Adaptive buffer latching to reduce display janks caused by variable buffer allocation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
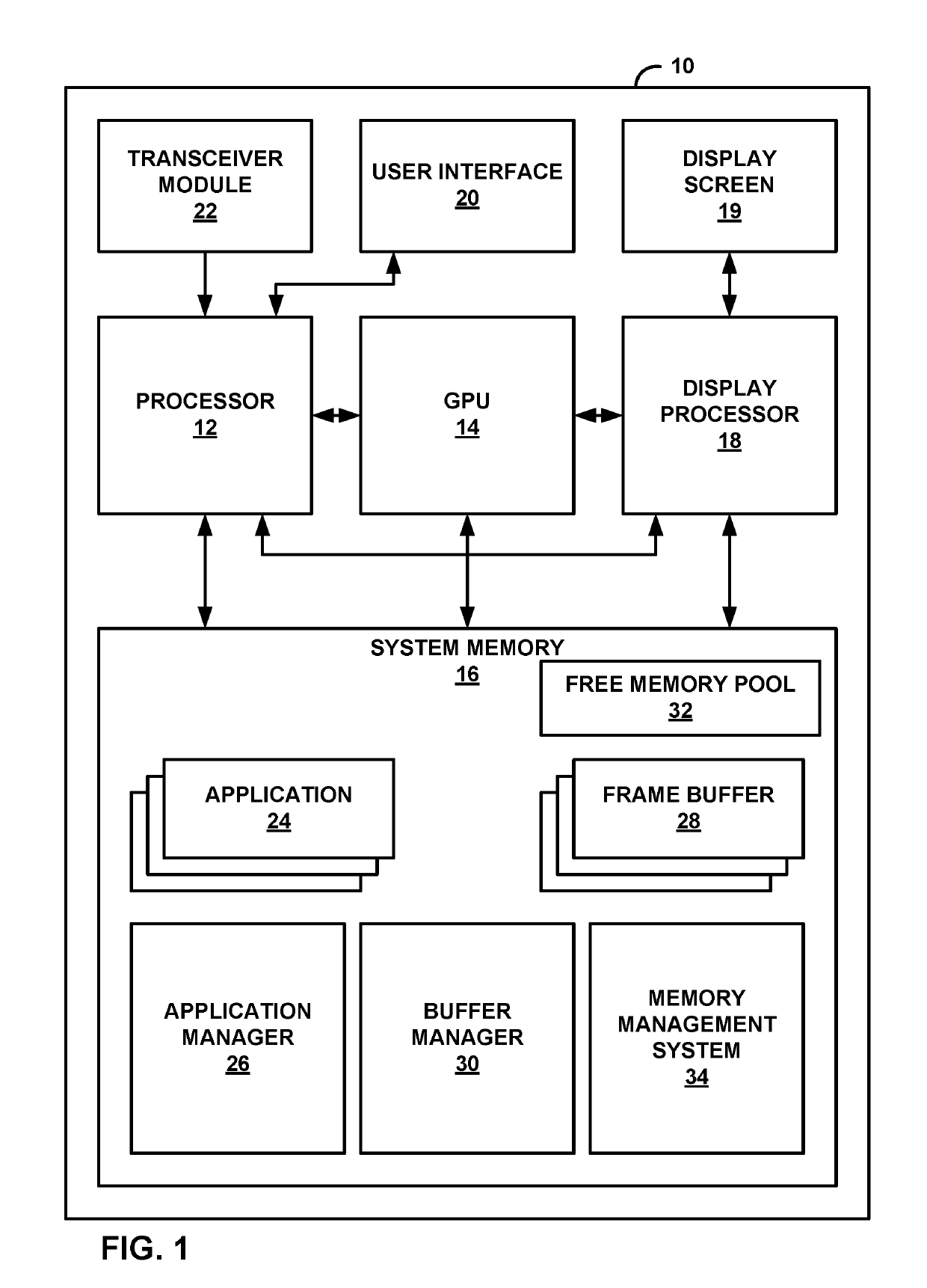
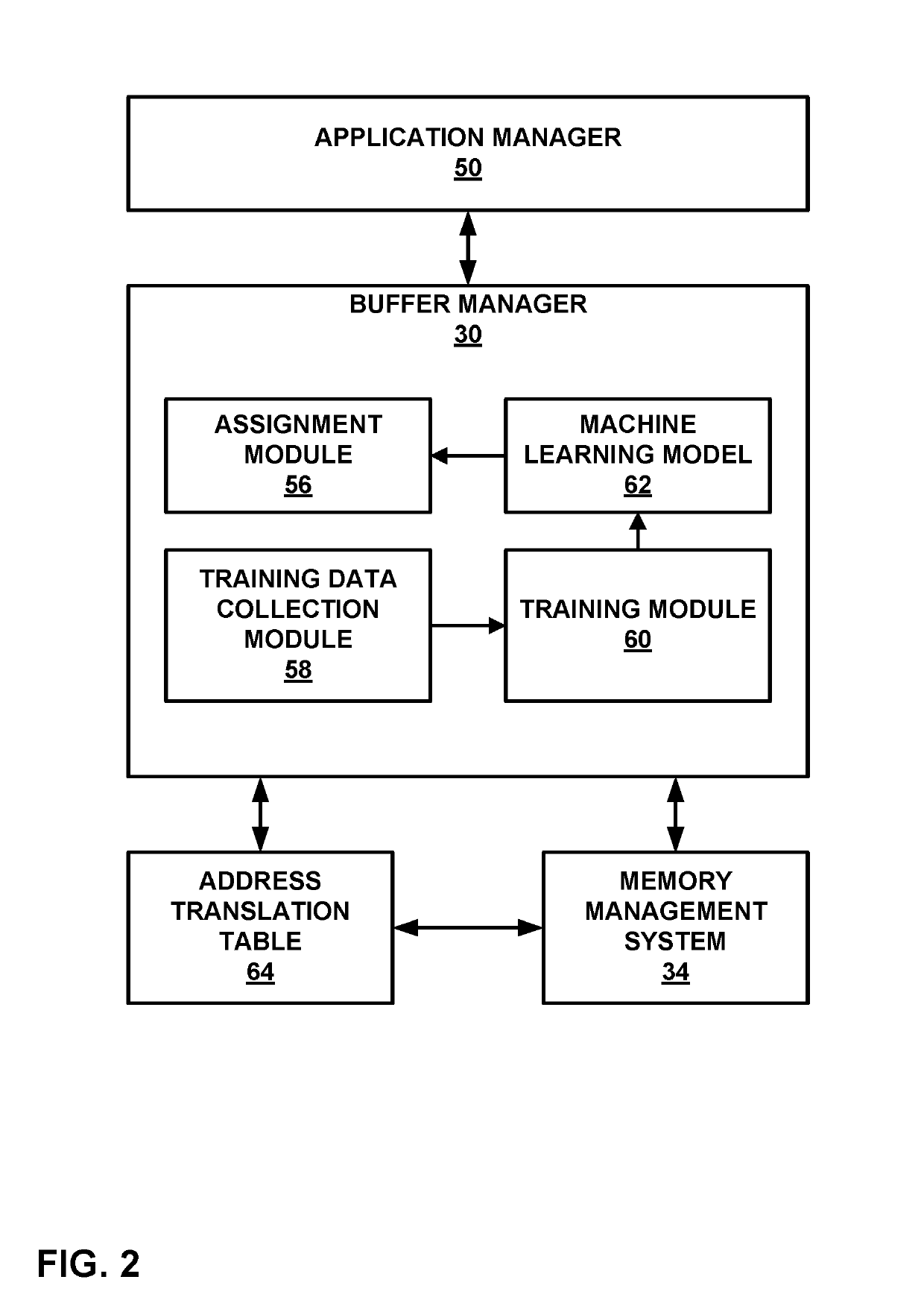
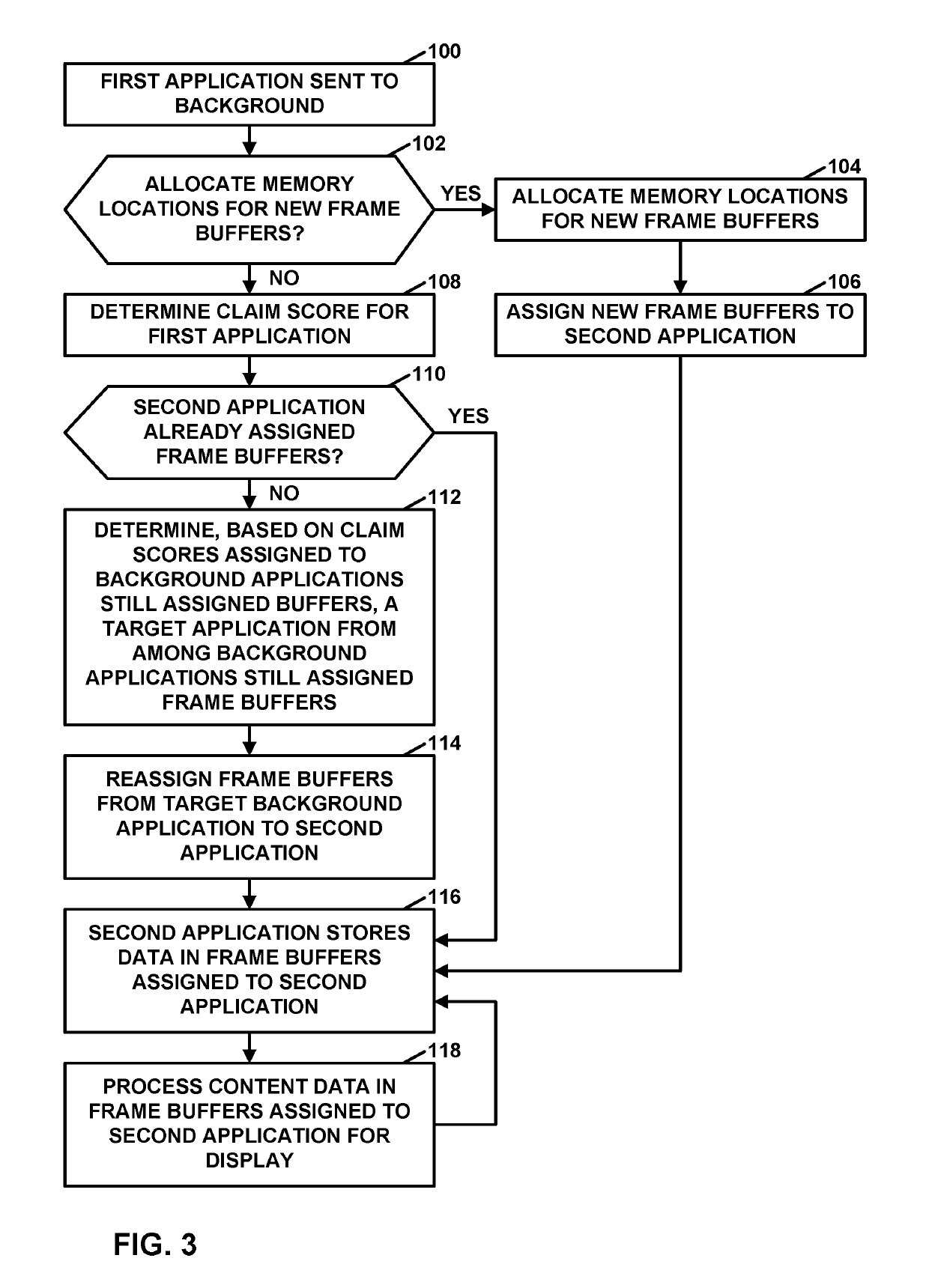
[0019]Visual artifacts called “janks” may occur when switching between applications because delays in allocating memory locations of frame buffers may result in there being insufficient time for the switched-to application to store data into a frame buffer prior to an output time for content data in the frame buffer. Techniques of this disclosure may address this issue, resulting in a potentially smoother experience. For instance, in accordance with a technique of this disclosure, a computing device may assign frame buffers to a plurality of applications. In response to a command to open a first application in addition to the plurality of applications, the computing device selects, based on statistics regarding reuse of content data in the frame buffers assigned to the plurality of applications, an application from among the plurality of applications. Furthermore, the computing device reassigns, one or more of the frame buffers from the selected application to the first application....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com