Splitting and moving ranges in a distributed system
a distributed database and range technology, applied in the field of large group splitting in a distributed database system, can solve the problem of not uncommonly large splits that exceed the size threshold
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
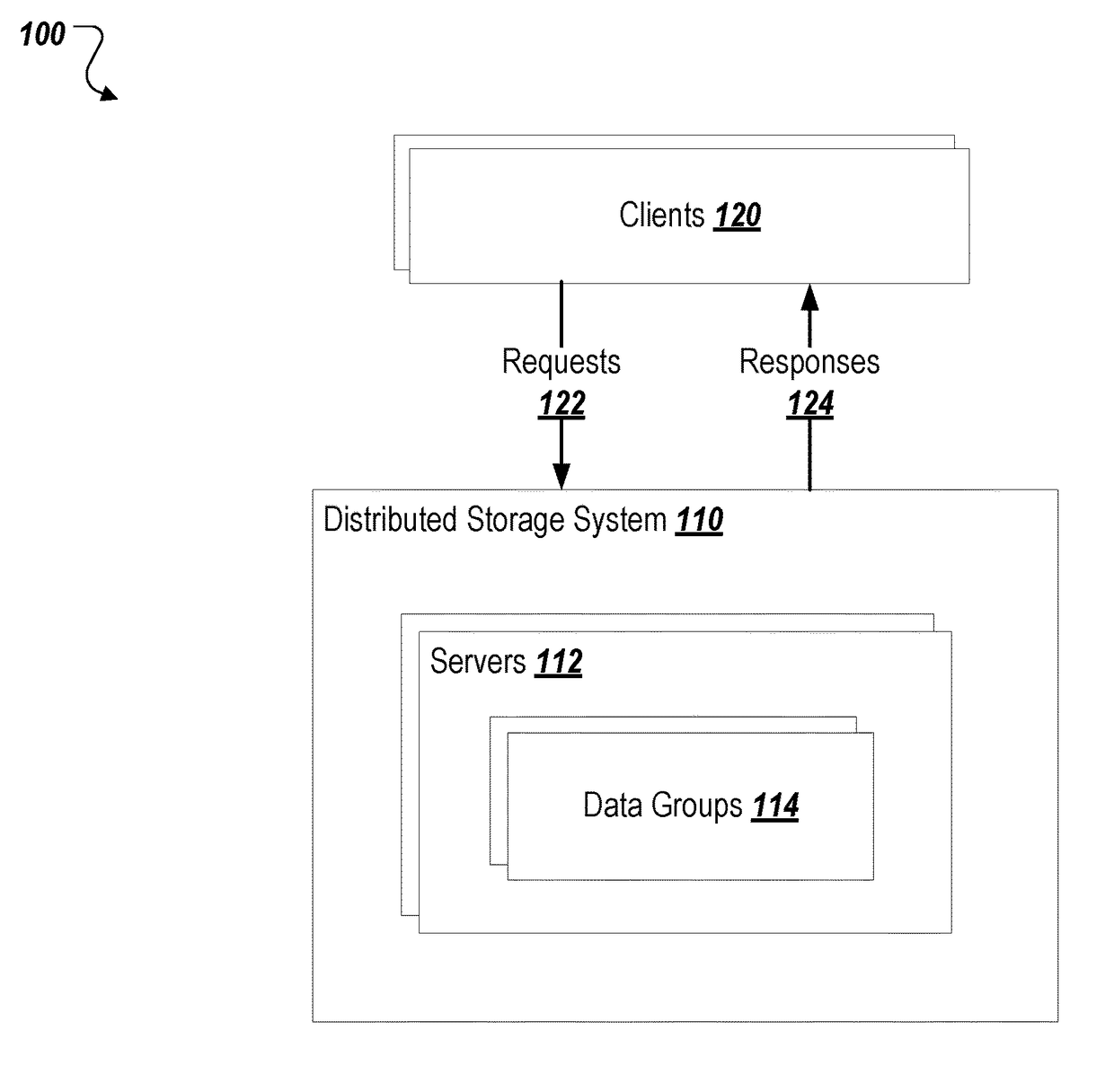
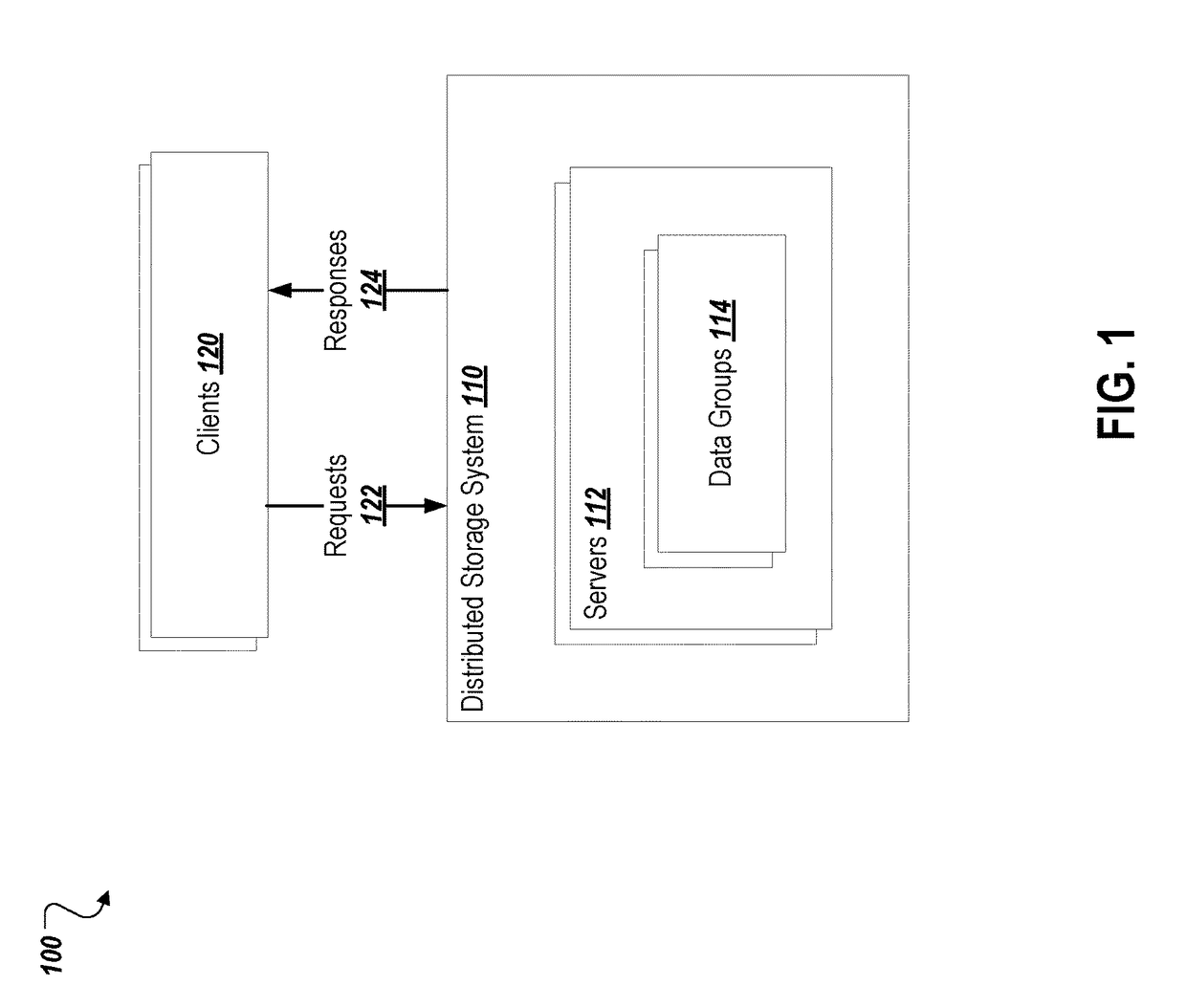
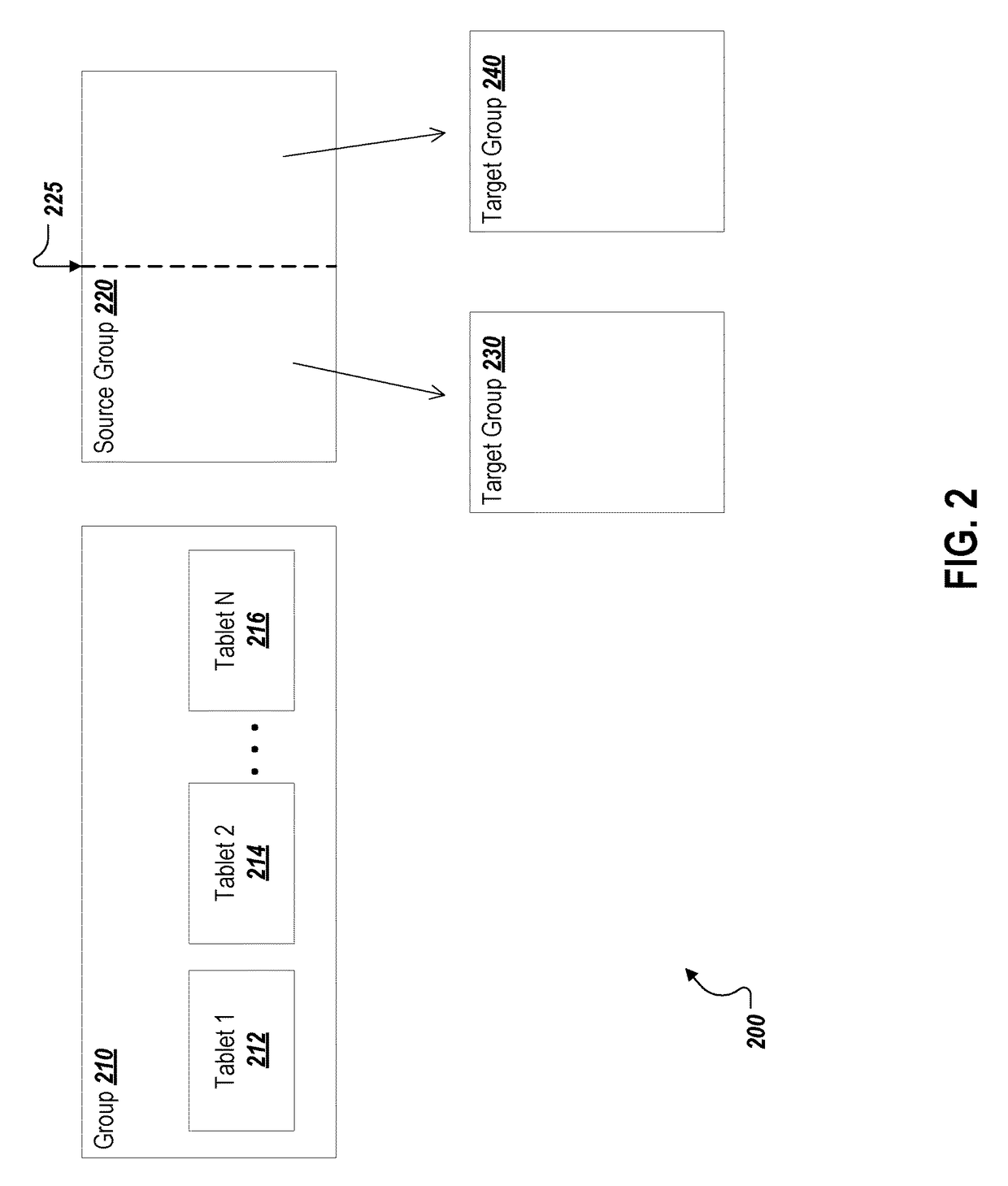
[0014]When repartitioning data in a distributed database, standard implementations copy the entirety of data to be moved. For example, splitting data or changing a replication level requires making a whole new copy of the data in the new configuration. Embodiments described herein provide a mechanism to avoid this extra copy by sharing on-disk copies of the data whenever possible. For example, when splitting data, rather than making a new copy of the two partitions, a virtual view of the existing partition may be provided that makes the existing partition usable as two separate portions. Only when a new copy of the data would otherwise be made, for example when rewriting data into a more compact form (i.e., a “compaction”), does the virtual copy need to be resolved into a real copy of the data. According to certain embodiments, a database is partitioned into groups, where each group is a replicated set of tablets. A tablet includes a list of immutable files, also called layers, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com