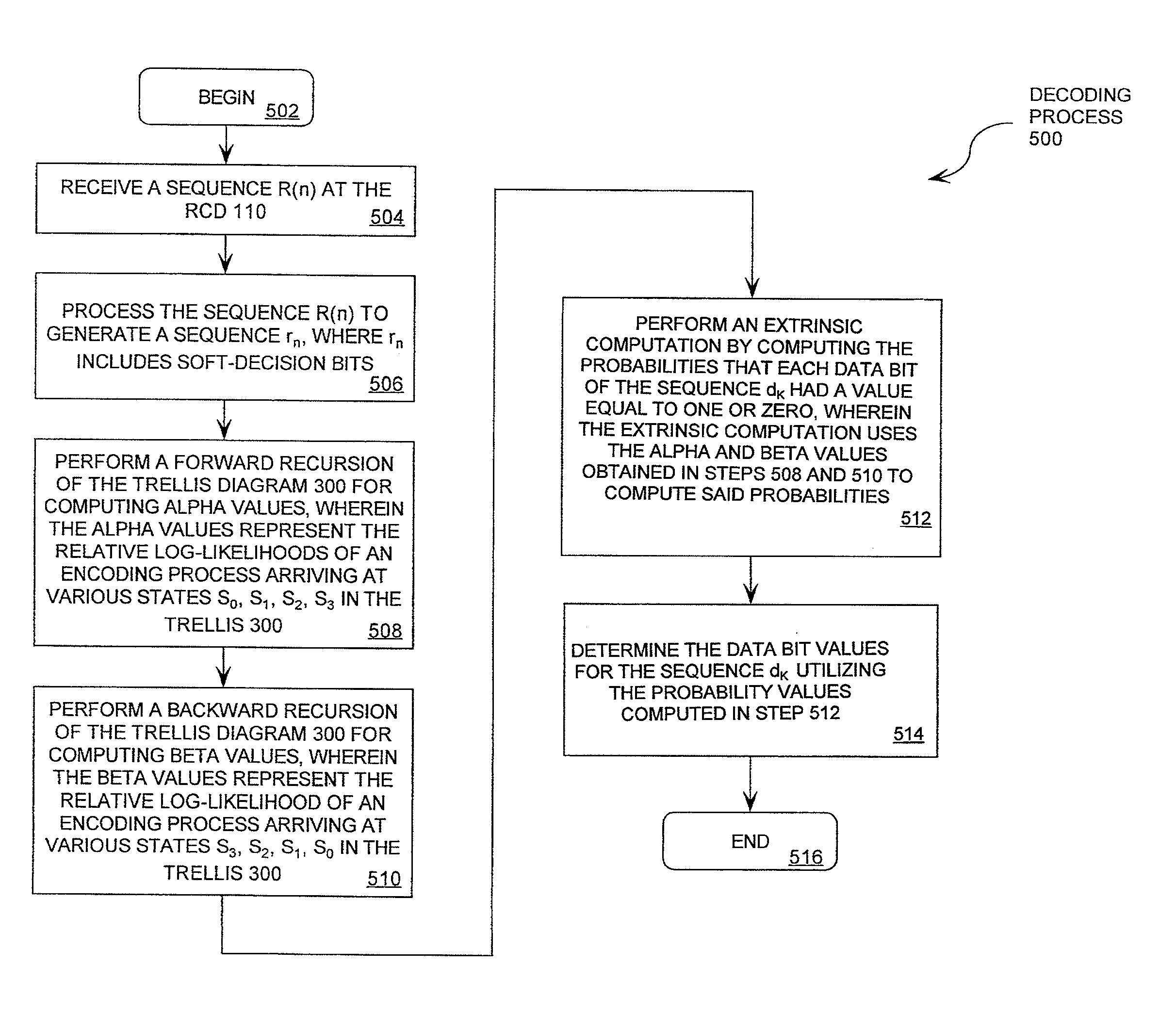
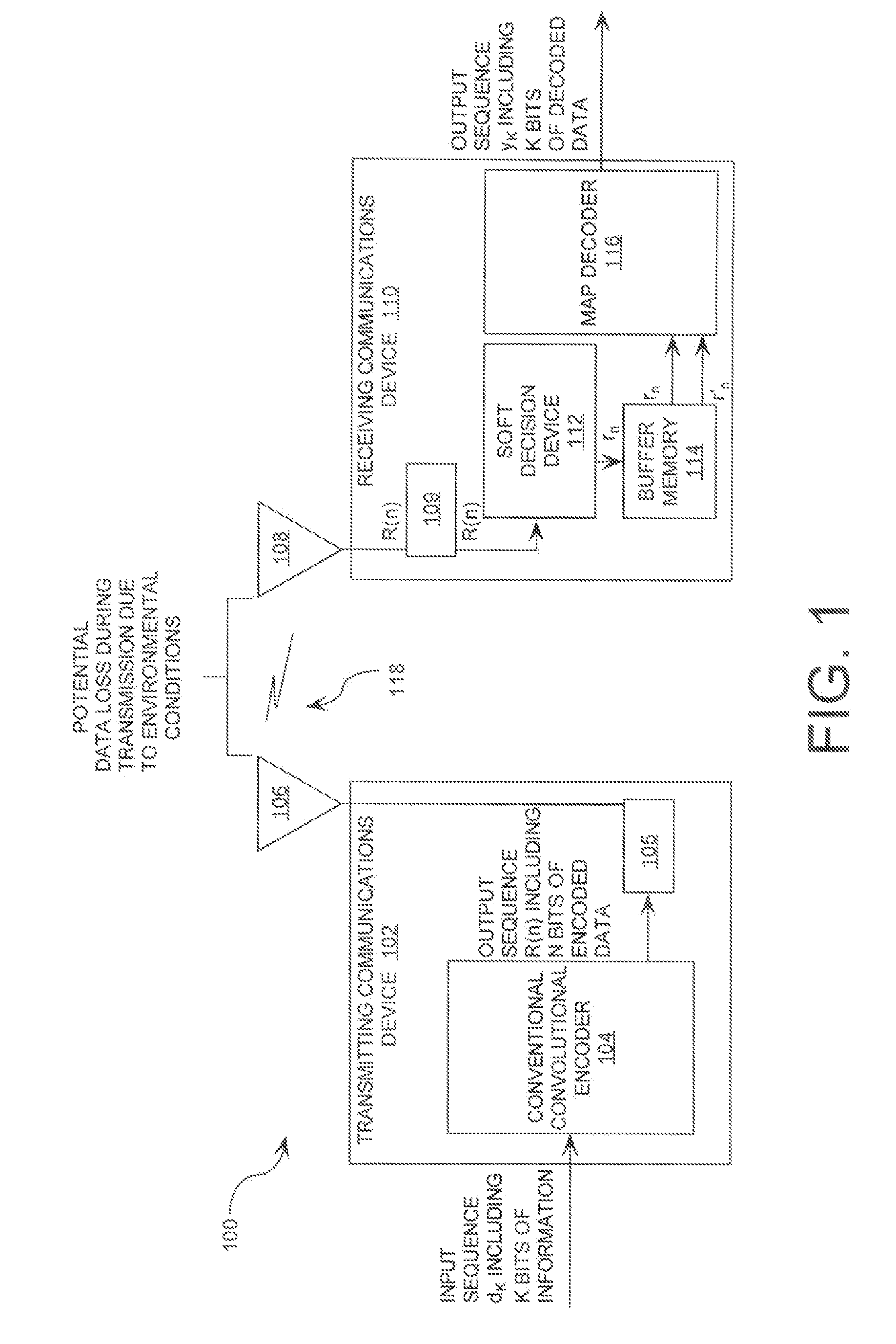
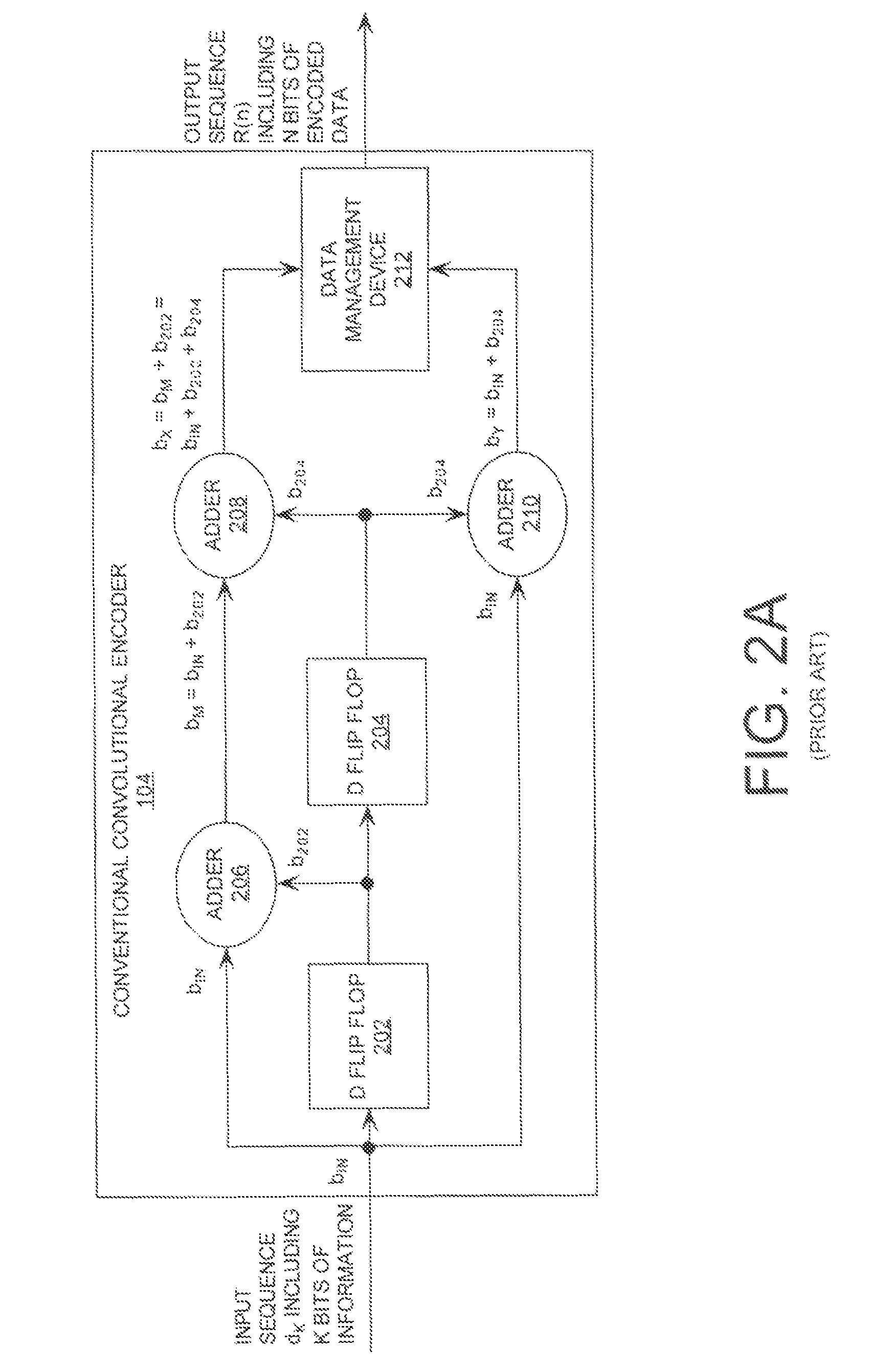
Maximum a posteriori probability decoder
a probability decoder and probability decoder technology, applied in the field of communication systems, can solve problems such as hardware intensiveness of map decoders and certain drawbacks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0069]In this scenario, the CCE is selected as the CCE 104 shown in FIG. 2A. The description provided above in relation to FIGS. 2A-2E is sufficient for understanding the CCE of the present example. The data stream dK input into the CCE 104 is defined as 1 0 0 1 1 0 (as shown in FIG. 2E). Accordingly, the CCE 104 generates an output sequence R(n) defined as 11 10 11 11 01 01. If there is no corruption of the signal R(n), then the sequence rn of soft-decision bits can be defined as rideal(n)=7 7 7 −7 7 7 7 7 −7 7 −7 7. It should be noted that a positive seven (+7) is the highest assignable soft-decision value and negative seven (−7) is the lowest assignable soft-decision value. More particularly, a positive seven (+7) indicates a strong probability that a bit of the sequence R(n) has a value equal to one (1). A negative seven (−7) indicates a strong probability that a bit of the sequence R(n) has a value equal to zero (0).
[0070]Alternatively, if there is corruption of the signal R(n)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com