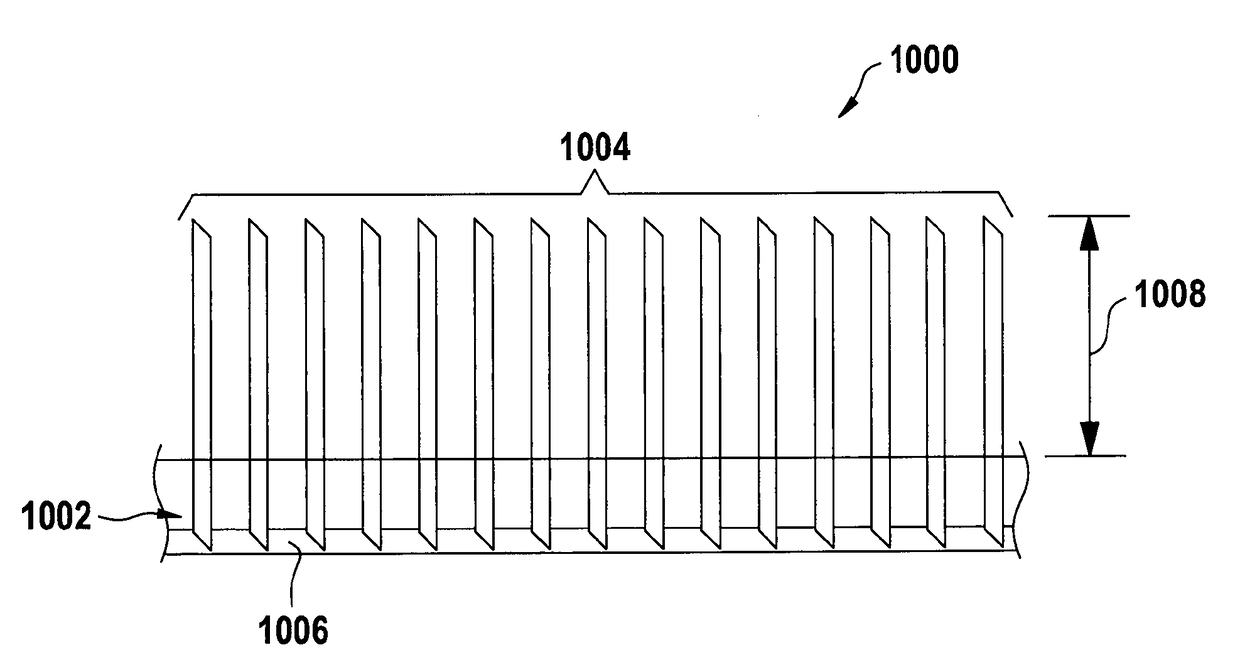
Artificial turf and production method
a production method and technology of artificial turf, applied in the direction of melt spinning methods, ground pavings, ways, etc., can solve the problems of slow re-growth of grass and closed grass cover, inability to delaminate, and difficulty in watering, so as to improve long-term elasticity, reduce maintenance costs, and improve resilience and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0069]Like numbered elements in these figures are either equivalent elements or perform the same function. Elements which have been discussed previously will not necessarily be discussed in later figures if the function is equivalent.
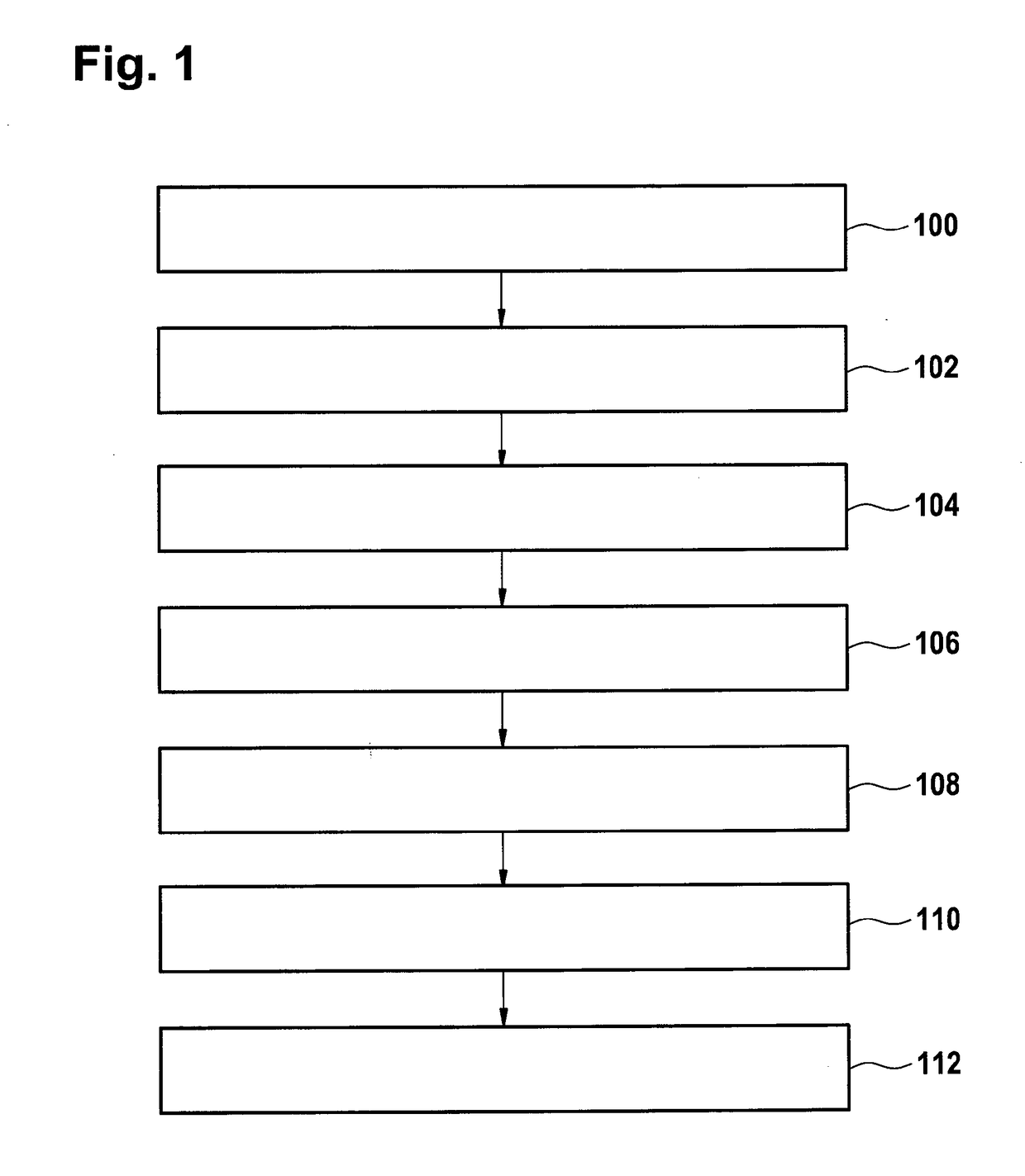
[0070]FIG. 1 shows a flowchart which illustrates an example of a method of manufacturing artificial turf. First in step 100 a polymer mixture is created. The polymer mixture is at least a three-phase system. The polymer mixture comprises a first polymer. The polymer mixture further comprises a second polymer and a compatibilizer. The first polymer and the second polymer are immiscible. In other examples there may be additional polymers such as a third, fourth, or even fifth polymer that are also immiscible with the second polymer. There also may be additional compatibilizers which are used either in combination with the first polymer or the additional third, fourth, or fifth polymer. The first polymer forms polymer beads surrounded by the compatibilizer...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com