Pump With Segmented Fluid End Housing and In-Line Suction Valve
a technology of fluid end housing and in-line suction valve, which is applied in the direction of pump components, positive displacement liquid engines, liquid fuel engine components, etc., can solve the problems of fluid end structural failure, high stress in the sharp cornered thread roots, and cyclic fatigu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
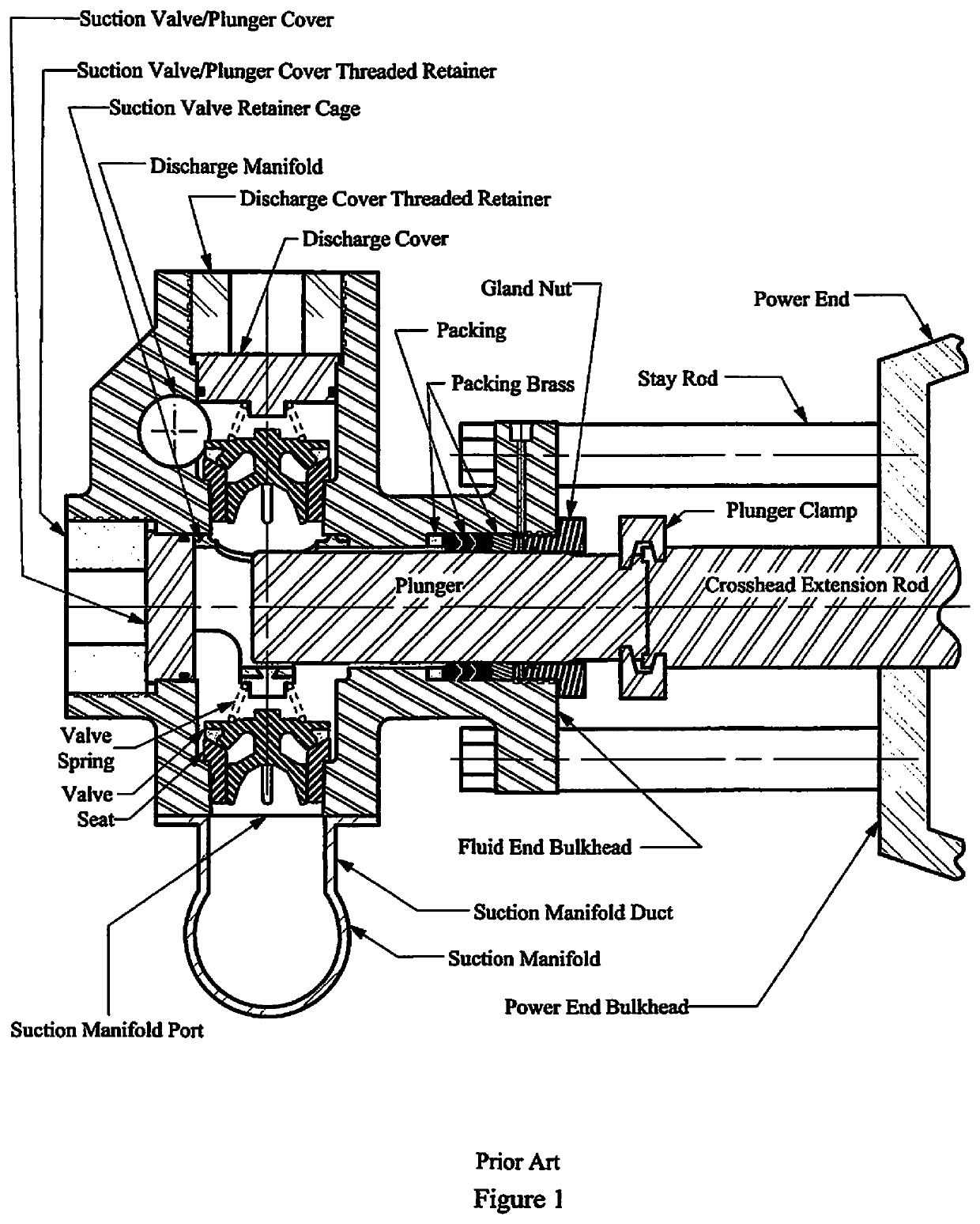
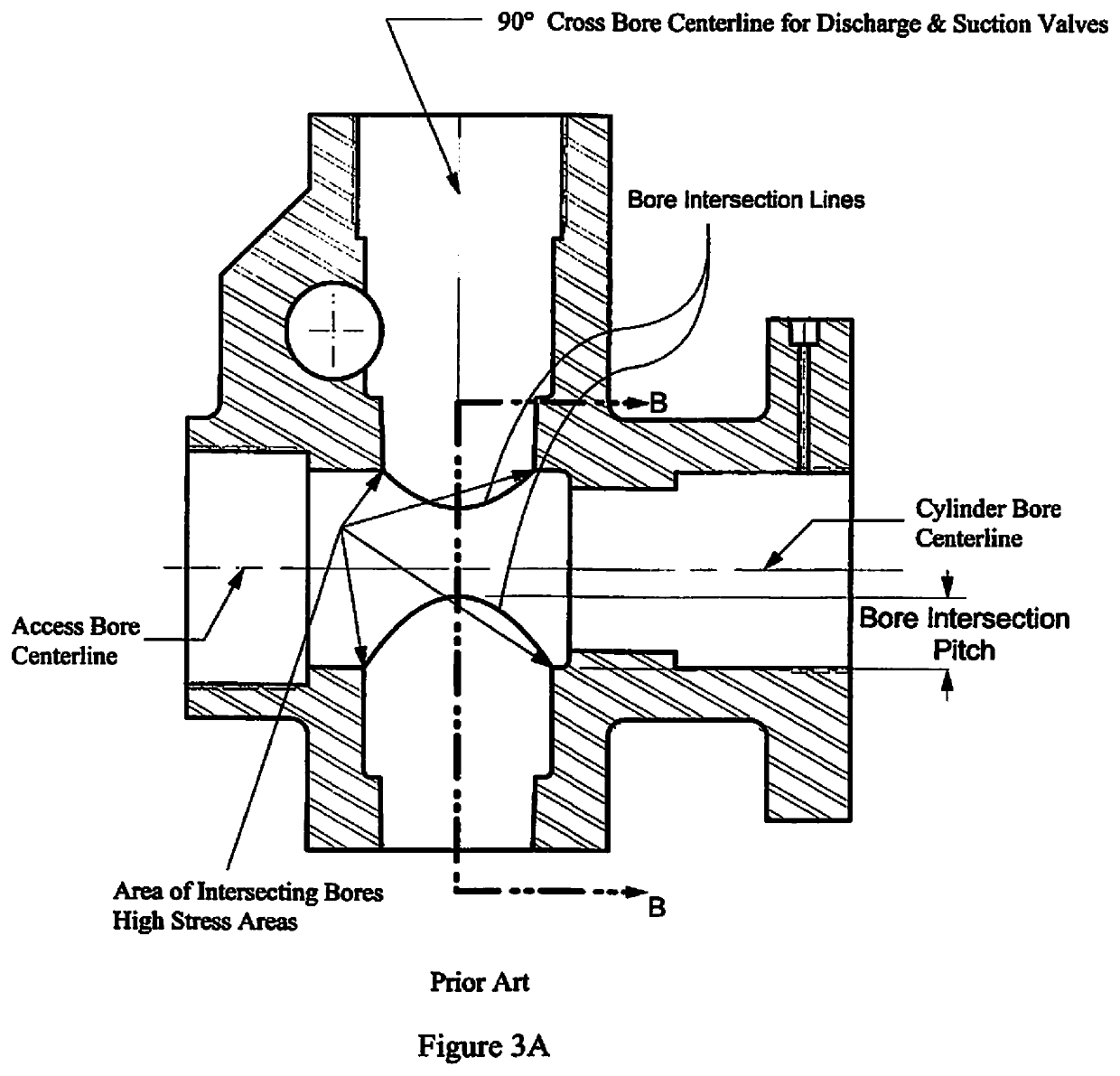
[0055]FIG. 8 schematically illustrates a cross-section of an embodiment of the fluid end assembly 100 of the present invention showing its connection to a power end by multiple stay rods 6. As opposed to the fluid end housing of the prior art as illustrated in FIG. 1, fluid end assembly 100 of the present invention is configured with the suction manifold 5 mounted in a position on the fluid end housing opposite the power end of the pump. The primary component of the fluid end assembly 100 of the present invention is modular housing 101 which is connected to the power end by multiple stayrods 6 and stayrod retaining nuts 7.
[0056]FIG. 9 and FIG. 10A schematically illustrates an orthogonal and top view respectively of the exterior of the fluid end assembly 100. Fluid end assembly 100 comprises modular housing 101, suction manifold 5, and various internal components. The modular housing 101 includes one central fluid module 2 and multiple packing box modules 3, suction seat modules 1, s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com