Methods and apparatus for scout-based cardiac calcification scoring
a cardiac calcification and scoring technology, applied in the field of scout-based cardiac calcification scoring, can solve the problems of major problems for cardiac calcification scoring, insufficient speed to avoid motion-induced image artifacts in cardiac ct imaging, and high cost of ct imaging systems employing scanning electron beams
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
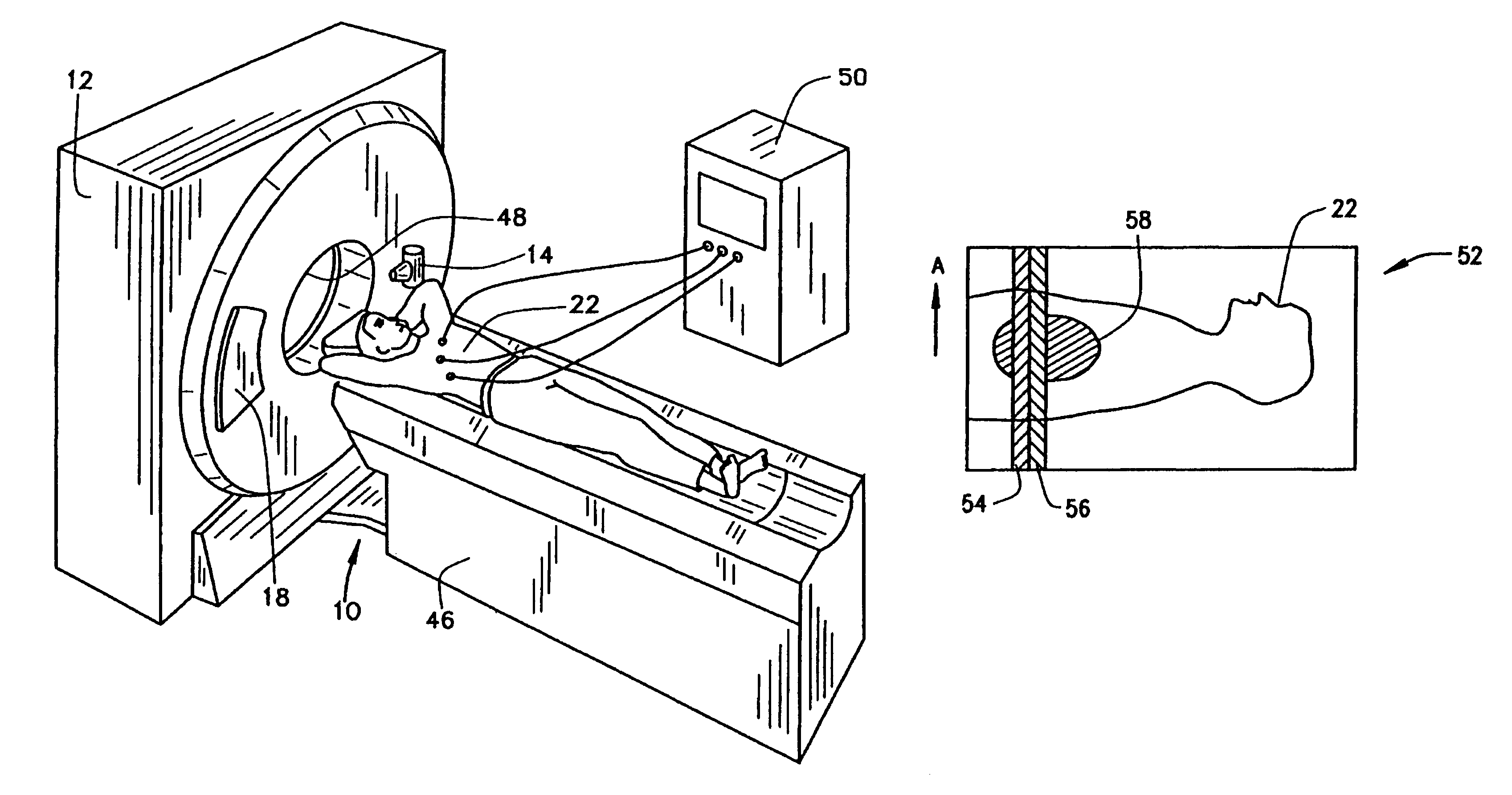
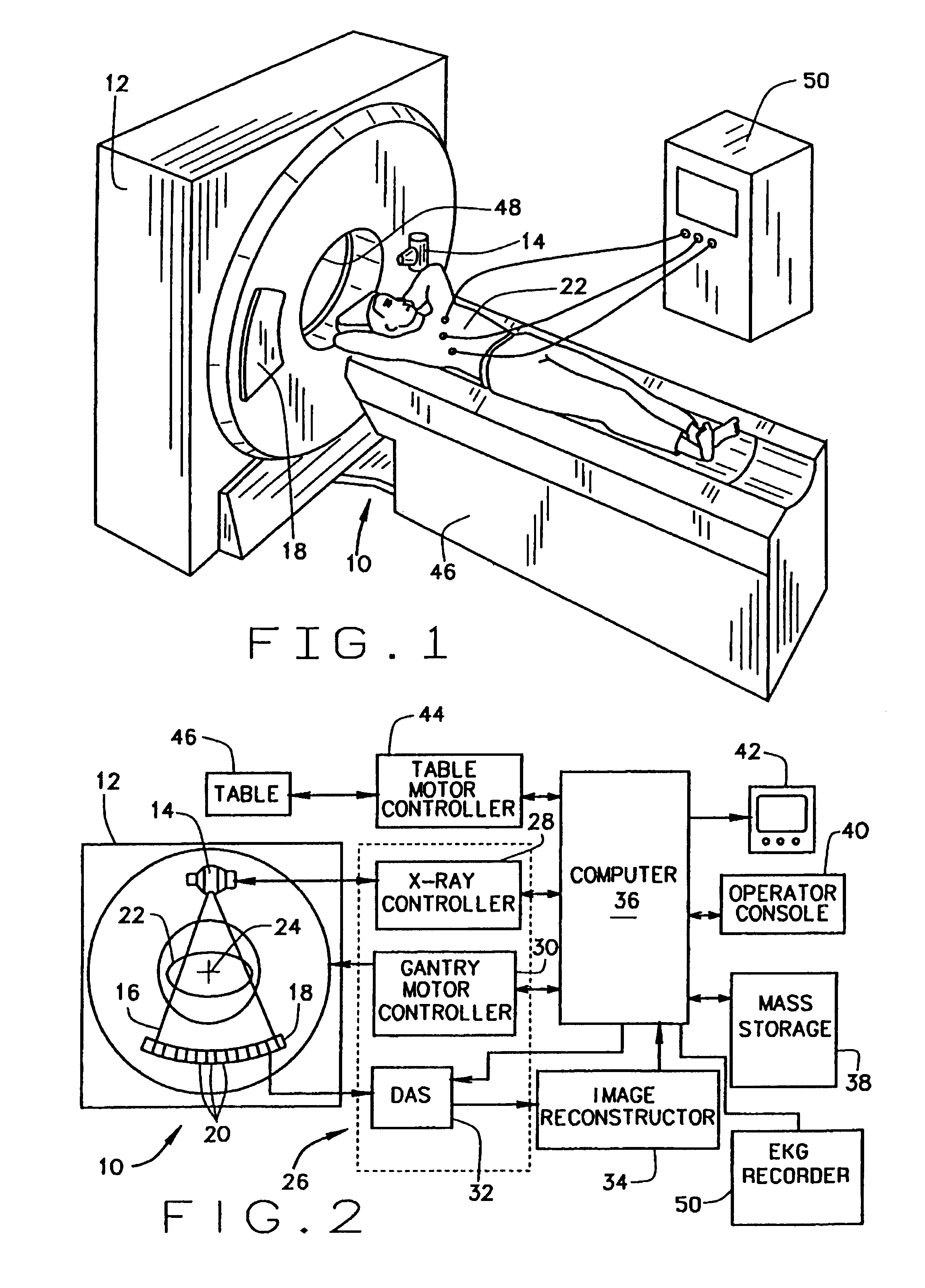
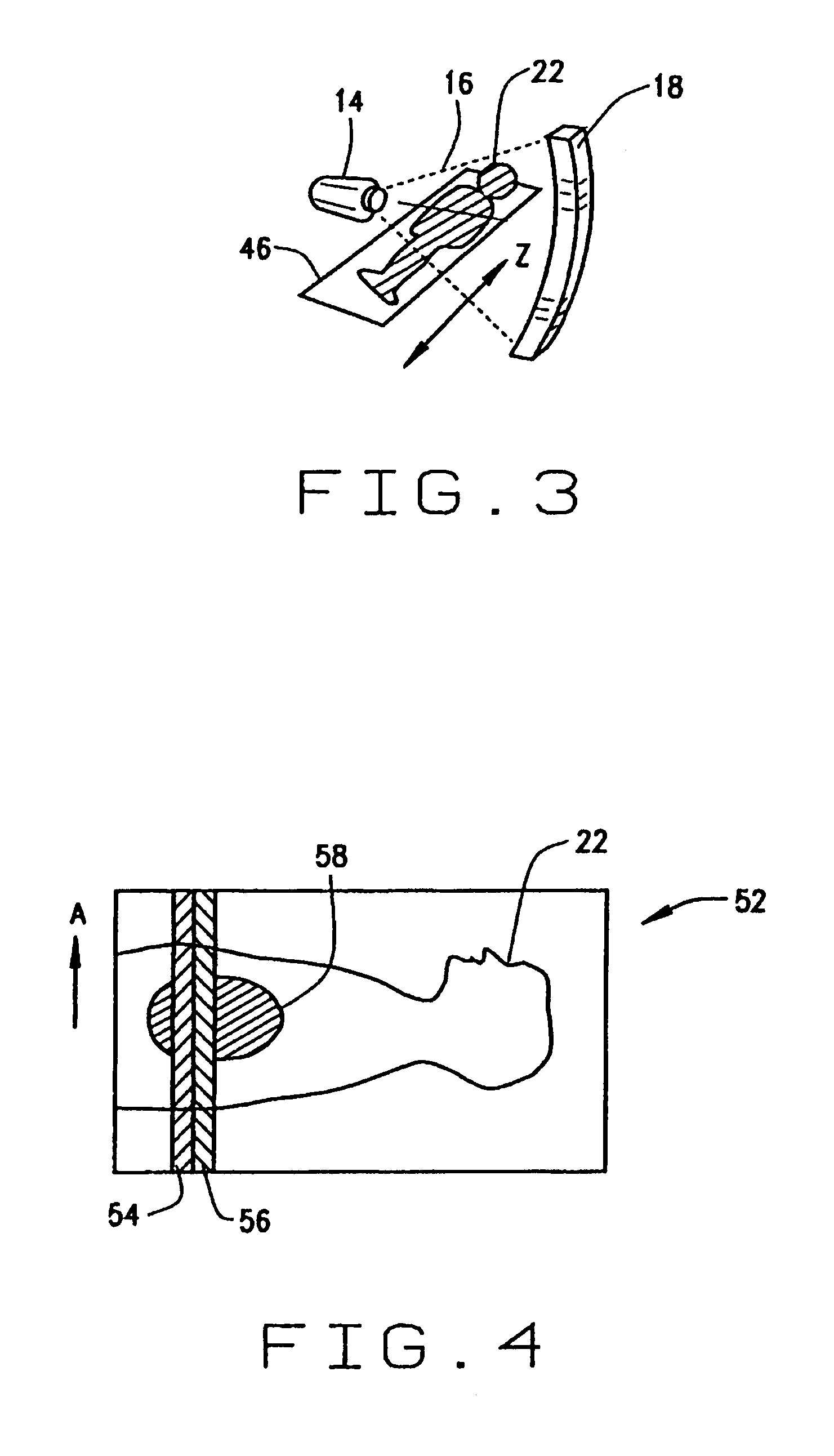
[0018]Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, a computed tomography (CT) imaging system 10 is shown as including a gantry 12 representative of a “third generation” CT scanner. Gantry 12 has an x-ray source 14 that projects a beam of x-rays 16 toward a detector array 18 on the opposite side of gantry 12. Detector array 18 is formed by detector elements 20 which together sense the projected x-rays that pass through an object 22, for example a medical patient. Detector array 18 may be fabricated in a single slice or multi-slice configuration. Each detector element 20 produces an electrical signal that represents the intensity of an impinging x-ray beam and hence the attenuation of the beam as it passes through patient 22. During a scan to acquire x-ray projection data, gantry 12 and the components mounted thereon rotate about a center of rotation 24.
[0019]Rotation of gantry 12 and the operation of x-ray source 14 are governed by a control mechanism 26 of CT system 10. Control mechanism 26 includes...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap