Cationic lipid compositions for tissue-specific delivery
a lipid composition and tissue technology, applied in the direction of hydrolases, drug compositions, organic active ingredients, etc., can solve the problem of design lipid nanoparticles capable of targeting specific organs, tissues, or cell types without the use of canonical biomolecular targeting techniques, and achieve the effect of improving the stability and stability of the lipid nanoparticl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
id Nanoparticles for In Vivo Lung Targeted mRNA and siRNA Delivery
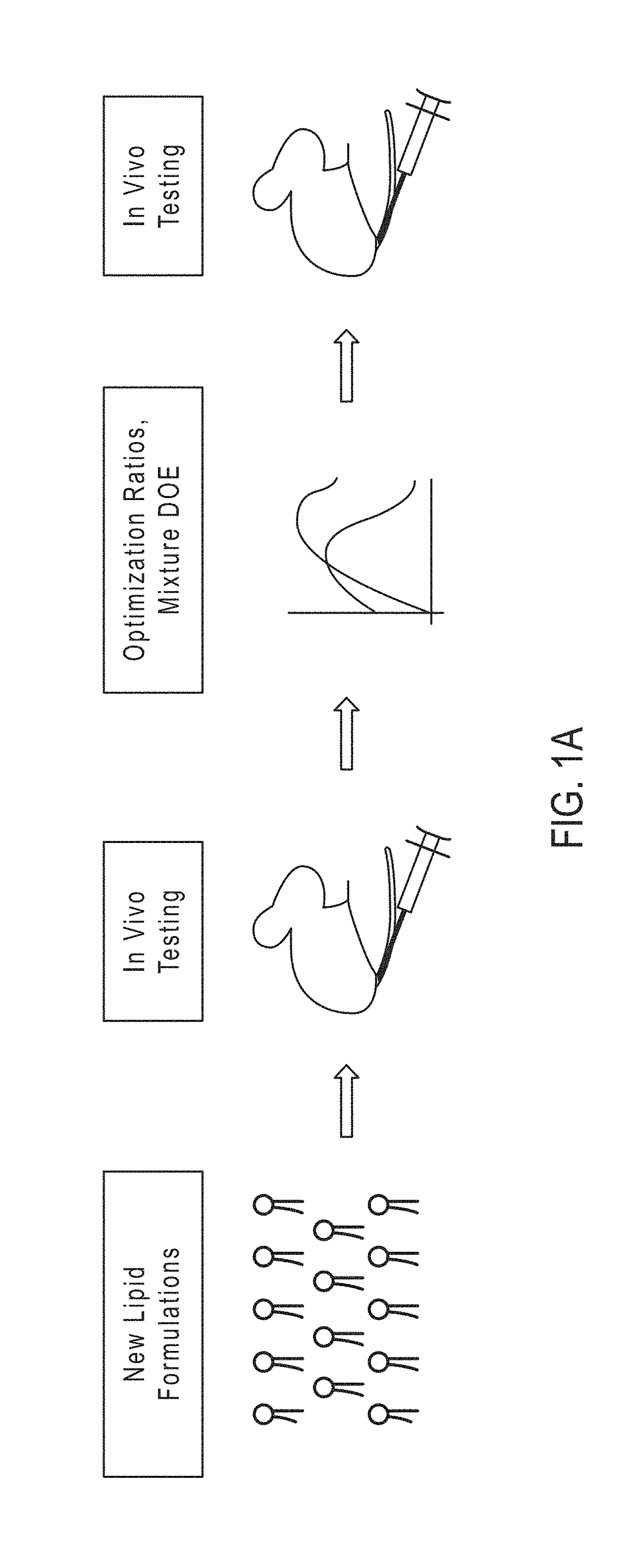
[0218]The rapidly expanding utilization of nucleic acids as a therapeutic tool has presented the field with the task of optimizing and innovating delivery methods. Lipid nanoparticles are a common delivery vehicle due to their ability to facilitate cellular uptake while protecting the payload from extracellular enzyme degradation. Organ and tissue specific delivery of sensitive payloads such as mRNA is of great importance in tailoring therapeutic functionality. This is commonly achieved using biomolecular targeting via ligand or receptor expression on the surface of the nanoparticle. However, manipulation of the inherent properties of nanoparticles affords the opportunity to tailor the location of delivery to a specific organ of interest.
[0219]Applicants have developed novel lipid nanoparticles that are specifically optimized for use in vivo, and engineered to inherently target and deliver nucleic acid payloads (mRNA ...
example 2
nt of Novel Lipid Nanoparticles for In Vivo Lung Targeted mRNA Delivery
[0220]Abstract.
[0221]The rapidly expanding utilization of mRNA as a therapeutic tool has presented the field with the task of optimizing and innovating delivery methods. As the applications for RNA based therapeutics continues to rise, a parallel emerging need to improve upon and develop novel technology has come to the forefront. Lipid nanoparticles area common delivery vehicle for mRNA due to their ability to facilitate cellular uptake while protecting the mRNA from extracellular enzyme degradation. Organ and tissue specific delivery of mRNA is of great importance in tailoring therapeutic functionality. This is commonly achieved using biomolecular targeting via ligand or receptor expression on the surface of the nanoparticle.
[0222]Applicants have developed novel lipid nanoparticles that are specifically optimized for use in vivo, and engineered to inherently target and deliver mRNA to murine lungs and spleen wi...
example 3
on and Complexation
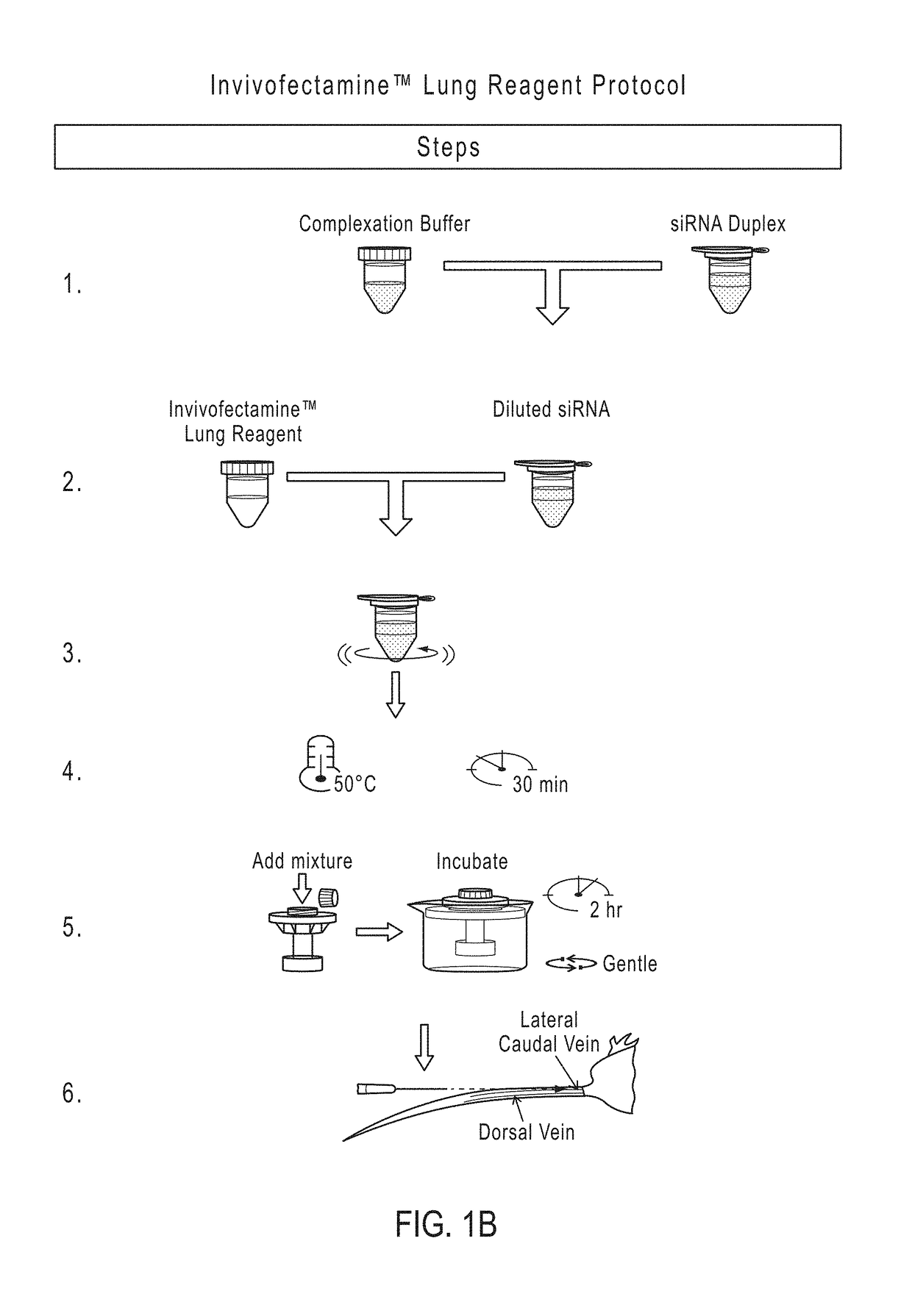
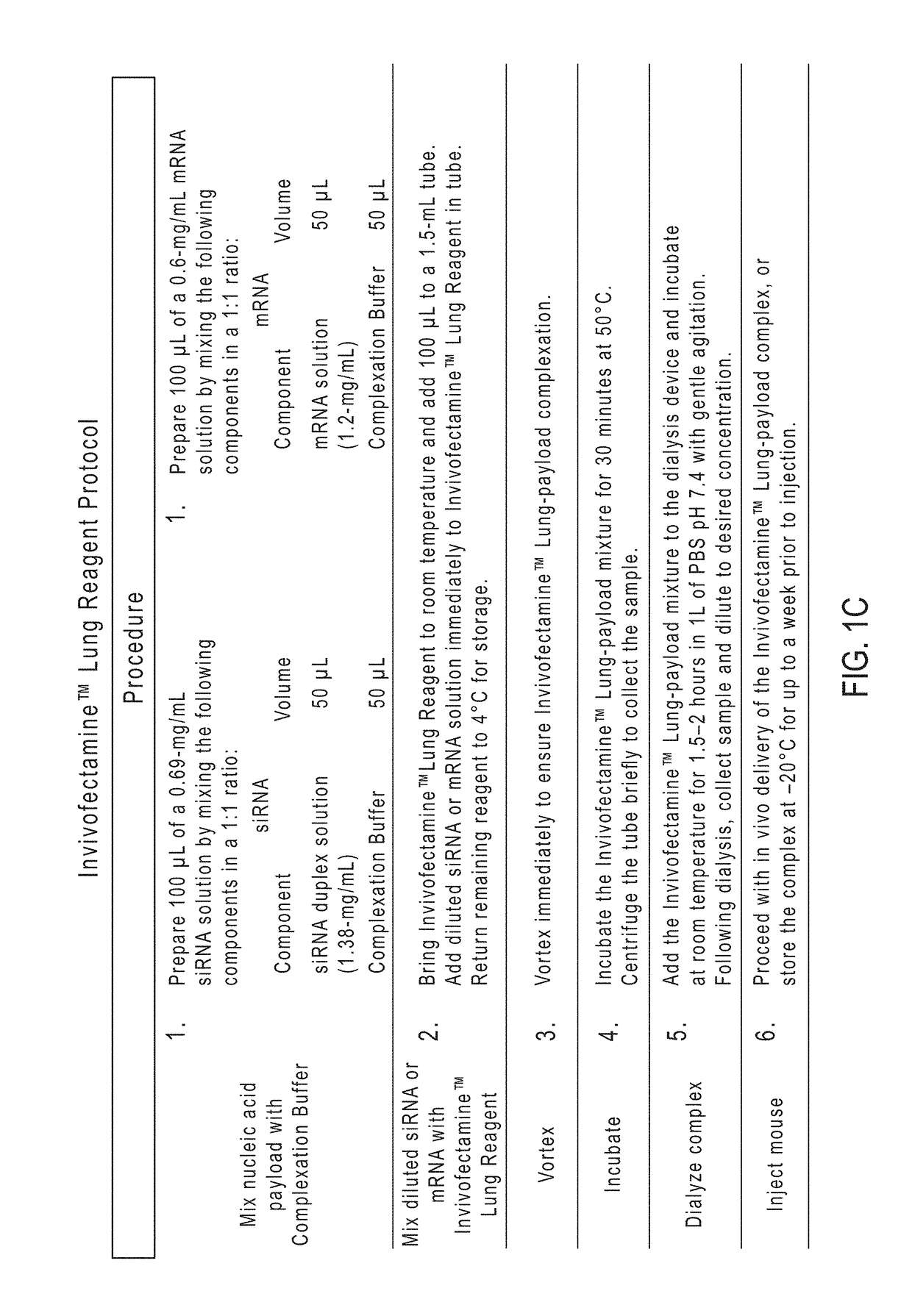
[0237]Formulation Preparation.
[0238]Prepare stock solutions of the individual lipid components in 100% Ethanol (EtOH) at appropriate concentrations based on individual lipid solubility. Heat to 50° C. to dissolve lipids completely in the EtOH. In a glass vial, combine all 5 lipid components using a pipette in volumes calculated according to Molar ratios listed in Table 1. Dilute the combined lipids using 200 mM Sodium Acetate at a dilution ratio of 1:4 by volume. Seal lid with paraffin. Store at 4° C.
[0239]Complexation Preparation.
[0240]Concentration of lipid is delivered at a 3 mg / kg concentration. Concentration of mRNA is a 10:1 dilution, so 0.3 mg / mL total mRNA are administered. Label 2 screw-cap plastic sample tubes as ‘lipid’ and ‘mRNA’. Transfer 100 μL of prepared lipid formulation to tube labeled ‘lipid’. Calculate amount of mRNA needed for 200 μL total volume of complex. (0.6 mg / mL) Since lipid formulation is at a 25% EtOH solution following the 1:4 diluti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap