the rotational speed of the stirrer 75 min−1. The release medium used was an intestinal j...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com