Method for testing energy consumption of dynamic software in embedded system simulator
An embedded system and simulator technology, applied in the field of dynamic software energy consumption testing, can solve problems such as insufficient accuracy of energy consumption estimation and inability to predict programs, and achieve the effects of accurate statistics, accurate energy consumption, and integrity assurance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
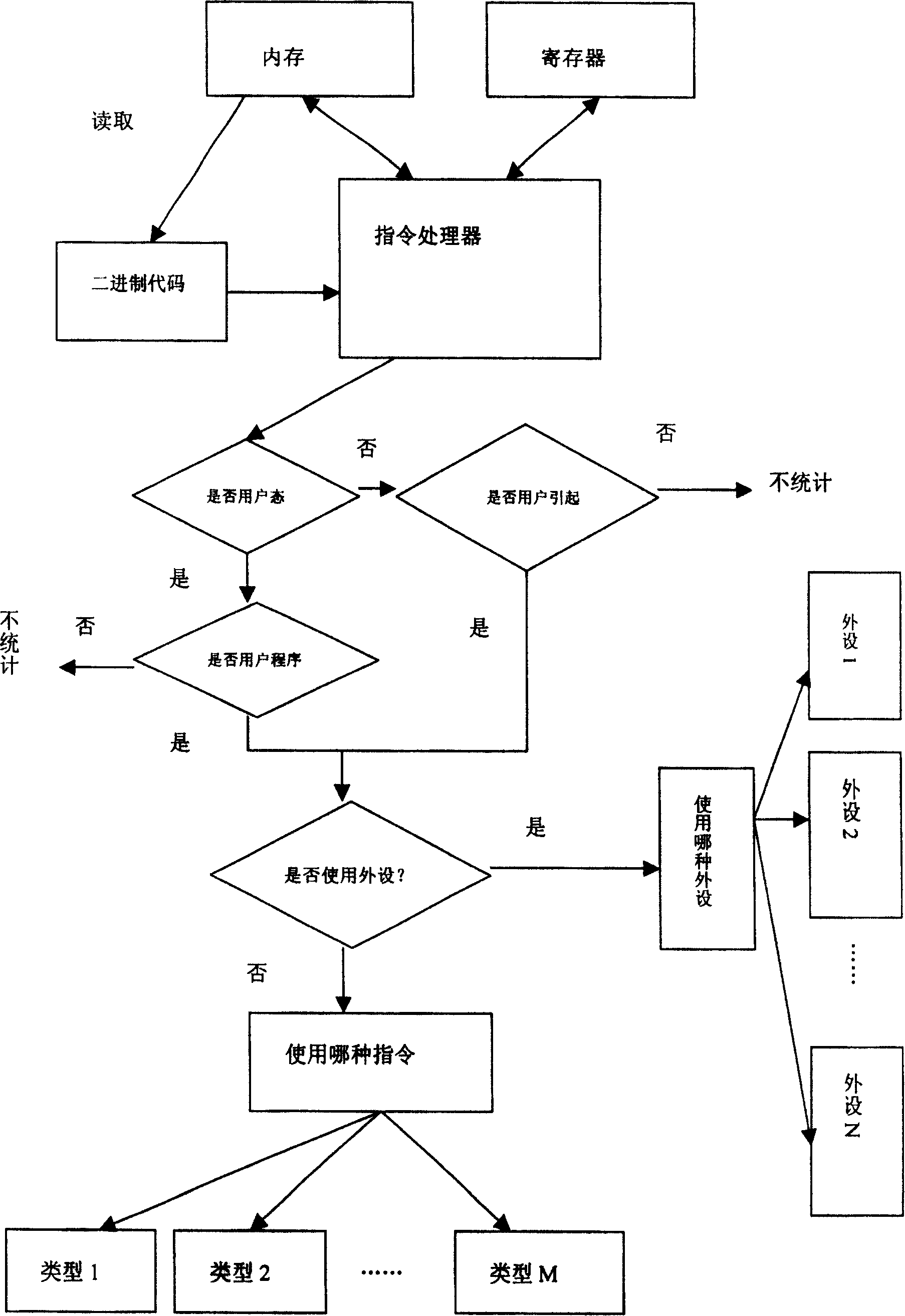
[0044]There is a program source code A, which is cross-compiled to generate binary code and compiled into the image file of the operating system kernel. The image file is loaded by the Wukong emulator. Start uart, click the menu bar to start counting power consumption. Run the A program. After the emulator runs the A program, the power statistics module starts to work. After the program A runs, the emulator gets the power consumed by the program A running.
[0045] The running process of program A is the process of power statistics. For program A compiled into binary code. The Wukong emulator runs instruction by instruction. After A starts executing, maintain an array B[M] and C[N] for A, M is the maximum number of instructions, and the meaning of array B is the number of each type of instruction driven by A; N is the number of types of peripherals , the meaning of the array C is the cumulative time used by the peripherals driven by A. For the command a run by the simul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com