Recovery from errors in a redundant array of disk drives
a disk drive and array technology, applied in the field of redundant arrays of disk drives, can solve problems such as loss of fault tolerance to error conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
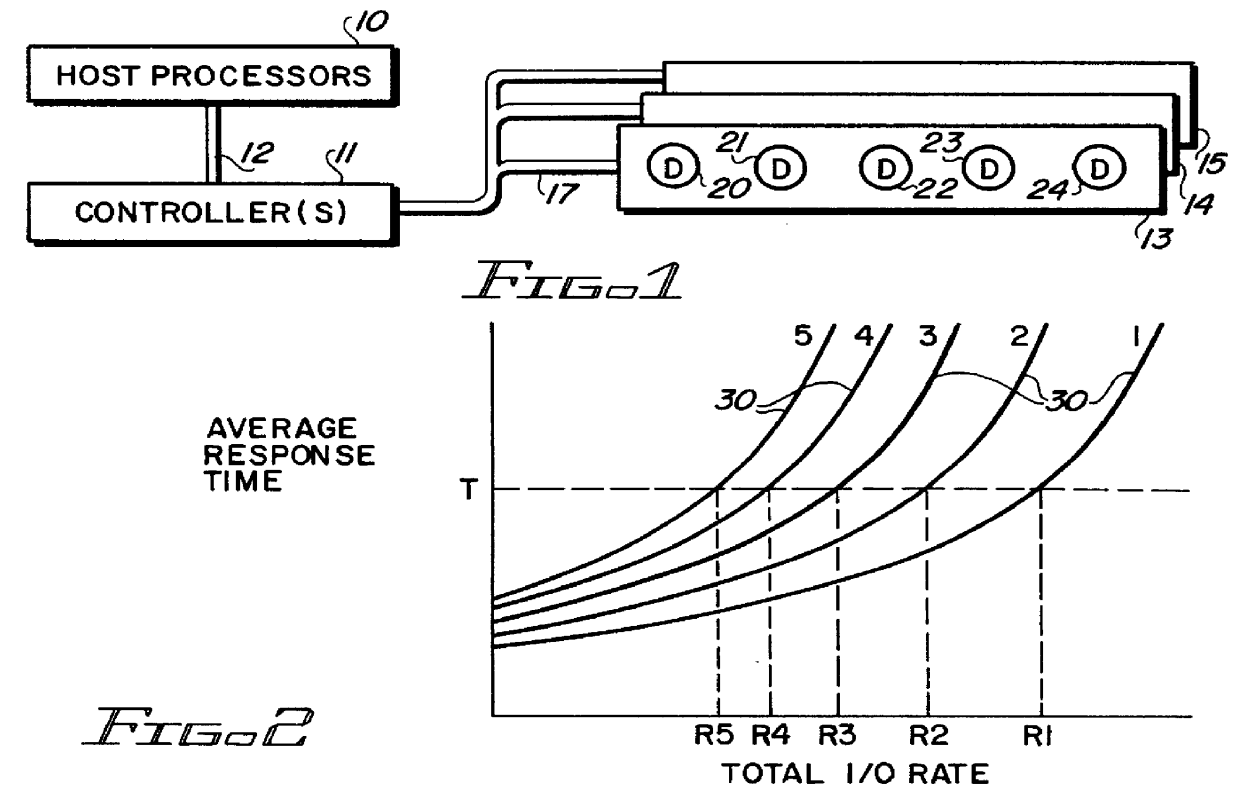
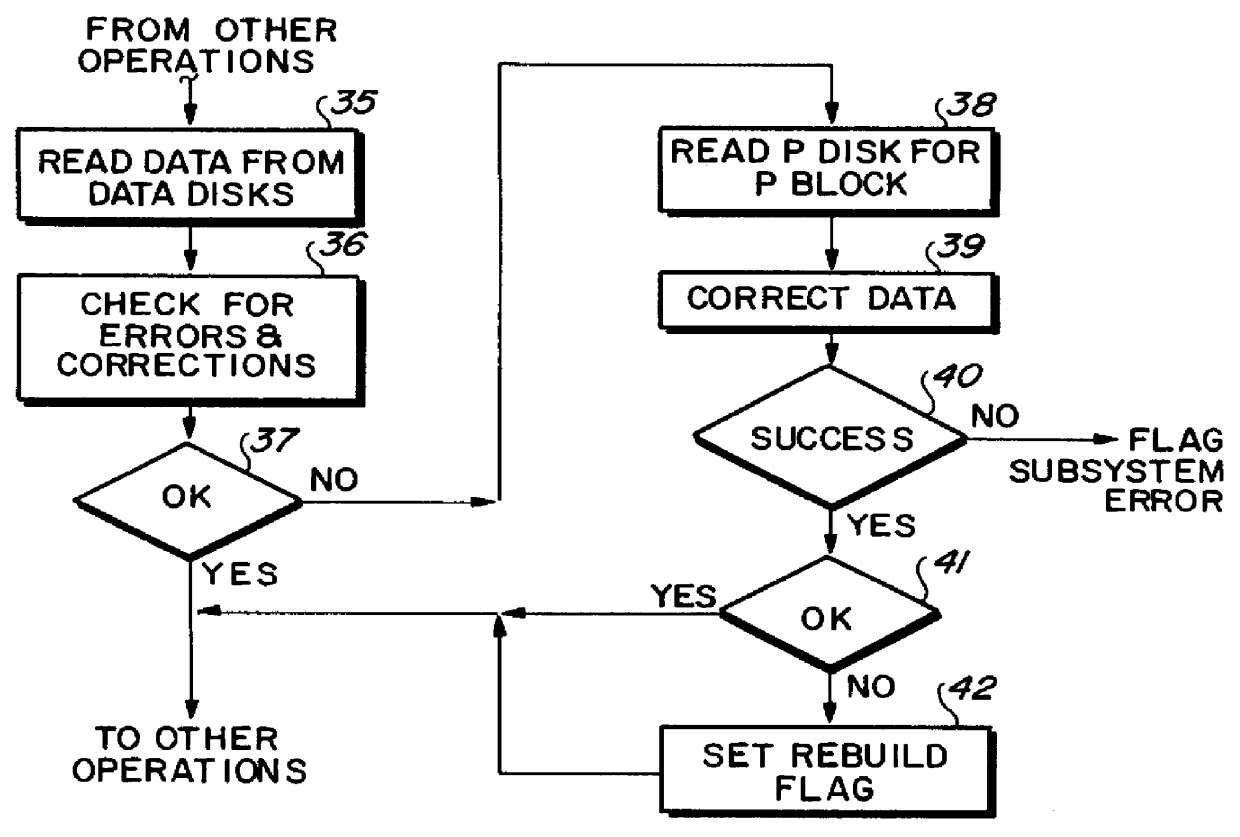
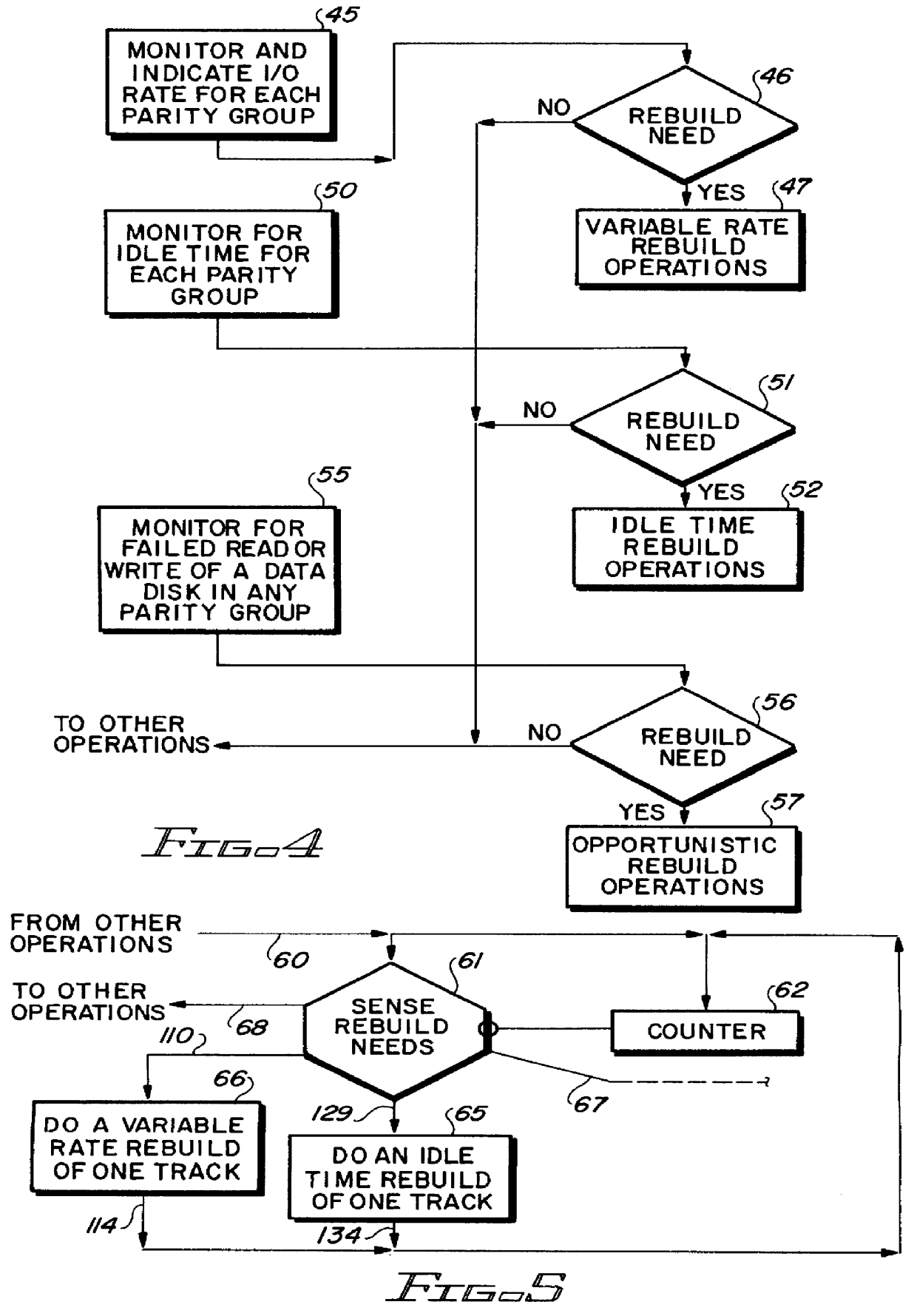
Referring now more particularly to the appended drawing, like numerals indicate like parts and structural features in the various figures. Host processor(s) 10 (FIG. 1) are respectively connected to one or more controller(s) 11 by host to peripheral interconnection 12. A plurality of parity arrays 13, 14 and 15 are connected to controller 11 by a usual controller to peripheral device connection 17. Each of the FIG. 1 illustrated arrays 13-15 include five disk drives 20-24, no limitation thereto intended. Four of the disk drives 20-23 store like-sized blocks of data of one data unit. The block sizes may vary from data unit to data unit. A data unit can be an amalgamation of files, one file, graphic data, and the like. A fifth disk drive 24 is a parity or error detection redundancy storing drive P. The redundancy is a parity data block having the same size as the corresponding data blocks of the data unit. The redundancy is computed based upon any algorithm, including simple parity fo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| idle time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com