Map matching for security applications
a mapping and object technology, applied in the field of object position data calculation, can solve the problems of not being able to provide any information, not always allowing, limited to the direct field of vision of the vehicle, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the alignment of a measured position
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0068]In the descriptions of the figures which follow, the same reference numerals are used for the same or similar elements.
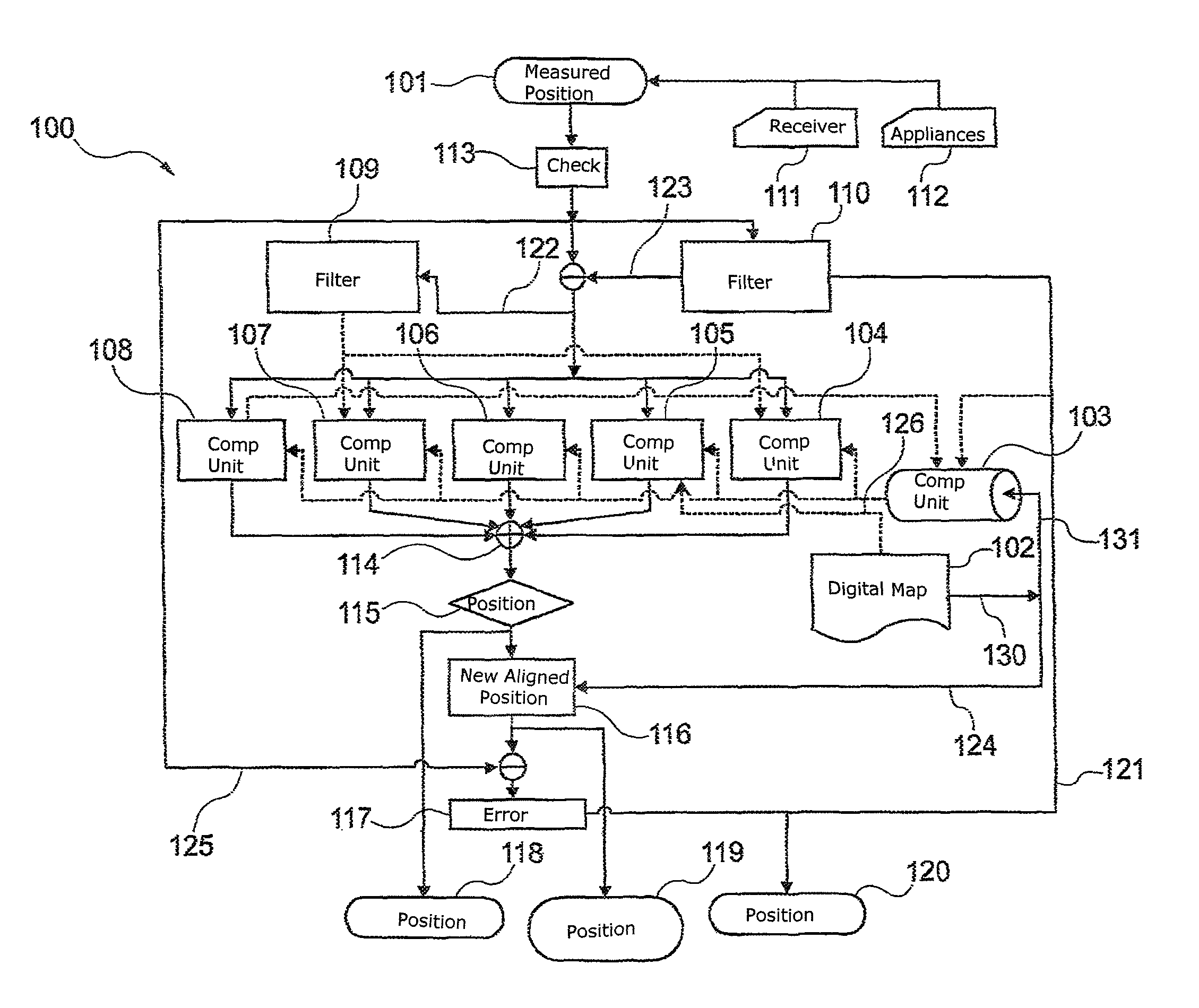
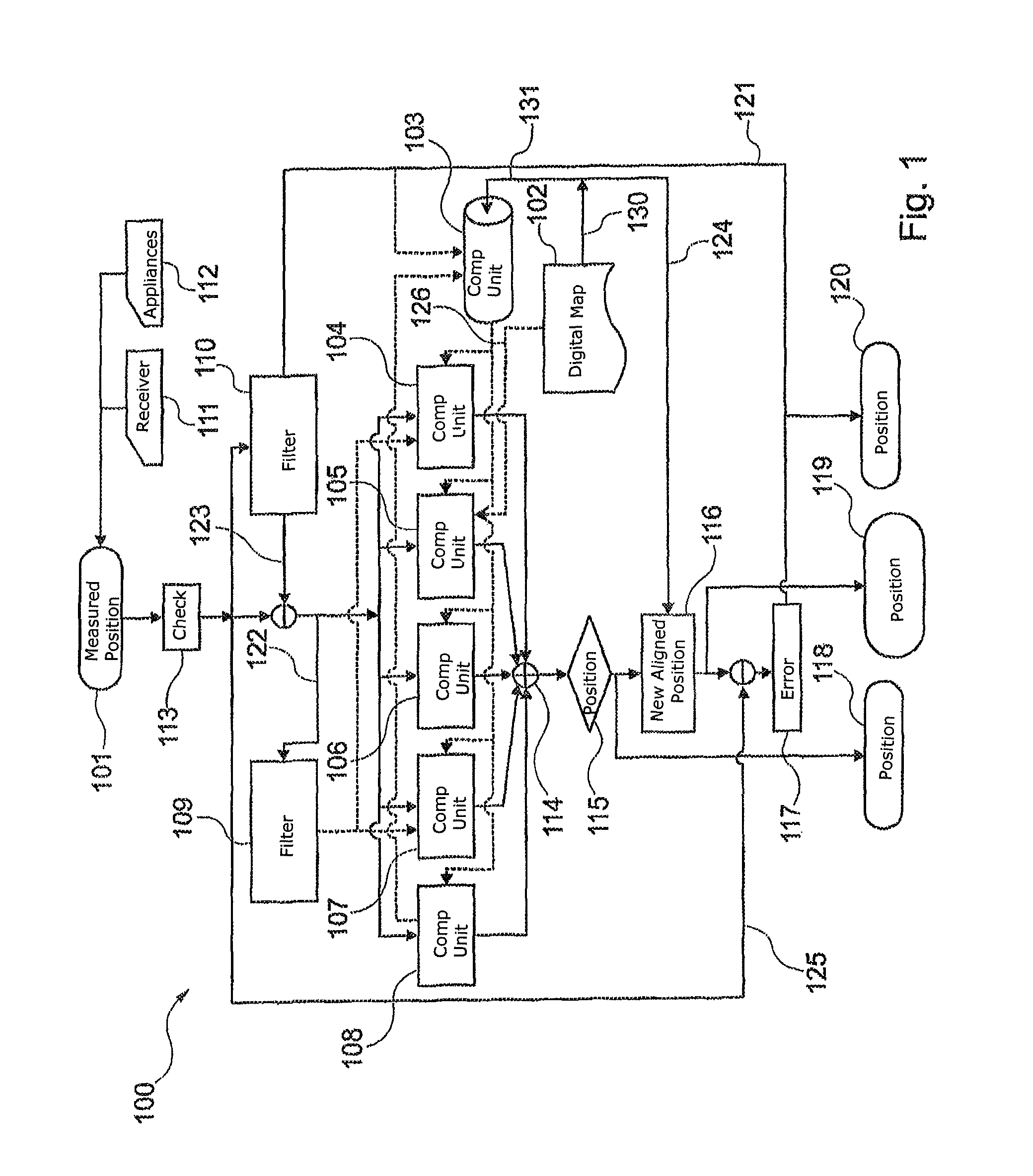
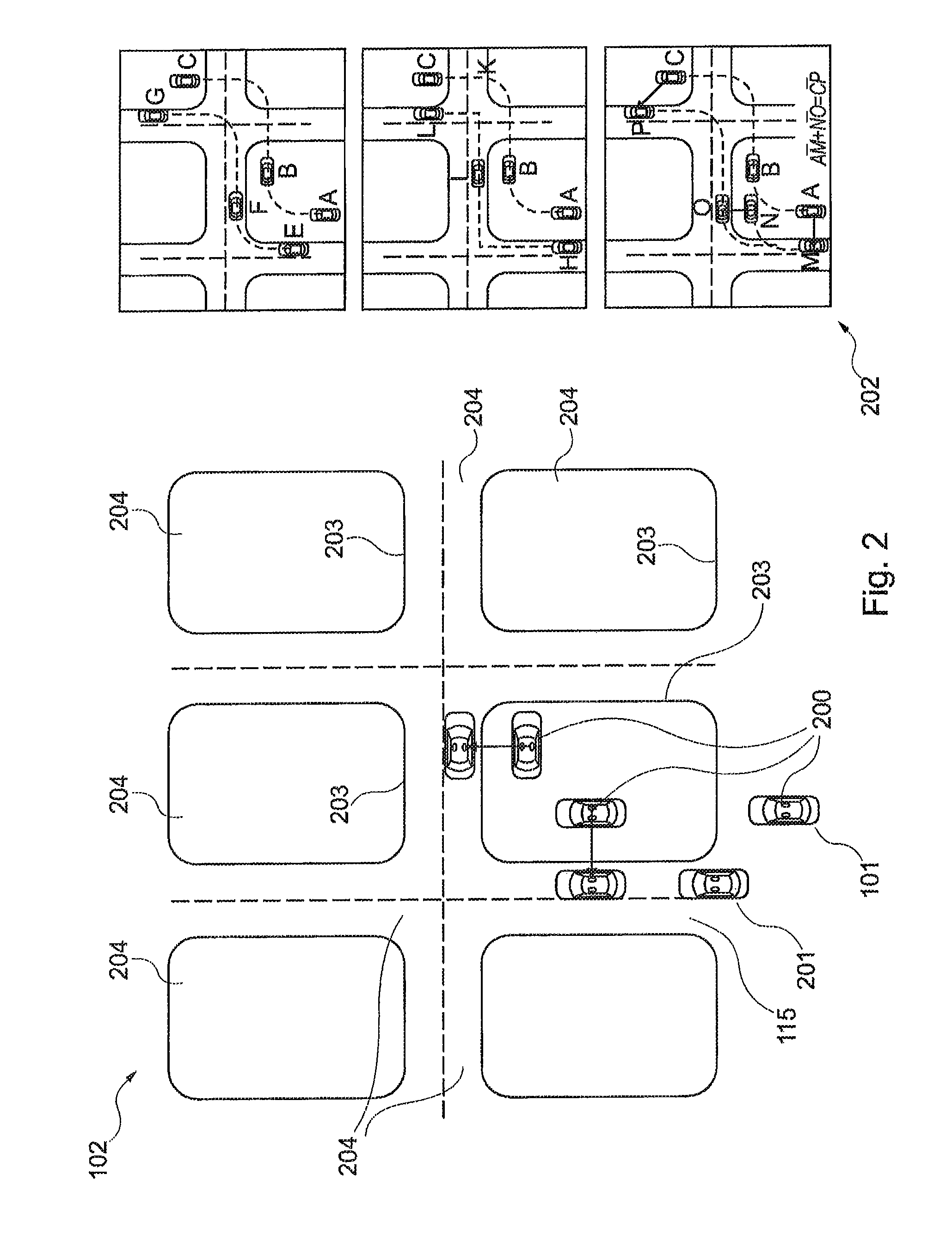
[0069]FIG. 1 shows an apparatus 100 for aligning a measured position 101 for an object with information on a digital map 102. The information on the map may be provided by cartography elements and corresponding data, for example. In addition, a computation unit 103, which may also be in the form of a fast exclusion filter, is provided. In this case, the digital map 102 provides the information stored in it, such as the information about positions of various cartography elements, for the computation unit 103. This is illustrated by the arrows 130, 131. Similarly, this information can be passed directly to the secondary computation units 104, 105, 106, 107 and 108, which is shown by way of example by the arrow 126.
[0070]To eliminate unusable cartography elements, the computation unit 103 performs one of several possible algorithms, which selects the suitable car...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com